Renal Physiology: Glomerular Filtration and Water Excretion
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
Glomerulus
Specialized structure for blood filtration.
Afferent Arteriole
Larger diameter vessel supplying glomerulus.
Efferent Arteriole
Drains blood from the glomerulus.
Peritubular Capillaries
Arise from efferent arterioles, drain into venules.
Vasa Recta
Capillaries associated with the nephron loop.
Filtration Membrane
Barrier preventing large molecules from passing.
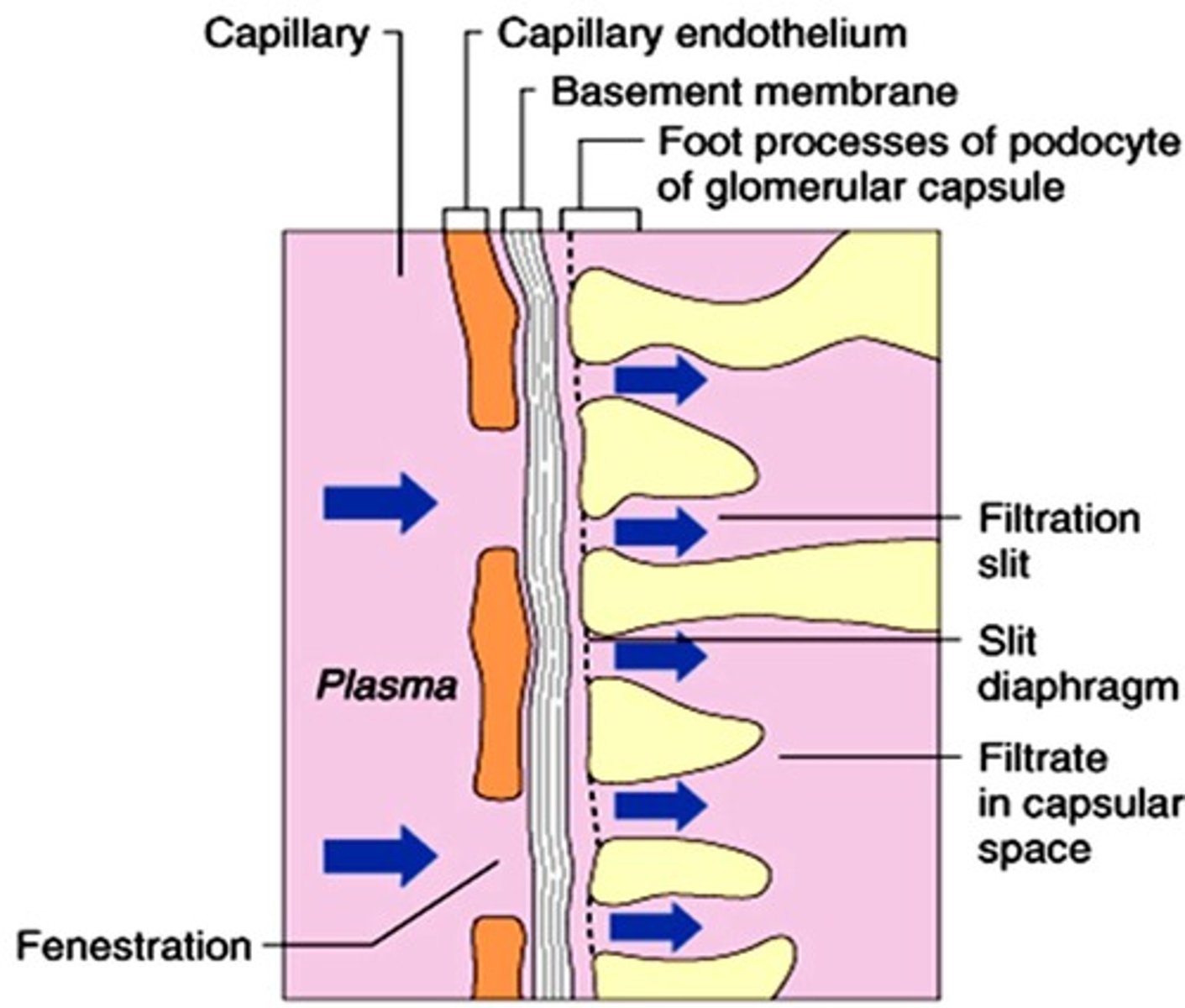
Net Filtration Pressure (NFP)
Pressure driving fluid from glomerulus to capsule.
