BT3: Reinforced Concrete Construction
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
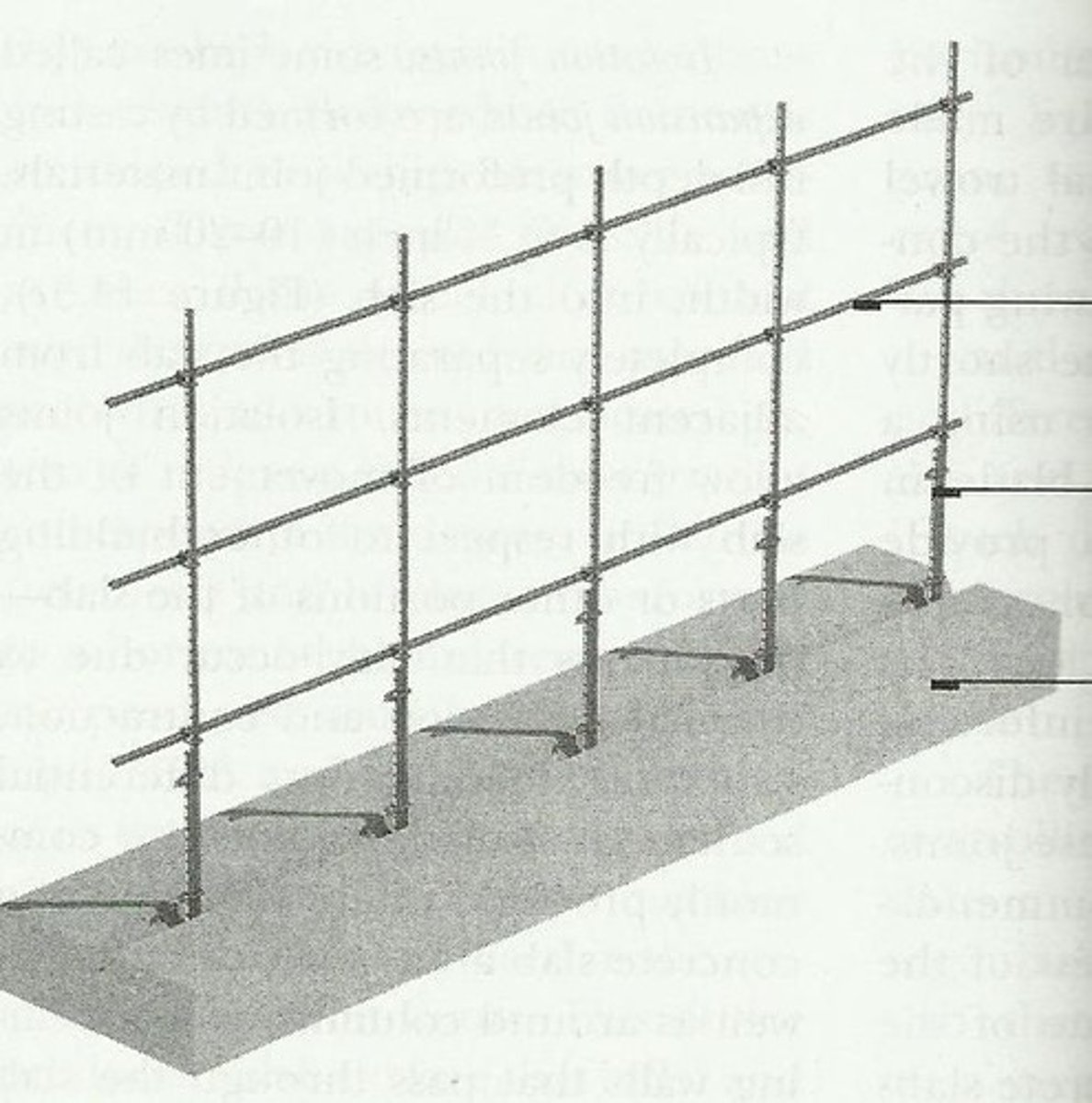
Reinforced Concrete
Concrete into which steel reinforcing bars have been embedded to impart tensile strength to the construction.
Plain Concrete
Concrete having no reinforcement, or reinforced only for drying shrinkage or thermal stresses.

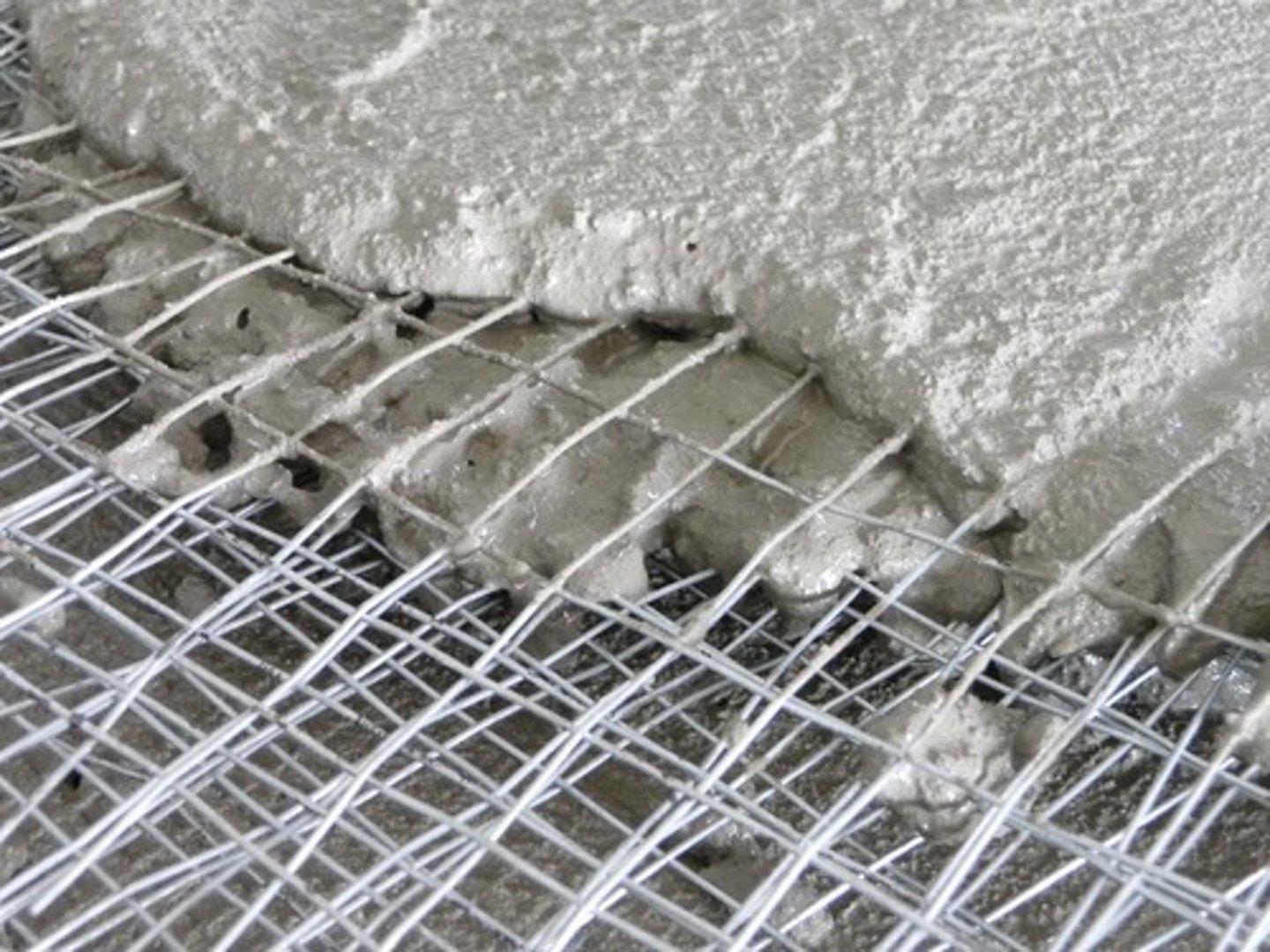
Ferrocement
Constructed of cement-sand mortar over a wire mesh that has been preshaped over a mold.

