bio 12 unit 1
5.0(2)
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/50
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
1
New cards
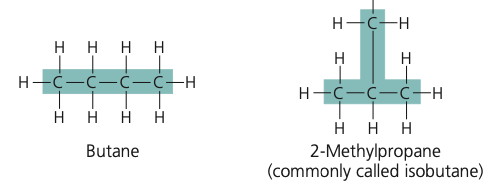
structural isomer
2
New cards
structural isomer
3
New cards
cis-trans isomer
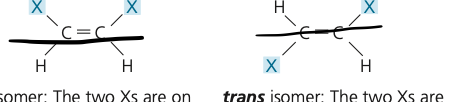
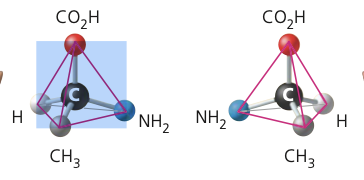
4
New cards
enantiomer
5
New cards
hydroxyl group

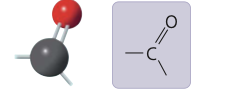
6
New cards
carbonyl group
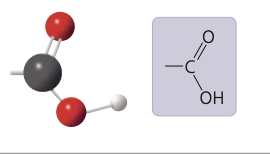
7
New cards
carboxyl group
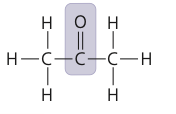
8
New cards
any of a class of organic compounds having a carbonyl group linked to a carbon atom in each of two hydrocarbon radicals
ketone
9
New cards
the chemical group -CHO
aldehyde group
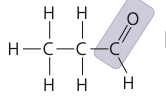
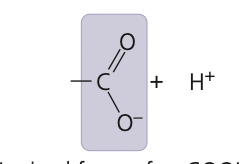
10
New cards
carboxyl group ionized
11
New cards
sulfhydryl group
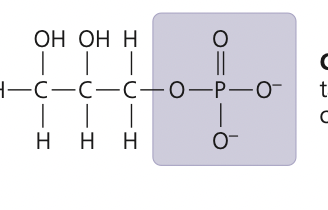
12
New cards
phosphate group
13
New cards
amino group
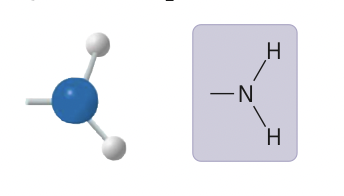
14
New cards
amino group ionized
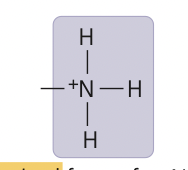
15
New cards
polymers resulting from the removal of water
dehydration
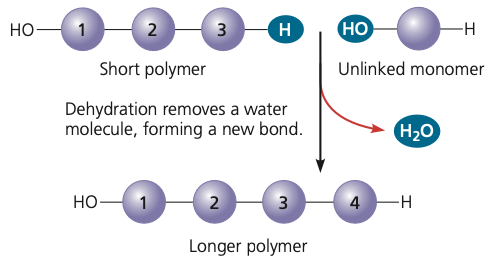
16
New cards
a chemical reaction in which water reacts with a compound to produce monomers
hydrolysis
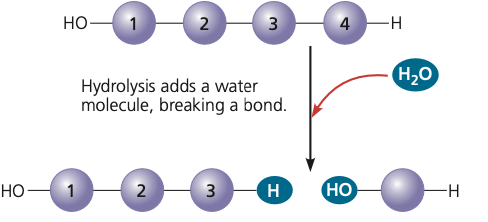
17
New cards
bonding carbon of one sugar to an oxygen that binds to another sugar
glycosidic linkage
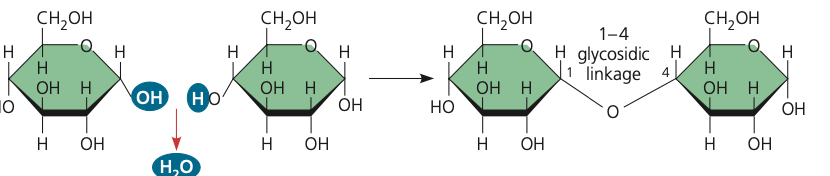
18
New cards
maltose
glucose+sucrose-> ? (draw)
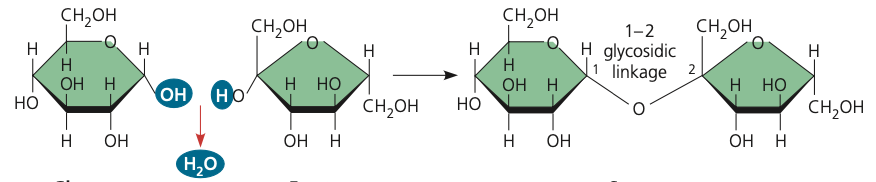
19
New cards
many OH (hydroxyl) groups and one carbonyl group
carbohydrate functional group
20
New cards
- simple sugars ending in "ose"
ex: ketose, aldose, fructose, glucose e.c.t
ex: ketose, aldose, fructose, glucose e.c.t
monosaccharide examples
21
New cards
CH2O
monosaccharide ratio
22
New cards
they are structural isomers
relationship between glucose and fructose
23
New cards
starch, cellulose, chitin, glycogen e.c.t
polysaccharide examples
24
New cards
extra glucose is DEHYDRATED and turned into polymer starch and stored in roots
how and where do plants store energy
25
New cards
food is turned into monomers to use, unsed glucose turns into glycogen and stored.
