Bio Test Unit 1
1/208
Earn XP
Description and Tags
All 450 Slides of Unit 1 Condensed into 214 Q-Cards. Still have to add the Lab.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
209 Terms
Trace Elements
Required by organisms in minute quantities. Boron, Chromium, Cobalt, Copper, Flourine, Iodine, Iron, Manganese, Molybdenum, Selenium, Silicon, Tin, Vanadium, Zinc.
Elements to make up 96% of an Organism
Oxygen, Carbon, Hydrogen, Nitrogen.
Orbital Energy
There is more potential energy in the higher the shell you go.
Ionic Bonds
Can be between metals and non-metal or IONS.
Weak Chemical Bonds
These are IONIC BONDS and HYDROGEN BONDS, they reinforce shapes of large molecules and help molecules adhere to each other.
Strong Chemical Bonds
Covalent and form a cells molecules.
Van der Waals Interactions
LDF, With non-polar.
Chemical equilibrium
When the forwards and reverse reaction rate are equal.
Temperature and Water
Water absorbs heat from warmer air then releases the stored heat when cooler.
Kinetic energy and Heat
The total energy of movement (DUE TO MOLECULAR MOTION) is measure of heat.
Temperature and KE
Temp is the measure of the intensity of heat due to the average kinetic energy of molecules.
Calorie
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1g of water by 1C.
Calorie to Joule
1cal= 4.184J
Joule to Calories
1J=0.239Cal
Specific Heat
Amount of heat that mist be absorbed or lost for 1g of that substance to change its temperature by 1C.
Waters specific heat and WHY
1cal/g/C = HIGH
High because of all the hydrogen bonds
heat released when they are formed
absorbed when break
Heat of vaporization
The heat a liquid absorbs for 1g to be converted to gas
Evaporative cooling
The water absorbs the heat so as it evaporates the remaining surface cools.
Helps stabilize the temperature in organisms (eg Sweating) and bodies of water.
Why does ice float?
The hydrogen bonds in ice are more ordered so making ice less dense. There is also small air pockets trapped.
Waters Greatest density
4C
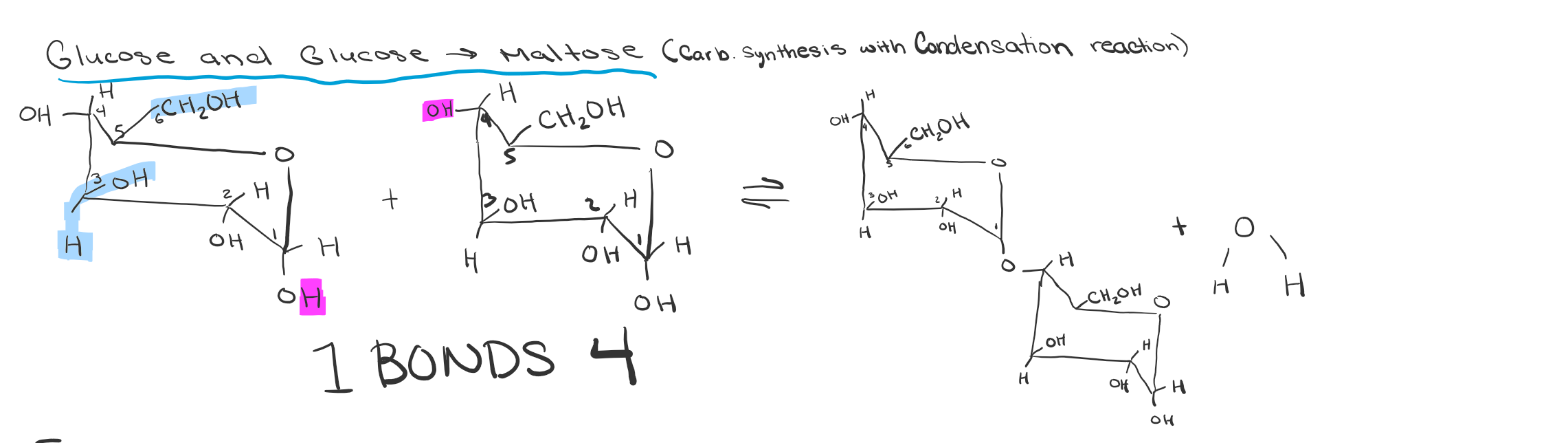
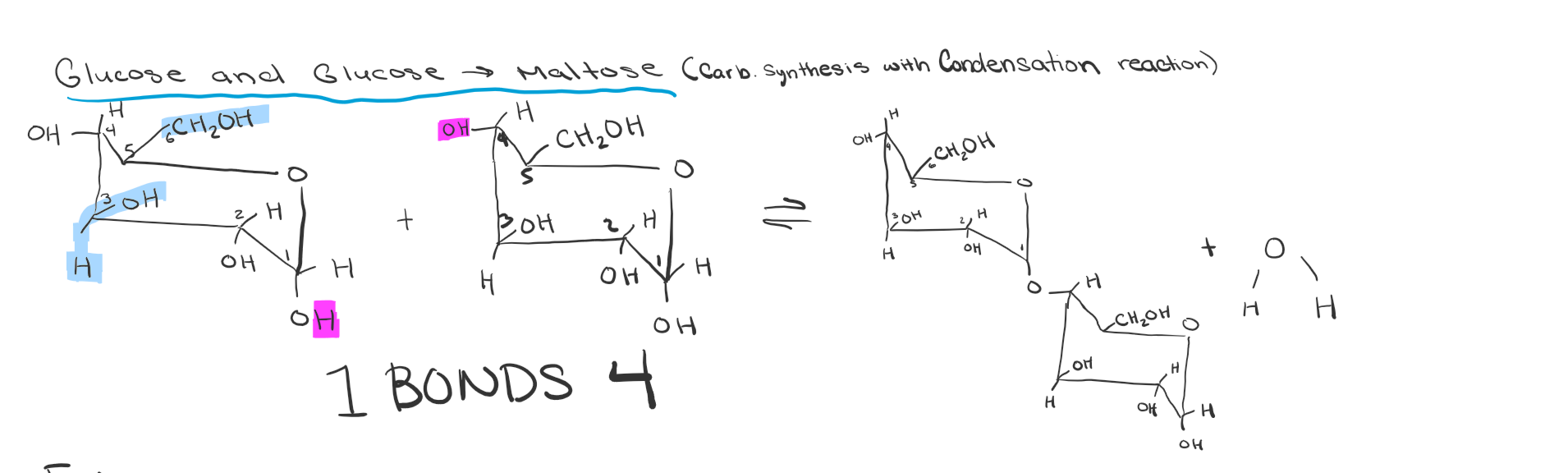
Maltose Creation Draw
Hydration Shell
