Lecture 7: Flatworms
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Phylum Platyhelminthes
flatworms, flukes, & tapeworms
tripoblastic: ectoderm, endoderm, mesoderm tissue layers
Organ level of structural complexity
acoelomates
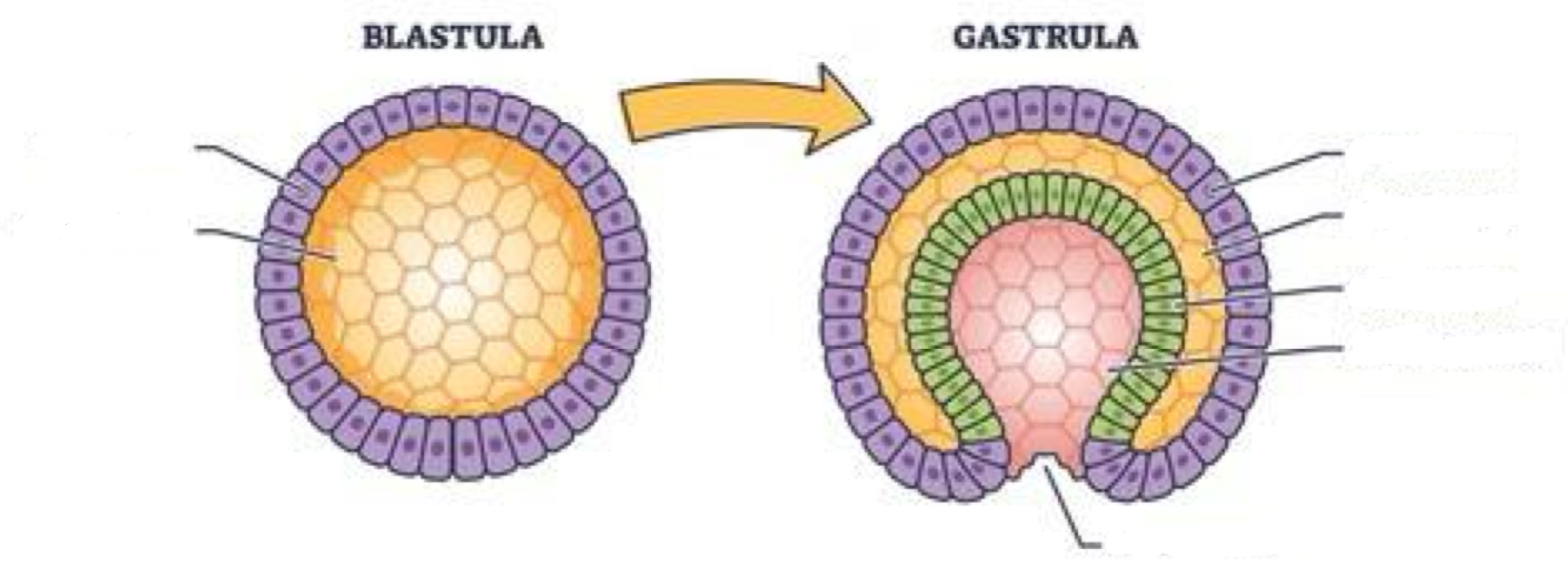
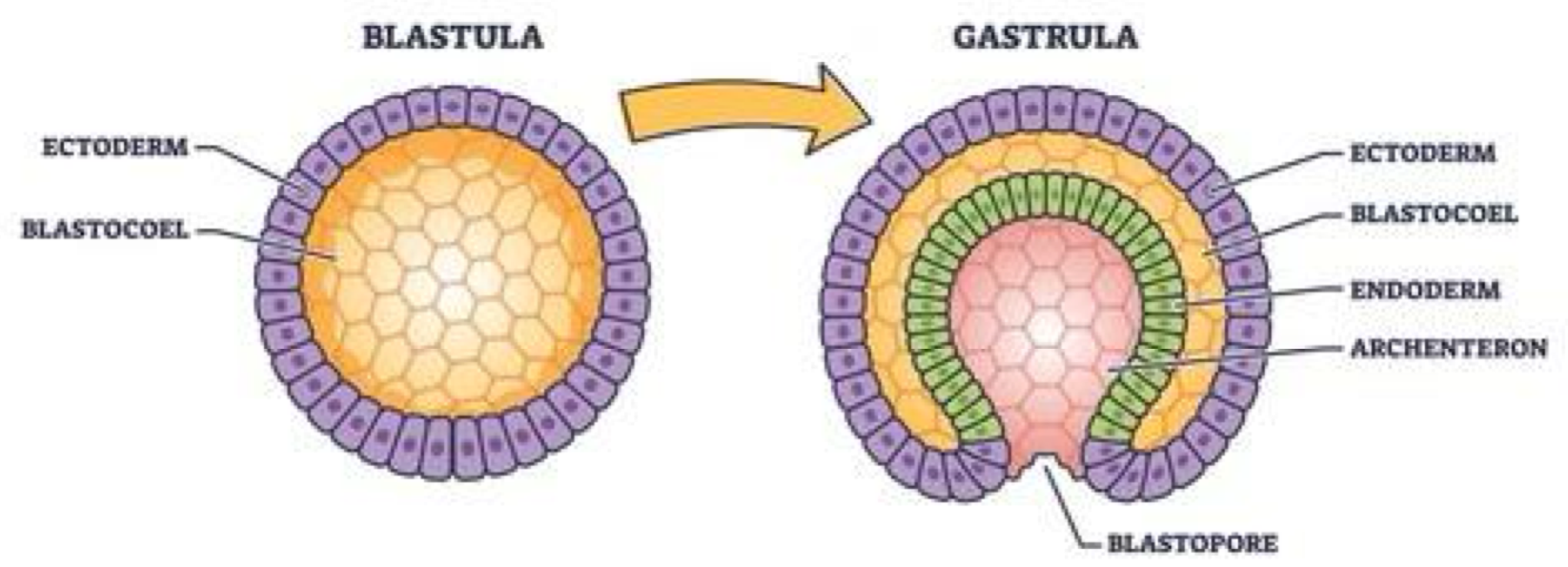
Gastrulation
early stage of animal developement when embryo folds inward & forms basic tissue layers
Non parasitic worms are part of which group ? What are some of their characteristics?