how do animals store excess carb?
26
New cards
hydrophobic due to non polar nature
lipids hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
27
New cards
- cushion and protect
- part of membrane
- hormolne regulators
- energy dense
- part of membrane
- hormolne regulators
- energy dense
what do lipids do
28
New cards
- long carbon skeleton
- carboxyl group
- saturated = single bonds
- unsaturated= double bonds
- carboxyl group
- saturated = single bonds
- unsaturated= double bonds
fatty acid (carboxylic acid) components
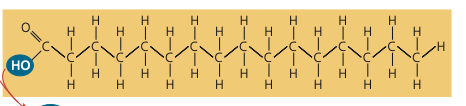
29
New cards
another name for fat
triacyglycerol draw
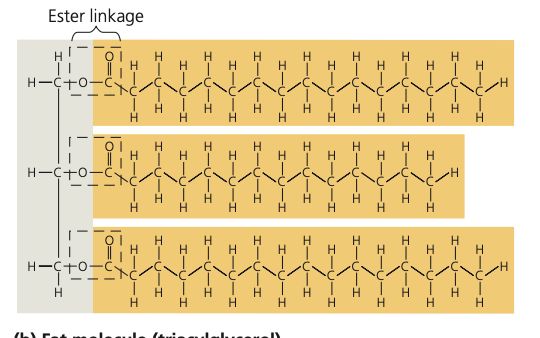
30
New cards
- 3 fatty acids and glyceride
fat monomers
31
New cards
- any of various compounds composed of fatty acids and phosphoric acid and a nitrogenous base
- has a phosphate group
- forms bilayer
- tail=non polar
- head= polar
- has a phosphate group
- forms bilayer
- tail=non polar
- head= polar
phospholipid
32
New cards
- regulators
- 4 carbon rings
- 4 carbon rings
steriods
33
New cards
- work as enzymems catalizing reactions
- transport things (hemoglobin oxygen)
- immune system
- cell structure
- muscles
- communication between cells
- transport things (hemoglobin oxygen)
- immune system
- cell structure
- muscles
- communication between cells
protein functions
34
New cards
- organic compounds containing an amino group and a carboxylic acid group
- monomer
- asymmetrical carbon
- monomer
- asymmetrical carbon
amino acid
35
New cards
the simplest amino acid found in proteins and the principal amino acid in sugar cane
glycine
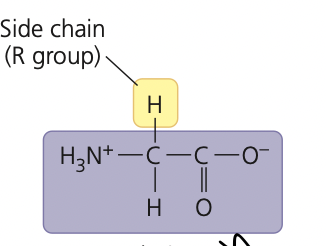
36
New cards
a crystalline amino acid that occurs in many proteins
alanine
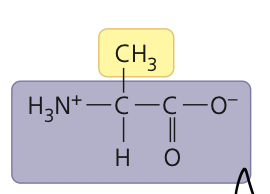
37
