CHP 5 human development
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
is a developmental checklist reason enough to warrant OT services?
NO always perform your own assessments
prenatal period
conception to birth; gestational period
SENSORIMOTOR:
all neonatal reflexes are present at 29wks gestation (not fully developed)
innate tactile, prop, and vestibular rxn
response to tactile as early as 5.5 wks
response to sound at 24wks
early infancy
birth to 3 mos
SENSORIMOTOR:
tactile, prop, and vestibular begin to integrate and refine
visual continues to develop with response to stimuli 10in from face
auditory system develops to orient to typical voices
integration of primitive oral motor reflexes for feeding
integration of motor skills for head righting and turning head
changes in sensory input may overstimulate
middle infancy
4-6 mos
general SENSORIMOTOR:
tactile and prop continue to refine = incr awareness and interest in world
vestibular, prop, and visual integrate for postural control and facilitating stable visual field
visual and tactile system become integrated for reaching and primitive grasp
play at midline
movement patterns progress from reflective to voluntary and goal directed
late infancy
7-9 mos
general SENSORIMOTOR:
vestibular, visual and somatosensory responses incr in quality = more mobile and coordinated movements
tactile and prop become more refined allowing development of FM skills and motor planning
transitional infancy
10-12 mos
general SENSORIMOTOR:
tactile and prop improve = development of midline skills and crossing midline
auditory, tactile, and prop heightened for development of sound and communication
tactile, prop, gustatory, and olfactory integrated for self-feed
infancy
earliest period of post-natal life
birth through 1 year
divided into 4 periods
early infancy
middle
late
transitional
emerging toddler
13-24 mos
general SENSORIMOTOR
tactile becomes more precise for localization and discrimination
balance and dynamic posture control stronger
further integration for complex motor planning > incr self-concept
symbolic gesturing and vocalization > ideation and ability to conceptualize
toddler
2-3 years
general SENSORIMOTOR:
vestibular, prop, and visual further develop and refine for improved balance and postural control
tactile discrimination and localization skills > improved FM
motor planning and praxis ideation = incr planned actions and play
preschool/early childhood
3-5 years
general SENSORIMOTOR:
PLAY based improvements
child challenges and develops sensorimotor competencies for roughhouse play, playground ax, games, sports, dancing, arts, and school tasks
social development and self esteem
refinement of sensory systems for independence in mobility and improved FM skills
rooting reflex
stimulus, response, fxn sig, onset age, integration age
stimulus: stroke corner of mouth, upper lip, and lower lip
response: movement of tongue, mouth, and head during stimulus
fxn sig: helps body locate feeding source
onset age: 28 wks gestation
integration: 3 mos
suck-swallow reflex
stimulus: place index finger inside mouth with head in midline
response: strong, rhythmical sucking
fxn sig: facilitates nutritive sucking for ingestion of liquid
onset age: 28 wks gestation
integration: 2-5 mos
traction reflex
stimulus: grasp infant forearms and pull-to-sit
response: complete flexion of UE
fxn sig: promote momentary grasp to enabled child to hold onto mother when being pulled
onset age: 28 wks gestation
integration: 2-5 mos
moro reflex
stimulus: rapidly drop infants head backwards
response:
first phase: arm extension/abduction, hand opening
second phase: arm flexion and adduction
fxn sig: protective response to stress; helps develop extensor tone during period when flexor tone is dominant
onset age: 28 wk gestation
integration: 4-6 mos
plantar grasp reflex
stimulus: apply pressure with thumb on infant ball of foot
response: toe flexion
fxn sig: incr input to sole of foot; integration associated with readiness for indp gait
onset age: 28 wks gestation
integration: 9 mos
galant reflex
stimulus: hold infant in prone suspension, gently scratch or tap alongside spine with finger from shoulder to butt
response: lateral trunk flexion and wrinkling of skin on stimulated side
fxn sig: enhances trunk stabilization by facilitating lateral trunk movement
onset age: 32 wk gestation
integration: 2mos

Asymmetric tonic neck reflex (ATNR)
stimulus: fully rotate infants head and hold for 5s
response: extension of extremities on face side, flexion of extremities on skull side
fxn sig: promotes visual attention to UE; decr incidence of rolling
onset age: 37 wks gestation
integration: 4-6 mos

palmar grasp reflex
stimulus: place finger in infants palm
response: finger flexion; reflexive grasp
fxn sig:
incr palmar tactile input
prepares muscles for voluntary grasp
onset age: 37 wks gestation
integration: 4-6mos
tonic labyrinthine (supine) reflex
stimulus: place infant in supine
response: increased extensor tone
fxn sig:
facilitates full body extensor tone
allows posture to adapt to that of head
onset age: 37 wks gestation
integration: 6ms

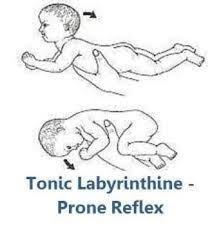
tonic labyrinthine (prone) reflex
stimulus: place infant in prone
response: increased flexor tone
fxn sig:
facilitates full body flexor tone
allows posture to adapt to head
onset age: 37 wks gestation
integration: 6mos
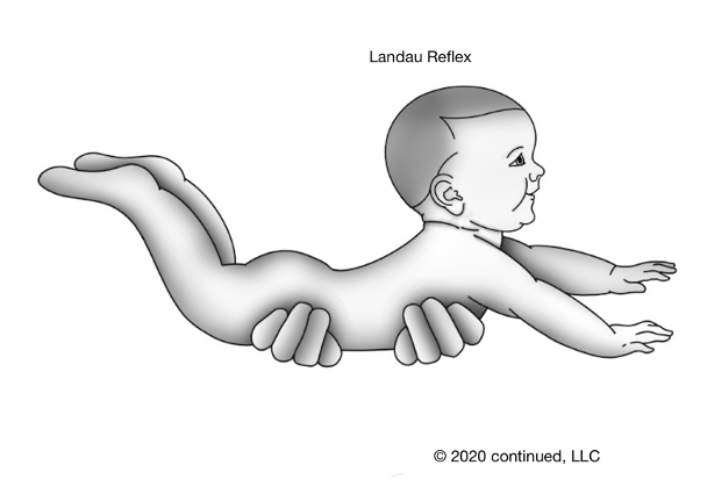
landau reflex
stimulus: hold infant in horizontal prone suspension
response: complete extension of head, trunk, and extremities
fxn sig:
regulates tone
promotes prone extension to manage flexor tone
onset age: 3-4 mos
integration: 12-24 mos
real EX: lifting baby in air over head to play and they have extremities ext
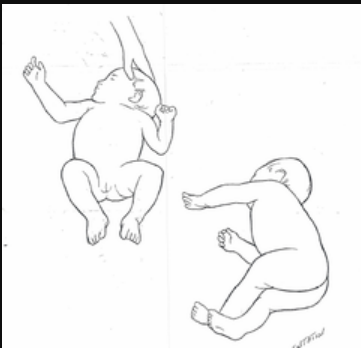
symmetric tonic neck reflex (STNR)
stimulus: place infant in crawling position and extend the head
response: flexion of hips and knees
fxn sig:
facilitates quadruped position in preparation for crawling
breaks up total-body extension
onset age: 4-6mos
integration: 8-12mos