Phylum Platyhelminthes
Class Turbellaria
ganglia
clusters of nerve cells (mini brains) located at front end (head)
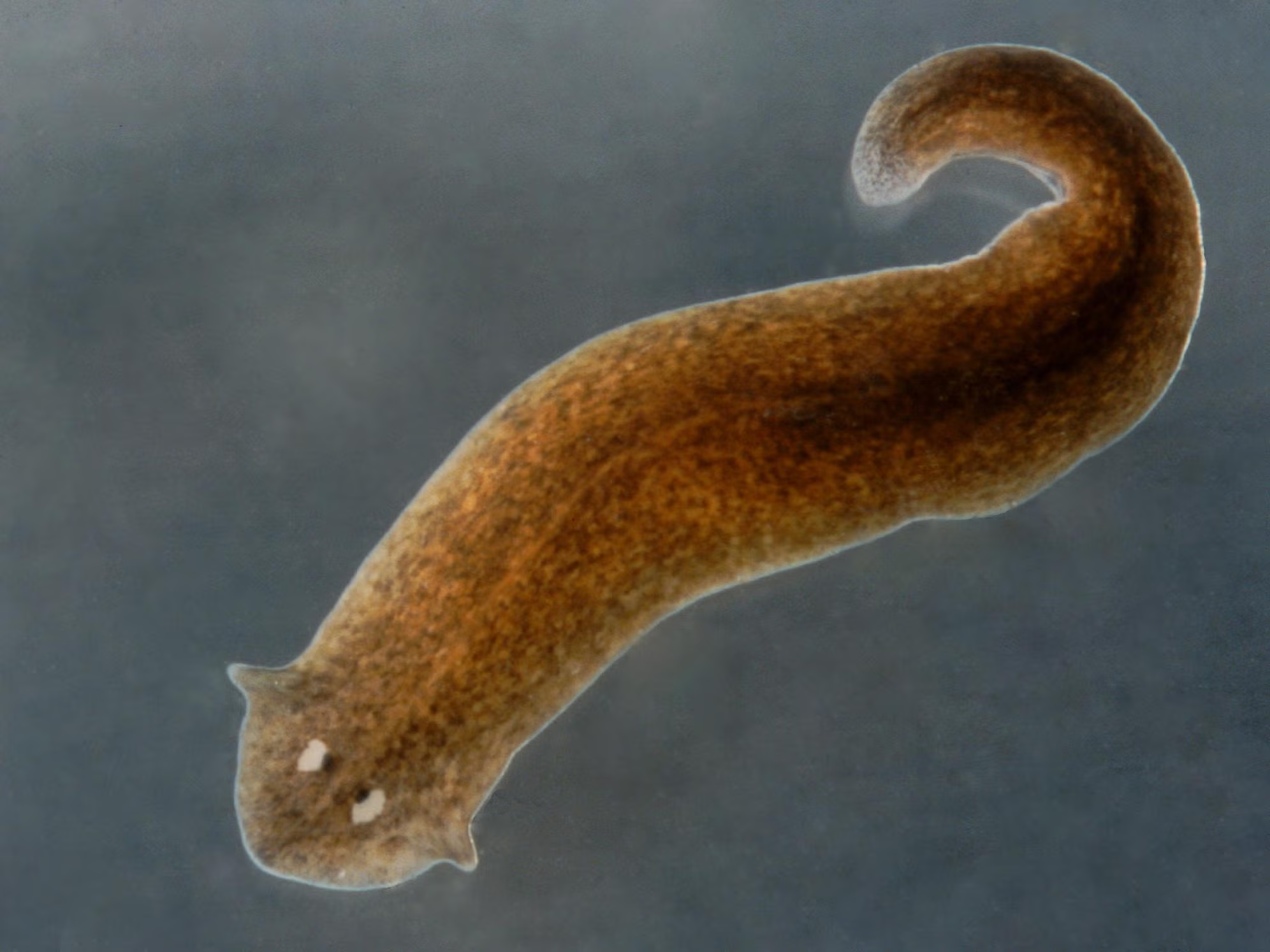
Planarians
Phylum Platyhelminthes, Class Turbellaria, Order Tricladida
Ciliated epidermis = glide on mucus
highly regenerative = can regrow lost parts
nerve net + ganglia
3 branched gastrovascular cavity = spread nutrients through body
