Biology 30 Chapter 16
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Which cells mitosis produce?
Mitosis: Cell division to produce somatic cells
Mitosis
PMAT ( Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase)
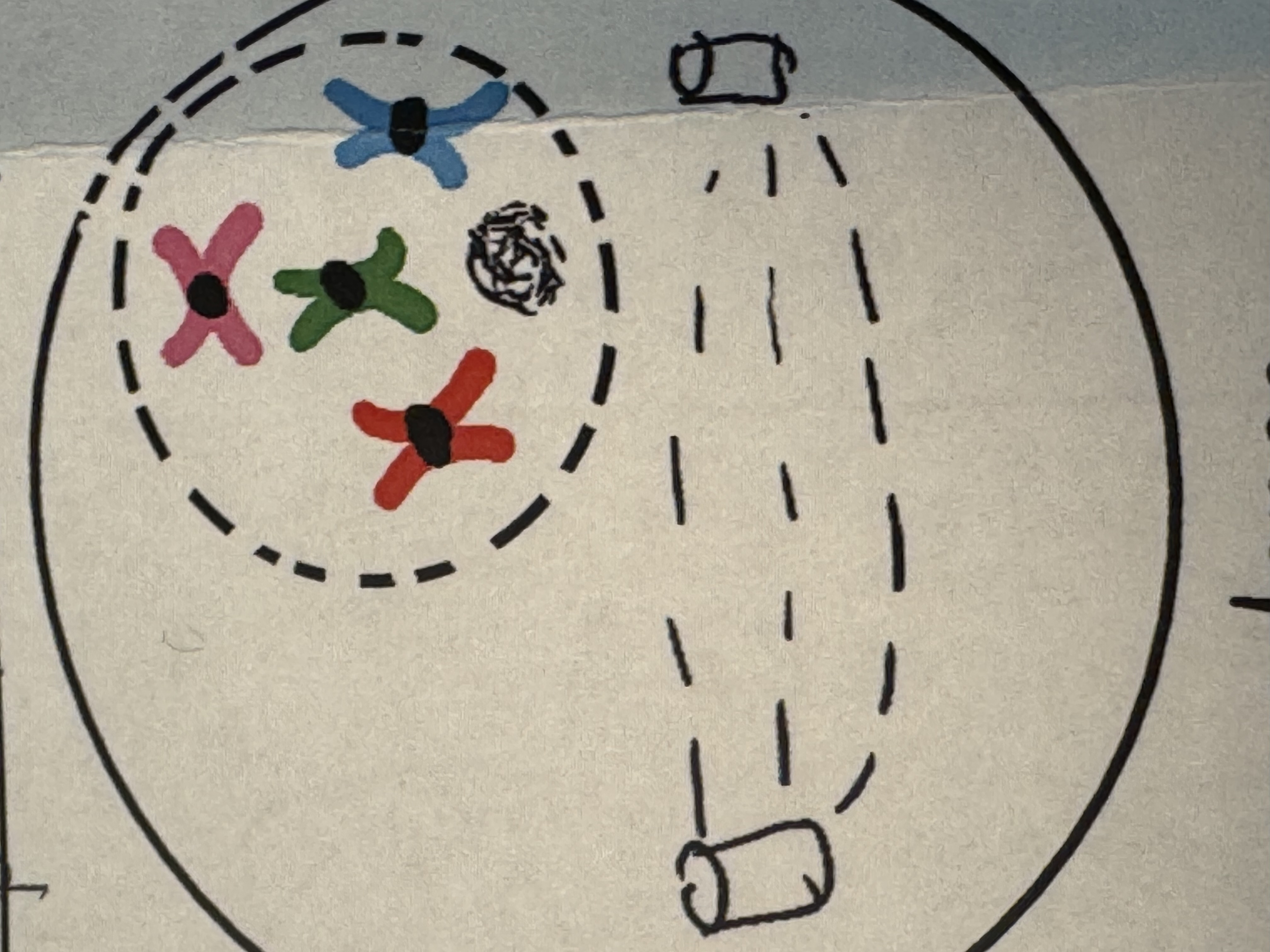
Prophase
1) Chromosome condense
2) Nucleus and nucleolus break down
3) Centrioles migrate to poles
4) Spindle fibers start to form
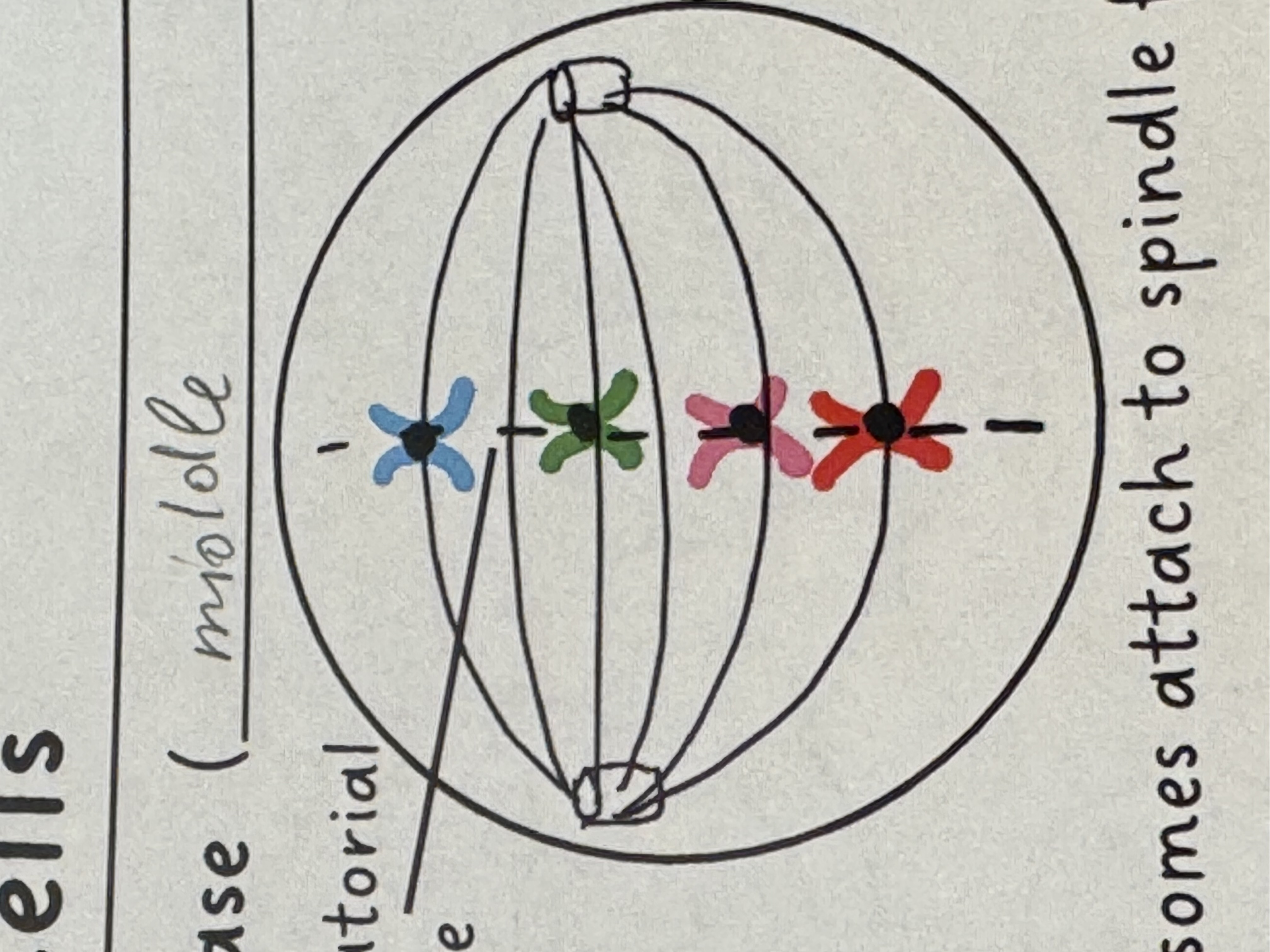
Metaphase
5) Chromosomes attach to spindle fibers at their centromere
6) Replicated chromosomes line up on one top of another along the metaphase plate
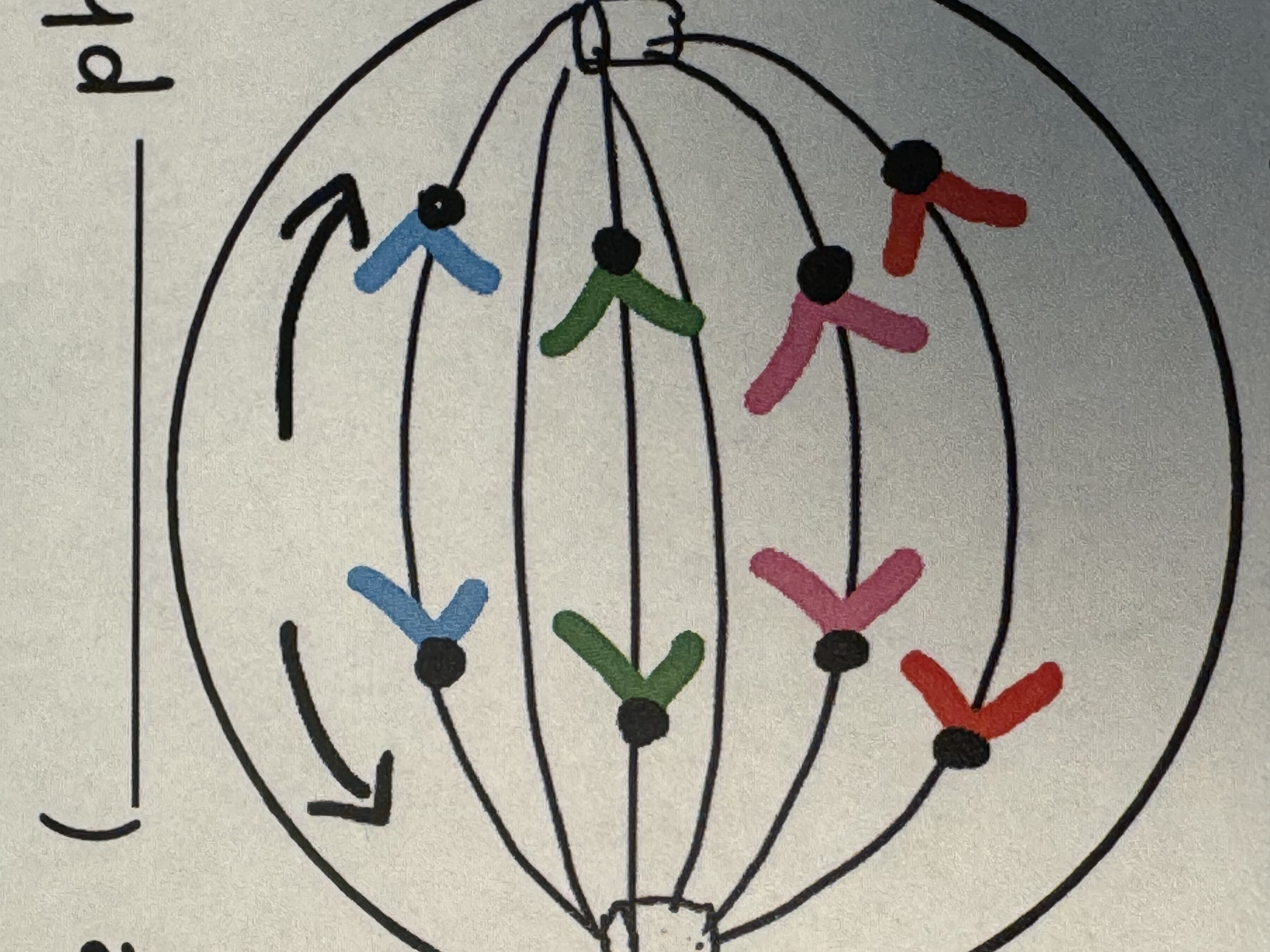
Anaphase
7) Centromere divide in half
8) Unreplicated chromosomes move to opposite poles
Telophase