neck righting on body (NOB)
stimulus: place infant in supine and fully turn head to one side
response: log rolling of entire body to maintain alignment with head
fxn sig:
facilitates rolling
maintains body orientation in response to cervical position changes
onset age: 4-6mos
integration: 5yrs
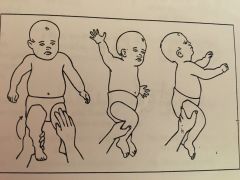
body righting on body (BOB)
stimulus: place infant in supine, flex one hip and knee toward the chest and hold briefly
response: segmental rolling of upper trunk to maintain alignment
fxn sig:
promotes trunk and spinal rotation to facilitate sitting and quadruped positions
onset age: 4-6mos
integration: 5yrs
reflexes that persist throughout life
3 main
labyrinthine/optical righting
protective extension:
downward parachute (protective extension downward)
forward parachute (protective extension forward)
sideward parachute (protective extension sideward)
backward parachute (protective extension backward)
tilting:
prone, supine, sitting, quadruped, standing
labyrinthine/optical (head) righting
stimulus: hold infant suspended vertically and tilt slowly (45deg) to side forward or backward
response: upright positioning of head
fxn sig:
basis for head management and postural stability
orients head in space vertically
onset age: birth-2mos
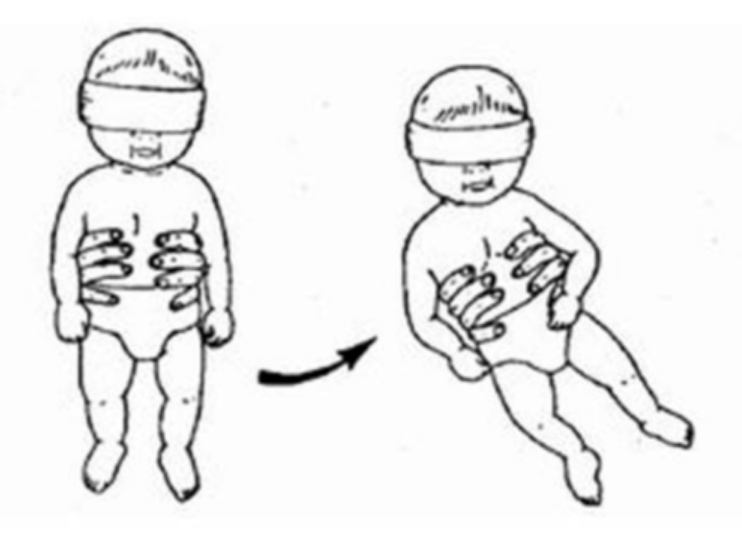
downward parachute (protective extension down)
stimulus: rapidly lower infant toward supporting surface while suspended vertically
response: ext of LE
fxn sig:
prepares LE for surface contact
breaks fall
onset age: 4mos
forward parachute (prot. ext)
stimulus: suddenly tip infant forward toward supporting surface while vertically suspended
response: sudden ext of UE, hand opening, and neck ext
fxn sig:
place UE in anticipation of surface to break fall
supports prop sitting
onset age: 6-9ms
sideward parachute (prot. ext.)
stimulus: quickly but firmly tip infant off balance to side while in sitting
response: arm ext and abduction to side
fxn sig:
unilateral support body for use of opposite arm
prevent fails
onset age: 7mos
backward parachute
stimulus: quickly but firmly tip infant off balance backward
response: backward arm ext or arm ext to one side spinal rotation
fxn sig: protect from backward fall
onset age: 9-10mos
tilting reflexes
what
types & onset age
stimulus: tilt baby while in appropriate position
rxn: curve spine toward raised side, abduction/extension of arms and legs
types:
prone: 5mos
supine & sitting: 7-8mos
quadruped: 9-12mos
standing: 12-21mos
purpose: adjust center of gravity and preserve balance
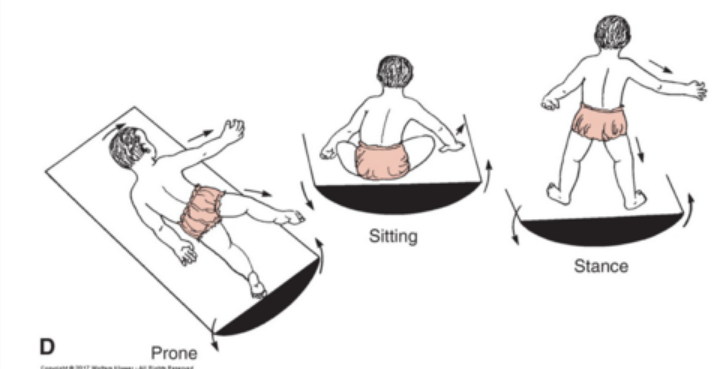
general principles for motor development (5)
occurs in cephalocaudal/proximal to distal direction
EX: core strength and sitting balance before standing and walking
progresses from gross to fine movement
progresses from stability to controlled mobility
occurs in spiraling manner, with periods of equilibrium and disequilibrium
sensitive periods occur when child is affected by environmental input
climbing
15-18ms
climbs on and off surfaces
creeps up stairs
18-24ms
walks up&down stairs while holding on
creeps backwards down stairs
2-2.5yr
walks up&down w/o support w/time and no alternating of feet
2.5-3yr
walks UP stairs alternating feet
3-3.5yr
walks DOWN stairs alternating
jumping
2yr
jump down from step
3yr
jump off floor with both feet
3-4yr
gallops
4-5yr
jump over object
hops on one foot
5yr
hops straight line
5-6yr
skips alternating feet
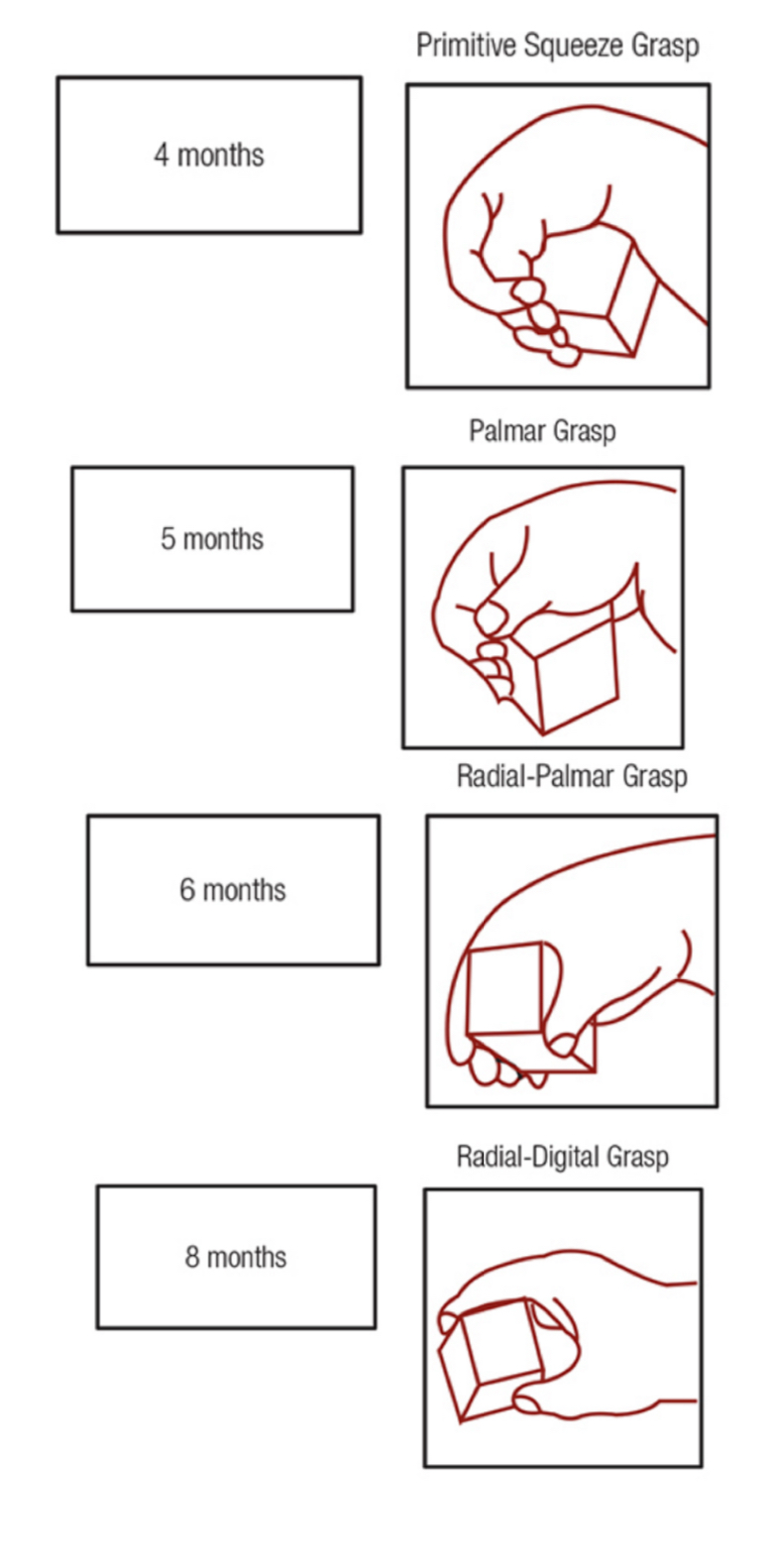
grasping a cube (power)
3ms
sustained voluntary grasp
uses ulnar side with no thumb involvement
4 MONTHS Primitive Squeeze Grasp
5 MONTHS Palmar Grasp
6-7ms
6 MONTHS Radial Palmar grasp
wrist straight (7ms)
8ms
8 MONTHS radial digital grasp
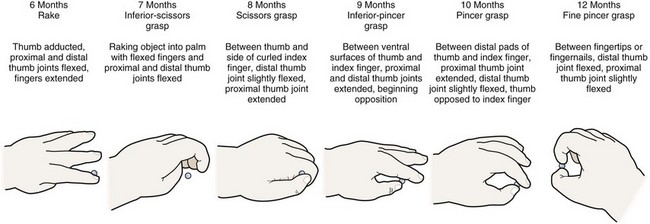
Grasping Pellet (precision)
0-3ms
NO voluntary grasp or NO visual attention to pellet sized object
3ms > visual attention w/out grasping attempts
6ms
swiping/raking
7ms
inferior-scissor grasp
raking with adducted, flexed thumb and flexed fingers
clawing with mittens
8ms
scissor grasp
thumb and side of index finger
9ms
inferior pincer grasp
10ms
pincer grasp
btw pads of fingers
12ms
fine pincer grasp
fingertips
power grasp
when
how
ex
WHEN: used to control tools or other objects & when hand strength is required
hook, spherical, and cylindrical are often considered types of power grasps
HOW:
object held obliquely in hand w/ ulnar fingers flexed and radial fingers less flexed. thumb ext and add.
stabilize with ulnar and control with radial
EX: using a hammer