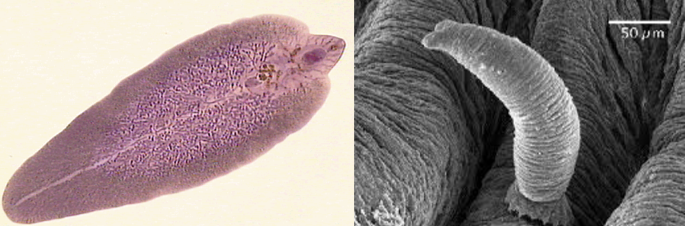
Flukes
Phylum Platyhelminthes
Class Trematoda
multiple hosts
internal parasite w/ hooks/suckers
Class Monogenea
One host
External parasites w/ hooks/suckers
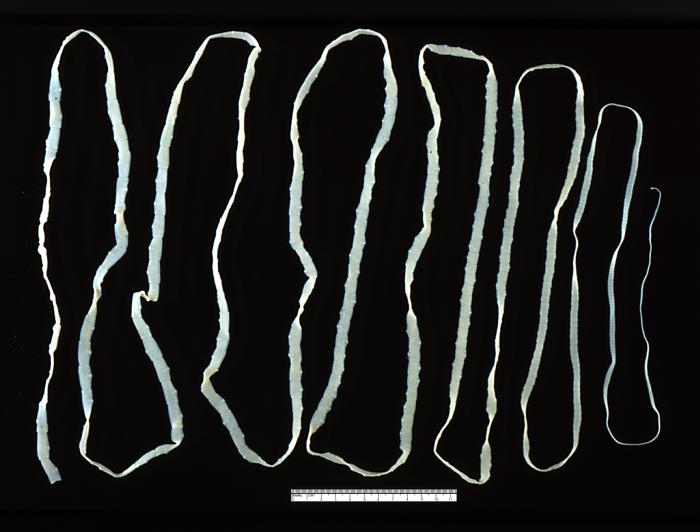
Tape worms
Phylum Platyhelminthes, Class Cestoda
internal parasites within vertebrate intestines
no digestive tract → absorb nutrients
scolex (hook & sucker head) + proglottids (hermaphroditic body)
