Nutrient Cycles
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Nitrogen and phosphorus are key nutrients which play pivotal roles in sustaining healthy nutrient cycles for organisms within ecosystems. A source of nitrogen and phosphorus for animals is through the direct consumption of plants.
ii) Apart from ATP generation, describe and explain why phosphorus is important for plant growth. [4 marks]
i) ANY 4
- Creation of nucleotides for DNA/rRNA/mRNA;
- (Required for) protein synthesis/ cell division.
-Make phospholipids
-Membrane integrity in cells
-Make NADP/RuBP
- carbon fixation

Nitrogen and phosphorus are key nutrients which play pivotal roles in sustaining healthy nutrient cycles for organisms within ecosystems. A source of nitrogen and phosphorus for animals is through the direct consumption of plants.
ii) Nitrogen is an important component of chlorophyll production in plants. Outline two important roles of nitrogen for all organisms. [2 marks]
ii)
-Manufacture/synthesis of proteins/ amino acids
-Creation of nitrogenous bases/nucleotides for DNA/rNA/mRNA

Nitrogen and phosphorus are key nutrients which play pivotal roles in sustaining healthy nutrient cycles for organisms within ecosystems. A source of nitrogen and phosphorus for animals is through the direct consumption of plants.
iii) There are two processes in which plants directly receive nitrogen. Name and describe these two processes. [4 marks]
iii)
-Absorbtion:
-Absorbing nitrate ions (NO_3) through the soil via active transport
-Nitrogen fixation
-Through conversion of nitrogen into nitrogen containing compounds via (mutualistic/free-living) nitrogen fixing bacteria
Describe the nature and role of mycorrhizae in nutrient cycling. [4 marks]
-Mycorrhizae are fungi on/connected to roots of plants
-Mycorrhizal relationship is mutual/symbiotic
-Plant ebenfits from improved water and inorganic ion uptake
-Fungi receive sugars and amino acids in return

Nitrogen-fixing bacteria are a fundamental part of an ecosystem. Describe the role of nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the nitrogen cycle. [2 marks]
-nitrogen is converted into amonia/ammonium/amino acids
-Whcih allows nitrogen uptake into organisms

Describe the role of saprobionts in recycling phosphorus in ecosystems. [5 marks]
[5 marks]
Up to 5 marks:
•1. Phosphate (ions) in dead plants / animals / waste;
•2. In named biological molecule (e.g. phospholipids / nucleic acids / DNA / RNA / ATP);
•3. Broken down / decomposed by saprobionts;
•4. Through (extracellular) digestion;
•5. Releasing phosphate (ions) into soil

Dead organic matter can be broken down by both decomposers called saprobionts and detritivores.
Detritivores physically break down dead or decaying plants and animals into smaller pieces. Examples of detritivores include worms, insects, or fungi.
i) Describe how saprobionts obtain their nutrients. [3 marks]
Part i) - Up to 3 marks:
•1. Secrete enzymes (onto dead organic matter);
•2. (Extracellular) digestion;
•3. Absorb products.
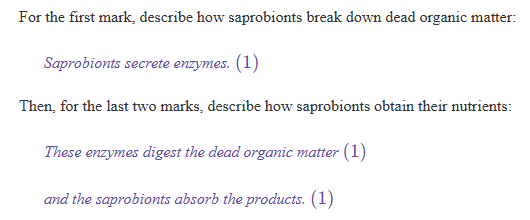
Dead organic matter can be broken down by both decomposers called saprobionts and detritivores.
Detritivores physically break down dead or decaying plants and animals into smaller pieces. Examples of detritivores include worms, insects, or fungi.
ii)Suggest how the presence of detritivores may cause the activity of saprobionts to increase. [2 marks]
Part ii) - Up to 2 marks:
•1. Increases surface area of dead / decaying matter;
•2. Increases rate of reaction of enzymes / digestion (by saprobionts);