hook grasp
when
how
EX
WHEN: to carry objects such as purse or briefcase
HOW:
transverse metacarpals arch is flat, fingers adduct w/flex at IP; MCP flexed or ext
EX: holding a purse or briefcase

spherical grasp
when
how
WHEN: to hold small ball
HOW:
wrist ext, fingers abduct w/flex at MCP and IPs; hypothenar eminence assists in cupping and control of objects

cylindrical grasp
when
how
WHEN: hold glass, cup, or can with hand around object
HOW:
transverse arch flat against object; fingers abduct; IP and MCP flex

disk grasp
WHEN: hold disk such as jar lid
HOW:
finger hold disk with ext of MCP and flex of IP; wrist flex and thumb ext with larger objects; only pads of fingers touch object

lateral pinch
when
how
WHEN: to exert power on or with small object
HOW:
index finger slightly flexed and thumb flexed and adduct'; pads of fingers on radial side of index finger near DIP
EX: holding a key
pincer grasp
WHEN: hold and handle small objects and precision tools
HOW:
thumb opposed to index finger pad and object held in finger pads; ulnar fingers flexed (pad to pad)
EX: holding a pencil, holding a coin, rolling a dough ball btw finger and thumb > using the PADS

three jaw chuck (tripod) grasp
WHEN: hold and manipulate writing utensil or eating utensil
HOW:
thumb simultaneously opposed to index and middle finger pads
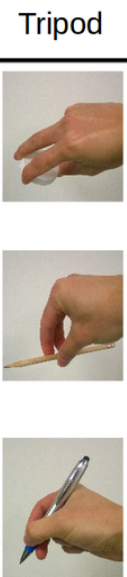
tip pinch
used to prehend and hold tiny objects
HOW:
thumb opposed with thumb tip meeting index tip forming circle