intermediate hosts (pig → human)
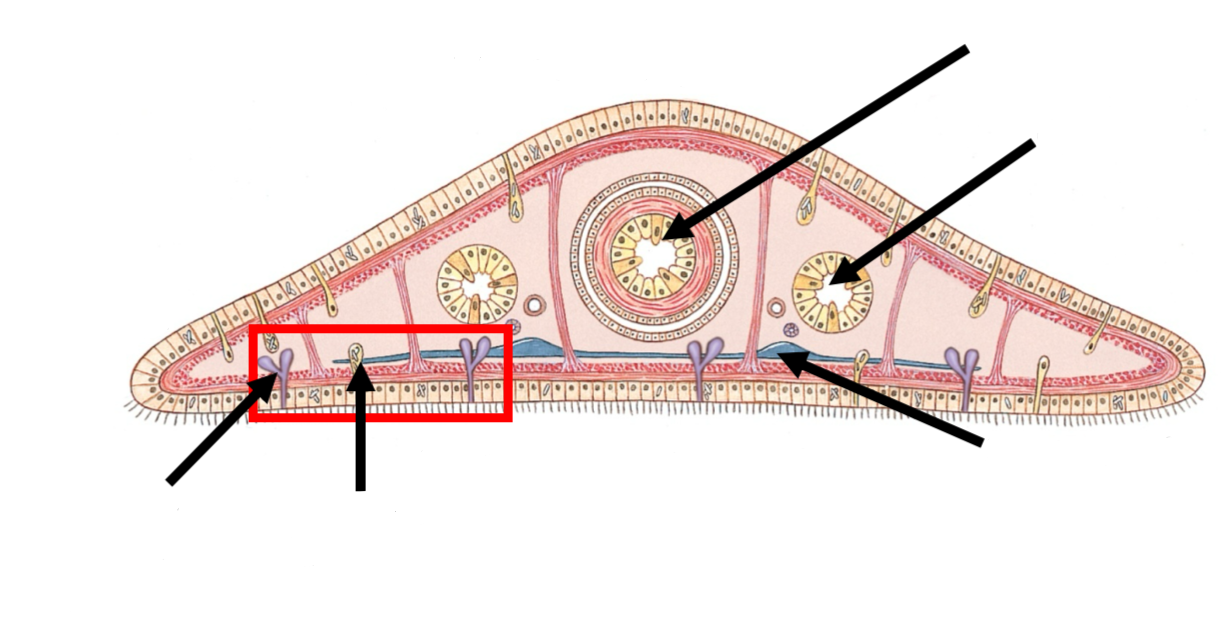
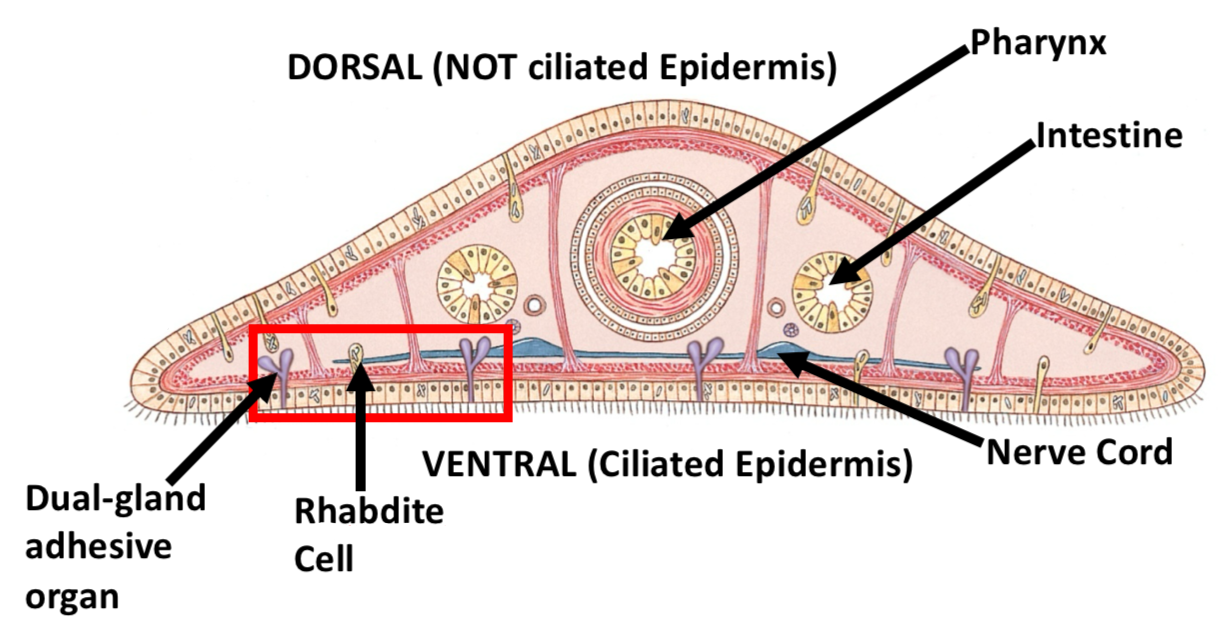
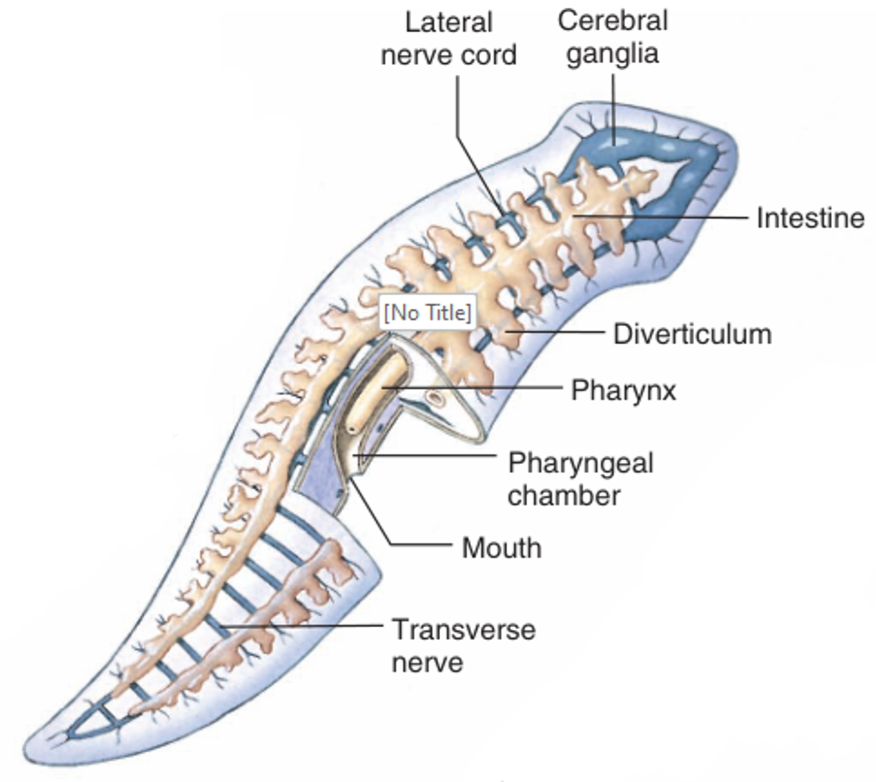
cross section of planarian
Pharynx = feeding tube
Intestine = branched gut
Nerve cord = movement & stimuli
Rhabdite cell = make slime for gliding
Dual gland adhesive organ = sticking & unsticking
a cross section is always going to be a _______ cut