![<p><strong>Figure 1 </strong><span><span>shows part of the nitrogen cycle.</span></span></p><p><span style="line-height: 1;"><span>$i)$</span></span><span><span> Name processes </span></span><strong>A </strong><span><span>and </span></span><strong>B </strong><span><span>in </span></span><strong>Figure 1</strong><span><span>. [2 marks]</span></span></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6b2f4857-6ccd-4eca-b637-e38546022959.png)
Figure 1 shows part of the nitrogen cycle.
$i)$ Name processes A and B in Figure 1. [2 marks]
Part i) - Up to 2 marks:
•1. A = denitrification
•2. B = nitrogen fixation
![<p><strong>Figure 1 </strong><span>shows part of the nitrogen cycle.</span></p><p>The process by which ammonia changes to nitrate involves oxidation.</p><p><span style="line-height: 1;"><span>$ii)$</span></span> Give one piece of evidence from the diagram in <strong>Figure 1</strong> <strong>that </strong>shows this. [1 mark]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/68308acb-c1d8-4b5d-b2c5-1e1dc1f3788c.png)
Figure 1 shows part of the nitrogen cycle.
The process by which ammonia changes to nitrate involves oxidation.
$ii)$ Give one piece of evidence from the diagram in Figure 1 that shows this. [1 mark]
Part ii) - Up to 1 mark:
•1. Oxygen added / hydrogen removed.

Soils can be sterilised by heating, which kills bacteria and seeds in the soil.
$i)$ Plants generally grow better in sterile soil than unsterile soil. Suggest why. [2 marks]
Part i) - Up to 2 marks:
•1. Less/no pathogens/diseases;
•2. Less/no (competition with) weeds;

In addition to bacteria and seeds, soils can also contain mycorrhizal fungi. Some scisentists investigated the effect of mycorrhizal fungi on plant growth.
They grew some plants in a plot with mycorrhizal fungi in the soil, and some plants in a plot without mycorrhizal fungi in the soil. They harvested $^{1\text{ m}^2}$ of each plot after $10$ weeks and recorded the biomass.
$ii)$ Suggest an appropriate set of units for biomass. [1 mark]
Part ii) - Up to 1 mark:
•1. Accept any mass per area unit (e.g. Grams per metre squared /gm2/g m−2;

The scientists found that the plants grown with mycorrhizal fungi had a greater biomass after $10$ weeks.
$iii)$ Using your knowledge of mycorrhizal fungi, explain why. [3 marks]
Part iii) - Up to 3 marks:
•1. Mycorrhizal fungi increase surface area of plant roots;
•2. (So) increased nutrient/mineral/ion/water uptake;
•3. (So) increased growth (and biomass).

A farm's ability to produce good crop yields is often limited by available soil nutrients, especially nitrogen. Nitrogen is not present at high levels in soil material despite the fact that nitrogen constitutes the majority of all atmospheric gases.
Give examples of processes and activities which can increase the availability of nitrogen and its compounds in the soil. [4 marks]
Any FOUR from: - Up to 4 marks:
•1. The fixing of nitrogen by nitrogen-fixing bacteria;
•2. The application of artificial fertilisers by farmers;
•3. Urination/defecation of animals/applying manure/silage onto soil;
•4. Lightning (causes) oxidation of atmospheric nitrogen to nitrogen oxide and carried to the soil by rain as nitrous or nitric acid;
•5. Decay of organic matter via saprobionts/saprophytes/decomposers/bacteria.

![<p><strong>Figure 1</strong> represents the movement of nitrogen in a goat farm used to source primarily goat’s milk. The width of the arrows represents the average amount of nitrogen.</p><p></p><p></p><p>Using information from <strong>Figure 1</strong>, explain why it is necessary for a farmer to add fertiliser in order to maintain production of goat's milk. [2 marks]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/96c7788d-3209-427c-a972-be2a6c229248.png)
Figure 1 represents the movement of nitrogen in a goat farm used to source primarily goat’s milk. The width of the arrows represents the average amount of nitrogen.
Using information from Figure 1, explain why it is necessary for a farmer to add fertiliser in order to maintain production of goat's milk. [2 marks]
Up to 2 marks:
•1. Nitrates are lost from soil (and) milk which is not recycled;
•2. (So) farmer must compensate for this loss by adding more nitrates / nitrogen (in the form of fertiliser) to enhance grass growth.