in-hand manipulation skill development
finger to palm translation
12ms - 15ms
palm to finger translation & simple rotation
24ms - 36ms
2yrs - 2.5yrs
shift: tabbing pages, turn page, buttoning, lacing, adjusting pencil
3yrs - 6yrs
complex rotation
6yrs - 7yrs
development of prewriting and writing skills
8-12ms
mouths writing utensil & crinkles paper
12-18ms
scribbles; arm moves are unit
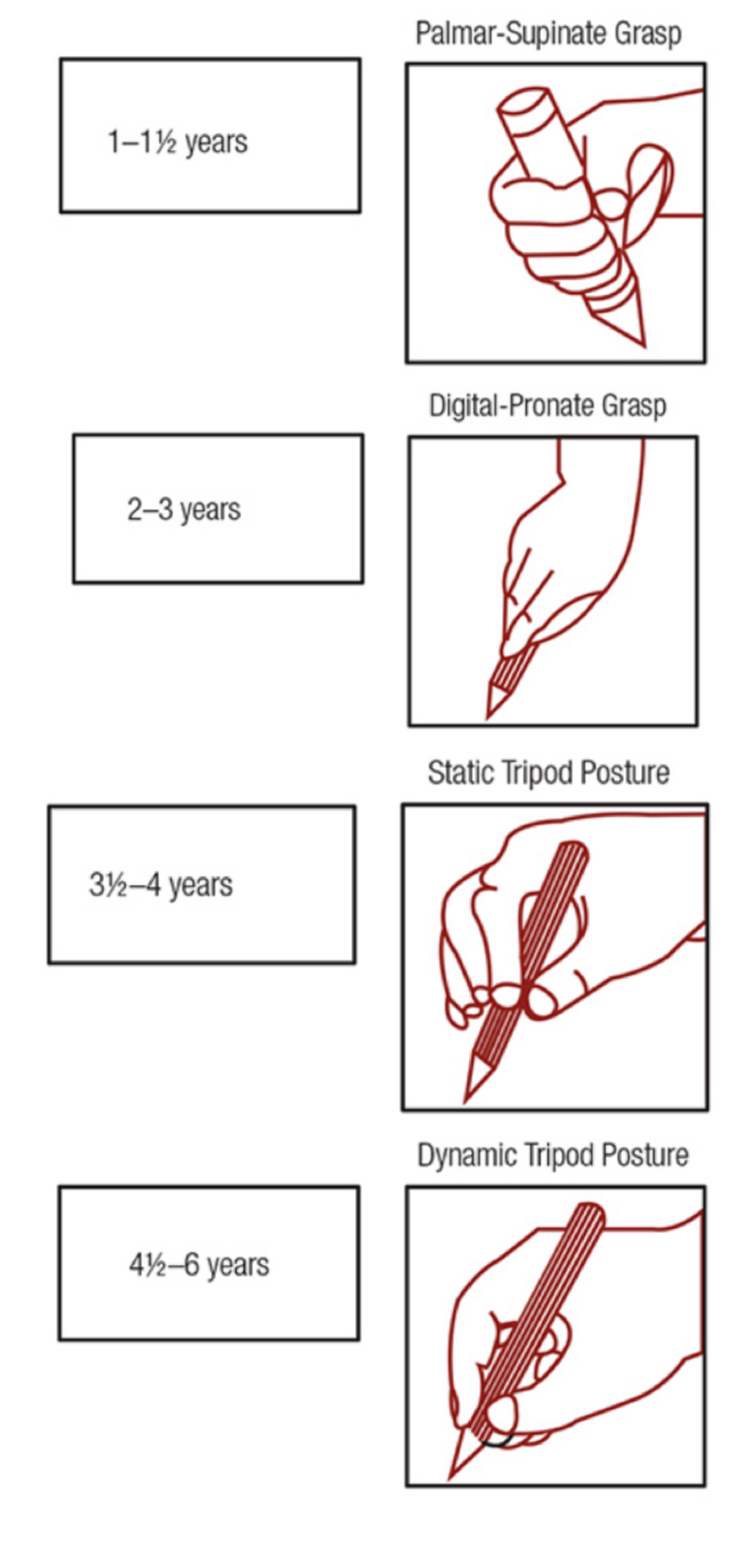
12-18 MONTHS palmar supinate grasp
2-3yrs
digital pronate grasp
circular scribbles with intent
imitates vertical and horizontal lines
3.5-4yrs
static tripod
draws more recognizable simple shapes
human figure with 1-3 features
4.5-6yrs
dynamic tripod
intentional drawings, recognizable but maybe unrealistic features
4-5yr: copies letters and numbers
5-6yr: write name with upper and lowercase, detail thoughtful drawings
scissor skills development
2-3yr
holds and snips; opens/closes in controlled fashion
3-4yr
cut straight and curved line with guide
3.5yr: cut circle using helper hand
4-5yr
cut simple shapes
circle > square, triangle
5-7yr
cut complex shapes
Piaget
4 stages
sensorimotor
birth to 2yrs
child uses sensorimotor skills to develop understanding of world and progress from reflexive activity to cognitive function
preoperational
2-7yrs
progresses from dependence on perception and egocentric thoughts to logical and problem solving; engage in symbolic and verbal play
concrete operations:
7-11yrs
use logical thinking on observed or mentally represented objects; enjoy games with rules
formal operations
11-teens
logic to hypothesize problem solving and can draw from past and present experiences
exploratory play
0-2yrs
child engages in play experiences to develop body schema
sensory integrative and motor skills develop
mostly with parent or caregiver
symbolic play development
12-18ms
basic make believe play, primarily involving self (sleeping, eating,)
imitates familiar activities
18-24mos
increases non-realistic objects in pretending (block for train)
inanimate objects perform familiar activities (doll washes herself)
2-4yrs
play experiences with refined ideas, emotions, and actions
creative play
4-7yrs
sensory, motor, cognitive, and social play to refine skills
explores combo of actions
cooperative peer groups
game play
7-12yrs
rules, competition, social interaction, and skill development
cooperative peer groups
oral motor development
4-5mos
strong sucking, good lip closure, tongue moves up and down, munching
7-8mos
mastication of soft and mashed foods with diagonal jaw movements
9mos
lateral tongue mvt for effective mastication of mashed and soft foods; drink from cup but jaw not firm
12mos
jaw is firm, rotary chewing for good bite on hard cookie
24mos
able chew most foods, well-graded sustained bite, drink from cup with firm jaw
development of self-feeding
5-7mos
take cereal or poured baby food from spoon
6-8mos
attempts to hold bottle; needs to be monitored for safety
6-9mos
hold and tries to eat cracker but sucks more than bites
consumes soft foods that dissolve in mouth
grabs spoon but bangs or sucks on either end
9-13mos
finger-feeds self portion of soft table foods
12-14mos
dips spoon in food, brings spoonful to mouth but spills by inverting spoon
15-18mos
scoops with spoon and brings to mouth
24-30mos
interest in fork; stab at food; proficient in spoon
development of toileting skills
1-2yrs
knows & is distressed when wet, cooperates with changings, regular bowel movements
2-2.5yr:
POTTY TRAINING
regular urination, bowel accidents rare, interest in toileting, knows when they need to go, cooperates for limited time when placed on potty; may need help with clothing managment
3-4yrs
toilet on own, may need help with hygiene or clothes management (fasteners)
4-5yrs
daytime & nighttime control
indep on toilet but may need help for difficult clothes
5-6yrs
completely indp
development of self-dressing
1yr
cooperates with dressing, puts arms up for don/doff, extends legs, removes socks
1.5-2yr
DOFF > unfastened clothes & shoes, mittens
helps pull pants down, pushes arms through holes when shirt placed on head
2.5-3yr
assist & attempts to DON » easy shoes, socks
DONS pullover shirt, open front jacket
unbuttons, unsnaps, unzips (&zips when on track) easy fasteners
3.5-4yr
DON > easy shoes, elastic pants, pullover shirt, mittens
recognizes correct clothing orientation
buttons, zips, snaps, fastens, and unbuckles easy fasteners
large buttons, 3-4 button series
4.5-5yr
indp don/doff body clothes
indp with buckles
minimal assist for difficult fasteners & tying laces
5-6yrs
INDP > difficult fasteners & tying shoes
development of IADLs
2-3yrs
imitate chores, follow easy cleanup directions, wipes up spills, fills pet food dish
4-5yrs
prepare simple snacks, set table, empty dishwasher, sort laundry, make bed, water, feed pets, sort trash, etc.
