Optics Science review
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
1
New cards
reflection
light hitting something and the rays ‘bouncing’ reflecting back to our eyes
2
New cards
What are the two important parts of glass? What is their purpose?
light rays pass through the front transparent glass and then hit the reflection layer (silver/aluminum) behind it, causing the rays to bounce back to our eyes (causes us to see the reflection)
3
New cards
Light Ray
electromagnetic waves - carry energy / travels
4
New cards
explain how light rays travel and transferrs
electromagnetic waves - carry energy / travels through a vaccum
light energy transferred through radiation
light energy transferred through radiation
5
New cards
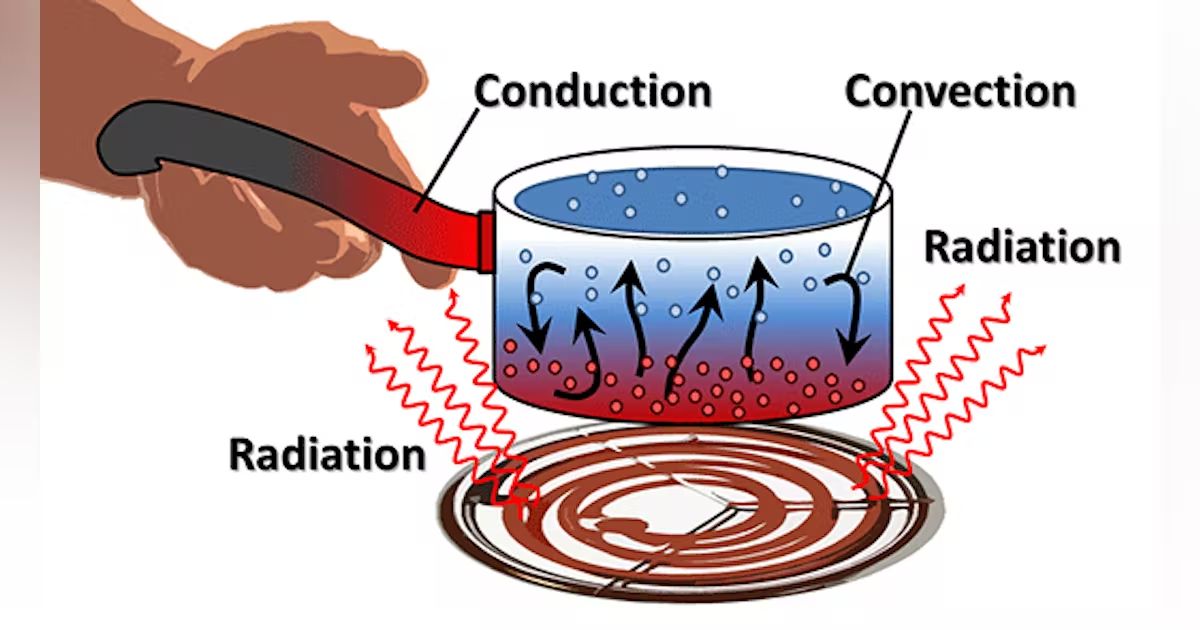
(transfer of heat) what is the difference between conduction and convection? give examples
conduction: direct contact with solids - transfer between adjacent molecules
ex. heating a pan on a stove
convection: movement of a fluid when heated fluid is caused to move away from heat source - carrying energy happens because of density (liquid heated > rises >cools > falls)
ex. lava lamps, burning paper, cooking beans in liquid,
ex. heating a pan on a stove
convection: movement of a fluid when heated fluid is caused to move away from heat source - carrying energy happens because of density (liquid heated > rises >cools > falls)
ex. lava lamps, burning paper, cooking beans in liquid,
6
New cards
(transfer of heat) what is radiation?
