AP Bio Unit 1: Chp 3: Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life (Nucleic Acids)
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Nucleic acids
2 types; Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) and Ribonucleic Acid (RNA)
DNA
Provides directions for its own replication , directs synthesis of messenger RNA (mRNA) and through mRNA controls protein synthesis
Nucleotides
Monomer of nucleic acids; consists of a nitrogenous base, pentose sugar, and one or more phosphate groups; Phosphate + Sugar + Nitrogenous Base
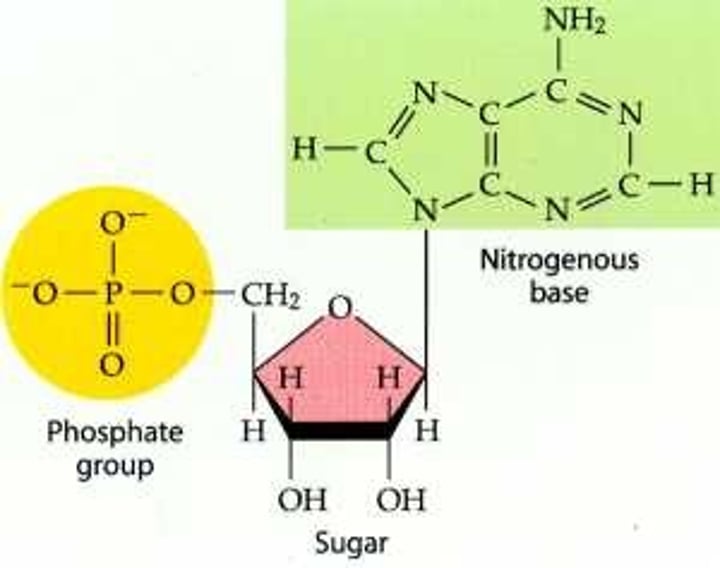
Nitrogenous bases
Contain 1 or 2 rings that include nitrogen atoms; Cytosine (C) pairs with Guanine (G), Adenine (A) pairs with Thymine (T) in DNA and Adenine pairs with Uracil (U) in RNA
Pyrimidines
(Single ring): Cytosine, Thymine, Uracil
Purines
(Two rings): Adenine, Guanine
Deoxyribose
The sugar in DNA (6 carbon sugar)
Ribose
The sugar in RNA (5 carbon sugar)
RNA molecules are
Single polypeptide chains (single stranded)
DNA double helix
2 backbones run in opposite 5' to 3' directions from each other, referred to as antiparallel
Base pairs (C,G,A,T,U) are joined by
hydrogen bonding