6-7yrs
make & pack lunch, help meal prep, wash & dry unbreakable dishes, tidy up
8-9yrs
prepare hot meal, load dishwasher, wash/dry breakable dishes, walk pets, mop, fold & put away laundry
10-11yr
clean kitchen/bathroom, help with shopping, change bed
12+
meal prep, laundry & ironing, grocery shop, wash car, simple home repair, manage house machines (washer/dryer)
neonatal assessments (2)
Assessment of Preterm Infants Behavior (APIB)
Neurological Assessment of Preterm and FullTerm Newborn Infant (NAPFI)
Comprehensive developmental assessments (7)
Bayley Scale of Infant Development 3 (BSID-III)
Developmental Assessment of Young Children (DAY-C)
Denver Developmental Screening Test II
First STEP Screening Test for Evaluating Preschoolers
Goal-Oriented Assessment of Lifeskills (GOAL)
Hawaii Early Learning Profile (HELP)
PEDI
Motor development assessments
BOT 2
EDPA
M-FUN
PDMS-2
TIME
issues important for aging
as you age, your body weakens and changes in every aspect; aging is complex and practice should consider an integration of theories
biological theory: focuses on cellular, molecular, and biological aspect of aging
psychological theories: address changes in cognitive, personality, and social development
sociological theories: considers context of aging
older adults are likely to have less education, altered support systems (widowed, etc.), insecure income, and possess a disability
heart disease is leading cause of death
account for a lot of healthcare costs
age-related changes to body
muscular system
muscle loss, endurance loss, balance loss > falls, sprains, tears
skeletal system
degenerative joints, stiffer, loss bone mass & density, spinal weakness, posture changes > kyphosis, falls, fractures
neurological system
atrophy nerves in brain, decr blood flow to brain, altered synaptic transmission, whole body nerve changes, tremors > decr speed, coordination, FM skills, cognition, homeostatic regulation
sensory system
loss of fxn
vision loss!!!, hearing loss, tactile loss, vestibular loss
ALL can lead to deprivation, isolation, confusion, senility, depression, decr social, decr QoL
cognitive system
Decr communication, memory, processing speed, perceptual skills
cardiopulmonary!!!
inactivity, degen of heart muscle, decr blood flow, conduction changes, changes in blood vessels incr BP, decr resp capacity, unproductive resp > reduced exercise capacity, orthostatic HTN, fatigue, decr ejection, hypoxia, no cough, aspiration
important to assess prior to exercise
integumentary (skin)
decr skin composition, decr sebaceous ax, brittle nails, loss protective barrier > skin tears & injury, dehydration, diminished touch and temperature sense
strategies to slow or reverse age-related muscular changes
improve health
increase physical activity
strength training
flexibility and ROM interventions
strategies for age-related skeletal system changes
postural exercises
weight-bearing
nutritional, hormonal, and medical therapy
strategies for age-related neurological changes
address medical problems (cerebral blood flow)
improve health, nutrition, and smoking cessation
incr physical activity
motor learning and control strategies
incr time for rxn, limited complex sequences, allow incr cautionary behaviors, promote familiarity
adapt to new body
strategies for age-related vision loss
max visual fxn (envir. mod)
allow extra time for discrimination
incr lighting, reduce glare
large print, high contrast
magnify
eye path for diplopia
safety education
signs & sx of elder abuse
physical abuse
sexual
emotional
financial
physical abuse
individual reports abuse
bruises, black eyes, lacerations, fractures and dislocations
rope marks, restraint signs
broken eyeglasses, hearing aids
under or overdosing drugs
sudden change in behavior, caregiver refuses to leave them alone with visitor
sexual abuse
individual reports
bruises around private areas
unexplained STI or genital bleeding
torn, stained, or bloody underwear
emotional abuse
individual reports
emotionally upset, agitated, withdrawn, nonresponsive
unusual behavior (sucking, chewing, biting, rocking)
financial or exploitation
sudden change in banking or account
inclusion of additional names on bank cards
unauthorized withdraw of money
abrupt changes in will or other documents
unpaid pills or substandard care despite funds
occupational perspective of health (OPH)
- DBBB
1. Doing
2. Being
3. Becoming
4. Belonging
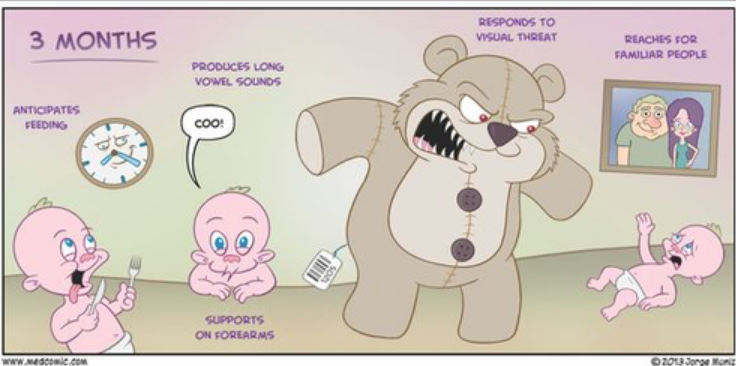
3 month milestones: gross motor skills
symmetrical UE and LE movements
sitting: head control in supported sitting
prone:
props on forearms
holds head at 45-90 degrees
supine:
bring legs together in midline
tuck chin and extend neck
standing:
bears some weight, head control while supported
roll tummy to back
supine to sidelying > prone to supine

