6. the senses: how companion animals can enjoy their surroundings
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
eye structure
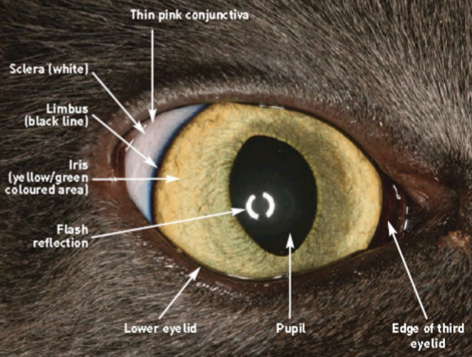
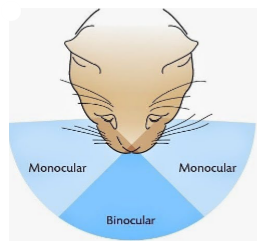
“monocular vision” definition
field of view of a singular eye
blind spot in the rear
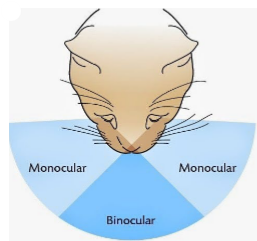
“binocular vision” definition
field of view of both eyes, overlap
depth perception
cat eyes
vertical slit pupils
gauges distance the best for nocturnal animals
near sighted
blurrier vision
better at catching movements & shadows
dogs & cats have more _____ which gives them better night vision
rods
“tapetum lucidum” definition
the reflective layer of the eye
magnifies incoming light
green/blue glint when light is shining on the eyes
“nictitating membrane” definition
the third eyelid
found under the other eyelids on the inside corner closest to the nose
extends up when needed to protect the eye
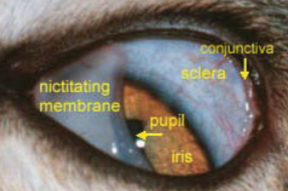
the _____ _____ and the _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ _____ are the collective preocular tear film
lacrimal glands
superficial tear gland of the nictitating membrane
tear film layers
outer lipid
middle aqueous layer
deep layer
“tarsal (meibomian) gland” definition
waxy substance that prevents the lacrimal secretions from flowing out of the face
“meibomian adenoma” definition
a tumor that grows on the eyelid typically caused by an overgrowth of cells in the meibomian gland
“cherry eye” definition
prolapse of the third eyelid
gland within the third eyelid pops out
gland usually anchored by a fibrous attachment but certain breeds, the attachment is weal
tear drainage system
2 lacrimal puncta
2 canaliculi
lacrimal sac
lacrimal duct: empty tears within nasal
“keratoconjunctivitis sicca (KCS)” definition
tear deficiency
persistent inflammation of the conjunctiva & corneal ulceration & scarring
“retina” definition
houses photoreceptors
rods & cones
area centralis: most sensitive area, tightly packed photoreceptors to make photos sharp
do dogs need prescription glasses/lens/goggles?
yes
contacts can be used as a bandage for dogs with slow-healing ulcers
goggles can be used to protect the eyes from injuries or the sun
dog cone types
yellow
blue
cat cone types
yellow/green
blue
ability to distinguish color is _____ pronounced in dogs & cats
less
“lenticular (nuclear) sclerosis” definition
cloudiness of the lens of the eye resulting from aging
older components of lens are compressed as new components form
affects lens’ ability to bend & allow light through
usually does not cause blindness
“cataract” defintion
cloudiness of lens from a significant change in the structure & integrity of proteins and/or other components making up the lens
result in opacification of lens preventing light from entering
various levels of blindness
“strabismus” definition
abnormal positioning/direction of eye
one muscle in one side of the eye may be stronger than the other causing eyeball to deviation from normal direction
cross-eyed: both eyes pointed towards the nose
divergent strabismus: both eyes deviate away from the nose
“albinism” definition
more fibers of the optic nerve crosses than normal
affects depth perception
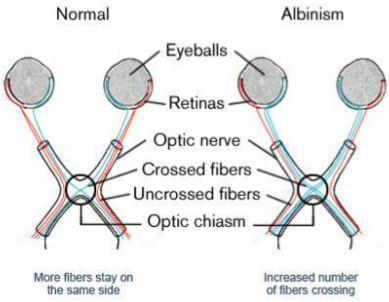
“creel theory” definition
lack of melanin pigment
triggers a switch resulting in the conventional genetic instructions not to be completed
abnormal vision system
“feline taurine deficiency” definition
a lack of the amino acid, taurine, that can not be synthetized in the body
can cause blindness & heart failure
caused by disease or diet
outer ear: pinna
captures sound waves & funnels them through ear canal to eardrum
mobile in cats
outer ear: ear canal
creates a funnel to carry sound to the eardrum
the middle ear
eardrum
hammer
anvil
stirrup
two muscles
tenor timpani M & stapedius M
oval window
eustachian tube: connects middle ear to back of nose allowing air through
inner ear: cochlea
organ of hearing
inner ear: vestibular system
organ of balance
filled with fluid to maintain balance
highly developed in cats
deafness
congenital/hereditary
associated with blue eyes & white pigmentation
acquired
toxin, trauma, drugs, etc.
sensorineural: loss of cochlear nerve cells
conductive: obstruction of sound reaching cochlea
“vestibular syndrome” definition
loss of balance, head tilt, rapid eye movement, & motion sickness
tilt always towards diseased side
peripheral: affects inner ear
central: affects nerves & brain
“righting reflex” definition
augmented by unusually flexible backbone & absence of collar bone
allows full upper body rotation so cat can land on it’s feet
cat olifaction
smell less developed than dogs
sniffing mechanism: rapid, short inhalations/exhalations
sniffing traps air in bony structure to allow molecules to interact with scent receptors
vomeronasal organ: essential in detection of pheromones
dog olifaction
acute sense of smell
can detect odors at extremely low levels
odor molecules dissolve in moisture on inside of nose
catnip response
most cats excited by catnip smell but not all
reaction is inherited
not addictive
no saliva, no _____
taste
chemicals from food must dissolve in saliva to be detected by receptors on tastebuds
“filiform papillae” definition
do not have taste buds
are instead used for grooming
dog taste
more taste buds than cats
4 classifications: sweet, sour, salty, & bitter
no affinity for salt
liking for sweet flavors like fruit
“strawberry furanone”
organic compound used in flavors derived from strawberries & other fruits
dislike bitter tastes
dogs & cats have special taste buds for _____ at the _____ of the tongue where it curls
water
tip
“umami” definition
the savory based taste
red meat, eggs, parm cheese, tuna, soy sauce
sense of touch
skin
whiskers
touch receptors
whiskers functions
help animal sense environment
judge size of opening before crawling through
sense objects without touching them
helps cats see at night
pattern of whiskers unique to every cat
can help show emotion & interest