Cast-in-Place Concrete or Cast In-Situ
Concrete that is poured in its final location.

Reinforcement
A system of steel bars, strands or wires for absorbing tensile, shearing and sometimes compressive stresses in a concrete member or structure
Deformed Bar
Reinforcing bar hot rolled with surface deformations to develop a greater bond with concrete

Tension Reinforcement
reinforcement designed to absorb tensile stresses
Compression Reinforcement
Reinforcement designed to absorb compressive stresses
Balanced Section
A concrete in which the tension reinforcement theoretically reaches its specified yield strength as the concrete in compression reaches its assumed ultimate strain
Overreinforced Concrete
- Good in tension, bad in compression
- An over-reinforced section in RCC structures is those in which the concrete reaches its collapse strain earlier than the steel reaches its yield strain
- More dangerous than underreinforced concrete
Unreinforced Concrete
- good in compression, bad in tension & bending
- Gives prior warning of impending collapese
Beam
A structural member, usually horizontal, that carries a load that is applied transverse to its length.
1. Simple Beam
2. Semi-continuous Beam
3. Cantilever Beam
4. Continuous Beam
5. T-Beam
Types of Beam
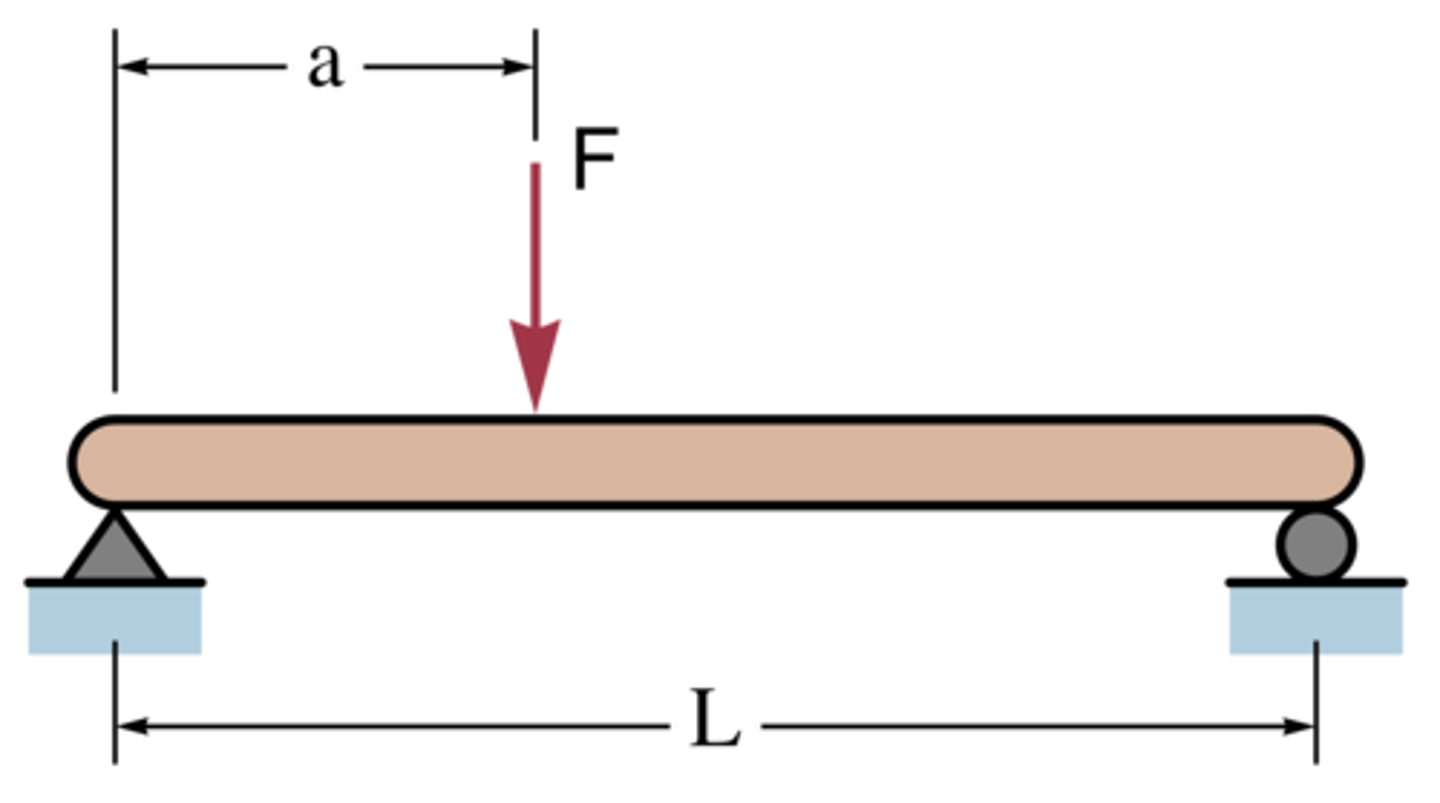
Simple Beam
A beam resting on a simple supports at both ends, which are free to rotate and have no moment resistance.
Semi-continuous beam
Refers to a beam with two spans with or without restraint at the two extreme ends
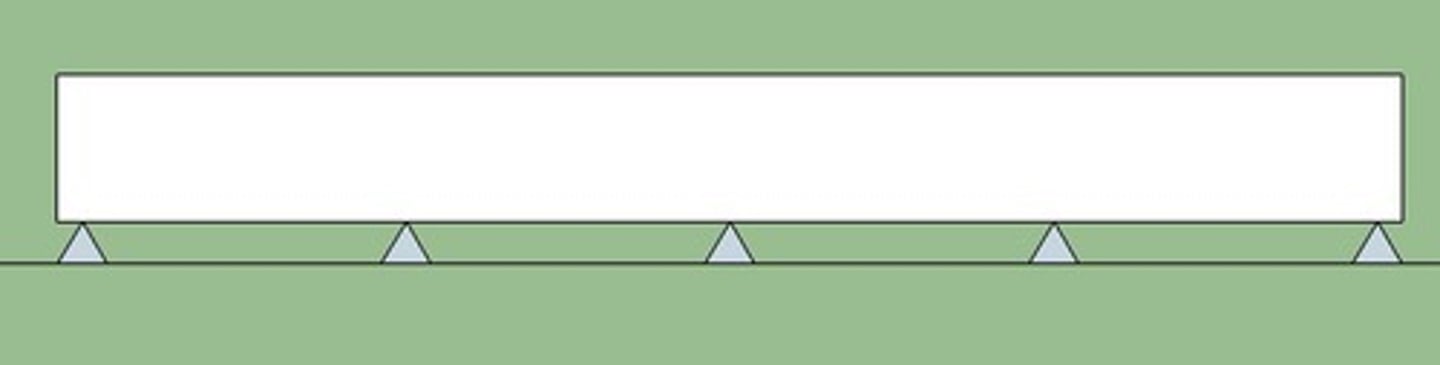
Continuous Beam
a beam that rests on more than two supports
Cantilever Beam
A projecting beam supported at only one fixed end.