3 month milestones: fine motor skills
visually tracks person or object
grasps rattle momentarily
voluntary grasp, involuntary release
poor power and precision grasp
bangs and shakes
brings hands to midline
begins to reach for objects
bilateral reach
3 month milestones: speech/language skills
quiets to familiar voice
smiles
coos & gurgles
cries to hunger, fear, discomfort, pain
6 month milestones: gross motor
prone:
extended arms, pivots
7ms > crawl
supine:
plays with feet
feet to mouth
kicks feet
no head lag
rolls back to tummy
supine to sidelying > prone to supine > supine to prone
sits independently
poor dynamic balance
stands with support
bounces
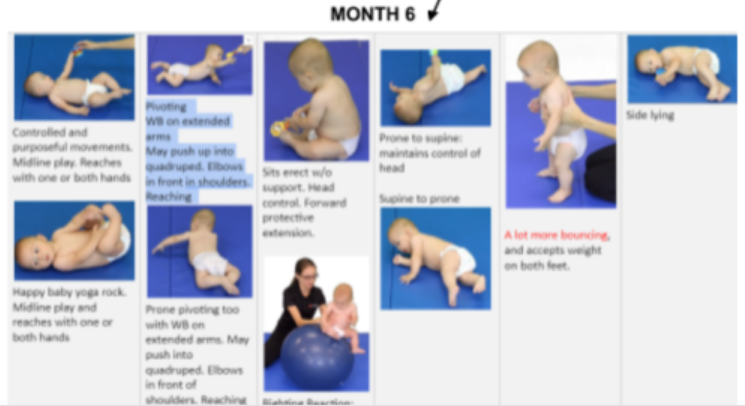
6 month milestones: fine motor skills
manipulation:
transfers object (two stage > one stage)
toys to mouth
bangs
voluntary release
unilateral reach
supine = success
prone = weight shifting for inrc success
grasp
pellet = swiping/raking
cube = radial palmar
4ms: primitive squeeze
5ms: palmar grasp
6ms: radial palmar

