BIOL21141 Cell Membrne structure and function
1/267
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
268 Terms
van der Waals forces
Lipids in a membrane do not interact covalently but by these forces instead
Permeability barrier
A role of membranes where they select how much of a molecule is allowed to enter the cell
Apical membrane outer leaflet
A part of the membrane that has lipid that help prevent transport of water molecules
Tight junctions
These prevent mixing between the apical and basolateral outer leaflets and seal gaps between epithelial cells and the sheet
6-10nm
The thickness of the cell membrane
Lipid:protein ratio
This in the cell membrane can varry from 1:4 to 4:1
membrane proteins
Can be pumps channels, receptors or enzymes
Glycoslyation
Carbohydrates linked to proteins or lipids
lipids
A large group of fats and fat-like compounds that occur in living organisms that are sparingly soluble in water.
Fluid mosaic model
The model used to describe cell membranes - the membrane is dynamic as lipid are able to move
Variety of lipids
This property leads to changes in membrane dynamics, surface biochemistry, formation of lipid subdomains and signalling
Cell membrane functions
Separation, exchange, integration and metabolism.
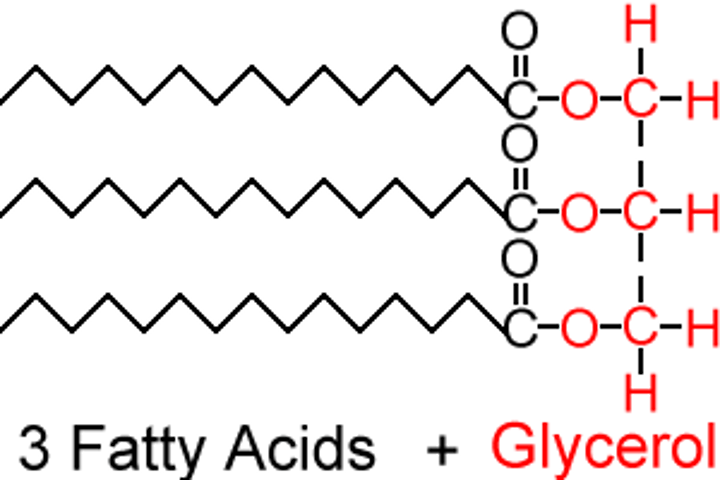
Triacylglycerols
Have a glycerol backbone with 3 fatty acid (acyl) group. Hydrophobic
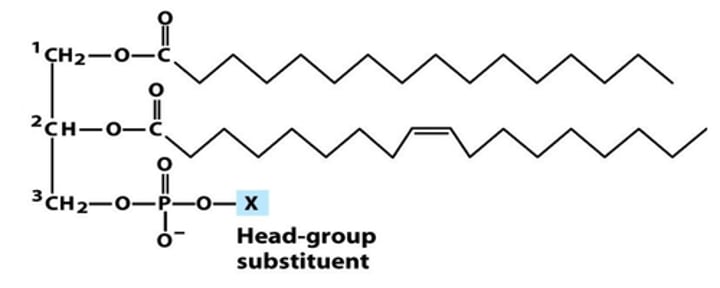
Glycerophospholipids
Glycerol backbone with a phosphate polar head group. Amphipathic
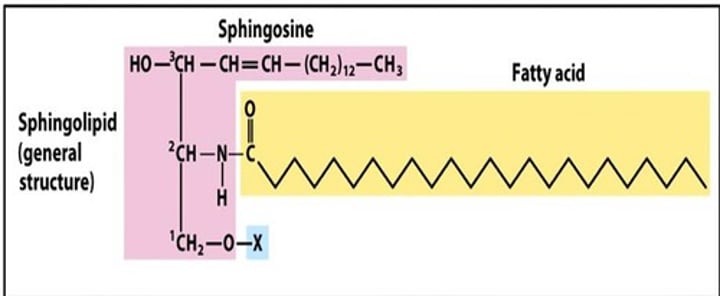
Sphingolipids
Lipid built on a sphingosine backbone. They are often glyco-conjugates. Amphipathic
Isoprenoids
A lipid class that includes lipid vitamins and hormones. They are largely hydrophobic but they have a variable polar group content
Head group of phospholipids
This is what determines the shape of the lipid bilayer. They can be positive, negative or neutrally charged. Also determines lipid subcategory.
