Kidney and bladder pathology
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Normal kidney size
9-12 cm long and 3-5 cm wide and 3 cm in thickness
EGFR test
Estimated glomerular filtration rate
A blood test that estimates kidney function by measuring the rate at which kidneys filter waste.
Renal function tests
EGFR, electrolytes. BUN, Creatinine
BUN test
Blood urea nitrogen
Blood test that measures blood urea nitrogen levels to assess kidney function and protein metabolism. BUN levels rise when kidney function decreases
Creatinine
A waste product formed from muscle metabolism, excreted by the kidneys. Measurement of creatinine levels helps evaluate kidney function. Creatinine levels rise as kidney disease progresses
parenchyma
The functional tissue of the kidneys
Dromedary hump
A bulge of cortical tissue on the lateral border of the kidney. Resembles a camel’s hump. echogenicity is identical to the rest of the cortex. Normal variation
Column of Bertin
hypertrophied columns of Bertin contain renal pyramids. Normal variation of cortical tissue extending between the renal pyramids, often mistaken for kidney lesions on imaging.
Junctional parenchymal defect
A triangular defect area in the upper pole of the renal parenchyma. normal variation
Persistent fetal lobulation
A normal variant of kidney morphology characterized by incomplete fusion of the renal lobes, resulting in a lobulated appearance
Renal sinus lipomatosis
A condition characterized by excessive fat deposition within the renal sinus. Normal variation
Extrarenal pelvis
A normal anatomical variant where the renal pelvis extends outside the renal outline. Appears as a central cystic area that is partially or entirely beyond the border of the kidney
Renal agenesis
Absence of one or both kidneys. Bilateral renal agenesis is fatal. Anomaly
Renal hypoplasia
A condition where one or both kidneys are underdeveloped, resulting in a smaller sized kidney. Anomaly
Duplex collection system
A developmental anomaly characterized by the presence of two renal collecting systems in one kidney, often associated with separate ureters and incomplete fusion of upper and lower pole moieties. there are multiple different types
Bifid renal pelvis
A condition where the renal pelvis is split into two ureteres that unite before draining into the bladder
Pseudotumor
term sometimes used to refer to hypertrophic column on Bertin and dromedary humps
Developmental anomalies
May be bilateral or unilateral, may cross midline. Malrotation is common in kidneys that didn’t end up in normal location
Can be thoracic, crossed, iliac or pelvic kidneys
Horseshoe kidney
A congenital condition where the two kidneys are fused together at their lower ends, forming a U-shape.
Cake kidney
a type of renal fusion anomaly where the kidneys are fused together at their lower poles, forming a "cake"-like appearance.
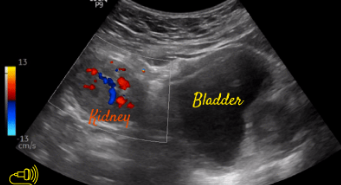
Pelvic kidney
A developmental anomaly where one or both kidneys fail to ascend to their normal position in the abdomen, remaining located in the pelvic region.
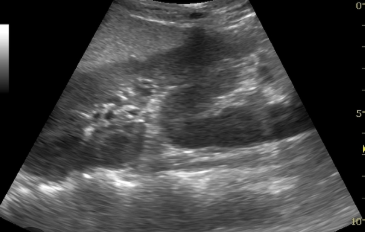
Crossed renal ectopia
A condition where one kidney is located on the opposite side of its normal position, sometimes fused with the other kidney. Malrotation is very common
Renal malrotation
a condition in which the kidney is positioned at an abnormal angle or orientation due to improper rotation during development.
Supernumerary kidney
A rare condition where an individual has an extra kidney in addition to the usual two. Sometimes fused to one of the kidneys. This additional kidney may be fully functional or may have varying degrees of function.
Stricture
Ureteral narrowing due to fibrosis or scarring, which can obstruct urine flow from the kidney to the bladder.
Uterocele
Cyst-like enlargement of the lower end of the ureter. caused by congenital or acquired stenosis of the distal end of the ureter
Cystoscopy
A diagnostic procedure using a thin tube with a camera to visualize the inside of the bladder and urethra.