transverse
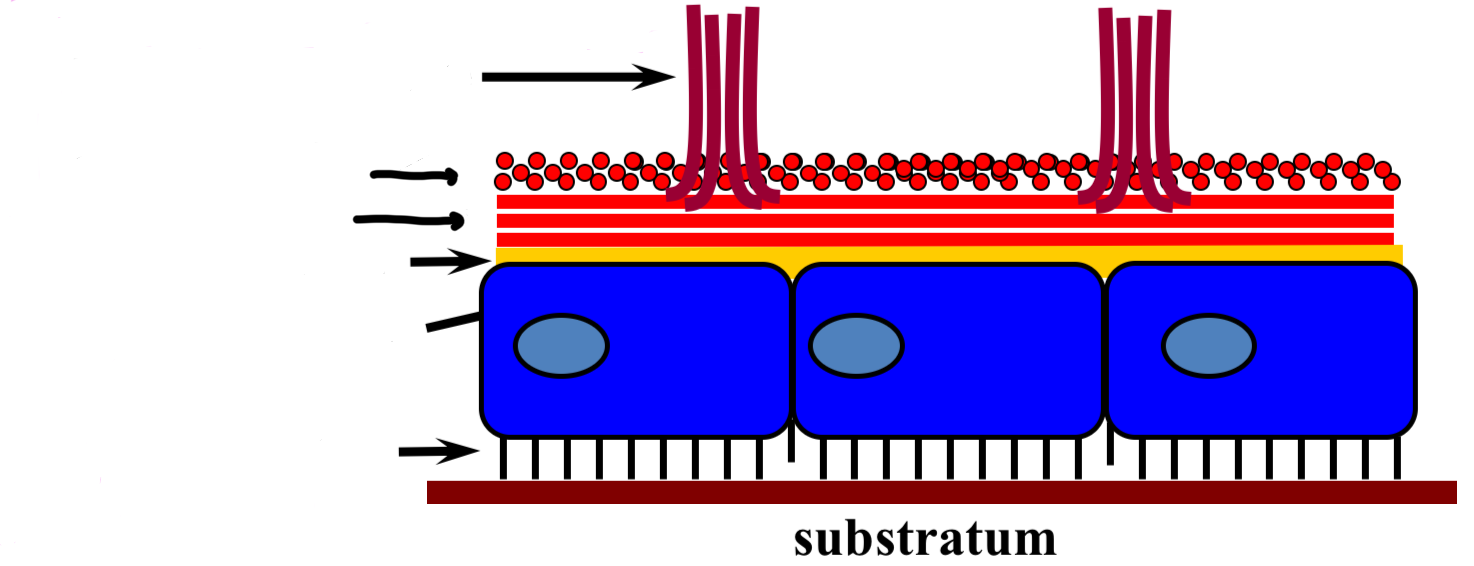
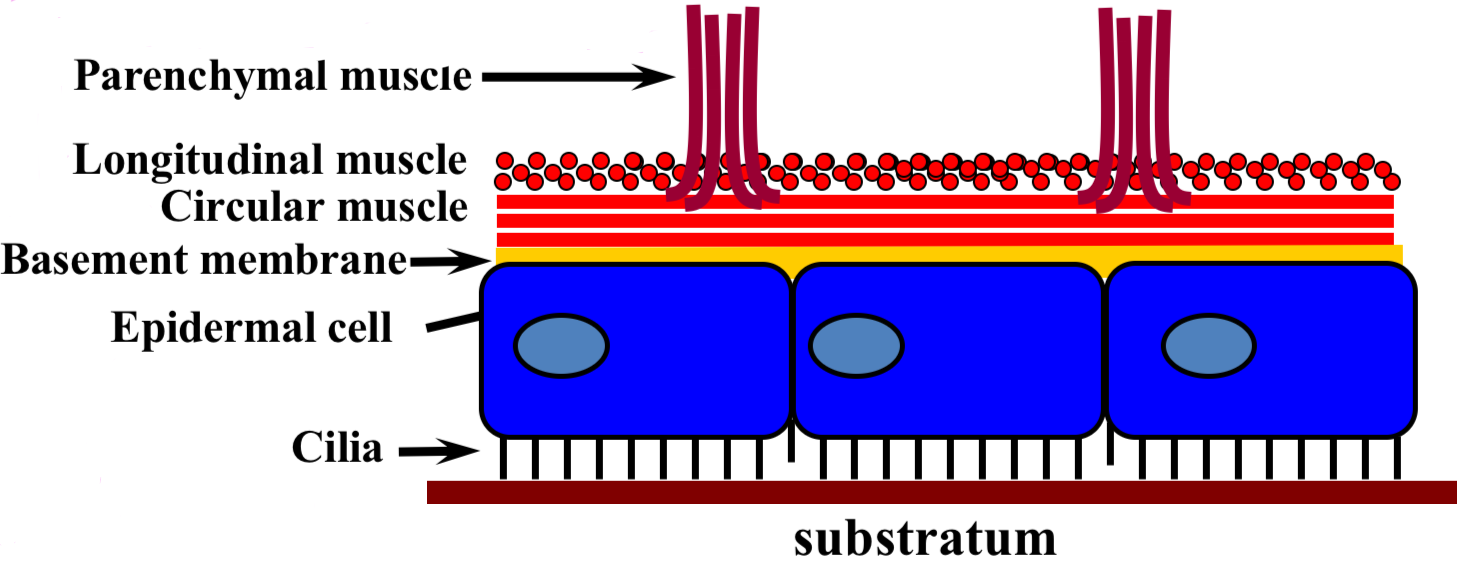
cells that create planarian movement
Parenchymal muscle fibers = shape & hardness
Longitudinal muscle = contract body to pull in
Circular muscle = elongate body
Basement membrane = support
Epidermal cell = rhabdite cells make slime
Cilia = beat in waves to glide in slime
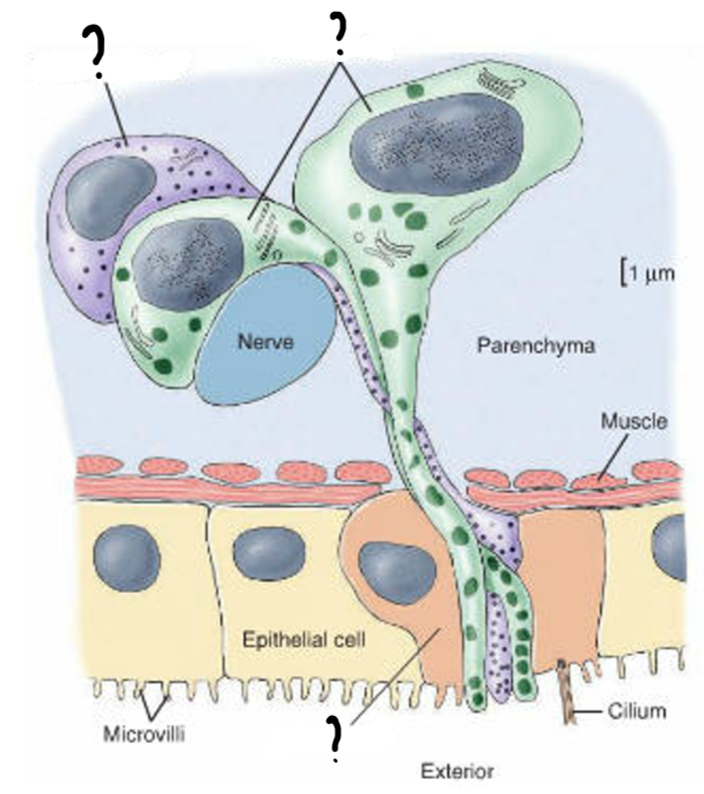
