Solubility Equilibria
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
solvent/solute
solute is dissolved in the solvent
saturated
maximum amount of solute is dissolved in a solvent
unsaturated
less than the maximum amount of solute is dissolved in a solvent
supersaturated
more than the maximum amount of solute is dissolved in a solvent
large Ksp
most soluble
smallest Ksp
least soluble
lewis acid
electron acceptorle
lewis base
electron donor
chelating agent
multi-denate ligands make many bonds to metal ions and can
“sequester” them
acidic salts
more soluble in basic solutions and less soluble in acidic solutions
basic salts
more soluble in acidic solutions and less soluble in basic conditions
neutral salts
Solubility is independent of pH
negligible cations
group 1 metals
group 2 metals
M+ (metals with +1 charge)
All others are acidic
more + charged, more acidic
negligible anions
Cl-
Br-
I-
NO3-
ClO4-
ClO3-
all others are basic
HSO4- IS ACIDIC
van’t hoff factor (i)
The number of ions a compound dissociates into per formula unit
Raoult’s Law
vapor pressure depression - partial pressure of a volatile solute above a solution
Boiling point elevation
highest boiling point - highest molality
freezing point depression
highest freezing point = lowest molal
colligative properties
Vapor pressure depression
boiling point elevation
freezing point depression
osmotic pressure
Henry’s Law
Henry’s Law
solubility of a gas in solution
bronsted- lowry acid
H+ donor
bronsted-lowry base
H+ acceptor
amphoteric
describes a substance that can act as both an acid and a base
amphiprotic
describes a substance that can act as both a proton (H+) donor or acceptor
HClO4
strong acid
H2SO4
strong acid
HI
strong acid
HBr
strong acid
HCl
strong acid
HNO3
strong acid
HClO3
strong acid
group 1 metals
strong bases
hydroxides
strong bases
Ba(OH)2
strong base
Sr(OH)2
strong base
Ca(OH)2
strong base
Mg(OH)2
strong base
buffers
resists changes in pH
made from weak conjugate acid/conjugate base pair
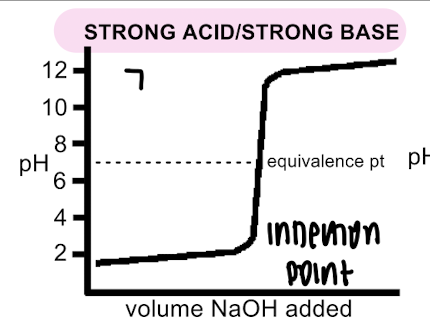
strong acid/base titration curve
pH equivalence point ~7
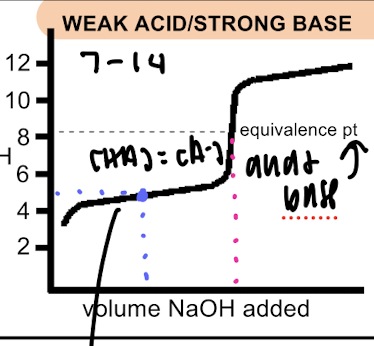
weak acid/strong base
pH equivalence point >7
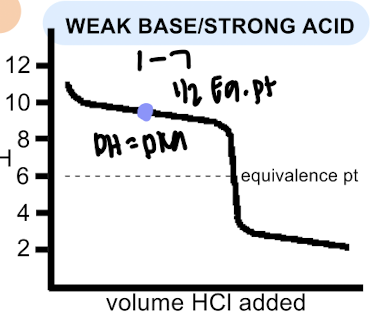
weak base/strong acid
pH equivalence point <7
bromcresol green
pka - 4.8 - turns solution green
bromothymol blue
pka - 7.1 — turns the solution blue
phenolphthalein
pka- - 9.7, will turn the solution pink
half equivalence point
pKa - half protonated and deprotonated
equivalence point
pH - all deprotonated