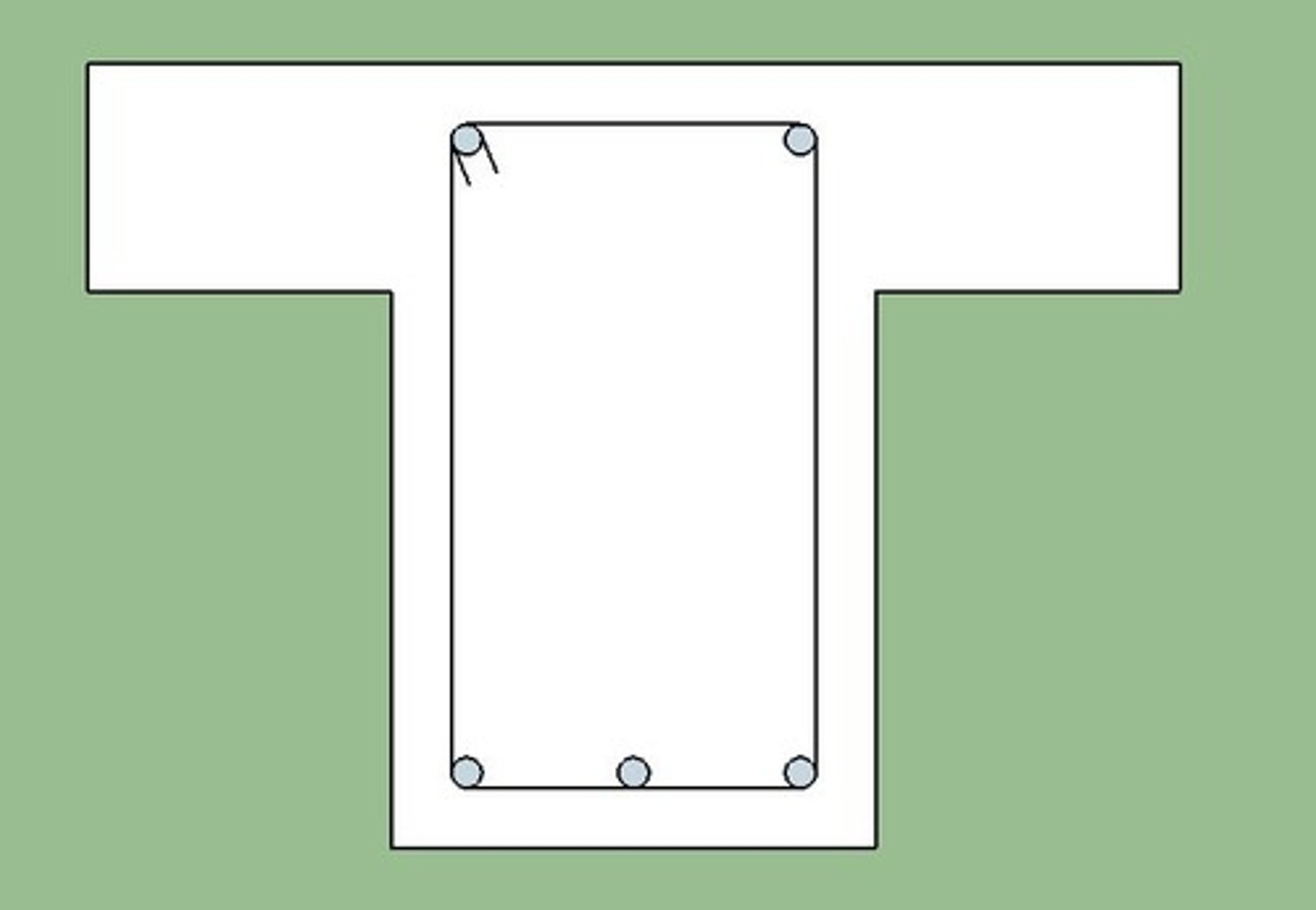
T Beam
a monolithic reinforced concrete construction in which a portion of the slab on each side of a beam acts as a flange in resisting compressive stresses, and the portion of the beam projecting below the slab serves as a web or stem in resisting bending and shear stresses
Reinforced Concrete Beam
A Concrete beam designed to act together with longitudinal and web reinforcement in resisting applied forces, formed and placed along with the slab they support

Effective Depth of Section
The depth of concrete section measured from the compression face to the centroid of the tension reinforcement.
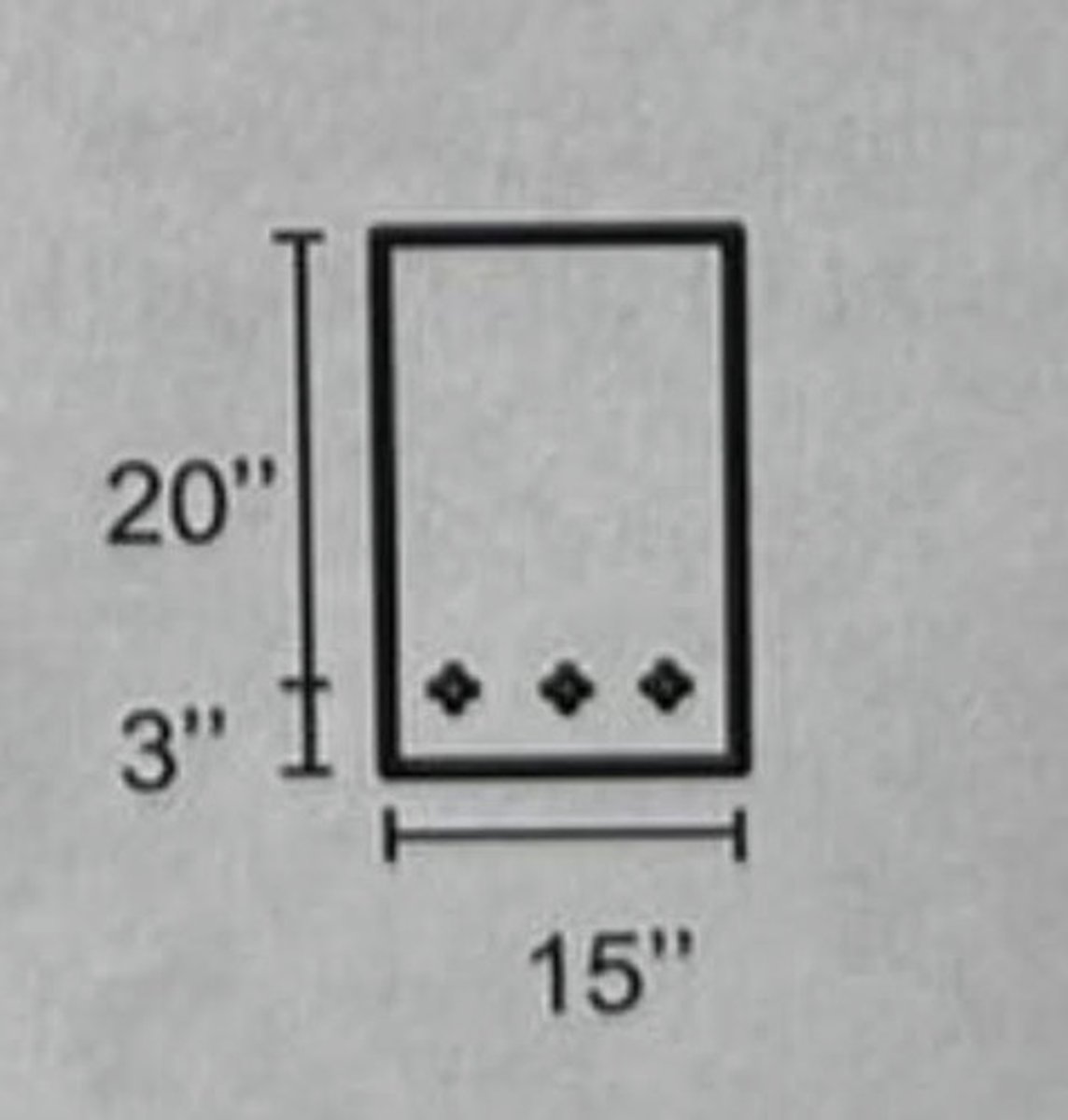
Bar Spacing
The center to center spacing of parallel reinforcing bar, resulting clear distance between the bar being regula ted by bar diameter, maximum size of coarse aggregate, and thickness of the concrete section
Span of Supports
pertains to the distances between the posts, columns or supporting walls
Concrete Cover
AMOUNT of concrete required to PROTECT steel reinforcement.