New cards
a sweetish crystalline amino acid involved in the synthesis by the body of cysteine
serine
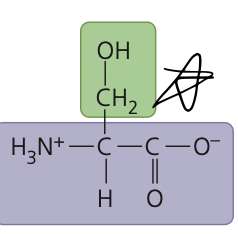
38
New cards
an amino acid containing sulfur that is found in most proteins; oxidizes on exposure to air to form cystine
cysteine
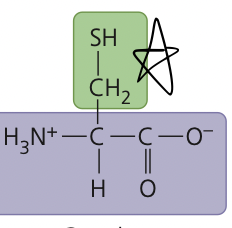
39
New cards
end of amino acid that has amino group
N terminus
40
New cards
end of amino acid with carboxyl group
c terminus
41
New cards
- order that amino acids appear on a chain
primary structure
42
New cards
- hydrogen bonds between parts of backbone
- creates pleated sheets or helix
- carboxyl groups attract to amino groups on diffrent parts of chain
- creates pleated sheets or helix
- carboxyl groups attract to amino groups on diffrent parts of chain
secondary structure
43
New cards
- attraction between the side chains
- SH side groups attract eachother to form disulfhyde bonds
- np groups attract to p groups
- SH side groups attract eachother to form disulfhyde bonds
- np groups attract to p groups
tertiary structure
44
New cards
- 2+ polypeptides joining and twisting together ex:hemoglobin
quaternary structure
45
New cards
glycerol draw
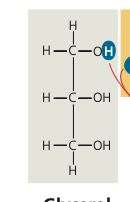
46
New cards
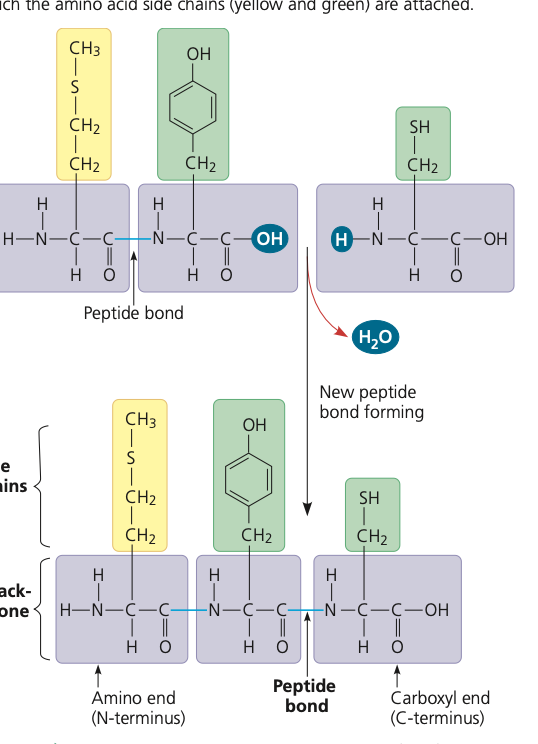
bond between amino acids
polypeptide bond draw + define
47
New cards
phosphodiester bond
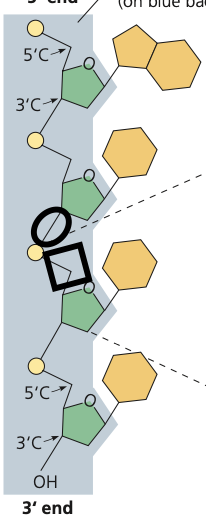
48
New cards
- adenine
- gaumine
- gaumine
purine name + draw
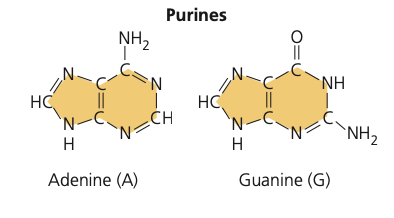
49
New cards
- urisil
- cytosine
- tymine
- cytosine
- tymine
pyrimidine
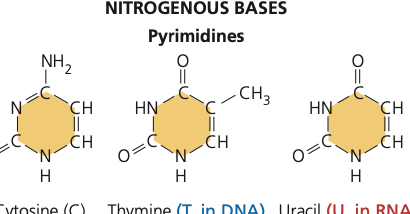
50
New cards
a sugar that is a constituent of nucleic acids
deoxyribose
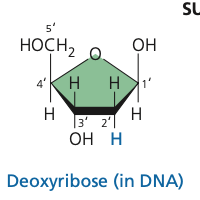
51
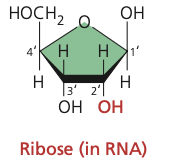
New cards
ribose