Bladder volume eqution
Length x width x height x 0.52
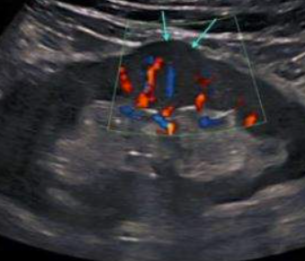
Ureteral jets
The urine flow from the ureters into the bladder, observable during ultrasound or imaging studies.
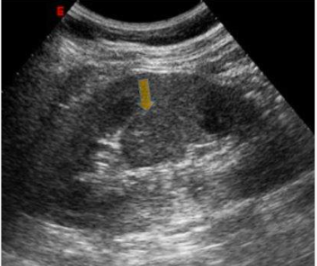
Column of Bertin
Dromedary Hump
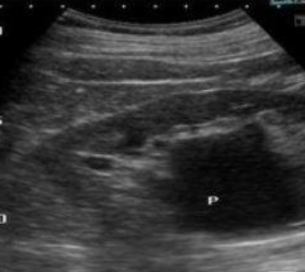
Extrarenal pelvis
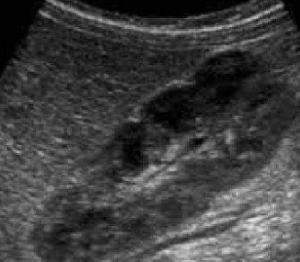
Persistent Fetal Lobulation
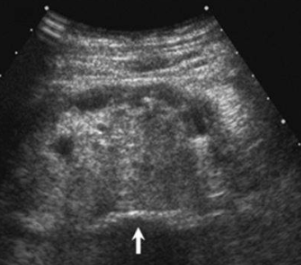
Sinus Lipomatosis
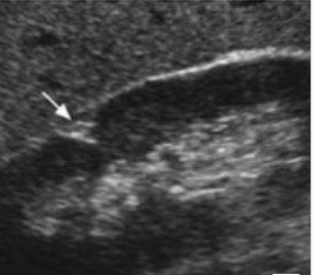
Junctional Parenchymal defect
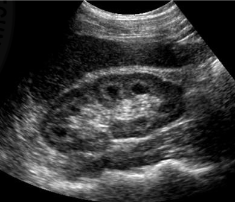
Normal kidney
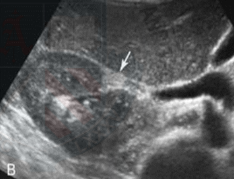
Junctional Parenchymal defect
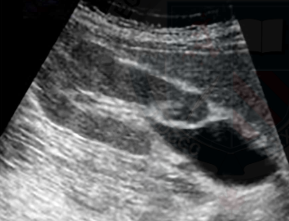
Extrarenal pelvis
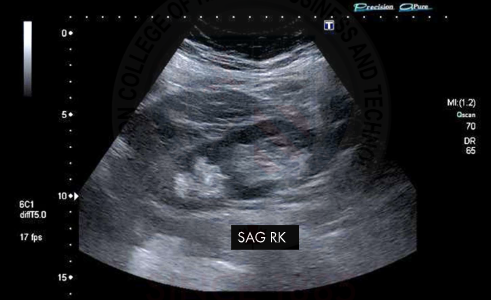
Duplex collection system
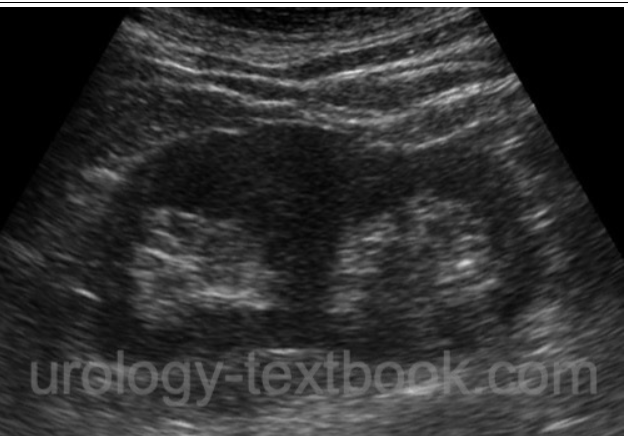
Duplex collection system
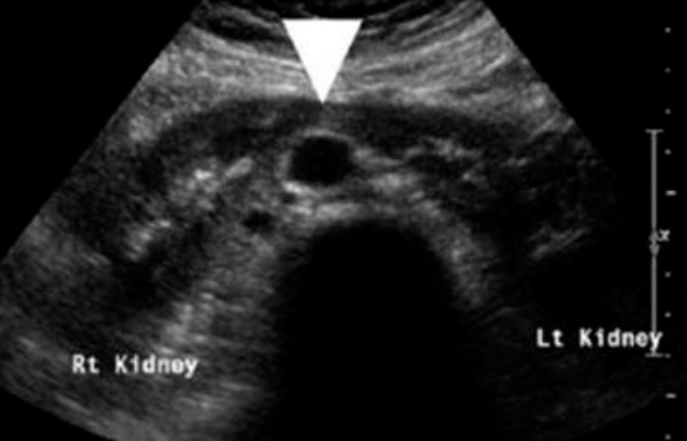
Horseshoe kidney
Cake kidney
Pelvic kidney
Crossed renal ectopia
Crossed renal ectopia
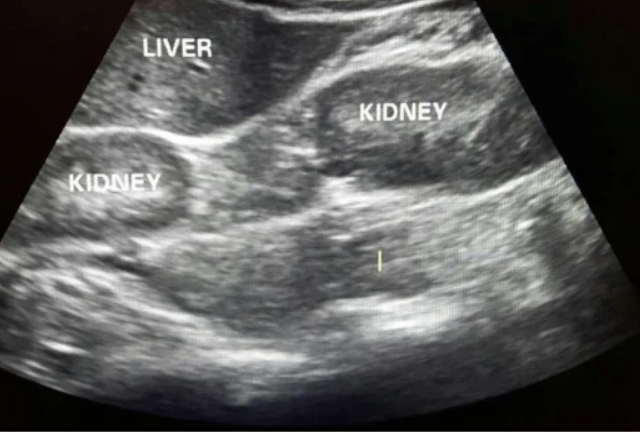