6 month milestones: speech/language skills & cognitive skills
uses consonant sounds (dada)
babbles for attention
takes cereal from spoon
holds large bottle (attempts feed self)
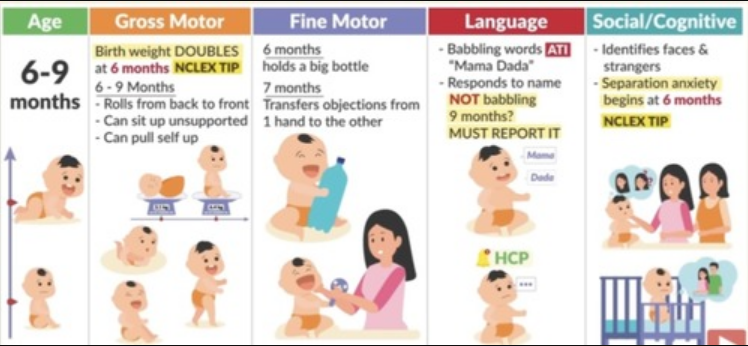
9 month milestones: gross motor skills
up on hands and knees
begins to dislike prone
crawls/creeps
reciprocal creep
transitions btw positions
in/out sitting
pulls to stand
cruises on furniture
sideways, around furniture, slight turn to direction
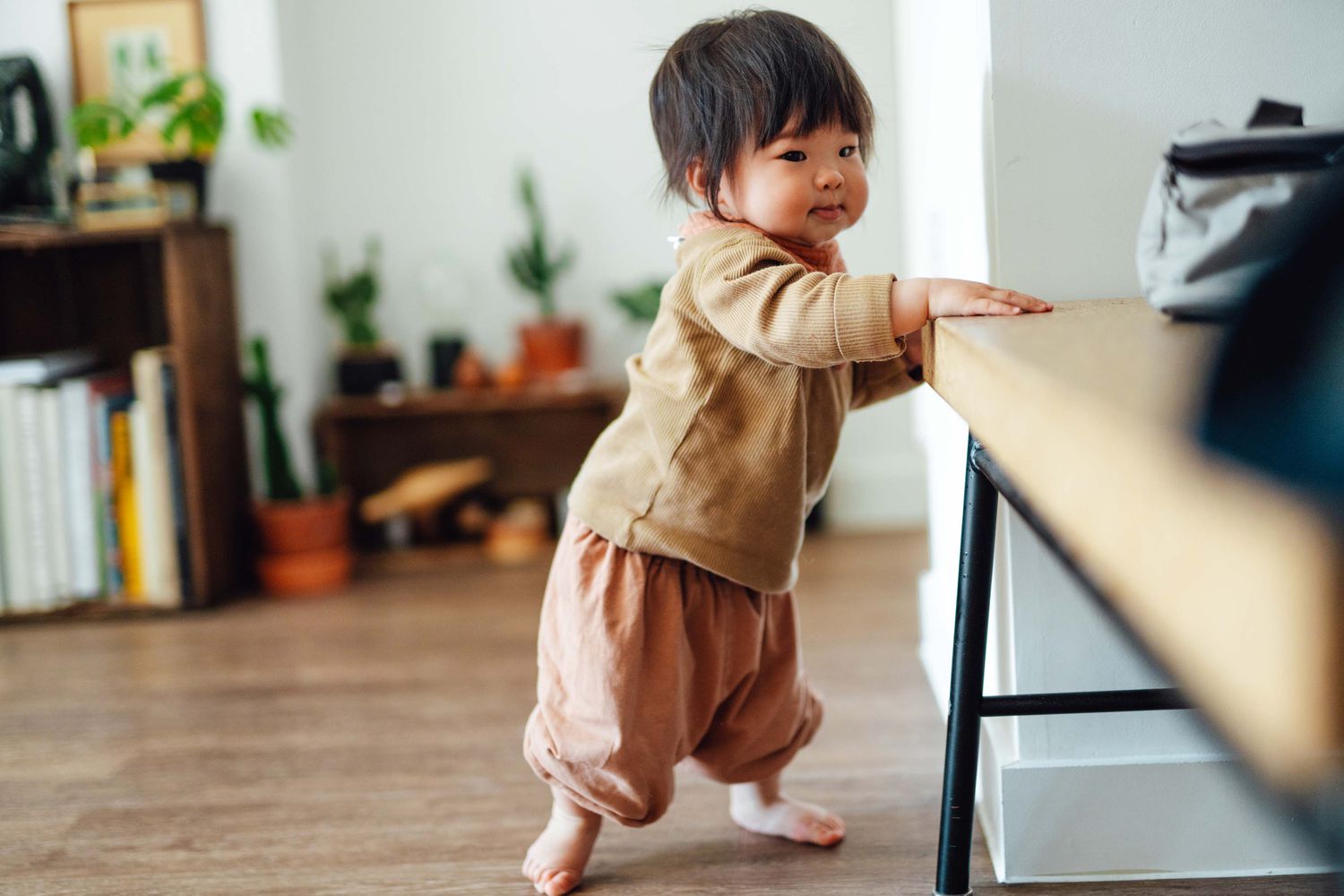

9 month milestones: fine motor
reaching
good unilateral & bilateral reach in all positions
sitting
indp sitting, reach w/no LOB, plays in sitting
grasp
cube: radial grasp (matured at 8ms)
pellet: inferior pincer grasp
7ms: inferior scissor
8ms: scissor grasp
9ms: inferior pincer grasp
claps hands
explores objects
pokes, pulls, turns, tears
bangs 2 cubes together
takes object OUT of container
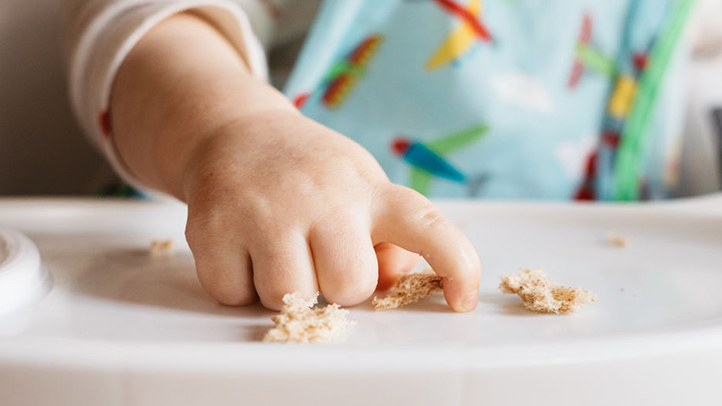

9 month milestones: speech/language skills
understands a few words (no, bye)
responds to own name
looks at familiar object when named
shows expression when babbling
waves Bye-Bye
cause and effect centered
anticipates consequences
repeats actions for consequences
interacts with peek a boo

12 month milestones: gross motor skills
efficient with creeping/crawling
inclines, uneven surfaces
stands unsupported momentarily
walking
takes first steps independently
mod support for walk
stoop & recover, wide gait
cruise:
expert, reaches for furniture, no hesitation

12 month milestones: fine motor
grasp:
cube: radial digital (matured)
pellet: fine pincer grasp (matured)
10ms: pincer grasp
12ms: fine pincer grasp
feeding:
finger feeds self
dips spoon
rotary chewing
bilateral hand use
use both hands for different fxns
manipulation:
points with index finger
puts 3+ objects INTO container
writing:
begins to scribble w/no intent using palmar supinate
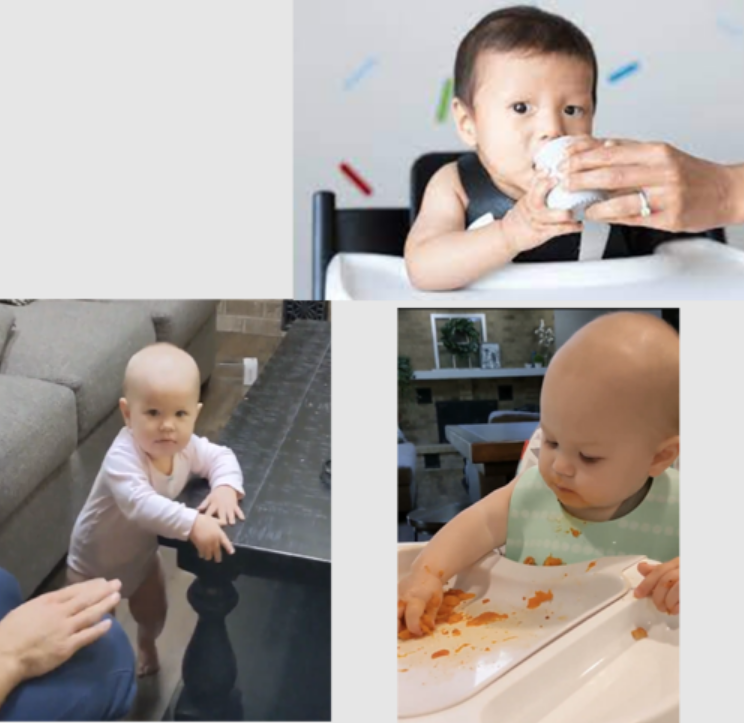