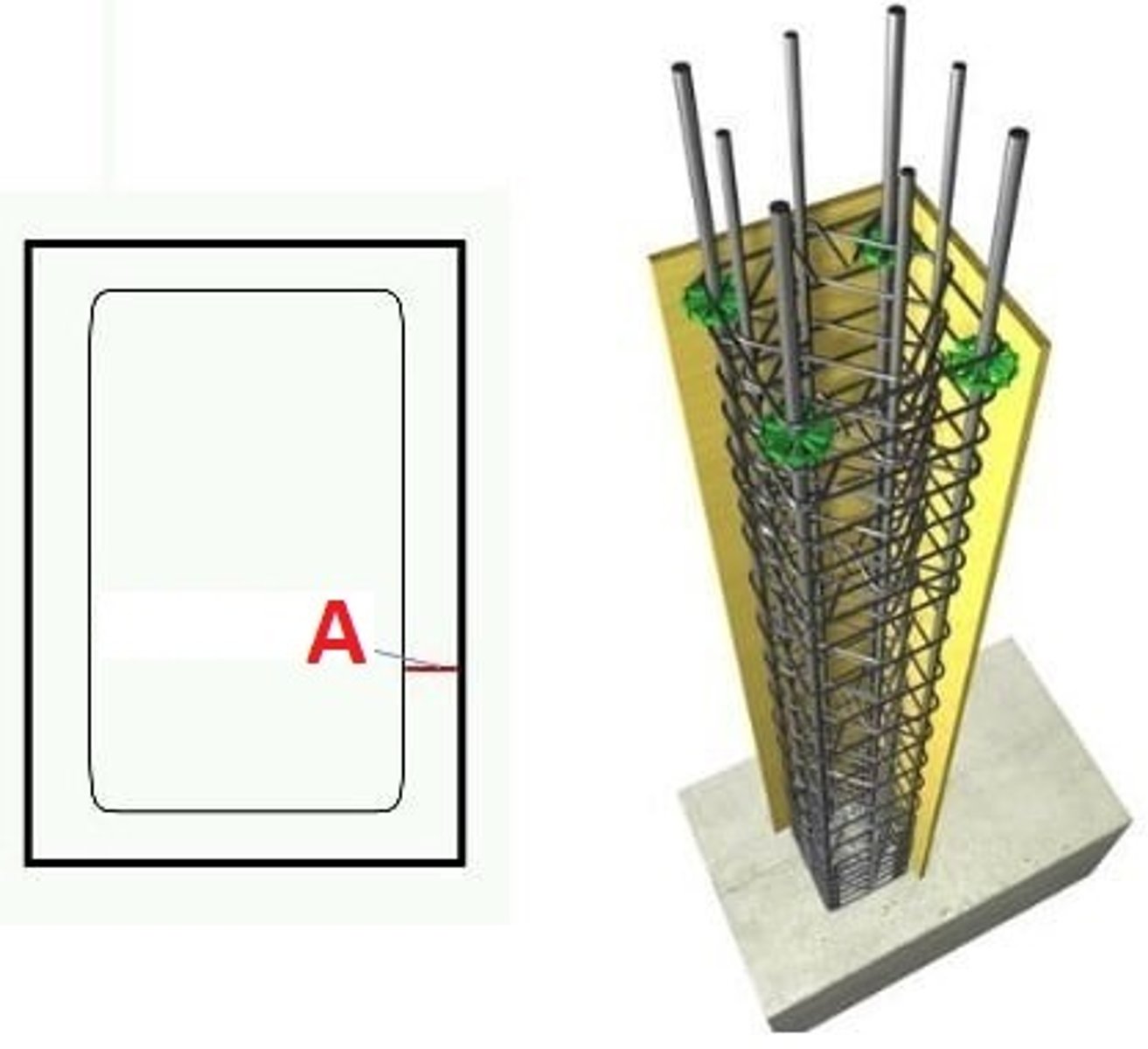
Bond
The adhesion between two substances, as concrete and reinforcing bar
Bond Stress
The adhesive force per unit area of contact between a reinforcing bar and the surrounding concrete developed at any section of a flexural member.
Development Length
Length of embedded reinforcement required to develop the design strength of reinforcement at a critical section.
Embedment Length
Length of embedded reinforcement provided beyond a critical section.
End Anchorage
Length of reinforcement or mechanical anchor or hook or combination thereof beyond point of zero stress in reinforcement
Hook
A bend or curve given to the end of a tension bar to develop an equivalent embedment length, used where there is insufficient room to develop an embedment length
Longitudinal Reinforcement
Reinforcement parallel to the horizontal surface of a slab or to the long axis of the concrete beam or column
Percentage Reinforcement
The ratio of effective area of reinforcement effective area of concrete at any section of a reinforced concrete member, expressed as a percentage
Top Bar
Any of the longitudinal bar serving attention reinforcement in the section of the concrete beam or slab subject to a negative moment
Bottom Bar
Any of the longitudinal bar serving as tension reinforcement in the section of a concrete beam or slab subject to a positive moment
Web Reinforcement
Reinforcement consisting of bent bars or stirrup,place in a concrete beam to resist diagonal tension
Bent Bar
Longitudinal bar bent to an angle of 30 degrees or more with the axis of a concrete beam, perpendicular to and intersecting. Cracking. Could occur from the diagonal tension
Bent Reinforcing Bar
Reinforcing bars that are bent up on or near the inflation point and are extended at the top of the beam across the support towards the adjacent span
Truss Bar
Longitudinal Bar bent UP OR DOWN at points of MOMENT REVERSAL in a reinforced concrete beam.
Stirrup
Any of the U-shaped or closed-loop bars placed perpendicular to the longitudinal reinforcement of a concrete beam to resist the vertical component of diagonal tension.
Admixture
1. Portland Cement (ASTM 150)
2. Blended Hydraulic Cement (ASTM C 595)
Cement shall conform to the following specifications for portland cement:
F
T or F:
Admixture should contain chloride ions
Not less than 25 mm
Minimum spacing of parallel bars
Reinforced Concrete Column
A concrete designed to act together with vertical and lateral reinforcement in resisting applied forces.