When an Ionic Compound is dissolved in water each ion is surrounded by a sphere of water molecules.
Colloid (Milk or a Gel)
A stable suspension of fine particles in a liquid
Acid and Basic Buffers
Substances that minimize changes in concentration of H and OH ions in a solution. They consist if an acid-base part that reversibly combines with H.
Polymers
Long molecule consisting of many similar building blocks.
Monomers
The small single building block molecules.
Dehydration reaction
When 2 monomers bond together through the loss of 1 water molecule
Dehydration reaction between 2 glycose molecules
Hydrolysis
Polymers break apart when water is added.
Carbohydrates
Are sugars ad polymers of sugars .
Monosaccharides and molecular formula
Singular sugar. Molecular formulas that are multiples of CH2O.
Classification of Monosaccharides
Location of Carbonyl group (ketose (at the end), Aldose (in the middle)
number of carbons in the skeleton
How are disaccharide bonded
Through a glycosidic linkage
Plant storage Polysaccharides
Starch, entirely glucose monomers, stored at granules within chloroplasts and other plastids. THIS HAS A ALPHA GLUCOSE RING.
Plant Structure
Cellulose. This is a polymer of glucose but has a BETA GLYCOSIDIC LINKAGE.
Human and vertebrates Storage of sugars
Polysaccharide call Glycogen stored in the liver or muscles.
alpha glucose
This is helical.
beta glucose
This is straight. Allows for H-atoms on one strand to bond with OH group on the other. This is then how the microfibrils are grouped.
Humans and B-glucose
They can’t hydrolyze the b-linkages so this is the insoluble fiber that we need microbes to digest.
Chitin
Structure polysaccharide.
Chitin usages
Structural support for fungi and in exoskeletons of arthropods.
Lipids hydro- and why?
Lipids are hydrophobic because they are made up of mostly hydrocarbons so they are ALL NON-POLAR.
Lipids and Polymers?
Lipids are the one class that do NOT form polymers.
What are fats made up of?
Glycerol and fatty acids
Another name for fats with 3 fatty acids
triacylglycerol
Glycerol
A three-carbon alcohol with a hydroxyl attached to each carbon.
Fatty acids
Consist of a carboxyl group linked to a long hydrocarbon chain.