HPgc
Glomerular hydrostatic pressure, 55 mm Hg.
OPgc
Osmotic pressure in glomerulus, 30 mm Hg.
HPcs
Capsular hydrostatic pressure, 15 mm Hg.
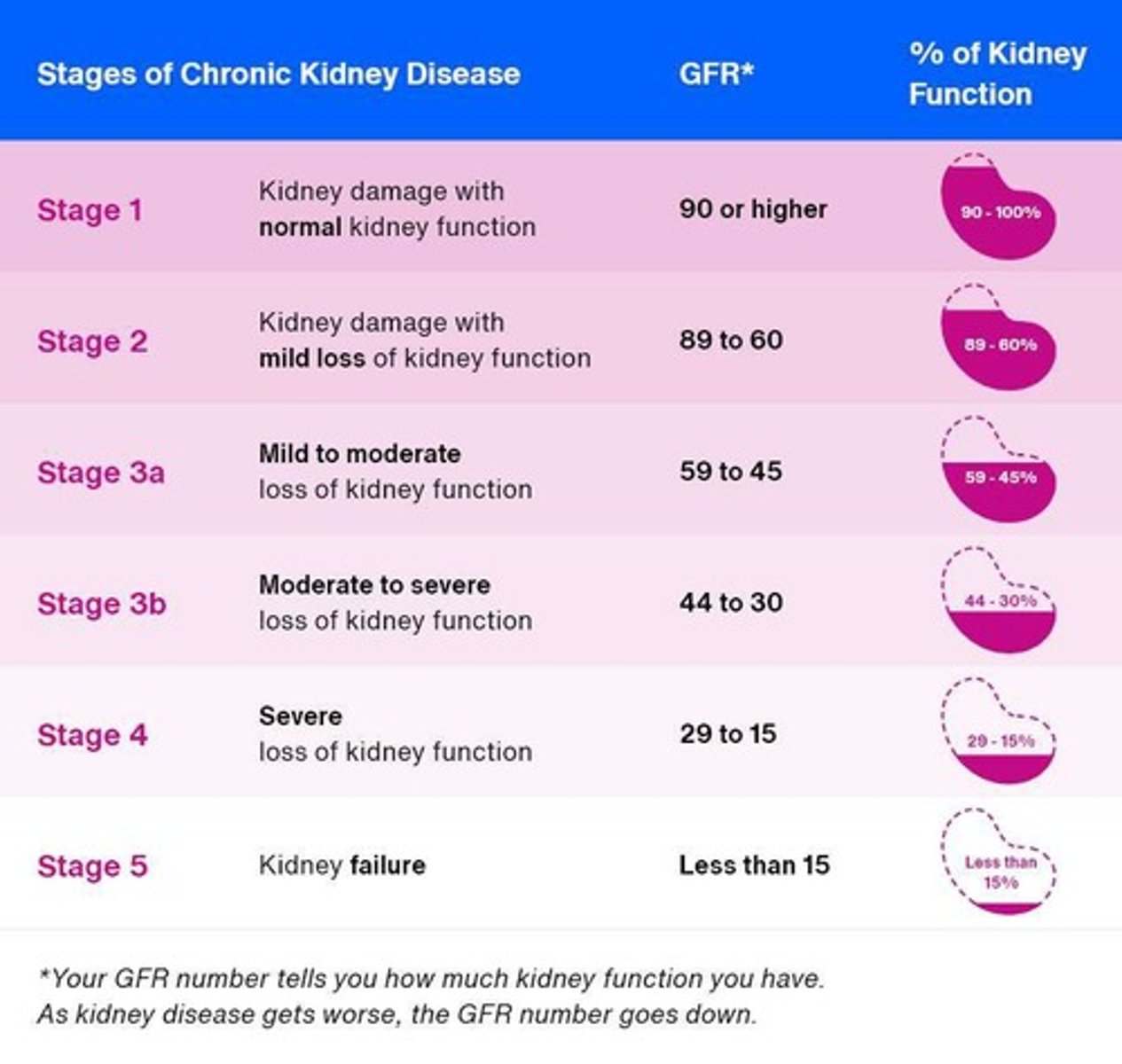
GFR
Glomerular filtration rate, volume filtered per time.