Short Column
A column when the unsupported height is not greater than ten times the shortest lateral dimension of the cross section
Long Column
A column when the unsupported height is more than ten times the shortest lateral dimension of the cross section
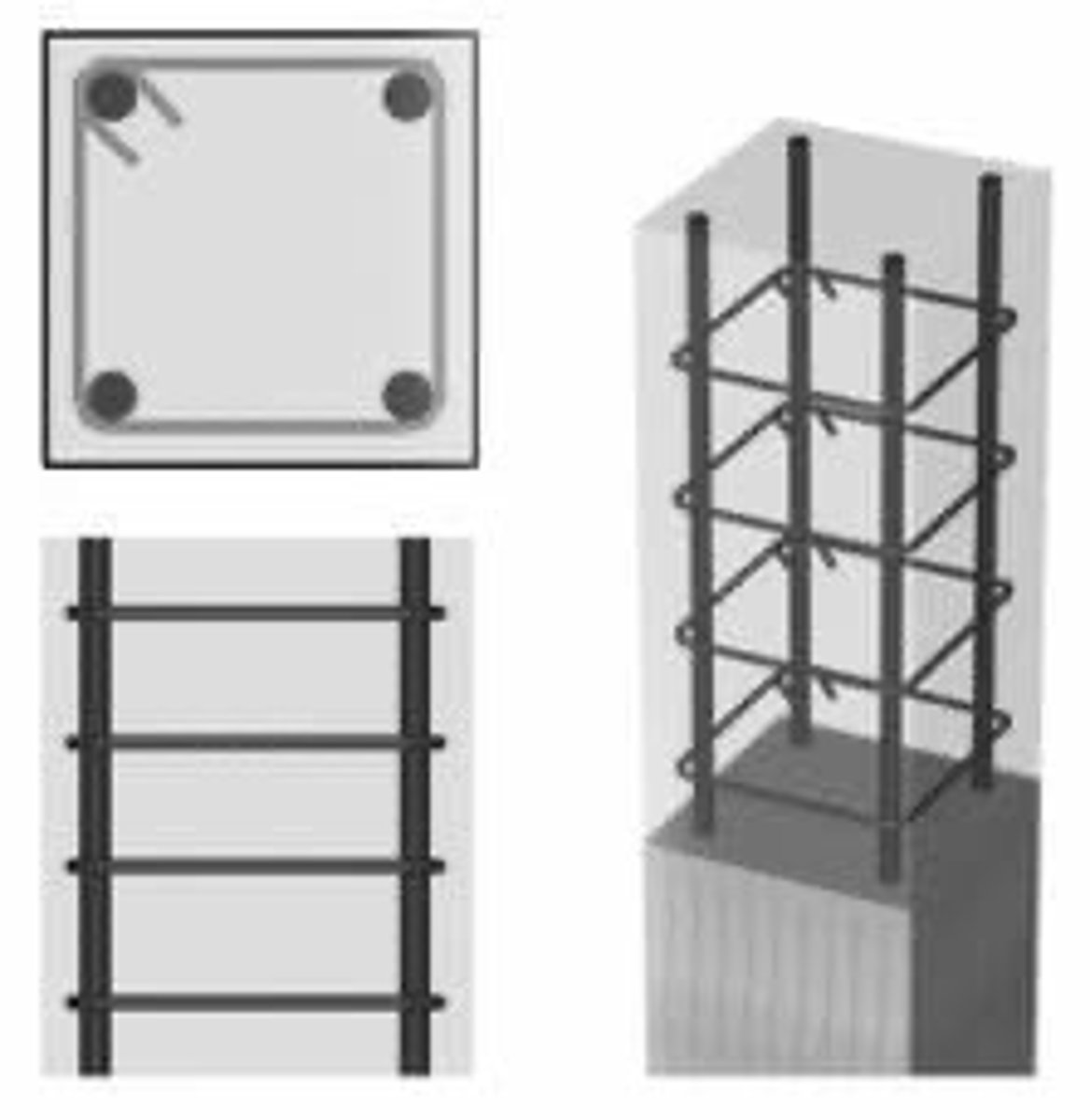
Tied Column
A concrete column reinforced with vertical bars and individual lateral ties

10 mm
Lateral ties should have a diameter of atleast ______ mm spaced apart not more than 48 tie diameter
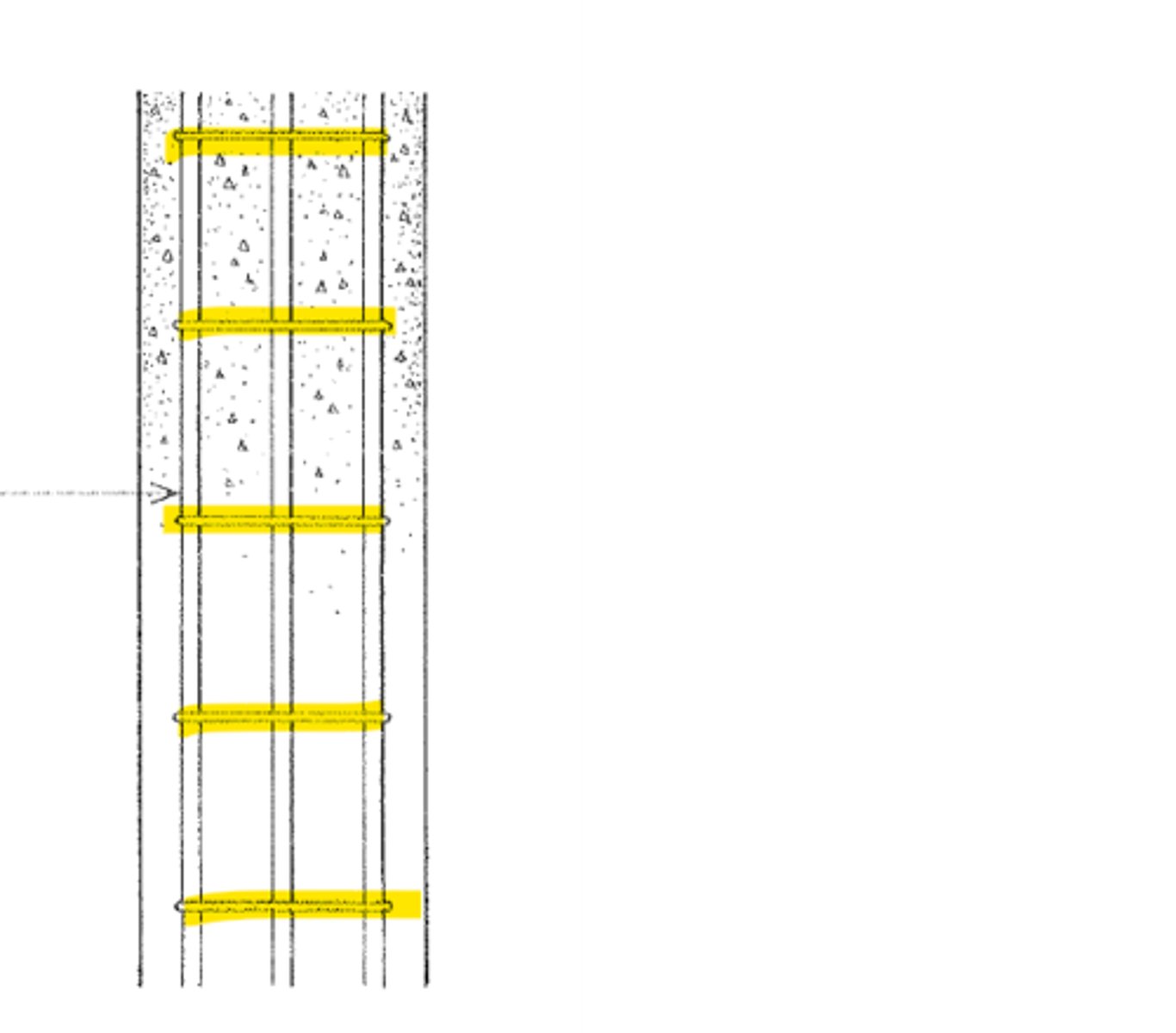
Vertical Reinforcement
Longitudinal reinforcement placed in concrete column to absorb compressive stresses, resist bending stresses and reduce the effects of creep and shrinkage in the column
Lateral Reinforcement
Spiral reinforcement or lateral ties placed in a concrete column to laterally restrain the vertical reinforcement and prevent buckling
Spiral Reinforcement
lateral reinforcement consisting of an evenly spaced continuous spiral held firmly in place by vertical spacers
Bundled Reinforcement
Reinforcement employed consisting of two to four bars tied in direct contact with each other to serve or act as one unit reinforcement placed at the corner of lateral ties
Spiral Column
A concrete column with spiral reinforcement enclosing a circular core reinforced with vertical bars.
Composite Column
type of column where structural steel column is embedded into the concrete core of a spiral column
Combined Column
a column with structural steel encased in a concrete of at least 7 cm thick reinforced with wire mess surrounding the column at a distance of 3 cm inside the outer surface of the concrete covering
Lally Column
A fabricated post made of steel provided with a plain flat steel bar or plate which holds girder, girt or beam.

Floor System
Horizontal plane that must support both live and dead loads
Live Load
The weight of movable objects such as people, furnishings, machines, vehicles, and goods in or on a building.
