Ops Final Topics
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What is a project?
set of activities aimed at meeting a goal with a defined beginning and end
What is the work breakdown structure (WBS)?
a hierarchical listing of what must be done in a project
What is risk pooling?
inventory held in one warehouse to service a large number of retailers
- requires less inventory than if held at individual retailers
What is a project champion?
person who promotes and supports a project
What are two network approaches to project management and what do they focus on?
- Critical Path Method (CPM): single time estimate
- Program Evaluation & Review Technique (PERT): duration of activity varies
What is an activity?
one of the project tasks
What is an event?
completion of an activity
What is a network?
set of all project activities shown in a graph
What is a path?
sequence of connected activities from start to finish
What is a critical path and some characteristics?
- any path that if delayed will delay the project
- longest path in the network
- minimum time needed to complete the project
What should the slack of the critical path activities be?
0
Explain the contents of the activity circle and how to calculate each?
- Top left: ES = 0 for starting and then the longest EF for next circle
- Top Right: EF = ES + activity time
- Bottom left: LS = LF - Activity Time
- Bottom right: LF = the smallest LS from the ones before
How do you find slack?
LS - ES or LF - EF
How do you find mean for Project Management with Uncertainty?
Mean = (o + 4m + p)/6
How do you find variance for Project Management with Uncertainty?
Variance (o^2) = (p-o)^2/36
Z-Score =
(given - found statistic) / STDEV
What is crashing a project and how do you do it?
methodical approach to reducing project duration
- look for greatest improvement with least cost on the critical path
- start with cheapest cost activity
- if two critical paths and both have lowest cost, do them both
What is logistics?
the art and science of obtaining, producing, and distributing material and product in the proper place and in the proper quantities
What is third-party logistics company (3-PL)?
outside company used to handle logistics functions
Logistics-System Design Matrix
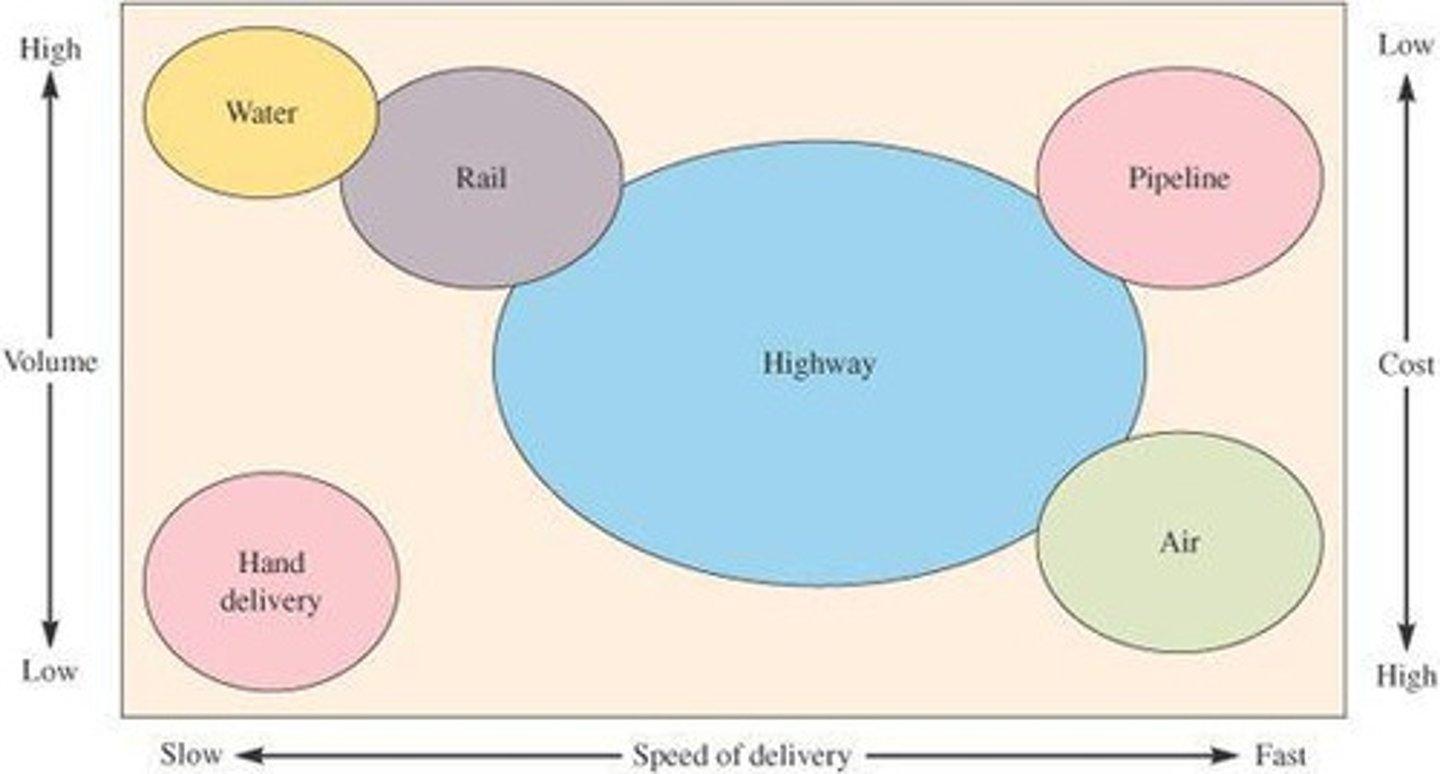
What is multimodal?