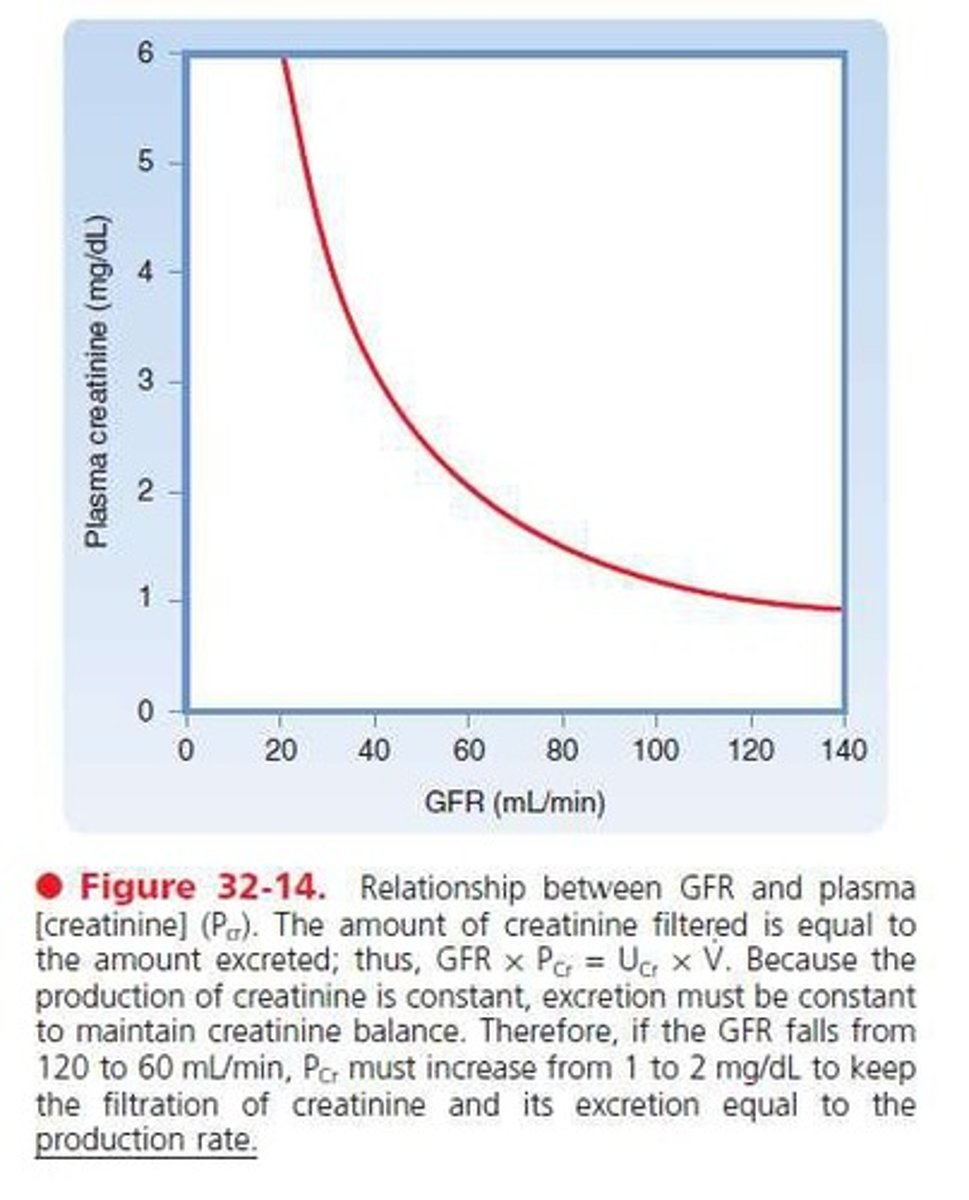
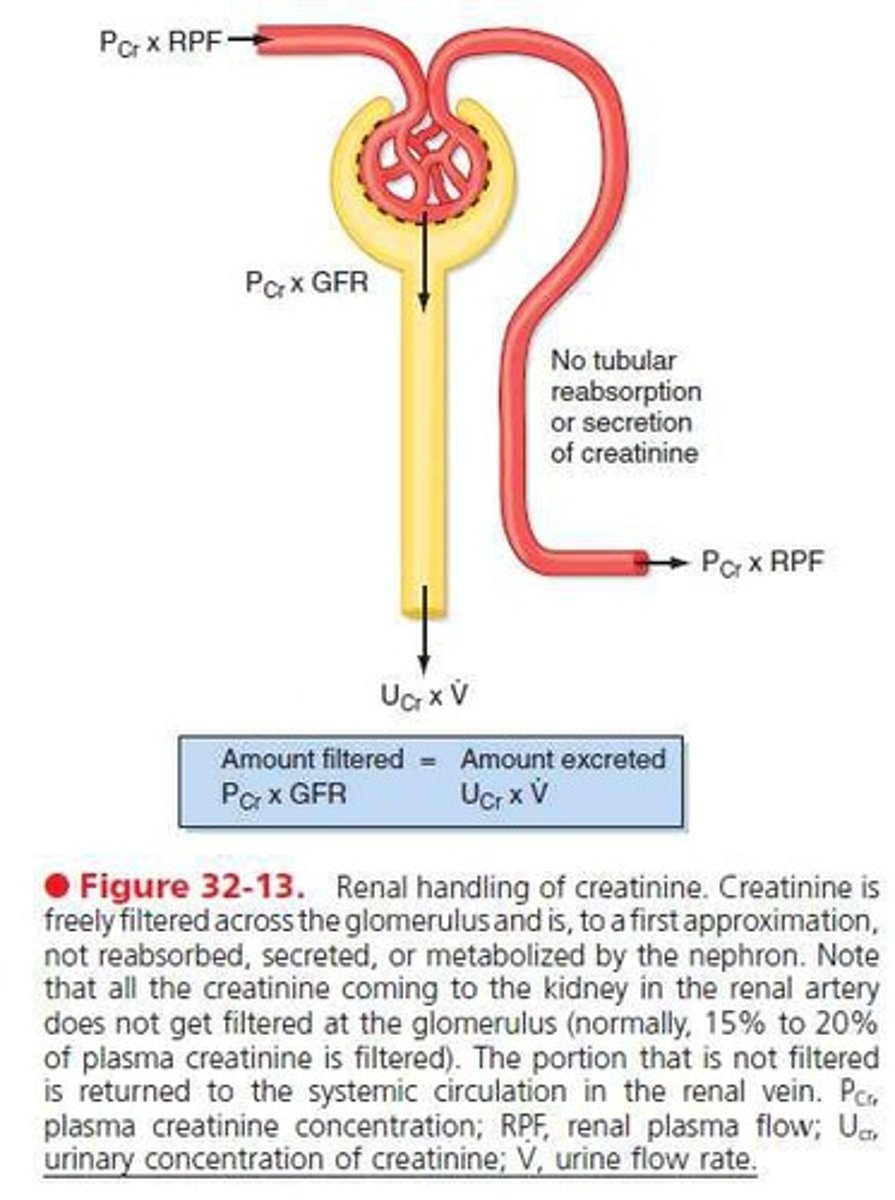
Plasma Creatinine
Used to estimate GFR in clinical settings.
Plasma Urea Clearance
Measurement of urea excretion efficiency.
Tubular Reabsorption
Returns 99% of filtrate back to blood.
Tubular Secretion
Moves substances from blood to filtrate.
Clearance
Volume of plasma cleared of a substance.
Filtration Fraction (FF)
Ratio of GFR to renal plasma flow.
Myogenic Mechanism
Intrinsic response regulating renal blood flow.
Juxtaglomerular Feedback
Regulates GFR through feedback mechanisms.
Sympathetic Mechanism
Extrinsic control affecting GFR and blood pressure.
