psych vocab (copy)
1/63
Earn XP
Description and Tags
will keep adding to during semester
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
64 Terms
critical thinking
thinking that does not blindly accept arguments and conclusions, rather it examines assumptions, appraises the source, discerns hidden biases, evaluates evidence, and assesses conclusions
Empiricism
the idea that knowledge comes from experience, and that observation and experimentation enable scientific knowledge
Structuralism
an early school of thought promoted by Wilhem Wundt and Titchener: used introspection to reveal the structure of the human mind
Introspection
the process of looking inward in an attempt to directly observe one’s own psychological processes
Functionalism
an early school of thought promoted by William James and influenced by Charles Darwin; explored how mental and behavioral processes function-how they enable the organism ro adapt, survive, and flourish
behaviorism
the view that psychology (1) should be an objective science that (2) studies behavior without reference to mental processes, most psychologists today agree with 1 but not 2
Humanistic psychology/humanism
a historically significant perspective that emphasized human growth potential
Psychoanalytic
Sigmund Freud, emphasized the ways our unconscious mind and childhood experiences affect our behavior.
Cognitive psychology
the study of mental processes, such as occur when we perceive, learn, remember, think, communicate, and solve problems
cognitive neuroscience
the interdisciplinary study of the brain activity linked with cognition ( perception, thinking, memory, and language)
psychology
the science of behavior and mental processes
nature v nurture issue
the longstanding controversy over the relative contributions that genes and experience make to the development of psychological traits and behaviors ( used to be god(s), nature, and the outside world, nurture, but now it is genes and how you were raised)
natural selection
the principle that inherited traits that better enable an organism to survive and reproduce in a particular environment will most likely be passed on to succeeding generations
evolutionary psychology
the study of the evolution of behavior and the mind, using principles of natural selection
behavior genetics
the study of the relative power and limits of genetic and environmental behavior
culture
the enduring behaviors, ideas, attitudes, values, and traditions shared by a group of people and transmitted from one generation to the next
positive psychology
the scientific study of human flourishing with the goals of discovering and promoting strengths and virtues that help individuals and communities to thrive
biopsychosocial approach
an integrated approach that incorporates biological, psychological, and social-cultural, cultural veiwpoints
behavioral psychology
the scientific study of observable behavior, and its explanation by principles of learning
biological psychology
the scientific study of the links between biological ( genetic, neural, hormonal), and psychological processes
psychodynamic psychology
a branch of psychology that studies how unconscious drives and conflicts influence behavior and uses that information to treat people with psychological disorders
social cultural psychology
the study of how situations and cultures affect our behavior and thinking
testing effect
enhanced memory after retrieving, rather than simply rereading information
SQ3R
a study method incorporating five steps: survey, question, read, retrieve, review
psychometrics
the scientific study of the measuremnt of human abilities, attitudes, and traits
basic research
pure science that aims to increase the scientific knowledge base
developmental
studies physical, cognitive, and social change throughout the lifespan
educational psychology
the study of how psychological processes affect and can enhance teaching and learning
personality psychology
the study of inividuals’ characteristic patterns of thinking, feeling, and acting
social psychology
the scientific study of how we think about, influence, and relate to one another
applied research
scientific study that aims to solve practical problems
industrial organizational psychology
the application of psychological concepts and methods to optimizing human behavior in workplace
human factors psychology
a field of psychology allied with (I/O) psychology that explores how people and machines interact and how machines and physical environments can be made safe and easy to use
counseling psychology
a branch of psychology that assists people with problems in living and in achieving greater well being
clinical psychology
a branch of psychology that studies, assesses, and treats people with psychological disorders
psychiatry
a branch of medicine dealing with psychological disorders practiced by physicians who are licensed to provide medicine
community psychology
a branch of psychology that studies how people interact with their social environments and how social institutions affect individuals and groups.
hindsight bias
the tendency to believe, after learning an outcome, that one would have foreseen it.
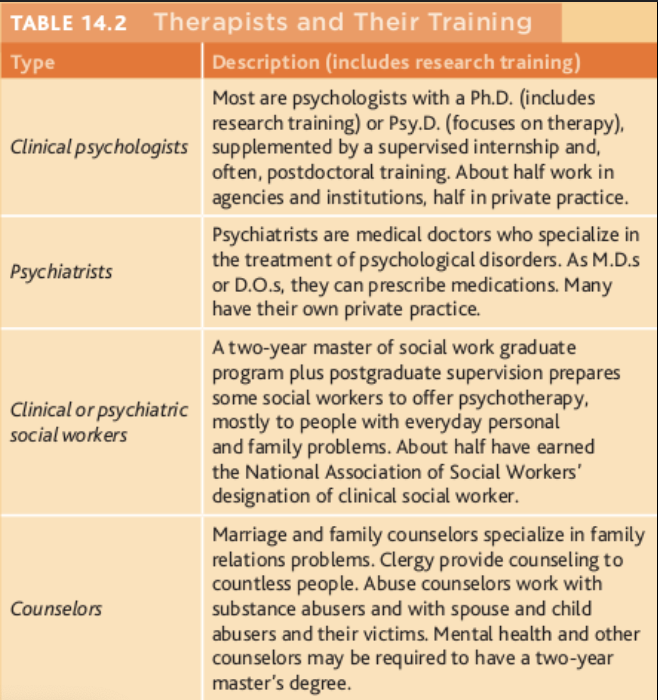
the difference in psychiatrists is the degree they have
Scientific method
a self-correcting process for asking questions and observing natural answers
Hypothesis
a theory that can be tested
theory
explains behaviors or events by offering ideas that organize observations.
operational definition
a carefully worded statement of the exact procedures used in a research study
replication
repeating the essence of a research study, usually with different participants in different situations, to see whether the basic finding can be reproduced
case study
a descriptive technique in which one individual or group is studied in depth in the hope of revealing universal principles
naturalistic observation
a descriptive technique of observing and recording behavior in naturally occurring situations without trying to manipulate or control the situation
survey
a descriptive technique for obtaining the self reported attitudes or behaviors of a particular group usually by questioning a representative
sampling bias
a flawed sampling process that produces an unrepresentative sample
population