Anatomy and Physiology - Basic Chemistry
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
Four elements that account for most of a human’s dry mass
Carbon, oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen
How are isotopes different from normal atoms of the same element
Isotopes have more neutrons
How is atomic weight calculated for an atom
multiply the mass of each isotope and add its results
1st shell
2nd shell
3rd shell
2, 8, 8
What solution has more H+? What solution has more OH?
Acidic, Basic
What is an electrolyte?
a liquid or gel that contains ions and can be decomposed by electrolysis
What is the most abundant inorganic substance in the body?
Water
What occurs in a covalent bond?
two atoms share valence electrons
What occurs in an ionic bond?
atoms transfer electrons to each other
What defines a substance as organic?
contains carbon and hydrogen, larger, carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
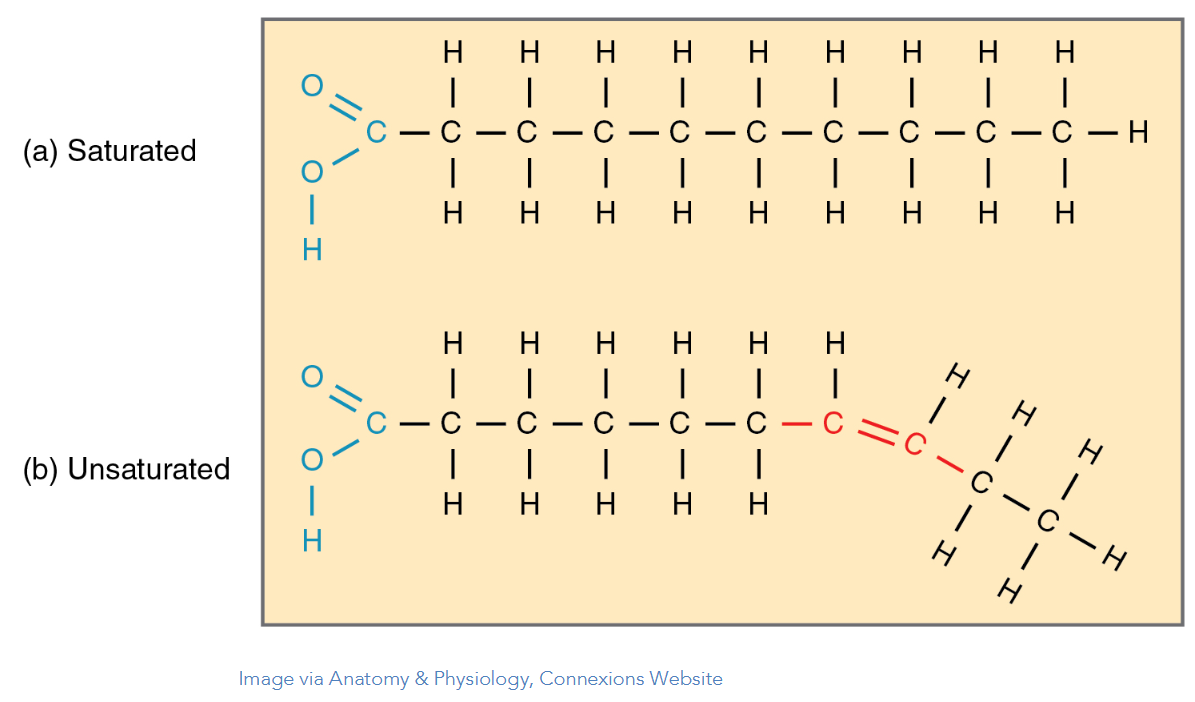
Saturated fats
Unsaturated fats
no double bonds between carbons, one or more double bonds between carbons
What is an enzyme?
proteins that help speed up chemical reactions in our bodies
DNA
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine, double helix, deoxyribose, lacks oxygen atom
RNA
Uracil, ribose
Carbohydrates
contains C, H, O, main energy source, monomer is monosaccharide
Lipids
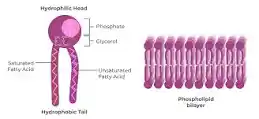
made of long hydrocarbon chains with occasional oxygen atom, hydrophobic
Proteins
enzymes, structural molecules, storage, transport, defense, communication, movement, hormones
Nucleic acids
store and transmit genetic information, C, H, O, N, P, DNA and RNA, monomer of nucleic acids
What kind of macromolecule is glycogen? What is its function in humans, where is it found?
carbohydrates (polysaccharides), It is an energy source found in the liver and skeletal muscle
Components of a nucleotide
nitrogen base (DNA and RNA), Five-carbon sugar (ribose and deoxyribose), phosphate group (DNA double helix)
What is the role of a buffer?
A substance that minimizes a change in pH function by accepting H+ in excess
Polar
electrons shared, not equally
Non polar
electrons are shared equally
What is a trace element?
required only in minute quantities
Roles of hydrogen bonds
easily broken/ reformed, holds water molecules together, protein folding, connects strands of DNA double helix
Carbohydrates

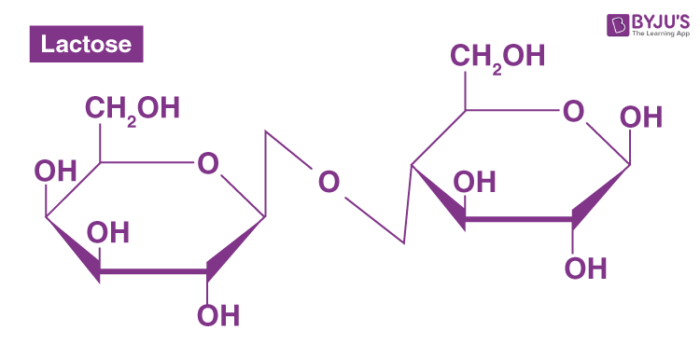
Disaccharide
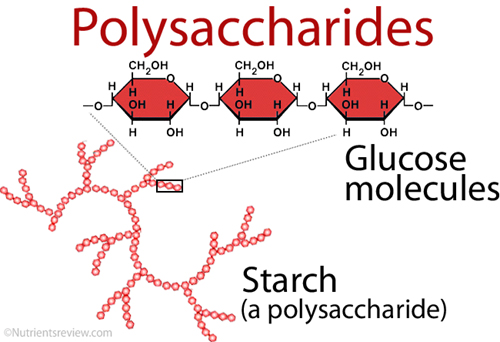
Polysaccharides
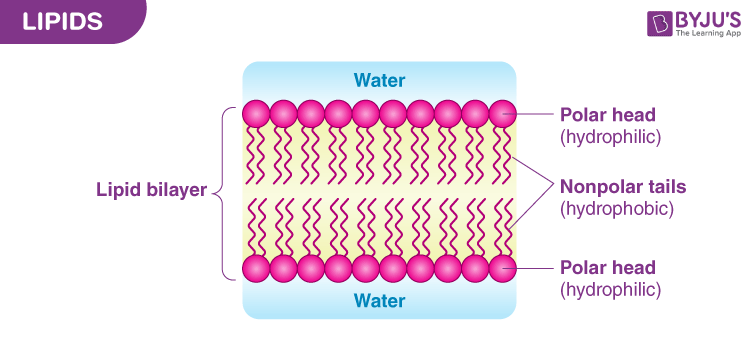
Lipids
Fats
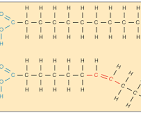
Saturated and Unsaturated
Phospholipids
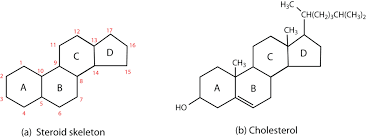
Steroids