Fatty acid chain
The shorter this is, the more fluid the lipid is. The average length is 18C.
Saturated.
No double bonds allowing lipid to have free rotation.
Unsaturated.
A double bond gives the fatty acid tail a kink and a point with no rotation. This leads to cis and trans conformations. These fatty acids are more fluid
Ester bond
A bond found in membrane lipid between and alcohol and carboxylic acid group
Ether bond
A bond found in membrane lipid between 2 alcohols.
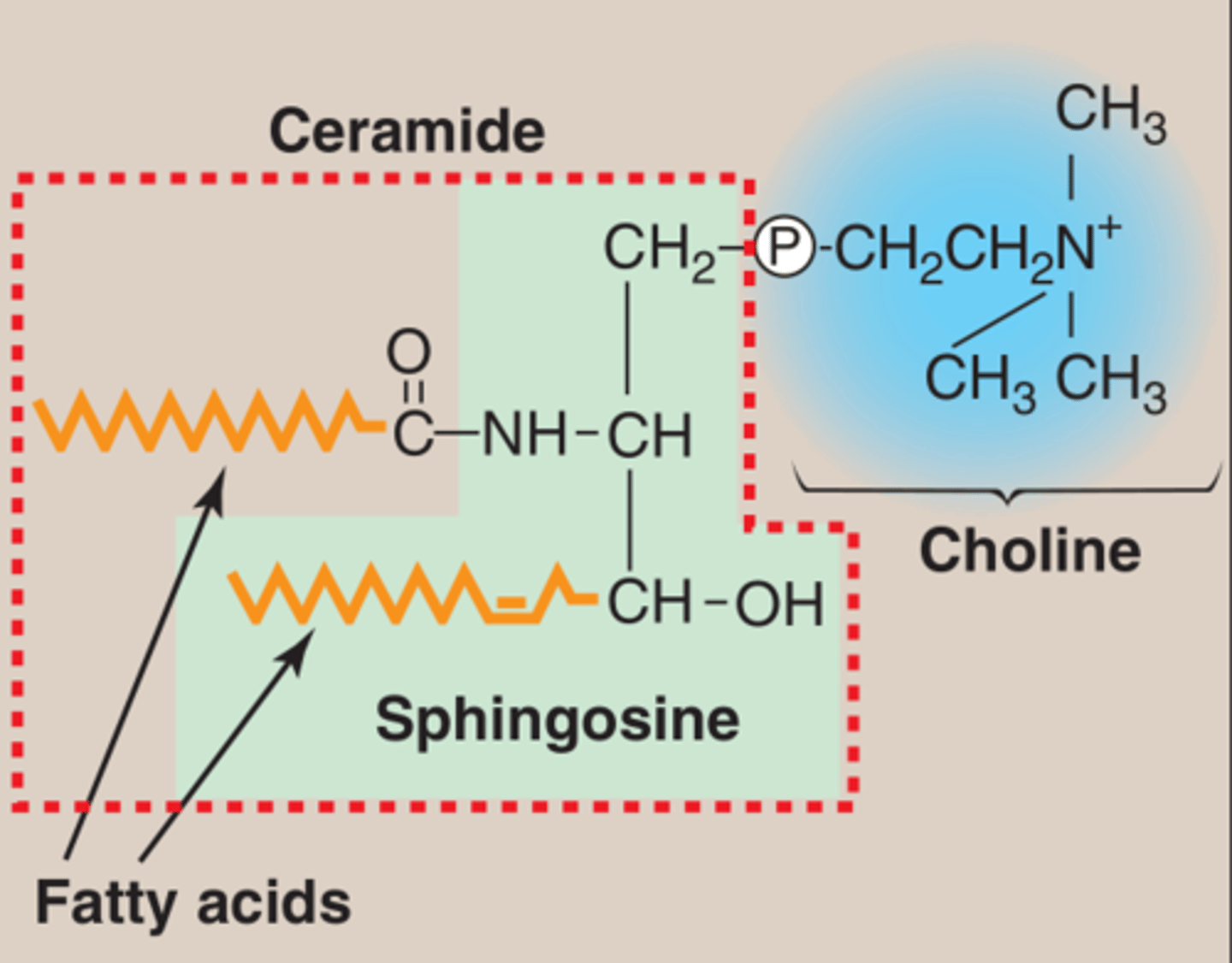
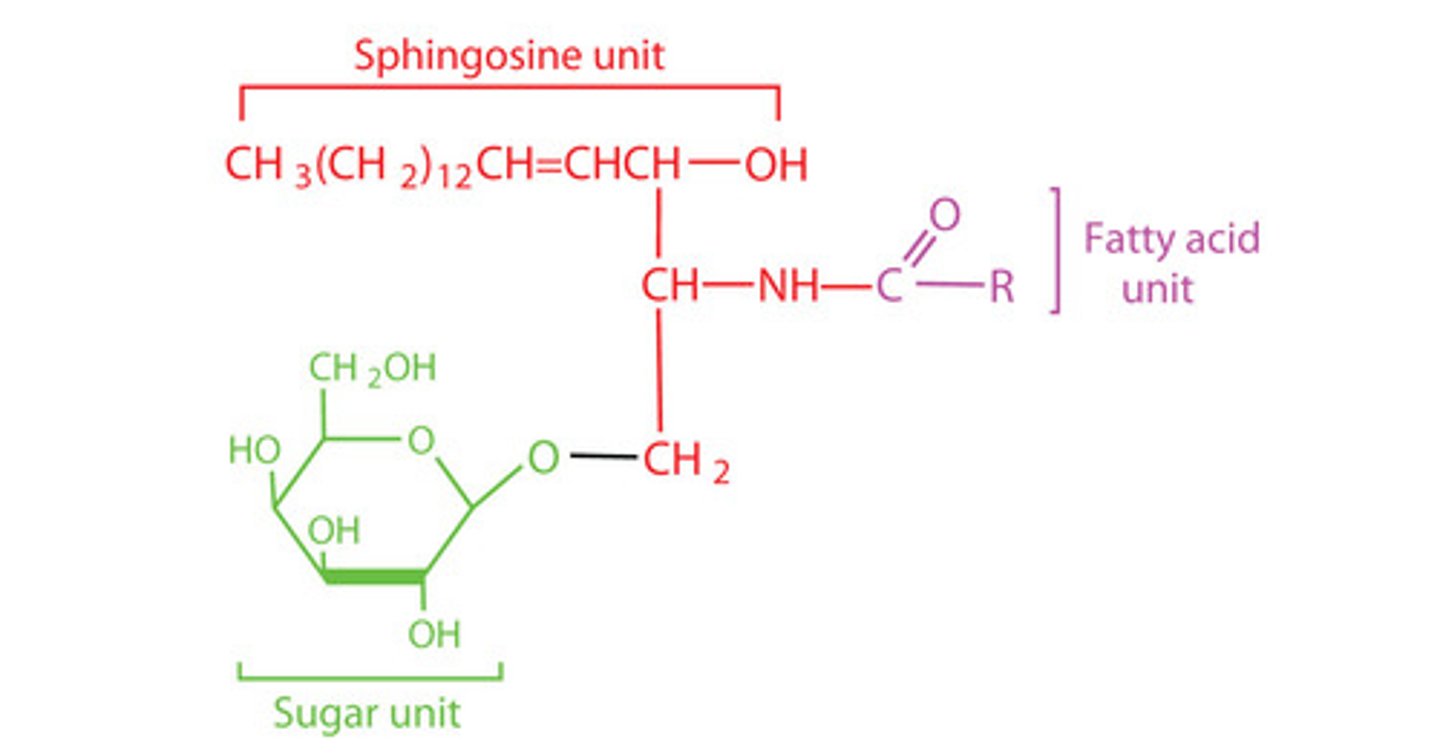
Sphingomyelin
A sphingophospholipid containing sphingosine, a phosphate group attached to choline and a fatty acid
Cerebrosides
A sphingophospholipid that have a ceramide unit linked by a glycosidic bond at C1 of a long chain base to glucose or galactose
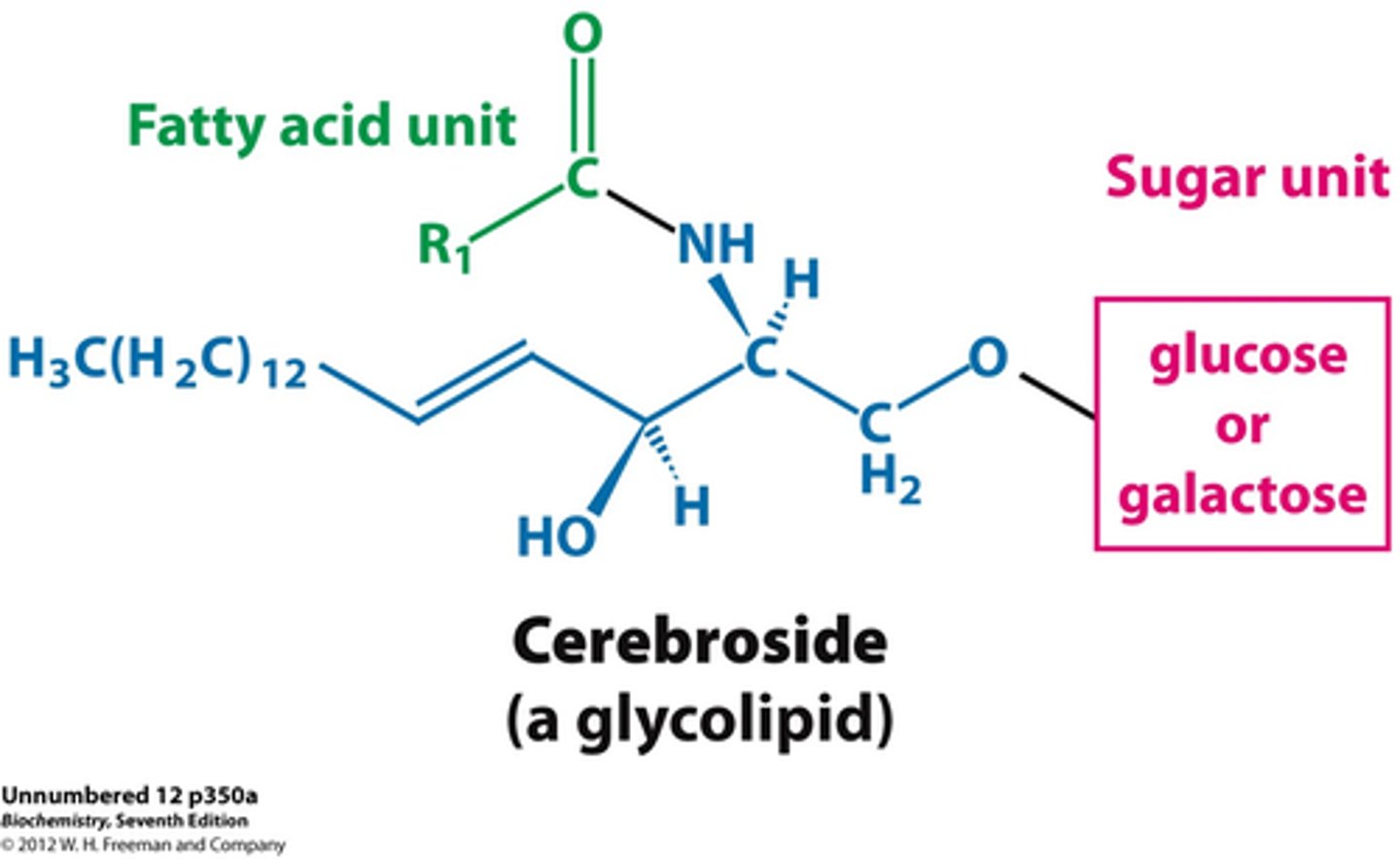
