MICROBIOLOGY TEST II
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What is a virus?
An intracellular obligate parasite which infects all forms of life
Who showed that Yellow Fever was caused by a virus transmitted by mosquitos?
Walter Reed. He studied the Tobacco mosaic viruses by isolating it in a filtered bacteria-free fluid; it was found that it could cause disease in healthy plants.
What is the structure of a virus?
RNA or DNA genome is enclosed in a capsid protein shell.
Some viruses contain a viral envelope - host cell derived membrane
Describe viral symmetry in viruses
Capsids are often in symmetrical helical or icosahedral shapes.
What do we call a virus with a viral envelope?
Enveloped virus.
Membrane surrounded by nucleocapsid
Common in animal viruses.
What is a virus without a viral envelope?
Naked viruses.
No host-derived membrane.
Common in plant viruses and bacteriophages.
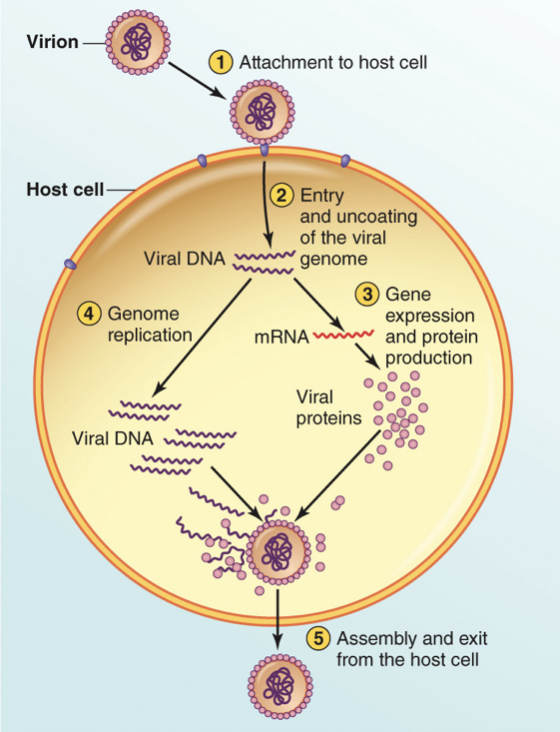
Describe the viral replication cycle
Adhere: stick to host cell
Penetrate and uncut: get into the cell and release genome
Synthesis: express its genes to make proteins & replicate its genome
Assembly and exit: put everything together (DNA and capsid) and get the new virus particles out
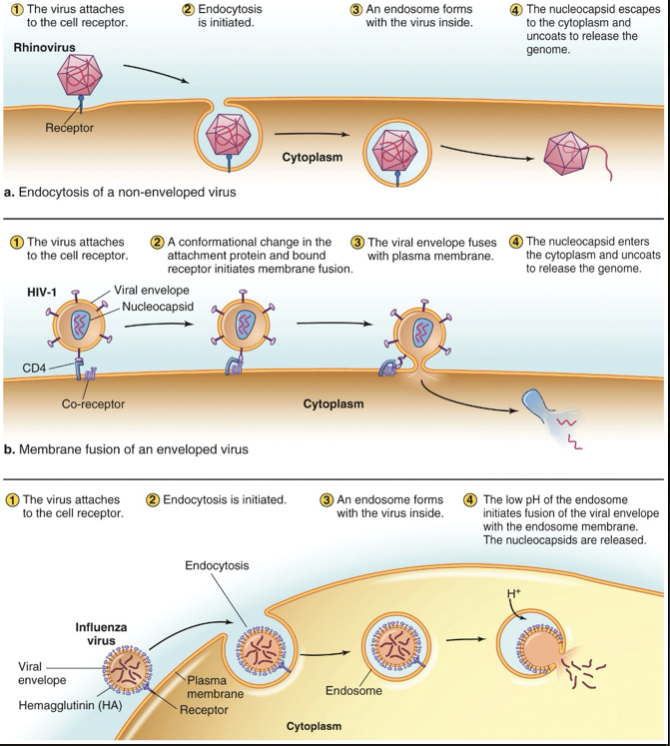
How do viruses get into animal cells?
Don’t have to deal with a cell wall
Receptor mediated endocytosis
Viral envelope fuses with plasma membrane
Viral envelope fuses with visible membrane
How do viruses get into plant cells?