9) Nucleus and nucleolus reappear at each pole
10) Spindle fibers disappear
11) Division of cytoplasm begins
Cytokinesis
After MITOSIS
Divides the parent cell into two daughter cell
Animal cells = a cleavage furrow
Plant cells = a cell plate forms
Mitosis
total cells created 2 in mitosis
Meiosis
total cell created 4 in meiosis
How chromosomes are sorted between daughters
Mitosis ( by sister chromatids)
Meiosis by homologous pair
Crossing over during meiosis 1 prophase
Cell cycle
A continuous sequence of cell growth and division; the life cycle of a cell
Chromatin
Long fibers that form chromosomes and contain DNA, non condensed form of genetic material that predominates for most of the cell cycle.
Diploid
Describing a cell that contains two pairs of every chromosome, designated as 2n; somatic cells. Diploid number in humans is 46 or 23 pairs.
Haploid
Unpaired chromosomes, (egg and sperm ( are haploid
n=23
Diploid 2n=46
Polyploid
They have sets of more that two homologous chromosomes,
3n triploid, octopod 8n
Mitosis
Making two identical daughter cells
Performed in all autosomes
Allows growth
Used for repair and replacement of cells
Uncontrolled, rapid cell division are known as cancer
Rather that spending much of their cell cycle as functioning tissue cells in interphase, cancerous cells move quickly from one ce division to the next.
Tumor
The result is a fast-growing mass of non-functional cells
Tetrad
A pair of homologous chromosomes is made up of four chromatids and is called a tetrad