Dead Load
the weight of the structure itself
Environmental Load
Consists of wind pressure and suctions, earthquake load, rainwater on flat roof, and forces caused by temperature differentials
Reinforced Concrete Slab
A rigid planar structure designed to act together with principal and secondary reinforcement in resisting forces
One Way Slab
- A concrete slab of uniform thickness reinforced in one direction and cast integrally with parallel supporting beams
- Supported by two parallel beams
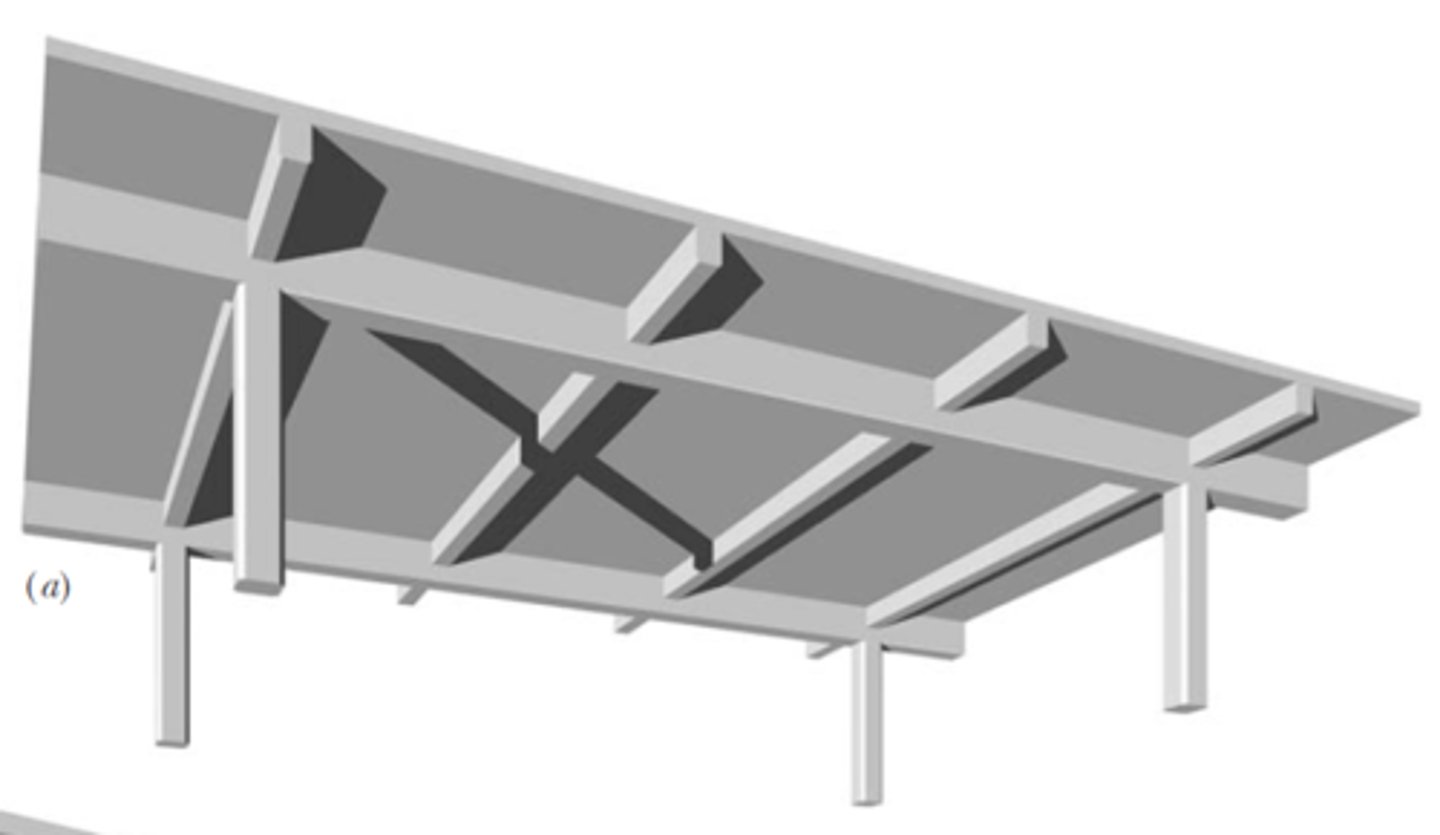
Two way slab
Concrete slab of uniform thickness being forced into direction and gas integrally with supporting edge beam or bearing wall on four sides
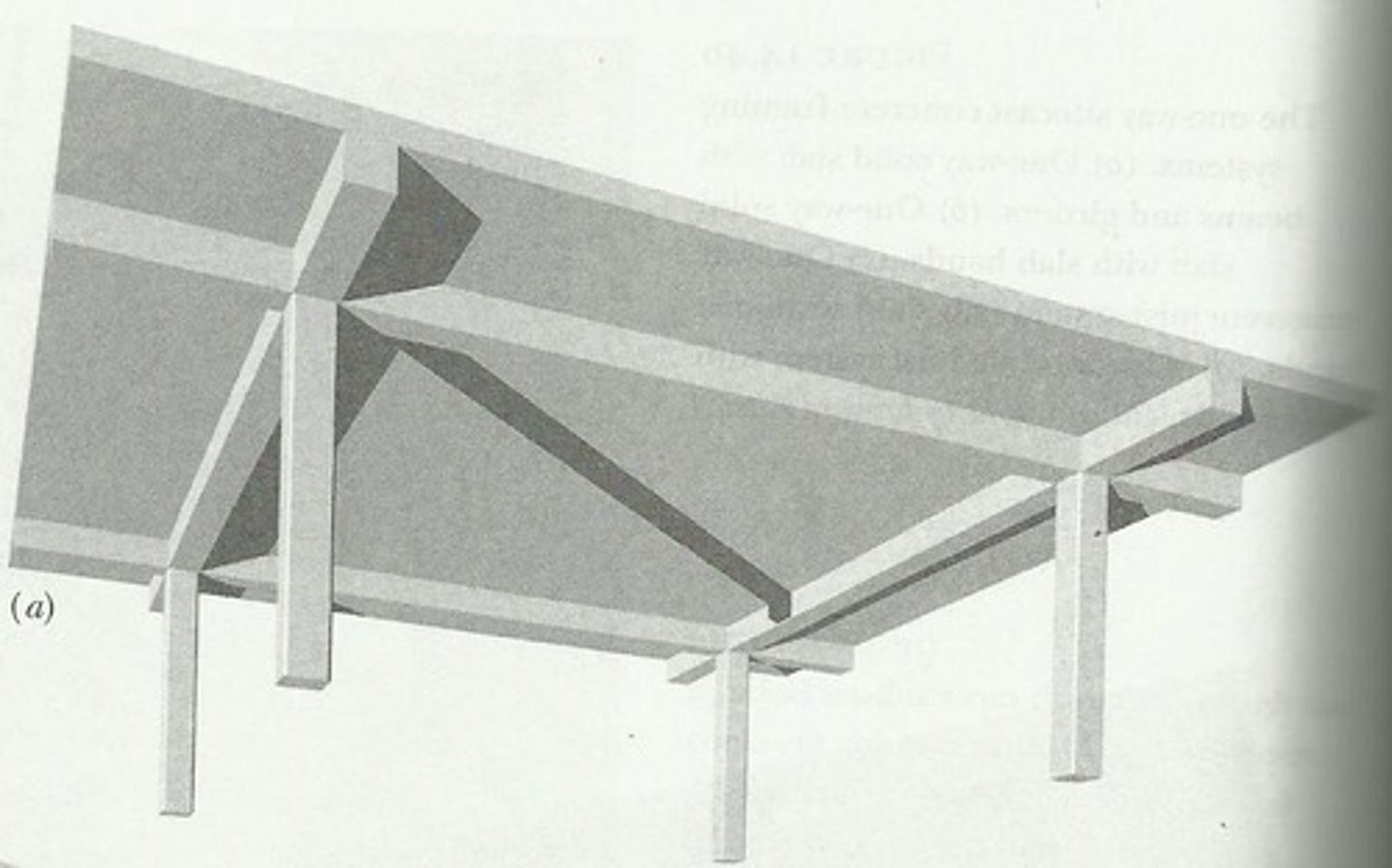
Beam-and-Girder Slab
A one-way slab supported by secondary beams which in turn are supported by primary beams or girders.
Girder
A horizontal beam that supports other beams; a very large beam, especially one that is built up from other sections.

Continuous Slab
A reinforced concrete slab extending as a structural unit over three or more supports in a given direction.