Supernumerary kidney
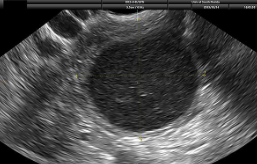
Complex cyst with debris
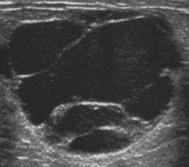
Complex cyst with thin and thick septations and debris
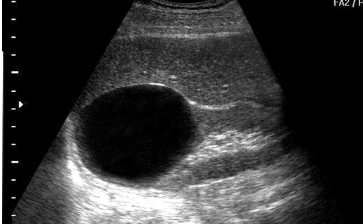
simple cyst
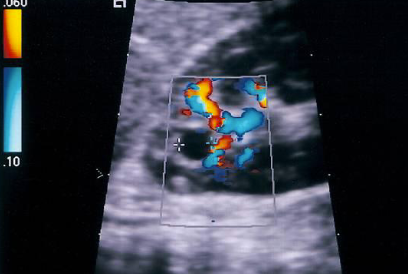
simple cyst
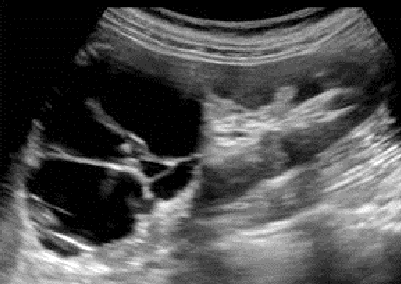
Complex cyst with septations
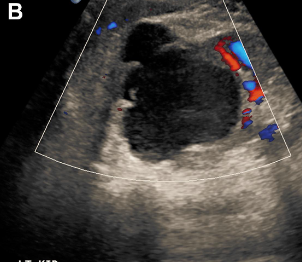
complex cyst with irregular borders
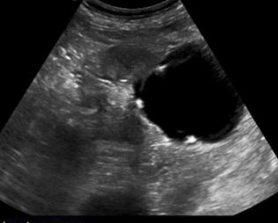
complex cyst with calcifications
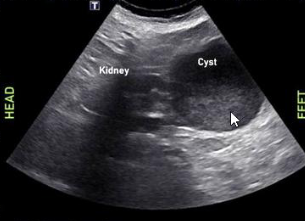
complex cyst with fluid fluid level
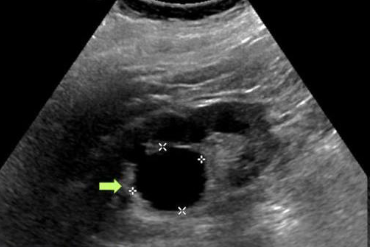
Renal sinus parapelvic cyst
acquired cystic kidney disease ACKD
a condition that occurs in patients with end-stage renal disease, cysts and tumors appear after long term dialysis use
Von Hipple Lindau
is a genetic disorder associated with the formation of tumors and cysts in multiple organs, including the kidneys. It increases the risk of renal cell carcinoma and other neoplasms.
