Week 3A: Vestibular system, somatonsensation and the chemical senses
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Somatosensory system registers
Touch
Vestibular system registers
Balance
Balance: The sensory receptors of the vestibular system are located in (…) ear (Outer, middle, inner)
Inner
Damage of sensory receptors of the vestibular system cause
Imbalance, nausea
Balance: What do otolith organs register
Linear acceleration and gravitation
Balance: What do semicircular canals do
Angular acceleration and one canal for rotation axis
Main functions of the vestibular system
Balance, stabilise retinal image and compensate for head movements
Balance: Each receptor consists of one tall thick hair, called the (…), flanked on one side by a group of thinner hairs, tapering in height, known as (…)
Kinocilium, stereocilia
Balance: What happens when the head moves counterclockwise?
Fluid moves (…) relative to the head
Haircells bend (…)
Left lateral rectus is (…)
Right lateral rectus is (…)
Opposite pattern for medial recti
Eyes move (…)
Clockwise, right, inhibited, excited, clockwise
Balance: What is motion sickness
Cue conflict between vestibular and visual senses
Balance: Oculogyral illusion and Coriolis effects
Dizziness from body rotation. When you stop spinning fluid in the semi-circular canals start moving
Balance: Oculogravic illusion
Illusory tilt percept during linear acceleration
Balance: Vection
Sensation of self-motion
Balance: The vestibular organ includes (…) canals and (…) sacs; each contains fluid or gel and a pathc of sensory ahir activitaded by fluid or gel displacement
3, 2
Balance: Rotational acceleration of the head activitates (…) in the canals
Receptors
Balance: Linear acceleration and head tilt activate (…) in the sacs
Otolith receptors
Balance: Two types of otolith receptors in the sacs
Utricle and saccule
Balance: The vestibular system does not encode (…) speed
Constant
Our oldest and most primitve sense
Touch
Touch is a (…) sense, we feel things close to us or that actually contact us
Proximal
Touch: Nociception registers
Pain, temperature and tickle
Touch: Proprioception registers
Information about position of body parts
Touch: Kinesthesis registers
Information about movement of the body parts
Touch: Risk of being unable to touch
Impared manipulation of objects and walking
Touch: Risk of being unable to feel pain
Risk of infections due to unattended injuries (leprosy)
Touch: Risk of being unable to sense proprioception and kinesthesis
Relearn walking and only visually guided motion
Skin: area
1.8 cubed meters
Skin: Pacinian corpuscle function
Fast changes
Skin: Meissner corpuscles function
Touch
Skin: Merkle discs function
Touch and pressure
Skin: Ruffini end organs function
Touch pressure, joint angulation
Skin: Nociceptors function
Pain, temperature and tickle
Skin: pacinian corpuscles function
Pressure and vibration
Skin: Ruffini’s corpuscles function
Stretching of skin
Muscle spindles
Muscle length
Gogli tendon organs function
Muscle tension
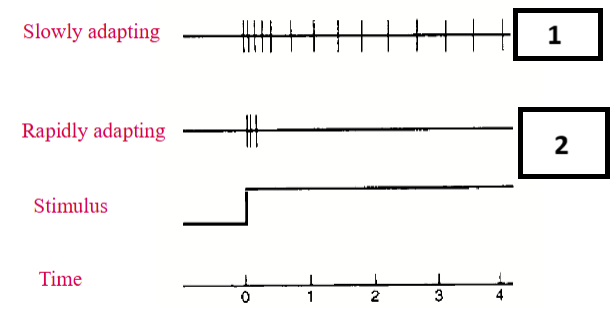
Difference slowly and rapidly adapting
First a few spikes, then spikes in timely order vs. few quick spikes and no spikes after that
Meissner corpuscles: (…) receptive fields (small or large)
Small
Pacinian and ruffini corpuscles and end organs: (…) receptive organs
Large
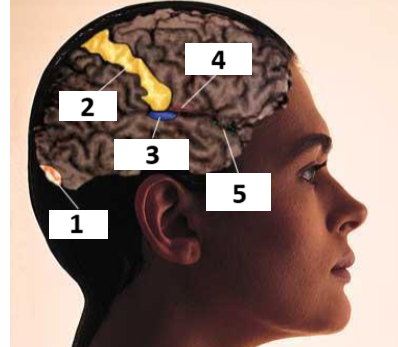
Senses: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5
Vision, Touch, Hearing, Taste, Smell
How do we find sensitivity on the skin
Tactual acuity: Two point thresholds
Where is the skin the most sensitive
Hands and face
Haptic perception definition
Sense an object’s properties through touch, proprioception and kinesthesis
Why is it hard to recognise 2D raised line drawings
The world is 3d and we perceive the world as 3d. Our haptic system is not trained in this.
Why is it easier to recognise a drawing by visual instead of by touch (if there were ridges to touch)
Visual: Fits entirely in your field of attention
Touch: temporal build up of information that you have to store.