the use of multiple modes of transportation
What is warehousing and the advantages called?
holding inventory received from suppliers in warehouse until it is needed by retailers (PERIODIC)
- Risk pooling
- Consolidation
What is consolidation?
reduced inbound costs because all shipments are going to the same place
What is direct shipment and an advantage?
direct ship from suppliers to retailers
- eliminates warehousing cost
What is cross docking and what are some things it requires?
continuous shipment from suppliers to warehouses
- requires reliable communication and transportation
What is a hub-and-spoke system?
hub warehouses sort the goods
What are the levels of location decisions (4) and what do they entail?
1. Global Perspective (choice of country): considering government rules, culture, economy, labor availability, etc
2. Regional Considerations: location of raw materials and markets, labor factors, and taxes/government incentives
3. Community Considerations: QOL, attitudes, taxes, etc.
4. Site Related Considerations: transportation options, site size, zoning restrictions
What is multifactor rating good for?
including various considerations besides overall cost
What is center of gravity model good for?
- finds the most central location of a facility that minimizes transportation costs
What is load-distance method good for?
locating a single facility within a set of existing facilities with the goal of minimizing overall transportation costs
What is the transportation method (linear programming) good for?
minimize overall transportation costs amongst different supplier warehouses and multiple store locations
What is strategic sourcing?
the development and management of supplier relationships to acquire goods and services in a way that aids in achieving the immediate needs of the business
What is specificity?
refers to how common the item is and how many substitutes might be available
What is request for proposal (RFP)?
used for purchasing items that are more complex or expensive and where there may be a number of potential vendors
What are the traits of Request for Proposal (RFP)?
short contract duration, low specificity, and high transaction costs
What is Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI)?
when a customer actually allows the supplier to manage an item or group of items for them
What are the traits of Vendor Managed Inventory (VMI)?
long contract duration, high specificity, and low transaction costs
What is the bullwhip effect?
- phenomenon of variability magnification as we move from the customer to the producer in the supply chain
- Slight change in consumer sales ripples backward as magnified oscillations upstream
What are the impacts of the bullwhip effect?
- Spiking demand: Bad for productivity
- High inventory: More carrying costs
- Mismatch between demand and design capacity
What are the causes of the bullwhip effect?
- demand forecast updating
- order batching
- price fluctuations
- rationing
What is a solution to the bullwhip effect and what is it?
Continuous Replenishment: inventory is replaced frequently, as part of an ongoing process
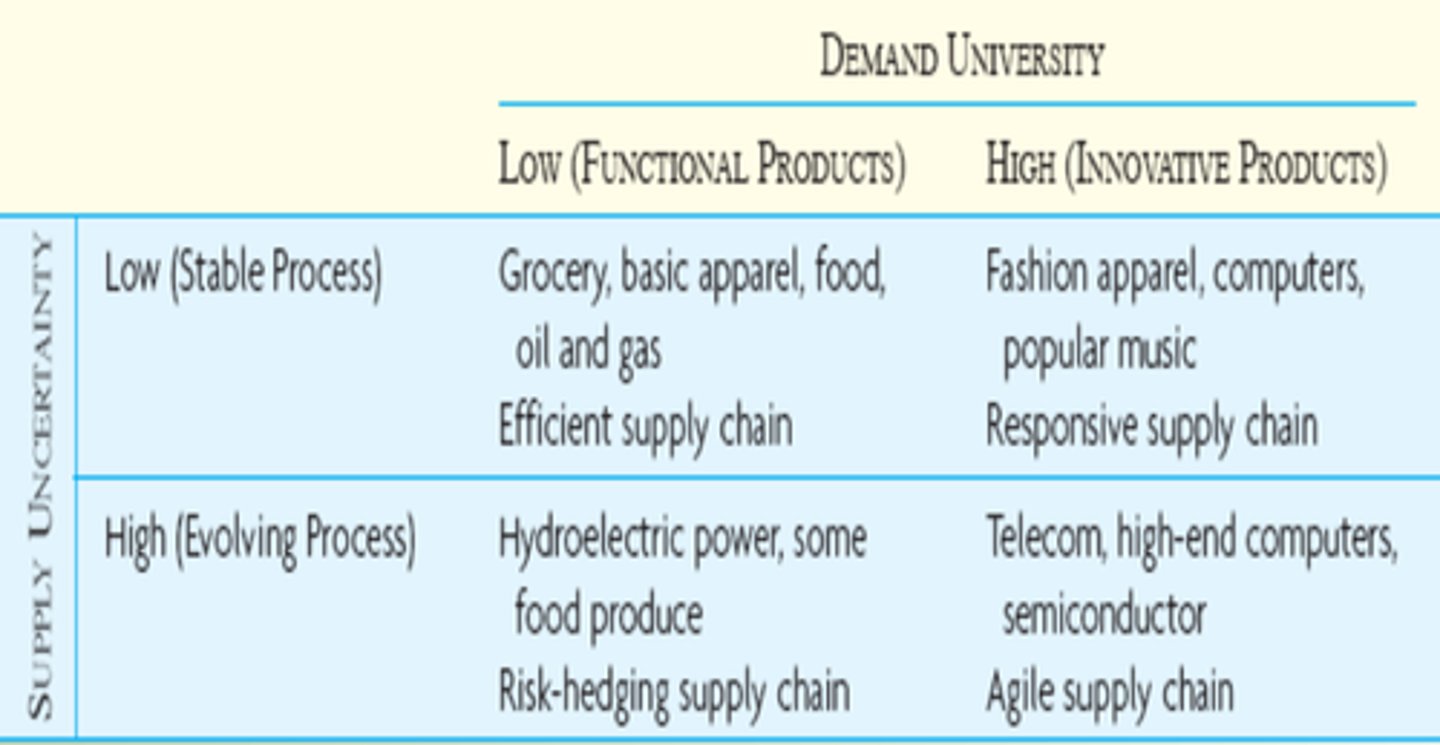
What are functional products?