Tuberous sclerosis TSC
is a genetic disorder that causes non-malignant tumors to form in various organs, including the kidneys. It may lead to renal cysts and tumors, increasing the risk of kidney complications.
adenomas
are benign tumors that can occur in the kidneys
carcionomas
that are malignant tumors originating from renal cells, commonly leading to kidney cancer.
angiomyolipomas AML
are common benign renal tumors composed of blood vessels, muscle, and fatty tissue that often occur in patients with tuberous sclerosis
solitary or multiple
Avascular and hyperechoic
Polycystic kidney disease PCKD
is a genetic disorder characterized by the formation of numerous cysts in the kidneys, leading to kidney enlargement and decreased function.
Also includes,
autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease ARPKD
autosomal dominate polycystic kidney disease ADPKD
Multicystic dysplastic kidney MCDK
autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease ARPKD
Aka Infantile polycystic kidney disease.
inherited disease of the kidney that causes renal collecting tubules to dilate causing renal failure
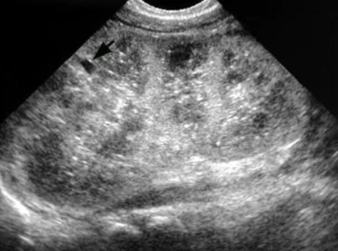
autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease ARPKD
Autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD
Most common form of PKD
affecting adults, leading to cyst formation and complications such as hypertension and kidney failure.
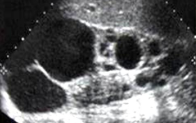
Autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease ADPKD
Multicystic dysplastic kidney MCDK
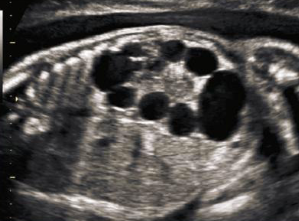
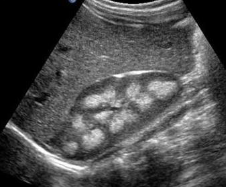
nonhereditary renal dysplasia. most common form of cystic disease in neonates. Usually, unilateral as bilateral is fatal
Multicystic dysplastic kidney MCDK Prenatal
Multicystic dysplastic kidney MCDK adult
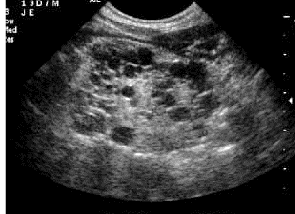
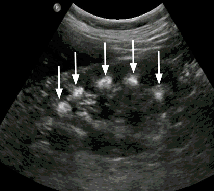
Medullary sponge kidney MSK
Development anomaly in medullary pyramids
MSK Medullary sponge kidney
MSK Medullary sponge kidney
End-stage renal disease ESRD
Final stage of chronic kidney disease where kidneys can no longer maintain balance of fluids, electrolytes, and waste products.
Medullary cystic disease
A genetic disorder characterized by kidney cysts, leading to progressive renal dysfunction and resulting in end-stage renal disease.