Gangliosides
A sphingophospholipid that has a sialic acid. component. They have large complex head groups
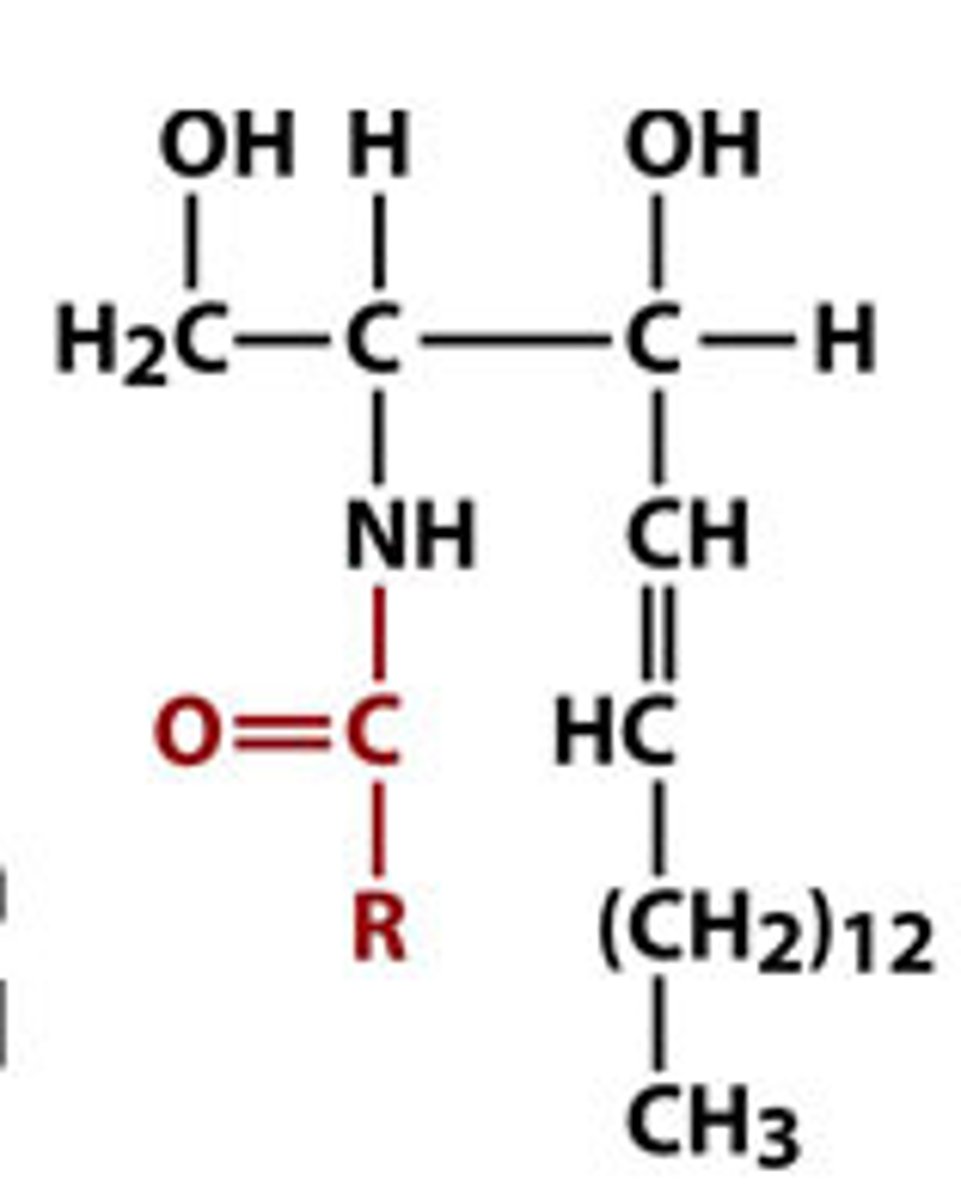
Ceramides
A sphingophosholipid that are known to function as intracellular signalling molecules that can affect cell growth, differentiation and programmed cell death. They have an alkyl group joined by an amide bond
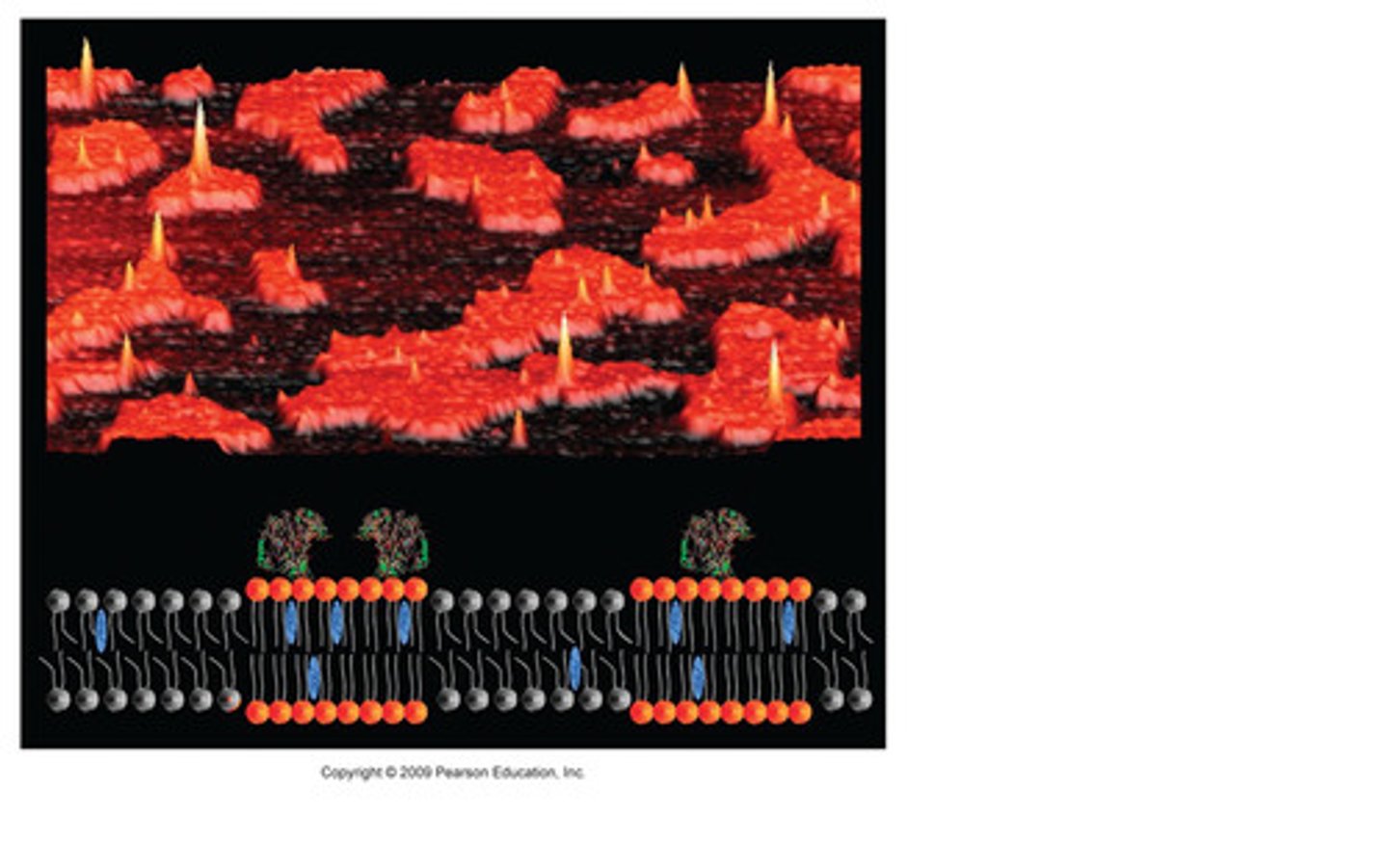
Lipid rafts
Sphingomyelin and gangliosides are found in these and they associate with cholesterol. They regulate the cell surface location of membrane proteins
Triacylglycerols
A neutral lipid made of 3 acyl groups and glycerol. Used as a fuel source.
Cholesterol
The steroid used in animal membranes to maintain fluidity. It has a tiny headgroup compared to phospholipids which is why it is hydrophobic. Has a rigid planar steroid ring structure which affects its bulkiness
Ergosterol
The steroid used by yeast membranes instead of cholesterol
Stigmasterol
The steroid used by plants in their membranes to maintain fluidity
Sphingolipid biosynthesis
This synthesis begins in the cystolic leaflet of the ER and finishes in the luminal leaflet of the golgi.
Sterol biosynthesis
This synthesis occurs in the luminal leaflet of the ER.