Renin-Angiotensin Mechanism
Hormonal response maintaining blood pressure.
Urine Flow Rate (V)
Rate of urine production, measured in ml/min.
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
Rate of plasma filtered by kidneys per minute.
Plasma Creatinine Concentration
Creatinine level in plasma, measured in µM/l.
Urine Creatinine Concentration
Creatinine level in urine, measured in µM/l.
Urine Flow Rate
Volume of urine produced per minute, in ml/min.
Creatinine Clearance (CCr)
Volume of plasma cleared of creatinine per minute.
Cockcroft-Gault Equation
Formula to estimate creatinine clearance based on age, weight.
Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD)
Equation to estimate GFR using serum creatinine and age.
Plasma Urea Clearance
Measurement of urea excretion relative to plasma concentration.
Blood Urea Nitrogen (BUN)
Measure of urea in blood, influenced by GFR.
Renal Blood Flow Proportions
Distribution of blood flow in renal cortex and medulla.
Filtered Load
Amount of substance filtered by kidneys per minute.
Secretion
Process of substances being added to urine from blood.
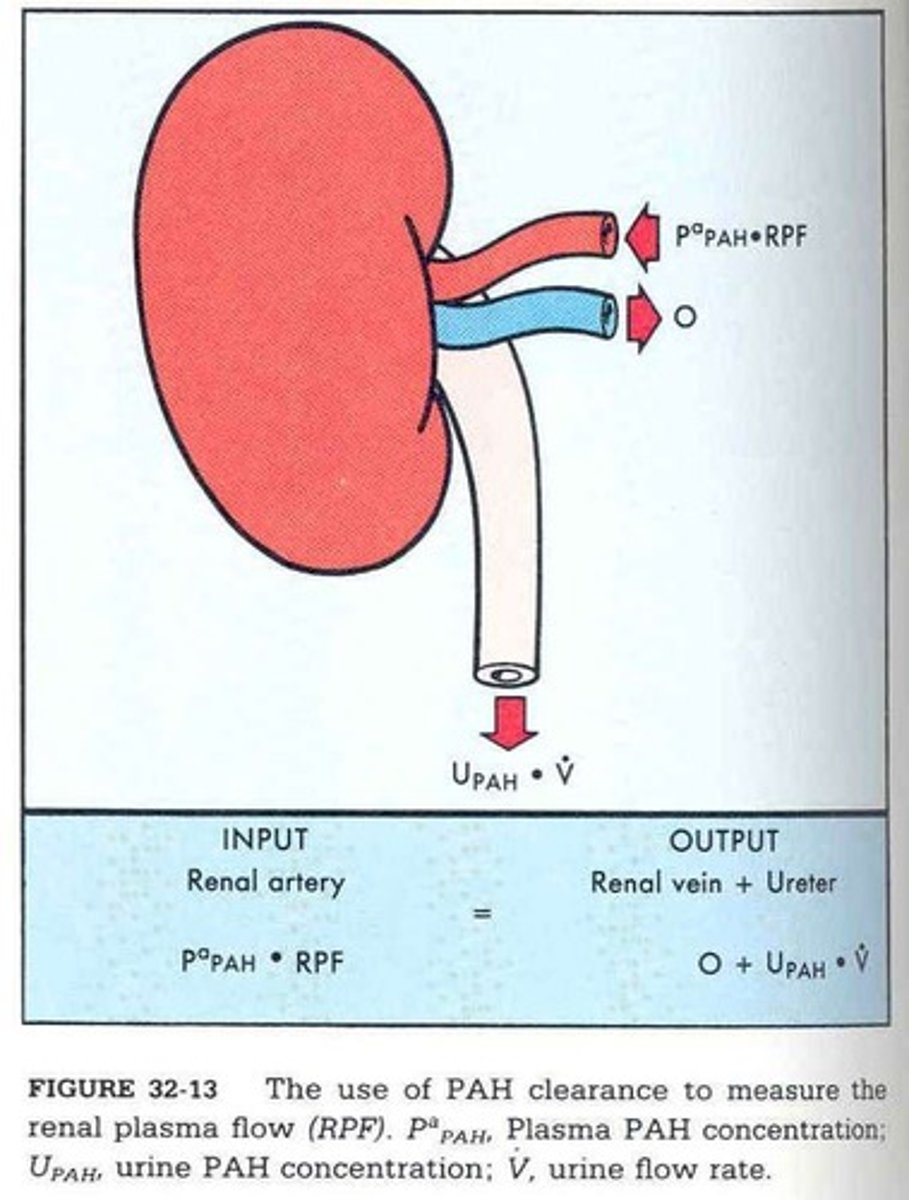
PAH Clearance
Measurement of para-aminohippuric acid clearance from plasma.