Often depends on some damage to the plant tissue to open a spot in the cell wall
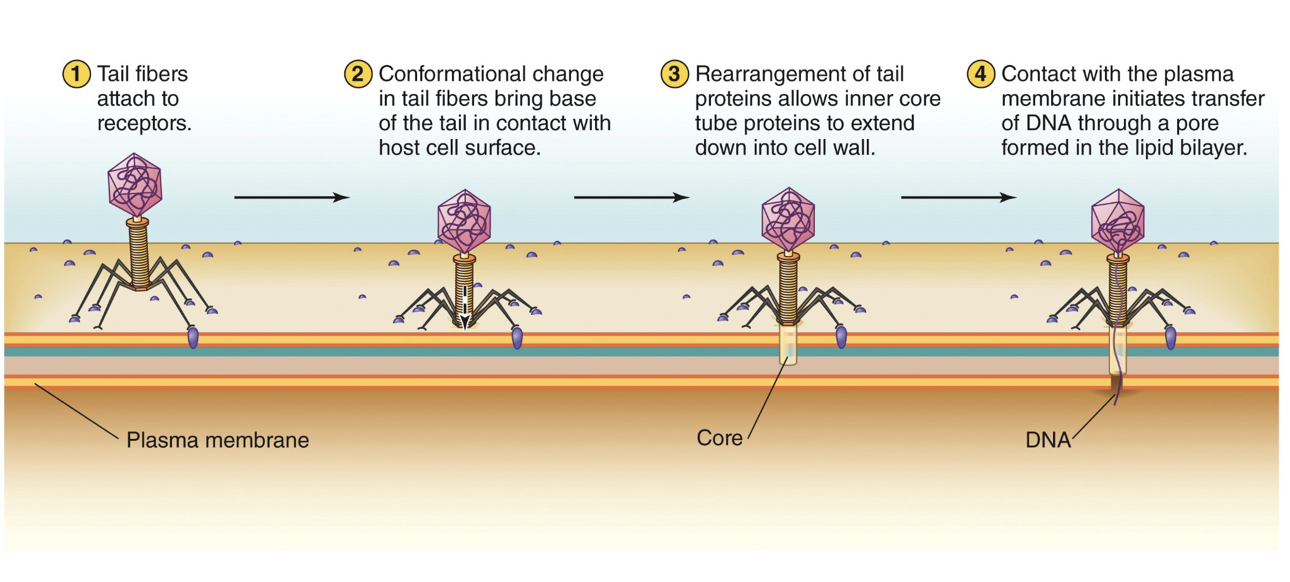
How do viruses get into bacteria?
Tail fibers are attached to cell wall and puncture into cell to transfer the viral DNA through a pore formed in the lipid bilayer.
What is the coevolution hypothesis?
Viruses developed along with their host cells
What is the regressive hypothesis?
Viruses are cells that lost some of the replicative and metabolic traits over time.
What is the progressive hypothesis?
Existing genetic elements gradually gained the ability to move from cell to cell.
Capsid vs nucleocapsid?
Capsid is just the protein shell whereas the nucleocapsid is the capsid containing the nucleic acid (genome).
What stranded structure of DNA/RNA do viral genomes consist of?
Either single or double stranded DNA or RNA.
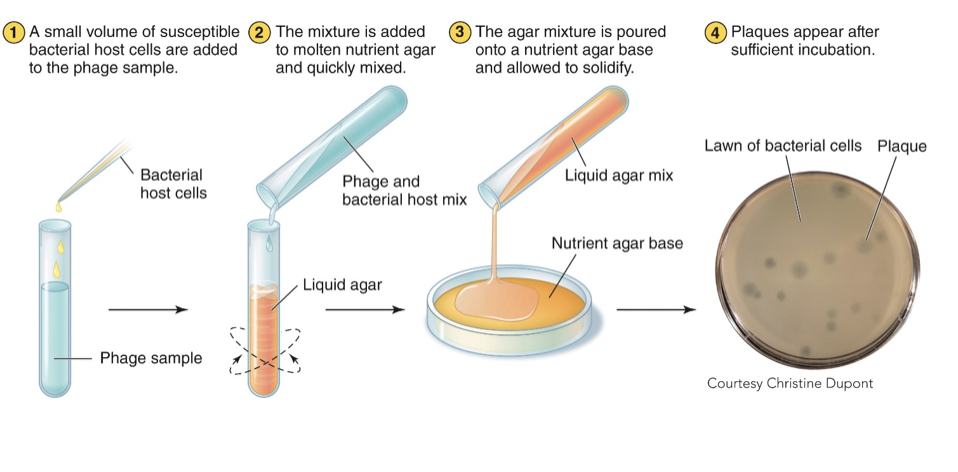
How do we cultivate bacteriophage?