Synthesis of Fats DRAW
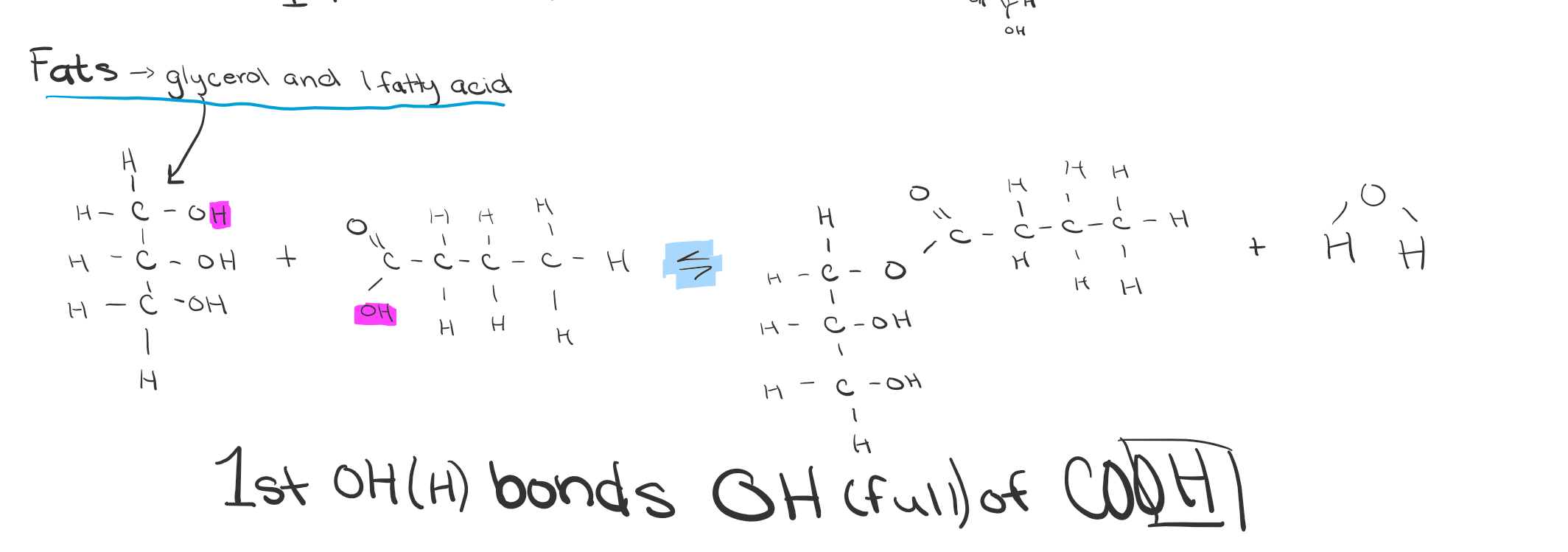
Fatty acid bonds?
Through a ester linkages. (O-C=O)
Saturated Fats
DO NOT have double bonds (very non-polar) and are solid.
Unsaturated fatty acids
Have 1 or more double bonds (Is slightly non-polar) and liquid.
Hydrogenation
The process of synthetically converting unsaturated fats to saturated fats with the use of trans double bonds.
Essential fatty acids
Unsaturated fatty acids not synthesized in the body so must be consumed. They are required for normal growth.
Adipose
Tissues cushion vital organs and insulate the body → WHERE THEY STORE ENERGY
Phospholipids
2 fatty acids and a phosphate group attached to glycerol. In water they automatically form into a bilayer with the tails inwards.
Steroids
Lipids with a carbon skeleton consisting of FOUR fused rings
Cholesterol
Component in animal cell membrane to make the membrane fluid.
Proteins functions (6)
Structural support, storage, transport, cellular communication, movement, and defense against foreign substances.
Enzyme proteins
Accelerates chemical reactions with out being using up. They are a catalyst that speeds up chemical reaction.
Defensive proteins
They protect against disease. They are antibodies.
Storage proteins
Store amino acids. ie. proteins of milk stores amino acids for babies.
Transport proteins
Transport of other substances. This is lie hemoglobin and across cell membrane.
Hormonal proteins
Coordination of an organism activities. Ie. insulin.
Receptor proteins
Response of cell chemical stimuli.
Contractile and motor proteins
Movement such as actin and myosin.
Structural proteins
Support. ie the proteins in hair
Polypeptide
Are an unbranched polymer built from the same set of 20 amino acids. This is a polymer of amino acids.
What is a protein?
A biologically functional molecule that consists of one or more polypeptides.