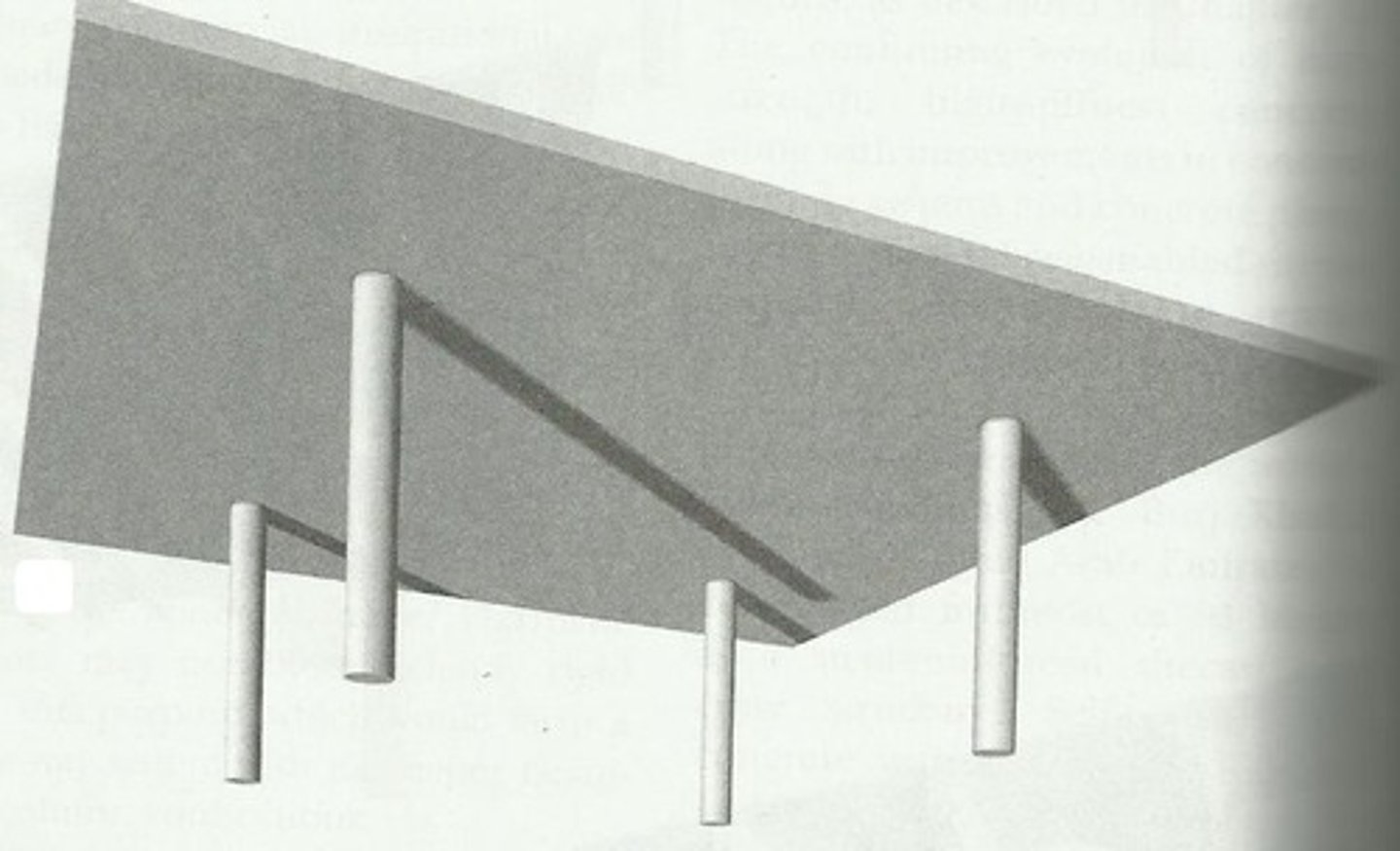
Flat Plate
A concrete slab of uniform thickness reinforced in two or more direction in the board that directly by columns without beams or girders; suitable for SHORT TO MEDIUM SPANS
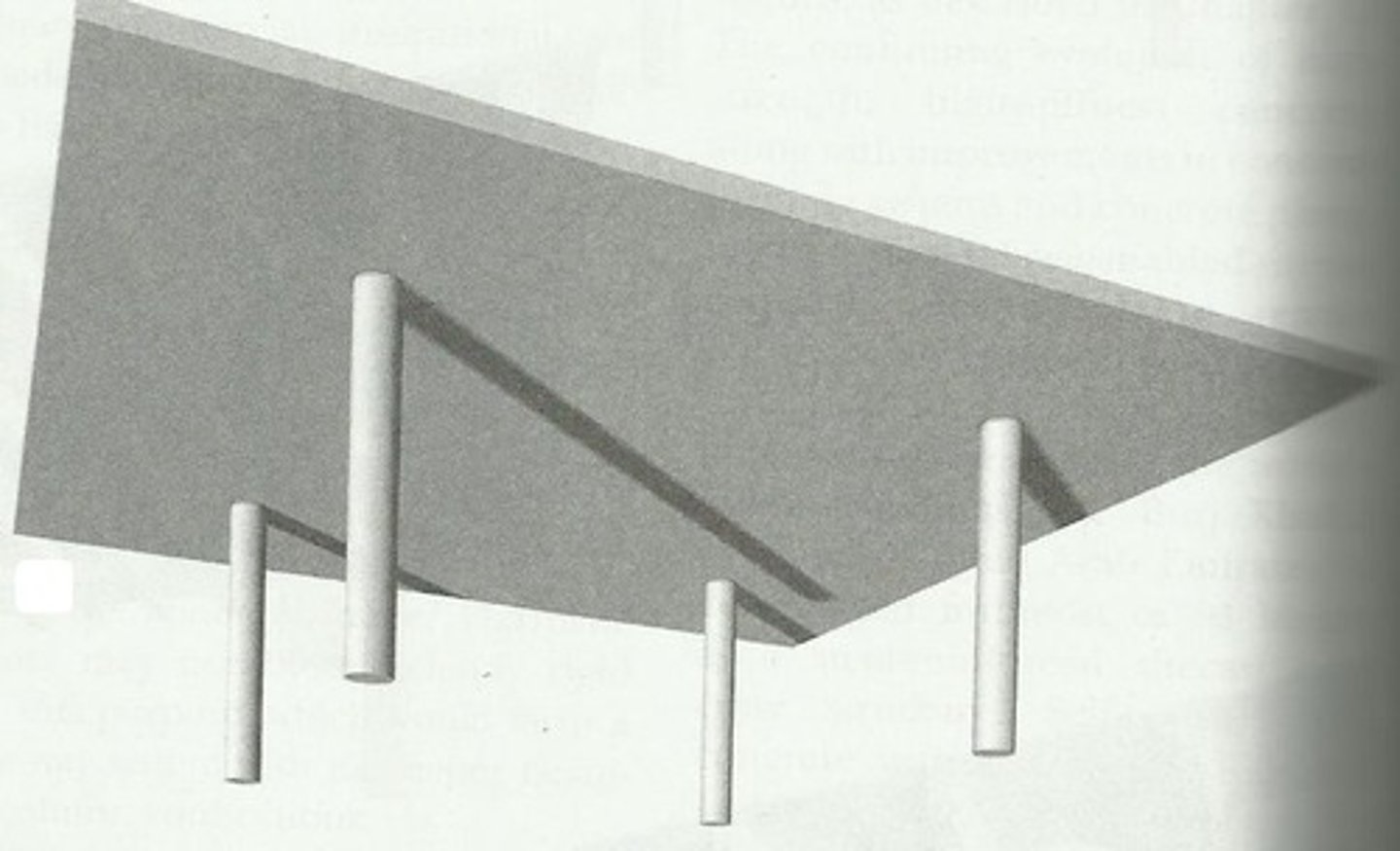
Flat Slab
a flat plate thickened at its column supports with column capitals and drop panels to increase its shear strength and moment-resisting capacity: suitable for HEAVY LOADED SPANS
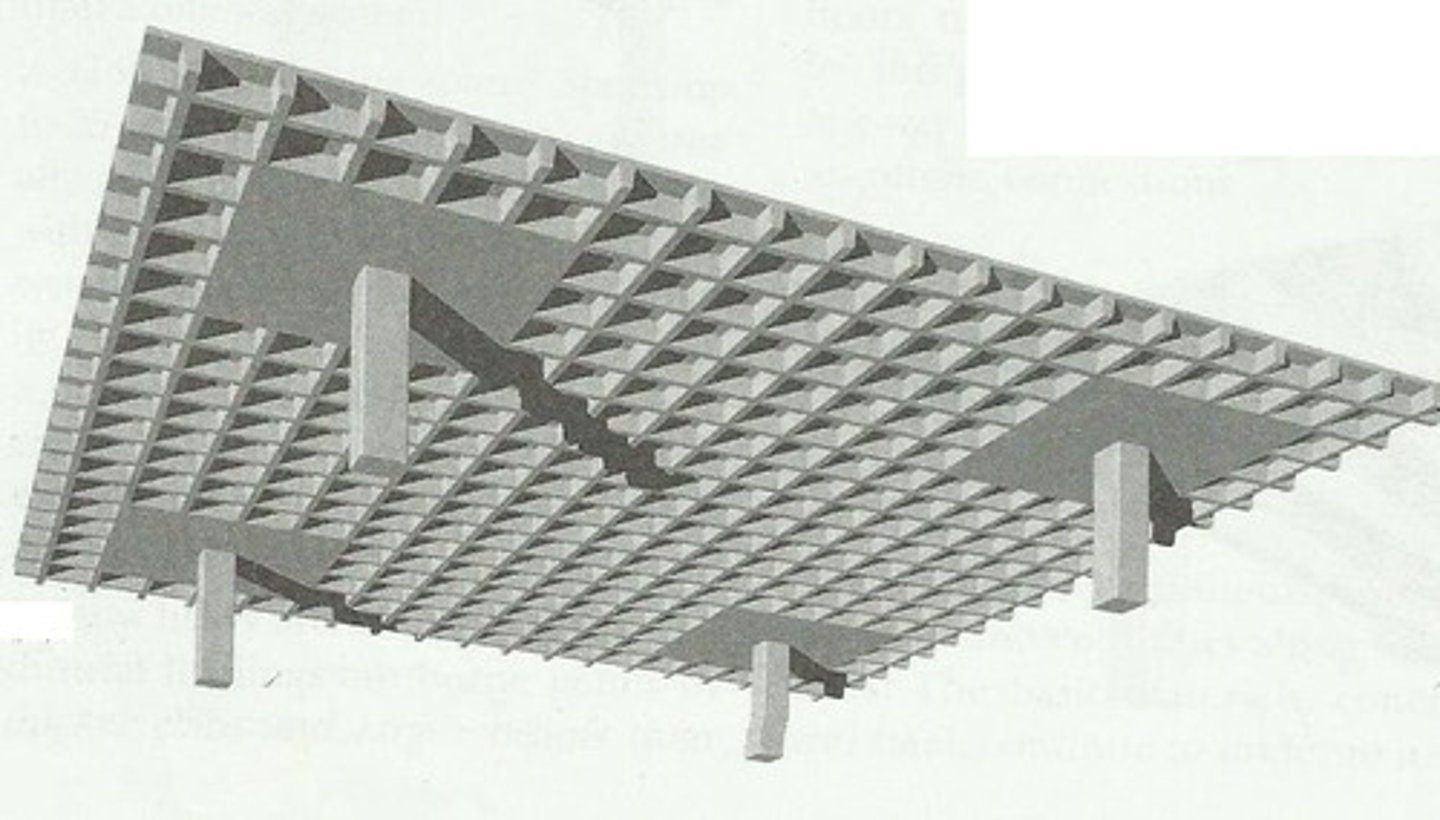
Waffle Slab
A two-way concrete joist system; can carry HEAVIER LOADS than flat slabs
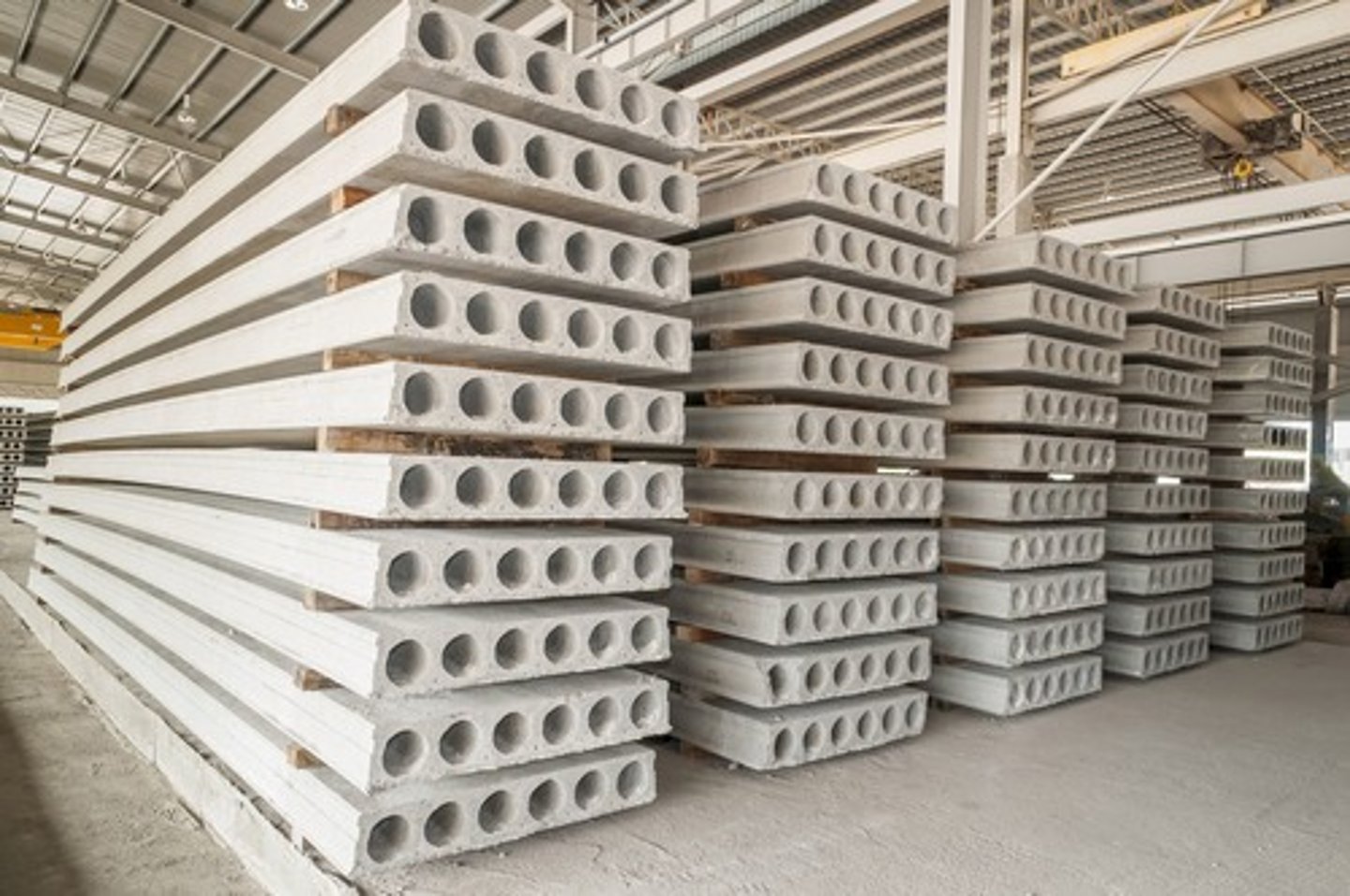
Precast Concrete Slabs
A concrete slab member or product that is cast and cured in a place other than where it is to be installed in a structure

Foundation
The lowest support of a structure
Shallow Foundation
A foundation that transfers building loads into the Earth at the base of a column or bearing wall.
Deep Foundation
A foundation system that extends down through unsuitable soil to transfer building loads to a more appropriate bearing stratum well below the superstructure.
Footing
Part of the foundation bearing directly upon the supporting soil
Superstructure
the part of a structure that is above the foundation or ground
Substructure
The underlying structure forming the foundation of a building or other construction.