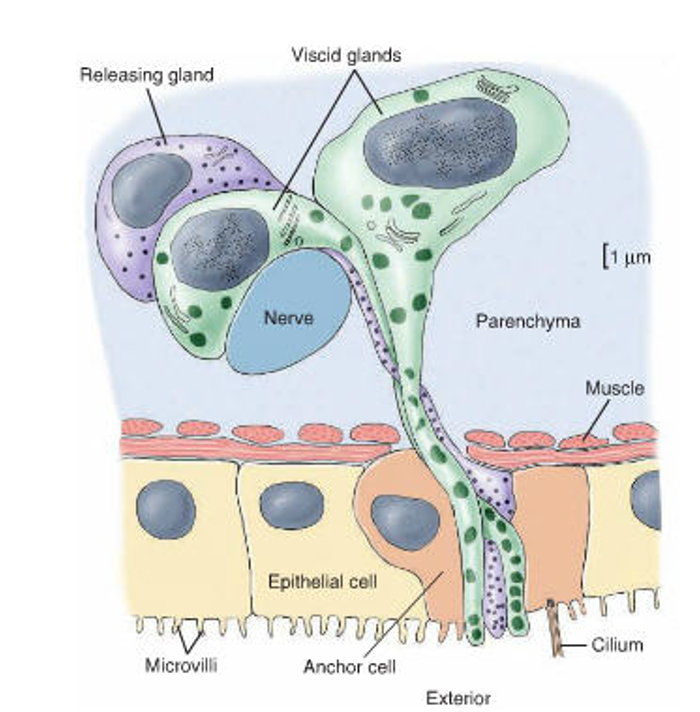
Dual gland adhesive organ cells
Paired viscid cells = produce adhesive that attach anchor cells to surface
Anchor cells = allow subtle muscle contractions to pull forward
Releasing cell = secretes chemicals that release attachment
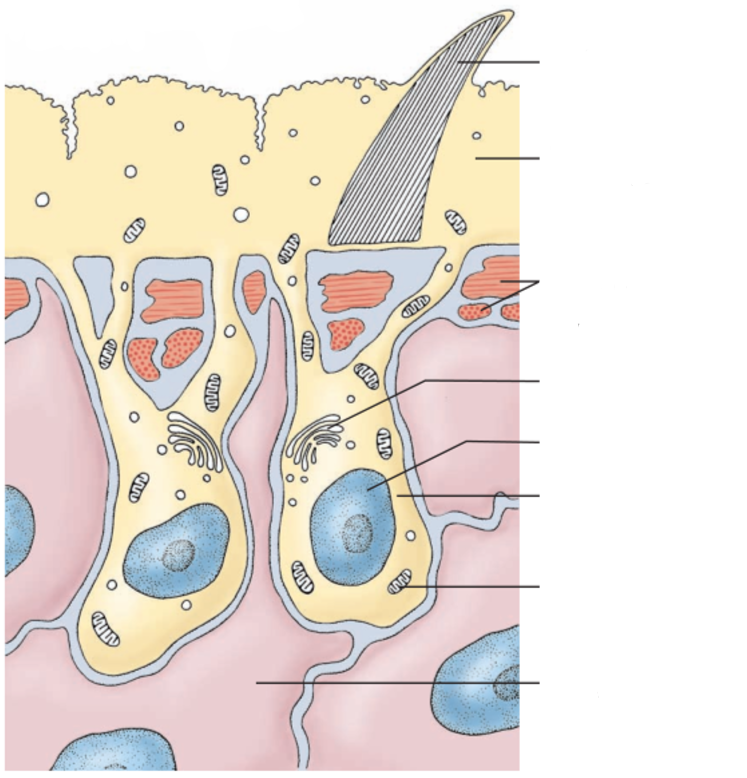
Tegument
syncytial epidermis covering of parasitic flatworms → protects worm + absorbs nutrients