Small echogenic kidneys and loss of corticomedullary differentiation
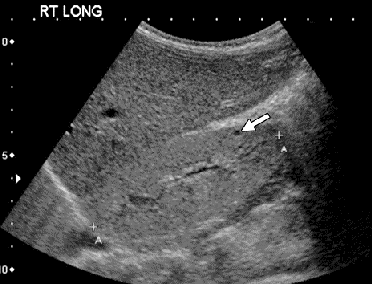
Medullary cystic disease
What to do when a renal mass is detected
If its not a simple renal cyst it is considered malignant until proven otherwise
Evaluate renal vein and IVC for thrombosis
Evaluate other kidney, liver and retroperitoneum for metastases
Benign renal tumors
Very rare
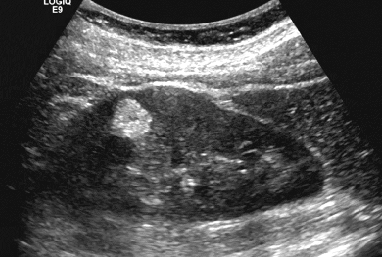
Adenomas and oncocytomas
oncocytomas
are benign tumors of the kidney characterized by large cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and a rich blood supply.
Hypoechoic, solid mass with star pattern in the middle
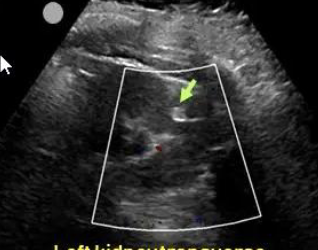
Renal angiomyolipoma AML
Renal angiomyolipoma AML
Renal adenomatous tumours
are benign or malignant neoplasms of the kidney
solid mass, hypovascular, hyper or hypoechoic
Oncocytoma
Lipomas
are benign tumors composed of adipose tissue. They typically appear as soft, movable lumps under the skin and are generally harmless.
Well defined echogenic mass
More common in women
Renal tuberculosis
involves both the kidney and collection system
Characterized by caseous (cheese like) lesions that may necrose and destroy functioning renal parenchyma
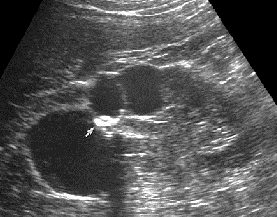
Renal tuberculosis
Malignant cystic mass
Wall thickness greater than 1mm
septations
calcifications
vascular
Renal cell carcinoma RCC
Most common renal neoplasm
twice as common in men
60-70 years of age
most unilateral, solid and iso/hypoechoic
tumor can invade renal vein and IVC
vascular
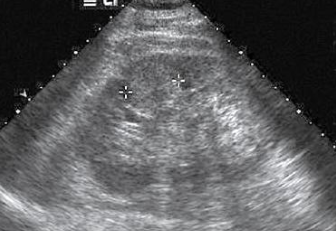
Renal cell carcinoma RCC
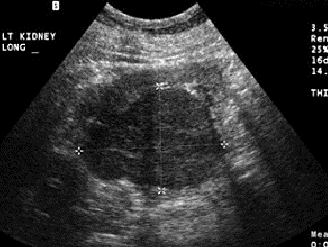
Renal cell carcinoma RCC
Transitional cell carcinoma TCC
Solid tumor
high-grade malignancy and spreads easily with a tendency to metastasize.
Hypoechoic mass in collecting system
low vascularity
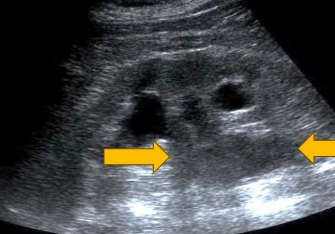
Transitional cell carcinoma
Renal lymphoma
Rare
May be a solid lesion of focal
May infiltrate entire kidney
Non-Hodgkin is more common than Hodgkin
Enlarged kidneys and hypoechoic tumors with poorly defined borders
Juxtaglomerular cell tumor
Extremely rare
Secreted renin and often causes hypertension
Most common in young adults
Benign with malignant potential
Hypoechoic
Secondary malignancies of the kidneys
Tumors that arise in the kidney after prior cancer treatment, often due to exposure to radiation or chemotherapy. These malignancies may include renal cell carcinoma and transitional cell carcinoma.
multiple hypoechoic masses
renal enlargement
may spread to renal vein and IVC
Nephroblastoma
Wilms tumor
Most common solid renal tumor in pediatric patients
2.503 years old
Hypoechoic to echogenic, mostly unilateral, 40% of patients have renal vein thrombosis or vena cava / atrial thrombusGv