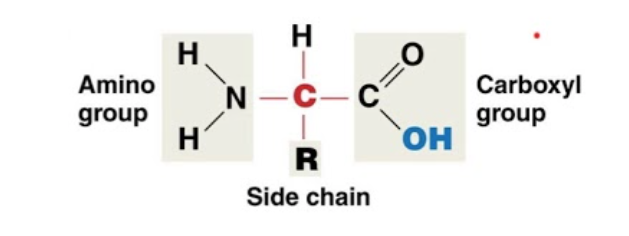
Amino Acid make up
Has a carboxyl and amino group (h-n-h and o=c-oh) and a side chain R that changes the properties
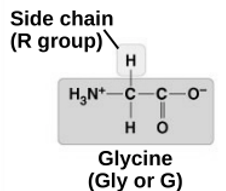
Glycine
non-polar
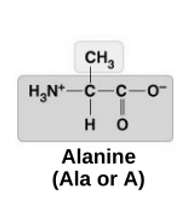
Alanine
non-polar
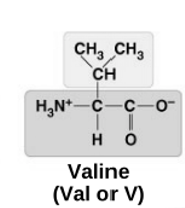
Valine
non-polar
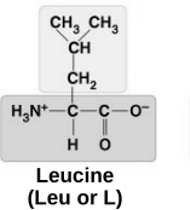
non-polar
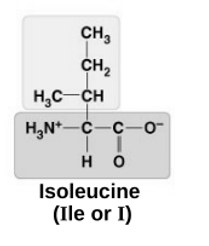
non-polar
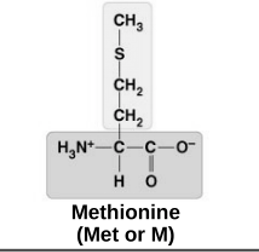
non-polar
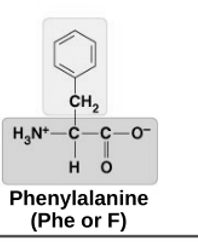
non-polar
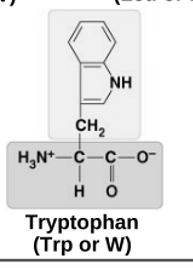
non-polar
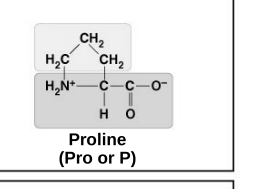
non-polar
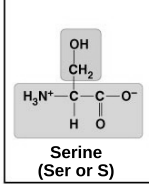
polar
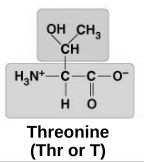
polar
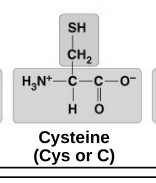
polar
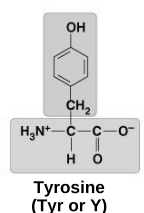
polar
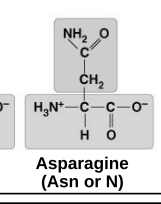
polar
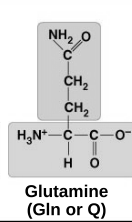
polar
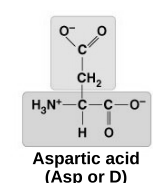
acid
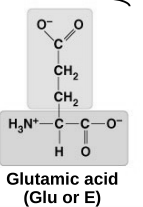
acidic
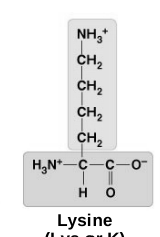
basic
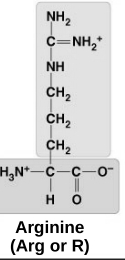
basic
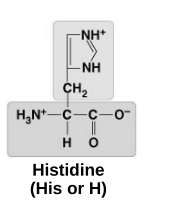
basic
Amino acid link
peptide bonds
Structure of Polypeptides
They have a unique linear sequence of amino acids. THEY ALWAYS HAVE A CARBOXYL AND AMINO ACID END (C-TERMIUS AND N-TERMIUS)
What determines the function of a protein?
There amino acids as it determines what it’s three-dimensional structure.
Primary structure of a protein
The sequence of amino acids in a protein. This is just how it is coded and is instructed on how to follow, uses genetic information.
Secondary Structures of Proteins
From a hydrogen bonds from the repeating of the BACKBONE.
2 types of secondary structures.
Coil - alpha-helix
Fold - beta-pleated sheet
Tertiary Structure
Determined by interactions between R-groups.
Tertiary structure interactions
Hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds (with charged molecules), Hydrophobic interactions, Van der walls interaction and DISULFIDE BRIDGES