Suggest two ways in which farmers can reduce leaching of nitrates. [2 marks]
Any TWO from: - Up to 2 marks:
•1. Crop rotation adds nitrogen / different organic matter to soils;
•2. (Using) urea or ammonium form of nitrogen where possible;
•3. Deep and extensive root system to capture available nutrients / no waste of applied fertiliser / nutrients;
•4. Using appropriate quantity of fertiliser / matching fertiliser quantity to crop demand.

![<p><strong>Figure 1</strong> shows an investigation into the effects of applying increased amounts of fertiliser on the yield of wheat.</p><p>Describe and explain the results in <strong>Figure 1</strong>. [6 marks]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1f77f34a-04cc-4235-8c61-4159bcab0027.png)
Figure 1 shows an investigation into the effects of applying increased amounts of fertiliser on the yield of wheat.
Describe and explain the results in Figure 1. [6 marks]
Up to 6 marks:
•1. (Initially) as fertiliser application increases so does yield;
•2. (Because) nutrients are limiting factor in determining growth of / nutrients are not optimum for maximum growth / soil is deficient in nutrients;
•3. (Then) yield plateaus / flattens / does not increase any more with increased fertiliser application;
•4. (Because) nutrients are no longer liming growth / nutrients have reached optimum for growth;
•5. (Eventually) yield decreases with more fertiliser application;
•6. (Because) nutrients are at toxic levels.

![<p>A sewage plant is releasing waste into the surrounding water containing algae. The release of waste causes the number of algae to increase. This results in a low secchi depth, indicating high water turbidity (unclear water).</p><p></p><p><strong>Figure 1</strong> shows the statistics for water turbidity, number of fish and secchi depths.</p><p><br></p><p>Using <strong>Figure 1</strong>, describe and suggest reasons for the change in fish population. [2 marks]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/c8e7fdce-2b3d-4880-a23b-12edca61defb.png)
A sewage plant is releasing waste into the surrounding water containing algae. The release of waste causes the number of algae to increase. This results in a low secchi depth, indicating high water turbidity (unclear water).
Figure 1 shows the statistics for water turbidity, number of fish and secchi depths.
Using Figure 1, describe and suggest reasons for the change in fish population. [2 marks]
Any TWO from - Up to 2 marks:
•1. As secchi depth decreases, so does the number of fish measured;
•2. (Because) when algae die oxygen is used by saprobionts that decompose them (due to aerobic respiration), leaving less oxygen for the fish (causing death);
OR
•3. As secchi depth decreases, turbidity increases (leading to low fish population numbers);
•4. (Because) when more algae are present more light is absorbed / reflected by them and so less light penetrates, causing visual issues for fish to see and catch prey, leading to starvation.

A lake is surrounded by farming fields. These fields are separated from each other by hedges.
Farmers removed the hedges near the edge of the lake. Soon after, the lake became green and all the aquatic plants and fish in the lake died.
Explain how removing hedges near the edge of the lake led to these changes. [6 marks]
Any SIX from: - Up to 6 marks:
•1. (Removing hedges led to) increased soil erosion;
•2. Fewer nutrients / fertilisers taken up by the hedges;
•3. Runoff / leaching of nutrients / nitrates / fertilisers (from fields);
•4. Leads to increased growth of algae / plants / algal bloom;
•5. Eutrophication;
•6. Competition for lightcauses death of aquatic plants;
•7. Increases microorganisms / decomposers / saprobionts;
•8. (So) increased respiration (of microorganisms) uses up oxygen (causing fish to die)
