Zwitterions, Carboxyl Group Reactions and Peptide Bond Formation
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Cationic Amino Acids
What is cation?
In what type of solution do aa become cationic?
Which part of aa act as cationic?
How can aa be cationic?
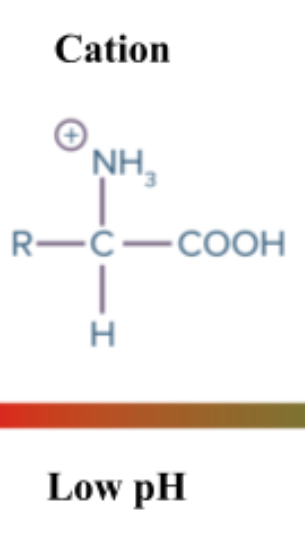
Cation: Ion with positive charge
Type of solution: Acidic solution
Part of aa that is cationic: Amine group (NH2+)
How aa be cationic: Amine group acts like a base and gains hydrogen, becoming NH3+
Anionic Amino Acids
What is anion?
In what type of solution do aa become anions?
Which part of aa act as anion?
How can aa be anion?
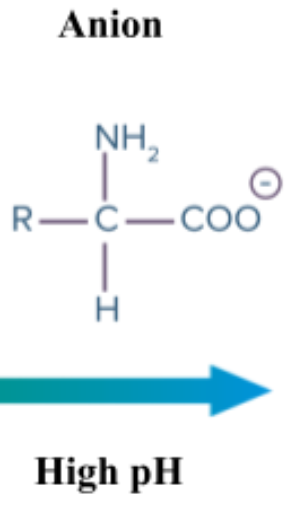
Anion: Ion with negative charge
Type of solution: Basic (alkaline) solution
Part of aa that is anionic: Carboxyl group (COOH)
How aa be anion: Carboxyl group acts like acid and loses hydrogen, becoming COO-
What is the iso-electric point?
the pH at which a particular molecule carries no net electric charge (around pH 7)
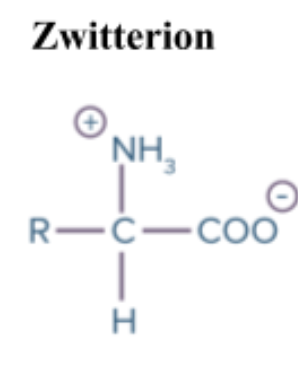
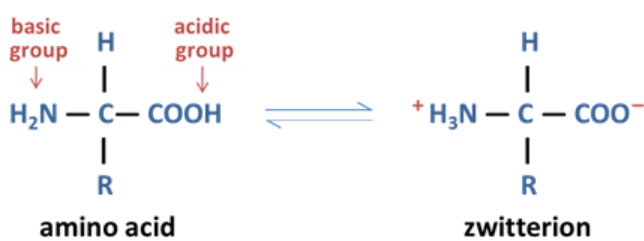
What are zwitterions
A molecule that has separate positively and negatively charged groups giving an overall net charge of 0
When and how can amino acids form zwitterions?
Amine group
Base or acid?
Gain or lose proton?
Functional group changes to
Carboxylic group
Base or acid?
Gain or lose proton?
Functional group changes to
When: Dissolved in aqueous solution at around pH 7
How:
Amine group:
It’s a base so it will gain a proton (H+), gaining positive charge and changing the functional group from NH2+ —> NH3+
Carboxylic group:
It’s an acid so it will lose a proton (H+), gaining negative charge and changing the functional group from COOH —> COO-
Both of these reactions are happening at the same time so there is no total net charge

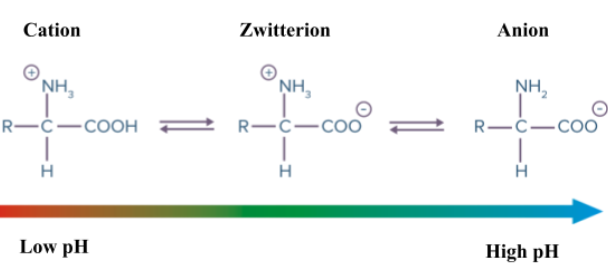
Cation, Zwitterion and Anion
-
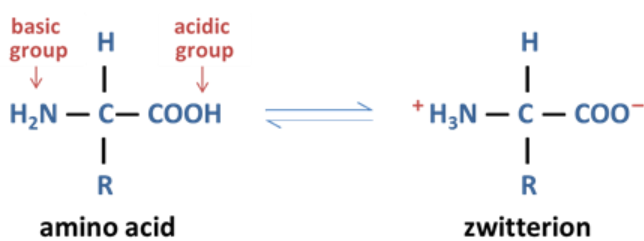
Unionized vs Zwitterion form
-
What is decarboxylation and what does it produce?
What: Reaction where CO2 is removed from carboxylic group
Produces: CO2 and Amine (ammonia derivative)
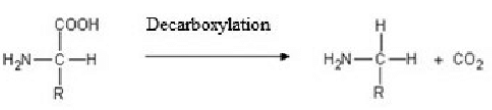
Decarboxylation of amino acids
Histidine
Tyrosine
Tryptophan
Lysine
Glutamic acid
Histidine —> Histamine + CO2
Tyrosine —> Tyramine + CO2
Tryptophan —> Tryptamine + CO2
Lysine —> Cadaverine + CO2
Glutamic acid —> Gamma Amino Butyric Acid (GABA) + CO2
What is GABA?
A neurotransmitter
How can amino acids be formed into amides (carboxylic acid derivative)
Through the reaction between carboxylic group (-COOH) and ammonia
-COOH + NH3 —> Amide
Amide Formation from Amino Acids
Aspartic acid
Glutamic acid
Aspartic acid + NH3 —> Asparagine
Glutamic acid + NH3 —> Glutamine
How are peptide bonds form?
Alpha carboxylic group of one aa reacts with alpha amino group of another aa forming the CO-NH bridge (peptide bond)
How are proteins made?
By the polymerization of amino acids through peptide bonds