Curvature aftereffect
After touching a convex shape for 10 seconds, a flat shape feels concave
Meaning veridical
Coinciding with reality
Why is our sense of smell blunted when we have a cold
Build-up of mucus in the nasal cavity that prevents odor molecules reaching the receptor cilia
Why can people smell less during or after covid
Brain damage
How do we smell
Molecules bind with receptor sites on the cilia
How long do odor receptors live
60 days
Detection
Airborne moleculs dissolve in the (…) mucus
Moleculs bind with receptor sites on the (…)
This results in a change in membrane potential
Mitral cells project to the (…) and the (…)
Olfactory, cilia, primary olfactory cortex, amygdala
What is population coding
Limited number of receptor types can detect many different smells by activating in various patterns
Odor adaptation is much stronger for (…)-adaptation than for (…)-adaptation
Self, cross
The perceived intensity of a smell drops to (…)% after (…) minutes of exposure
30, 12
Taste bud cells live about (…) days
10
5 basic tastes
bitter, salty, sweet, umami, sour
Cross-adaptation to taste
Adaptation to one sour taste will cause water to taste sweet
Taste: Labeled-line theory
Argues that each fiber codes the intensity of a single taste dimension
Taste: Cross-fiber theory
Taste quality is coded by the pattern of activity across all fibers
Cross-fiber theory
This theory suggests that the brain interprets sensory information by analyzing the pattern of activity across a group of nerve fibers
If a food induces illness, many animals later show a strong aversion to the food. The effect (…) be overruled by knowledge (can or cannot)
Cannot
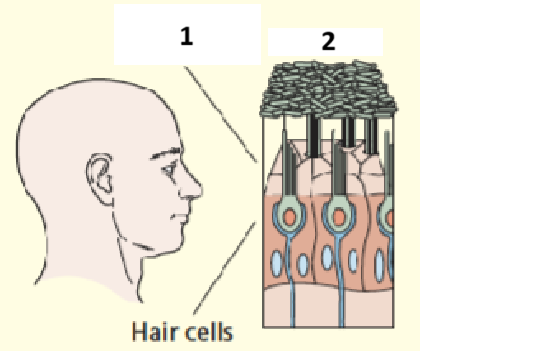
Balance: 1 and 2
Otolithic membrane, otoconia
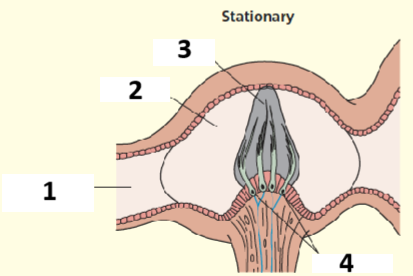
Balance: 1,2,3,4
Semicircular canal, ampulia, cupula, hair cells
Balance: The rate of (…) release from the base of the cell depends on the direction of hair cell (…), and affects spike activity in the (…) nerve
Neurotransmitter, displacement, efferent
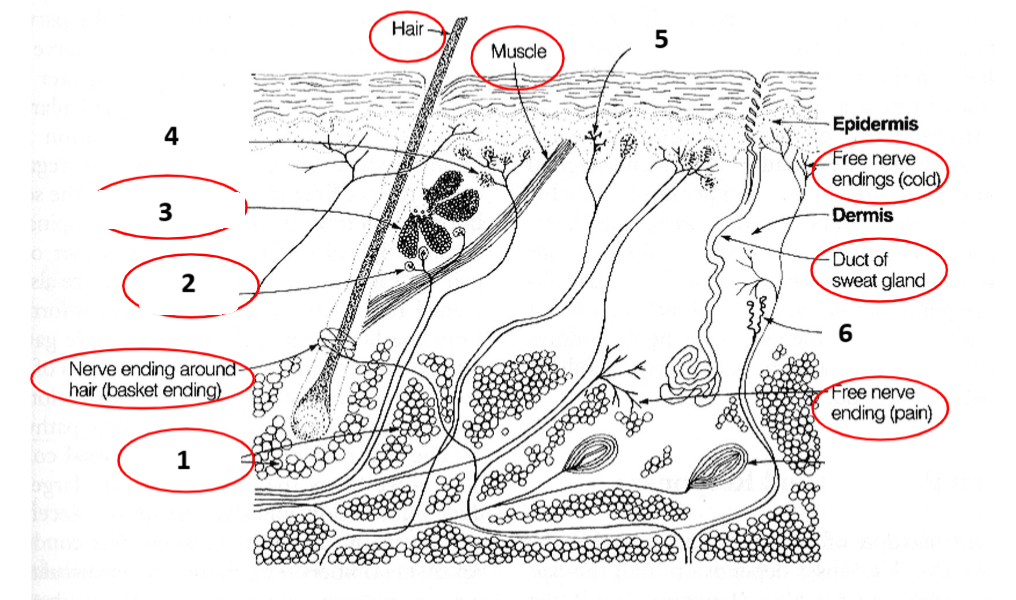
Skin: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6
Fat globules, end bulbs of Krause, Sebaceous gland, Meissner’s corpuscle, Merkle discs, Ruffini ending, Pacinian corpuscle
1, 2
Merkle Ruffini, Pacinian Meissner