Plasma Clearance
Volume of plasma cleared of a substance over time.
Plasma Clearance vs GFR
Comparison of clearance rates to assess kidney function.
Urine Concentration Ratio
Comparison of urine to plasma concentration for substances.
Serum Creatinine (SCr)
Creatinine level in serum, measured in mg/dL.
Age Factor in GFR
Age affects GFR calculations in Cockcroft-Gault equation.
Weight Factor in GFR
Weight is used in GFR calculations for accuracy.
Creatinine Excretion
Amount of creatinine excreted in urine per time.
Impact of GFR Decrease
Increased plasma creatinine indicates reduced GFR.
Juxtaglomerular Apparatus
Regulates renal function at nephron junction.
JG Cells
Granular smooth muscle cells; secrete renin.
Macula Densa Cells
Chemoreceptors monitoring filtrate osmolarity.
Filtrate Formation
Process of producing urine from blood.
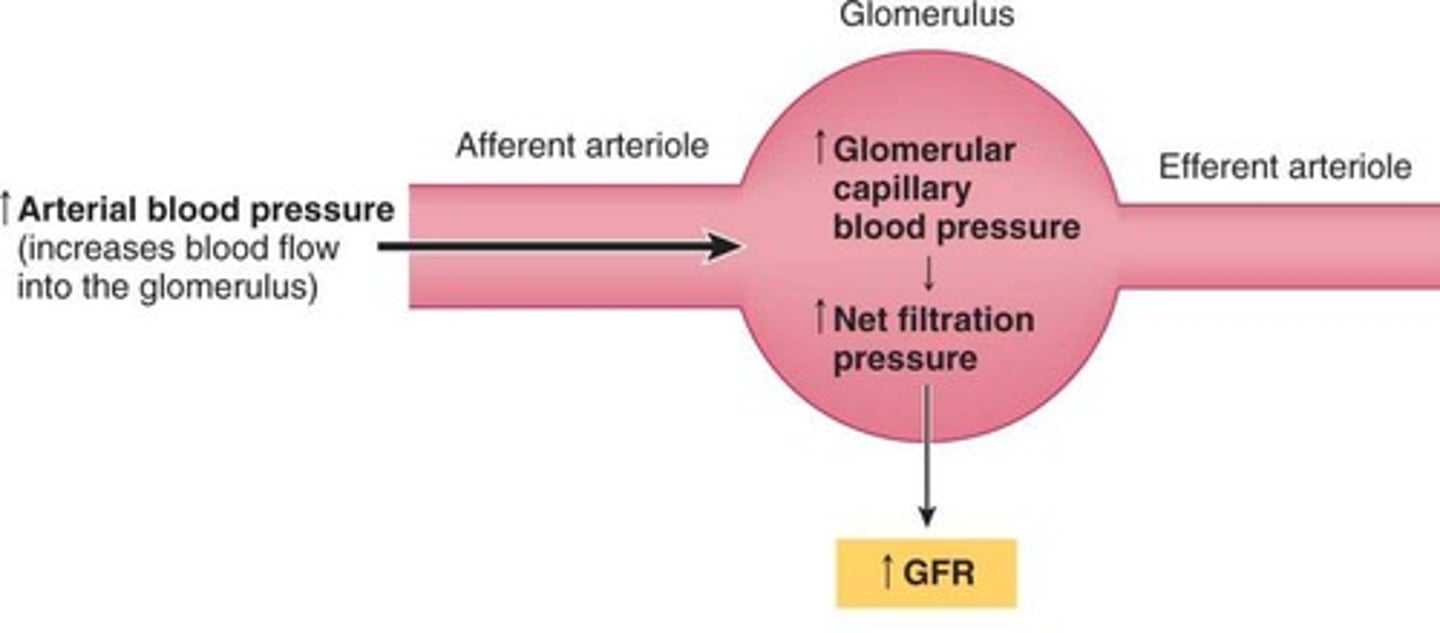
Systemic Blood Pressure
Overall pressure in the circulatory system.