staples that people buy in a wide range of retail outlets
Hau Lee's Uncertainty Framework
What is outsourcing and what does it allow a company to do?
- the act of moving a firm's internal activities and decision responsibility to outside providers
- allow a company to create a competitive advantage while reducing costs
What are the three reasons for outsourcing and some examples of them?
- Financially Driven Reasons: improve ROA, generate cash, etc.
- Improvement-Driven Reasons: improve quality and productivity, shorten cycle time
- Organizationally Driven Reasons: improve effectiveness by letting firm focus on what it does best, increase firm flexibility
What are the components of the framework for structuring supplier relationships?
- Coordination: how difficult it is to integrate activities to the overall process
- Strategic Control: degree of loss the organization may incur due to the relationship with the supplier
- Intellectual Property: decide how much to share and how the relationship would affect things
What is green sourcing and what does it do?
ensuring a companies supply chain is focused on being green
- being environmentally responsible has become popular
- Financial results can often be improved through going green
- Reduces waste
What is Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)?
an estimate of the cost of an item that includes all the costs related to the procurement and use of an item, including any related costs in disposing of them
What are the three costs that make up the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)?
- Acquisition Costs: purchases planning costs, taxes, purchase price, financing costs
- Ownership Costs: energy, maintenance, supply chain costs
- Post-ownership Costs: disposal, environmental costs, warranty costs
What is weeks of supply?
how many weeks' worth of inventory is in the system at a particular point in time
What is alliance?
Balance between commitment to low prices and commitment to the relationship
What is Collaborative Planning, Forecasting, and Replenishment (CPFR)?
approach to demand planning in which partners negotiate and agree on a plan for meeting demand
What does electronic commerce help with?
time reduction
What are some trends in Supply Chain Management?
- 3rd Party Exchange
- SCM Software
- RFID and SOA
- C-TPAT
- SCOR (Supply Chain Operations Reference Model)
Does the EOQ/ROP model or the Fixed-order interval model have higher safety stock?
fixed order-interval
What is materials requirement planning (MRP) and is it dependent of independent?
determines the number of subassemblies, components, and raw materials required and their build/order dates to complete a given number of end products by a specific date
- dependent
What is a bill of materials (BOM) and what type of demand is it used for?
Also what is another name for it?
list of subassemblies, components, RM, and their respective quantities required to produce a specific end item
- dependent demand inventory
- product tree
What is single period (newsvendor) model?
model for ordering of perishable goods and other items with limited useful lives - identify order quantity that will minimize the long-run excess and shortage costs