Bacteriophage need a host cell to replicate (bacteria) and can be grown in either liquid or solid culture
How do we cultivate animal viruses?
Tissue cultures of host cells are used to grow targets for the viruses. Methods of this have only been in place since the 1950s and many come from the first human cell line known as HeLa cells (isolated from Henrietta Lacks).
Cytopathic effects can be observed in virally infected cultured cells.
How do we purify viruses?
Centrifugation is the process of forcing the separation of particles in solution. We spin solutions very quickly and the largest particles pellet at the bottom.
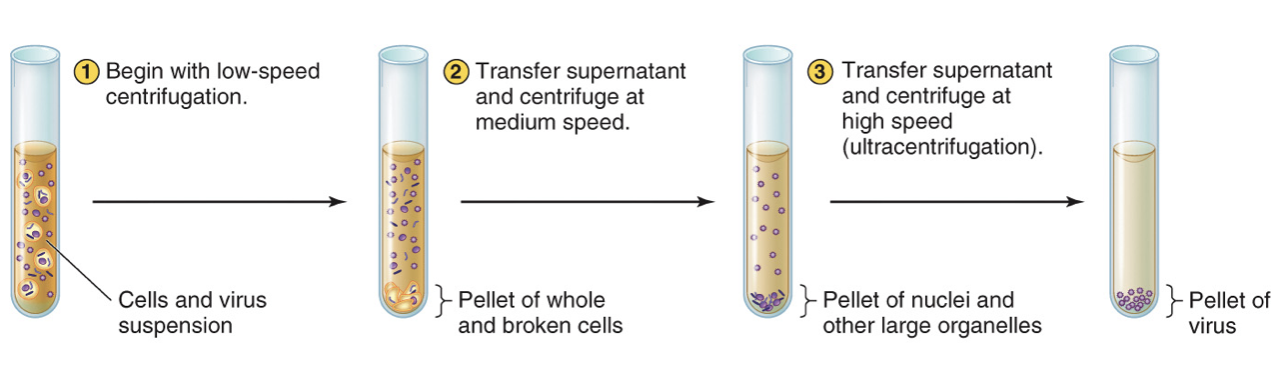
What is differential centrifugation
Differential centrifugation increases the speed in steps to separate different sizes of material
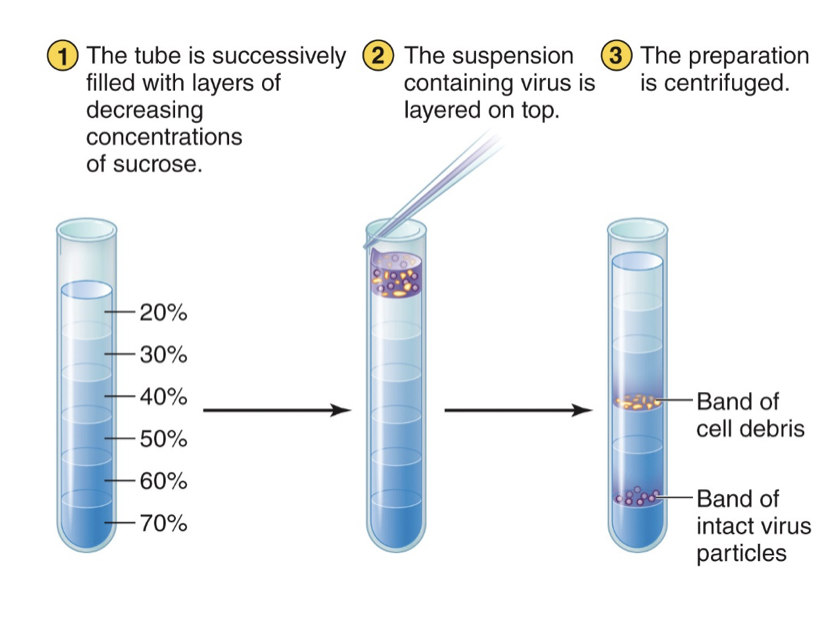
What is gradient centrifugation?
Depends on the different densities of viral components and particles.
Each piece with different density will settle into a different area (“band”) of a density gradient after centrifugation
How do we quantify viruses?
We use various tools/methods
What is the direct count method of viral quantification?
Electron microscope visualizes known volume.
Can determine concentration (titer)
However,
Not easy,
Requires expensive microscope
Doesn’t differentiate between infectious and noninfectious particles