Intrinsic Mechanisms
Body's internal controls for renal function.
Myogenic Mechanism
Smooth muscle contraction in response to stretch.
Tubuloglomerular Feedback
Feedback mechanism regulating GFR via NaCl.
Renal Autoregulation
Maintains constant GFR despite blood pressure changes.
Afferent Arterioles
Blood vessels supplying blood to glomeruli.
Efferent Arterioles
Blood vessels draining blood from glomeruli.
Hypovolemic Shock
Severe drop in blood volume affecting organs.
Vasodilation
Widening of blood vessels to increase flow.
Vasoconstriction
Narrowing of blood vessels to reduce flow.
Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR)
Rate of filtrate formation in kidneys.
Renin
Hormone regulating blood pressure and fluid balance.
Angiotensin II
Vasoconstrictor increasing blood pressure and volume.
Aldosterone
Hormone increasing sodium reabsorption in kidneys.
Neural Controls
Sympathetic nervous system response during stress.
Norepinephrine
Neurotransmitter causing vasoconstriction and increased BP.
Extrinsic Mechanisms
External factors influencing renal function and BP.
Na-K-ATPase
Enzyme regulating sodium and potassium balance.
ATP
Energy molecule; influences vascular responses.
CLEARANCE
Volume of plasma completely cleared of substances.
GFR
Glomerular filtration rate, measured in ml/min.
Creatinine
Muscle-produced substance used to estimate GFR.
Plasma Creatinine
Concentration of creatinine in plasma, mg/ml.
Urine Creatinine
Concentration of creatinine in urine, mg/ml.
Urine Flow Rate
Rate of urine production, measured in ml/min.
GFR Equation
GFR = (U x V) / P.
Filtered Load
Amount of substance filtered from plasma to urine.
Renal Blood Flow Proportions
Cortex: 93%, Outer medulla: 6.3%, Inner medulla: 0.7%.
PPAH
Para-aminohippuric acid, used to measure renal plasma flow.
RPF
Renal plasma flow, volume of plasma passing through kidneys.
Secretion
Process of substances moving from blood to urine.
ADH
Antidiuretic hormone regulating water retention.
Counter-current Multiplier
Mechanism concentrating urine in the kidney.
Vasa Recta
Blood vessels maintaining osmotic gradient in kidneys.
Hyperosmolality
Higher concentration of solutes in a solution.
Hypoosmolality
Lower concentration of solutes in a solution.
Juxtamedullary Nephrons
15% of nephrons, involved in urine concentration.
Cortical Nephrons
85% of nephrons, primarily located in cortex.
Antidiuresis
Conservation of water, reducing urine output.
Water Diuresis
Increased urine output due to excess water intake.
Plasma Osmolality
Concentration of solutes in plasma, affects ADH.
Nephron Loop
Structure involved in urine concentration processes.
Juxtamedullary Nephrons
Nephrons with long loops creating osmotic gradient.
Countercurrent Mechanism
Fluid flows oppositely in adjacent nephron segments.
Countercurrent Multiplier
Filtrate interaction in nephron loops enhancing concentration.
Countercurrent Exchanger
Blood flow in vasa recta maintaining osmotic balance.
Osmotic Gradient
Variation from 300 mOsm to 1200 mOsm.
Descending Limb
Permeable to water, concentrates filtrate osmolality.
Ascending Limb
Impermeable to water, reabsorbs Na+ and Cl-.
Filtrate Osmolality
Increases to ~1200 mOsm in descending limb.
Filtrate Dilution
Decreases to 100 mOsm in ascending limb.
Hyperosmotic Fluid
Interstitial fluid with higher solute concentration.
Active Transport
Energy-dependent process moving solutes against gradient.