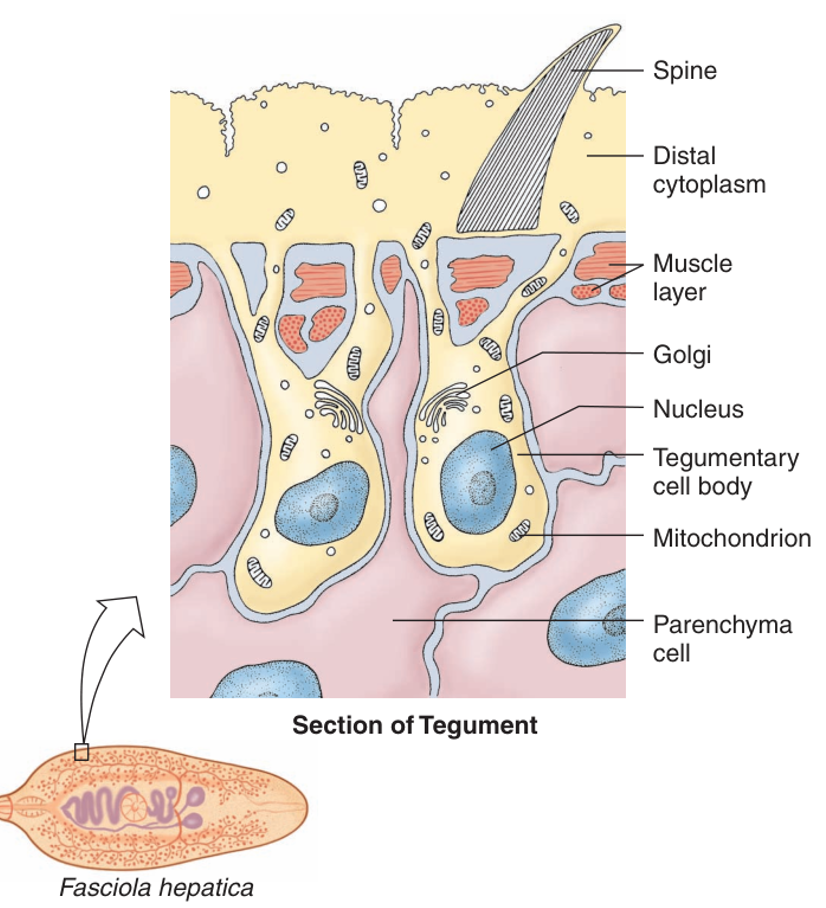
_______ is a defining trait of the clade Neodermata (parasitic flatworms) in the Phylum Platyhelminthes ?
Tegument
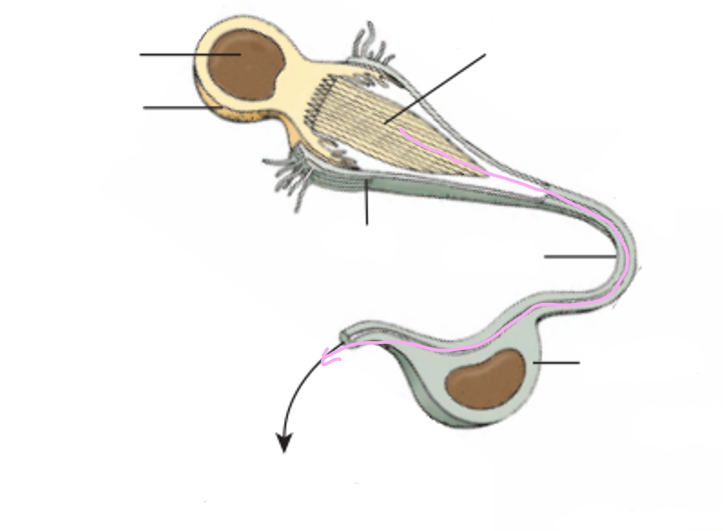
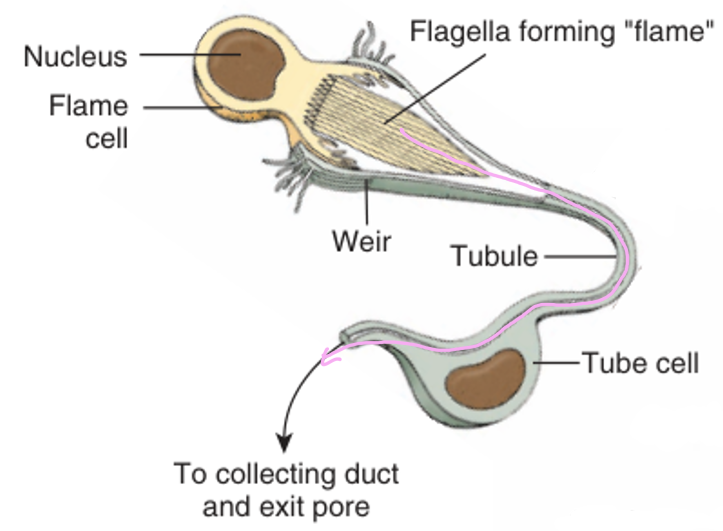
Protonephridial system
maintaining osmotic balance by pumping out excess water
Flame cells have flagella that beat which pulls water & waste into tubule system
Water flows through tubules → collecting ducts → nephridopore (exit pore) → out of body
Interdigitation: 2 cells’ membranes interlock like fingers to form a mesh filter (weir) to keep big particles out
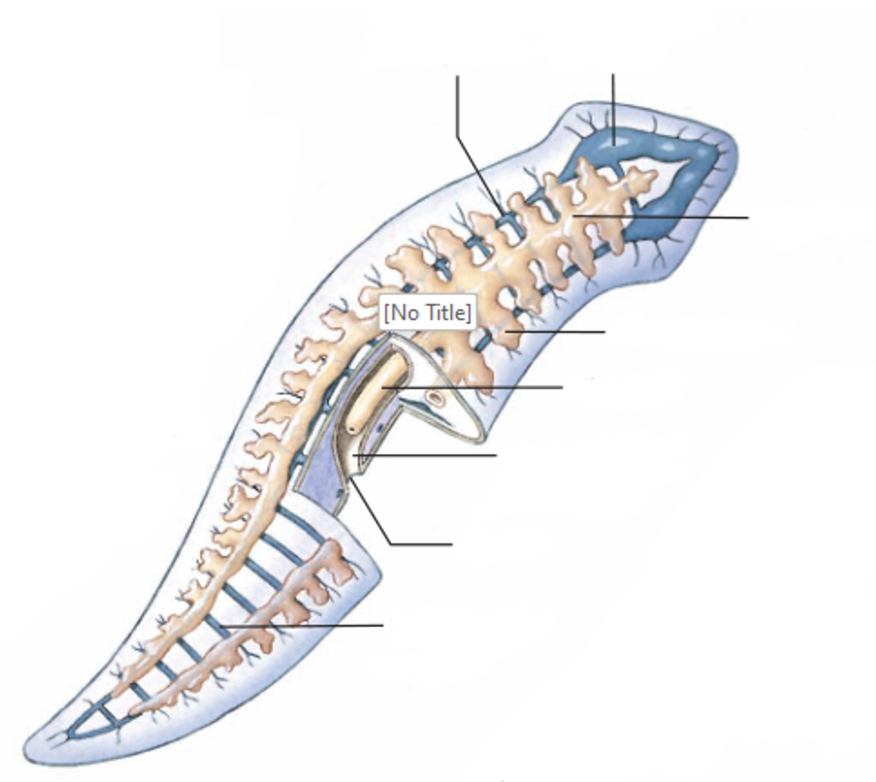
Digestive system of a planarian
Pharynx = sticks out to grab food
Food goes to Pharyngeal chamber → intestine