Phosphatidate
Synthesizing this molecules is the first step in in creating phospholipids. Acyl CoA is added to glycerol 3-phosphate to make lysophophatidatE. Another CoA is then added.
Glycerol-3-phosphate acyl transferase
The enzyme that catalyses the additions of CoA from Acyl CoA to glycerol 3-phosphate.
Cytidine triphosphate
CTP - this is added to phosphatidate to convert it it to CDP-diacyl glycerol.
Dehydrosphingosine
The 1st product in the biosynthesis of sphingolipids. Made by the reaction of palmitoyl CoA and serine
Serine palmitoyl transferase
The enzyme that catalyses the reaction of palmitoyl CoA and serine to make dehydrosphingosine.
Dihydrosphingosine
This is made from reducing dehydrosphingosine through oxidation of NADPH to NADP+. It is converted to sphingosine as FAD is reduced to FADH2.
Sphingomyelin synthase
The enzyme that catalyses the addition of choline headgroup from phosphatidyl choline to ceramide to make sphingomyelin.
Stage 1 cholesterol synthesis
Synthesis of isopentenyl pyrophosphate
Stage 2 cholesterol synthesis
Condensation of 6 isopentyl pyrophosphate to form squalene
Stage 3 cholesterol synthesis
Cyclisation of squalene. The tetracyclic product is converted into cholesterol
Negative Gibbs free energy
A theoretically value showing membrane formation is energetically favourable.
Hydrophobic effect
Hydrophobic solutes dont want to interact with water so adjacent water moelcules reorganize forming an more ordered lattice with higher free energy.
1.5x
The amount more of lipids in the outer leaflet compared to the inner
positive and negative curvature
these have to be formed in order to form a vesicle. Can be formed by flippase and floppase enzymes or by the different shape of lipids depending on the relative size of the head compared to tails
flipase
Amino phospholipid translocator. Uses. ATP to flip lipids from the outer to inner leaflet of the plasma membrane
floppase
ATP binding cassette transporters - uses ATP to move lipids from the inner to outer leaflets of the plasma membrane.
Phospholipase A
An enzyme the cleaves one fatty acid to form a lysophospholipid.
Phospholipase C
This enzyme cleaves the phosphate group to give diacylglycerol (DAG)
Outer membrane leaflet
This has a composition of 60% phosphatidylcholine, 30% sphingomyelin and 10% phosphatidylethanolamine. Most has cylindrical lipids and inverted cones
Inner membrane leaflet
This has a composition of 40% phosphatidylethanolamine and 60% phosphatidylserine/phosphatidylcholine. Most cyclindrical and cone shaped lipids.
Asymmetric
A property of membranes vital for function e.g. glycolipids are involved for cell signalling so are only found on the outer leaflet.
ER membrane
This membrane is much more symmetrical when compared to plasma membrane. It also does not contain cholesterol
Lateral diffusion
A method by which lipids an move along the membrane. It is very slow - 2micrometers per second.
aminophospholipid translocase
This transfers Phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine from the outer to inner leaflet
P family
This is a family of ATPases - some are involved in the transport of lipids
P4 ATPases
This is an ATPase known to transport and flip lipids. CDC50 binds to it and it becomes phosphorylated. ATP hydrolysis provides energy for function
ABC transporters
A large family of membrane transporters that bind ATP
ABC1
An ABC family protein that transports lipids. ATP binds to the cytoplasmic side. Hydrolysis provides energy for flopping
Scramblases
Enzymes that transport PC and PE bidirectionally from the inner to outer leaflet. Allows them to equilibrate rapidly.
TMEM16
A scramblase enzyme that binds to Ca2+. It is activated by high Ca2+ which will scramble phoshpholipids. This inactivaes P4-ATPase reducing flipping
Sphingolipids/glycolipids
These 2 lipids are post-Golgi outer membrane components so are not present in the ER membrane. They have to be trasnported to aneterograde (forward) vesicles not retrograde (reverse) vesicles
Phospholipid transfer/exchanage proteins
These proteins transport a lipid from one membrane to another - they have space in their tertiary strcuture to accomodate the lipid. they dock at the donor membrane where the lipid is deposited. They then dock at the acceptor membrane where the lipid is released
Tubular lipid binding domains
TULIP binding proteins. These proteins span the gap between two membranes and have a hydrophobic tube in the middle of them that lipids can diffuse through.