12 month milestones: speech/language skill & cognitive skills
1-2 words, social gibberish
recognizes own name
imitates sounds
responds to simple commands (No, Give me...)
cooperates w/dressing & changes
removes socks
goal directed actions
able to use tool after demo
variety of schemas

15 month milestones: gross motor
walks independently
wide gait, falls
squats without support to retrieve object
climb on/off surfaces, creeps UP stairs
flings ball forward

15 month milestones: fine motor
stacks two, 1" cubes
assists with undressing
doff simple
assist with don
scribbles w/no intent using palmar supinate
developing finger-palm translation
15ms-24ms
scoop with spoon

15 month milestones: speech/language
5-10 words
understands 50 words
identifies 2 body parts on self
simple schema linking
= symbolic play, make believe w/familiar
baby in carriage > push carriage
recruits help of adult
attempts simple mechanism
turns and inspects toys
trial and error approach to new challenges

18 month milestones: gross motor
walks efficiently (point of concern if not yet walking)
runs stiffly, eyes on ground
stairs:
walks up/down stairs w/support
creeps backward DOWN stairs
climbs into adult chair
18 month milestones: fine motor
builds 3 block tower
scribbles w/out intent using palmar supinate grasp!!
bilateral coordination:
one hand holds, one manipulates
finger to palm translation
15ms-24ms
attends to shapes and uses them appropriately
18 month milestones: speech/language
5-20 words including names
names pictures in a book
points to common objects
increasing non-realistic object play
pretend play
knows when wet/distressed, cooperates w/changes
doff simple, assist w/don
begins to think before acting
forethought beginning
operate mechanical toy
can predict or presume causes

24 month milestones: gross motor
runs
jumps off step
walks up/down stairs w/out support
NO alternating feet
throws OVERhand
24 month milestones: fine motor
strings 1" beads
recognize operations of mechanisms
matches circles, squares, triangles
discriminate size (24-27ms)
stack blocks (24-30ms)
manipulation:
palm to finger translation
simple rotation
shape sorter (manipulate into small openings)
snips with scissors
digital pronate grasp
draws VERTICAL line
circular scribbles w/intent
don shoes
fork use
24 month milestones: speech/language
has 50+ words
uses two-word phrases "more milk"
follows 1 & 2 steps commands
listens to short stories
makes animal noises
uses pronouns (me, mine)
asks for help
can feel frustrated
POTTY TRAINING = knows when wet and distressed
meaningful multischeme combos
put food in bowl, scoop food using spoon, feed doll
3 year milestones: gross motor
kicks ball without help
walks up stairs alternating feet
rides tricycle
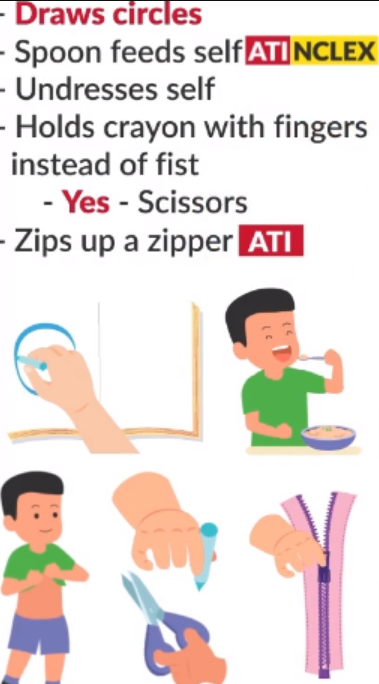
3 year milestones: fine motor
copies a Circle
imitates Cross
completes simple puzzle (3-5 pieces)
unbuttons 1" buttons
nine cube tower
organize objects by size and build from mental image
3 year milestones: speech/language
- Identifies parts on an object (nose on doll)
- Identifies complex body parts (knee, chin)
- Speaks in sentences
- Understands direction (in, out, on, under)

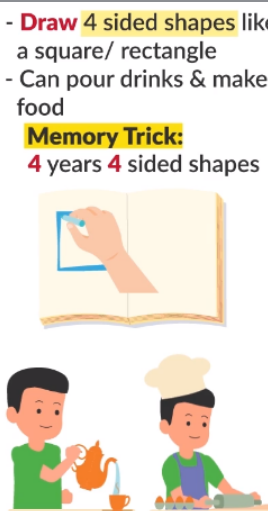
4 year milestones: gross motor
- Catches ball with hands
- Rides bicycle with training wheels
- Stands on one foot for 6 seconds
- Hops on one foot
- Jumps forward

4 year milestones: fine motor
- Draws person with 3 parts
- Builds 9+ block tower
- Cuts along line
- Static tripod grasp
4 year milestones: speech/language
- Knows difference between reality and pretend
- Understands descriptive words (long/short)
- Describes 3 step procedure
- Asks Questions (Why, where, what, how)
- Plays appropriately with other children
5 year milestones: gross motor
efficient with walking, running, and climbing
skips
walks downstairs holding object
throws ball at target
5 year milestones: fine motor
Copies Square & Triangle
Copies name
Dynamic tripod grasp
Cuts simple shapes
Prints some letters
Draws person with 5+ body parts
Established Hand dominance
Dresses self

5 year milestones: speech/language
speaks in conversations
speech 90% intelligible
able to follow rules
knows colors
knows opposites
counts 1-10
understands simple concept of time (tomorrow, yesterday, morning, night)