Intestine is branched (diverticula) to spread nutrients through body
waste goes back out through mouth
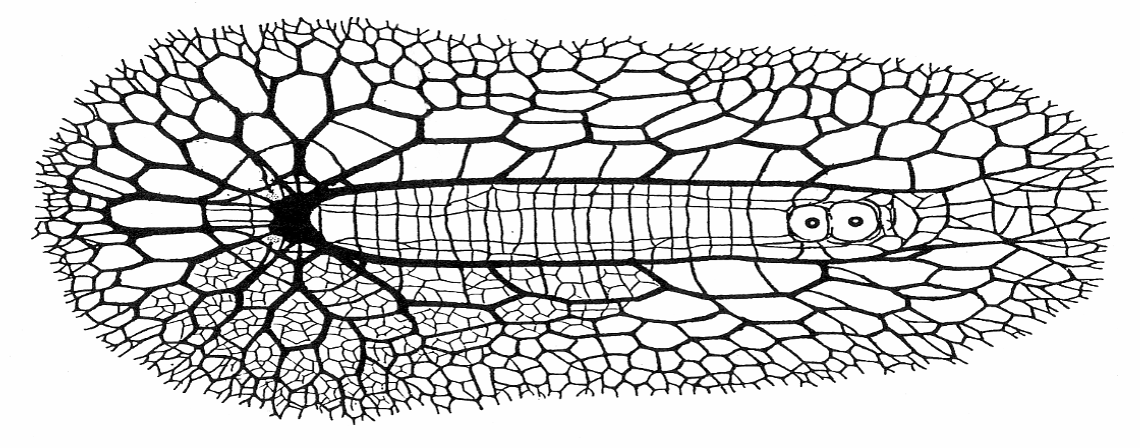
Subepidermal nerve plexus
net of nerves under the skin , no major nerve cords
simplest system
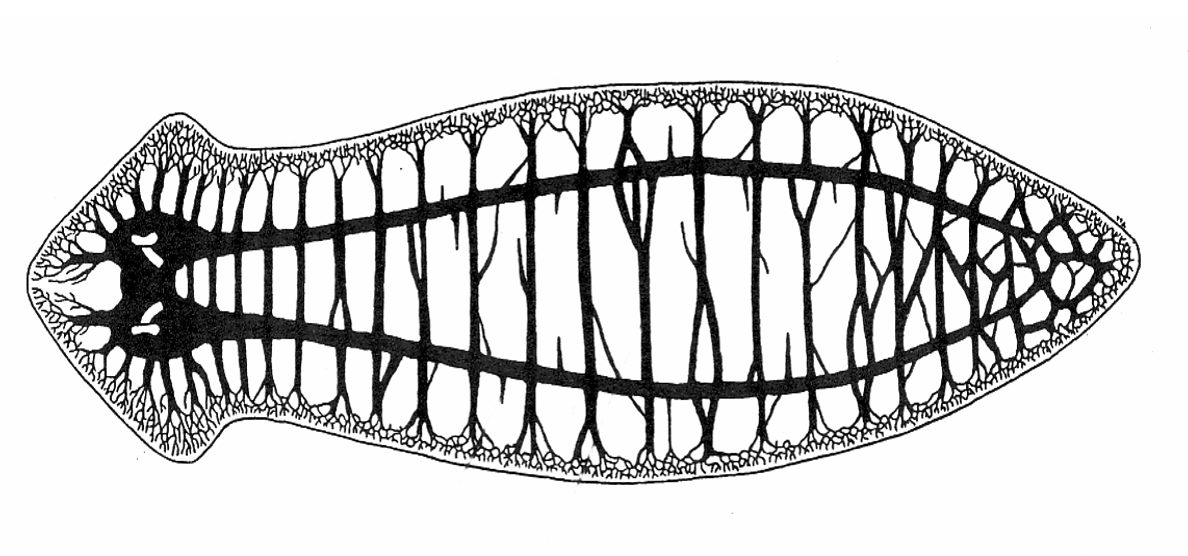
subepidermal nerve plexus + longitudinal nerve cords
1-5 nerve cord pairs under the muscles
cerebral ganglion = primitive brain collecting/sending sensory info
nerve cords + primitive brain
1-3 pairs of nerve cords, with connecting nerves left & right (ring commissures) forming a ladder pattern
has an auricle: sensing environment
what sensory types make up Auricle?
Tactile receptors = touch
Chemoreceptors = chemicals
Rheoreceptors = water currents
Statocysts = gravity
Photoreceptors = light/dark