Fluorescence photobleaching after recovery
FRAP - proteins are fluorescently tagged and an srea is bleached with a laser. The bleached patch disappears as fluorescent proteins diffuse into it - shows movement of proteins
Transmembrane proteins
Proteins that span the entire membrane. They have a hydrophobic core. They connect the outside of the cell to the inside
Monolayer proteins
Proteins that are embedded in one leaflet of the membrane.
Lipid anchored proteins
Proteins associated to the membrane by a lipid connection. Also known as surface bound peripheral membrane proteins.
Single pass transmembrane proteins
Proteins that have an alpha helix that passes through the membrane just once. Includes the epidermal growth factor
Multipass transmembrane protein
A membrane protein that has multiple alpha helices that span the bilayer multiple times. Includes ion channels and GPCRs
GPCRs
A type of multipass transmembrane proteins. They have 7 transmembrane helical domains. There are over 400 in humans
Rhodopsin
The most studied GPCR. It has TM domains with 20 hydrophobic residues that form alpha helices. These are flanked by charged residues that provide H bonding between helices to stabilise.
Glycosyl phoshatidyl inositol modifcation
A modification that can anchor proteins to the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane - the lipid acts as a lease. The protein can be released by a specific phosholipiase
Palmitolyation
A way of anchoring proteins through cysteine residues. It is reversible and carried out by palmitoyltransferase. Ras is an example.
N-terminal myristoylation
A way of anchoring proteins to the inner leaflet. The lipid is added to the N-terminus as the protein is synthesized in the ER by N-myristoytransferase. This is irreversible
Farnesylation
A prenylation of the C terminus. It involves a thioester linkage of the farensyl group catalysed by. the enzyme farnesyl transferase.
Geranylation
A prenylation of the C terminus. It is a thioester linkage of the geranylgeranyl group by the enzyme geranylgeranyltransferase.
Prenylation
The addition of specific carbon chains to proteins to help facilitate protein attachment to cellular membranes
Long range signalling
This includes synaptic and endocrine signalling
Short range signalling
This includes paracrine, juxtracrine and autocrine signalling
Paracrine signalling
A diffusible signal from an adjacent cell
Juxtracrine signalling
Contact depdent signalling between adjacent cells that are touching
Autocrine signalling
A signal that has arisen from the responding cell itself for positive or negative feedback.
ligand gated ion channel
specialised membrane proteins that allow ions to pass through a membrane once when a certain molecule has bound.
enzyme coupled receptor
A multisubunit protein in the membrane - a ligand binds to one area which activates the rest of the protein
receptor tyrosine kinases
An enzymes that phosphorylates tyrosine residues on proteins. They span the membrane once. They dimerize when activated and monomers phosphorylate each other.
autophosphorylation
Where monomers of a multisubunit protein phosphorylate other monomers activating them and increasing activity.
Phosphotyrosine binding domain
PTB - a domain on RTKs that signalling proteins can be recruited to
src homology 2 domain
SH2 - a domain on RTKs that signalling proteins can be recruited to.
Signal Bifurcation
Multiple effectors being recruited to one original signal
Signalling adaptor proteins
Proteins that have no enzyme or intrinsic activity. They bind to signalling proteins and help assemble multi-protein complexes at activated receptors.
IRS-1
A major substrate of the insulin receptor. It is an adaptor protein. It is recruited via a PTB domain, is phorphorylated and recruits further proteins.
Grb2
An adaptor protein that is recruited to RTKs via SH2 domains. It recruits Sos to the membrane
Sos
A protein recruits to RTKs by Grb2. It activates RasGTPase
Ras
A small GTPase. The 3 forms in humans are K, H and N Ras. It is attached to the membrane by a lipid anchor. It actiavtes the MAP kinase cascade.
MAPK pathway
A powerful ancient signalling pathway that consists of 3 protein kinases that subsequently phosphorylate each other.
ERK1/2
MAP kinase proteins that phosphorylate serine and threonine and are proline directed.
Raf
A MAP3K kinase activated by Ras. It phosphorylates MEK on 2 serine residues.