no physical contact - energy coming off of a source - travels through space at speed of light
ex. heating hands near a fire
ex. heating hands near a fire
7
New cards
types of light emissions
Luminous: an object that emits/produces its own light (eg. sun)
Non-luminous: an object that does not produce its own light and is visible due to reflected light (eg. a tree)
Non-luminous: an object that does not produce its own light and is visible due to reflected light (eg. a tree)
8
New cards
Geometric Optics
light rays to determine how light behaves when hitting objects
9
New cards
give an example of transparent, translucent, and opaque
transparent: air, water, clear glass
translucent: thin paper, vegetable oil
opaque: wood, concrete, floors
translucent: thin paper, vegetable oil
opaque: wood, concrete, floors
10
New cards
(model of light)
What are the 2 rays and line? Define all of them
What are the 2 rays and line? Define all of them
**Normal:** line __perpendicular__ to where ray of light meets
**Incident ray (ray coming in):** ray traveling from __source to surface__
**reflected ray (ray bouncing off)**: begins at point where __incident ray + normal__ meets
**Incident ray (ray coming in):** ray traveling from __source to surface__
**reflected ray (ray bouncing off)**: begins at point where __incident ray + normal__ meets
11
New cards
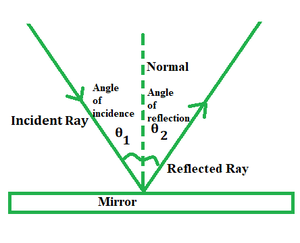
(model of light)
What are the two angles? Define all of them
What are the two angles? Define all of them
angle of **incidence**: between normal and __incident__ ray
angle of **reflection**: between normal and __reflected__ ray
angle of **reflection**: between normal and __reflected__ ray
12
New cards
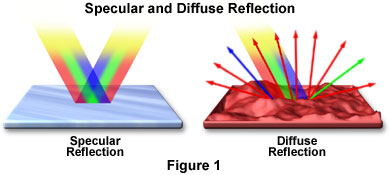
What is **specular** reaction and **diffuse** reaction?
**specular**: All angles of incident for light rays identical (light hits SMOOTH surface) - all angles of reflection identical
**diffuse**: When parallel incident rays are reflected off of an IRREGULAR surface - all angles of reflection different
**diffuse**: When parallel incident rays are reflected off of an IRREGULAR surface - all angles of reflection different
13
New cards
Name all the ways of production of light. what are the ones that are natural and the ones that are man-made?
**NATURAL**: Bioluinescence, trioluminescence
**MAN-MADE:** luminous, incondescene, electric discharge, phosphorescence, fluorescence, LED, Chemillumiescence,
**MAN-MADE:** luminous, incondescene, electric discharge, phosphorescence, fluorescence, LED, Chemillumiescence,
14
New cards
What are the two laws in Ray Model of Light?
* incident ray, reflection ray, normal to the surface of the mirror - lie on same plane
* angle of reflection = angle of incidence
* angle of reflection = angle of incidence
15
New cards
What are the similarities and differences of Phosphorus and Fluorescent light?
* both result from absorption of ultraviolet light
**Phosphorus** : - emission over period of time
**fluorescent** : - __IMMEDIETE__ emission of visible light
**Phosphorus** : - emission over period of time
**fluorescent** : - __IMMEDIETE__ emission of visible light
16
New cards
MEDIUM
physical substance through which energy is transferred (convection / conduction)
17
New cards
explain LANTA
* wave length - the distance waves travel within a period
\
from L → R: Lanta gets shorter
\
from L → R: Lanta gets shorter
18
New cards
what is electromagnetic spectrum?
light listed according to diff energy levels
19
New cards
what did maxwell predict about electromagnetic waves?
Electricity + magnesium work together - forms a chain travelling through space
the resulting electromagnetic waves doesn’t require a medium for transmission - travels speed of light
the resulting electromagnetic waves doesn’t require a medium for transmission - travels speed of light
20
New cards
Why is studying electromagnetic waves better than studying only visible light?
Most things in the universe aren’t in the electromagnetic range to be visible to us (radio waves, microwave, TV)
21
New cards
bioluminescence and triboluminescence - Give examples
**bioluminescence** : produced in living creatures
**triboluminescence** : light emitted because of friction with minerals / crystals
**triboluminescence** : light emitted because of friction with minerals / crystals
22
New cards
Does fluorescent brighteners in cleaners make clothes cleaner? explain
fluorescent brighteners in cleaners do not make clothes cleaner
* the brighteners absorb UV light, producing visible light and making clothes brighter
* the brighteners absorb UV light, producing visible light and making clothes brighter
23
New cards
What are some problems and dangers with fluorescent lights?
fluorescent light contains mercury (non-biodegradable)
24
New cards
Why are incandescent bulbs ineffective? Why are fluorescent bulbs better?
Incandescent bulbs are ineffective because they are constantly at a high temperature in order to produce light - it cannot be on for a long time or else it will overheat - can’t produce that much electricity / uses more energy + less reliable
25
New cards
Why are LED lights more effective than fluorescent bulbs?
LED lights use a majority of their energy focused on producing light (not much energy wasted and therefore can last longer) - unlike fluorescent bulbs, it has no mercury, so more biodegradable.
26
New cards
How do fluorescent lights work? What is inside it? What happens when it is turned on?
* both electric discharge and fluorescence
* tube filled with mercury vapour - emits UV light
* tube has fluorescent inner surface
\
when on:
* electric current causes mercury to emit UV light
* UV hits fluorescent inner surface - produces visible light
* tube filled with mercury vapour - emits UV light
* tube has fluorescent inner surface
\
when on:
* electric current causes mercury to emit UV light
* UV hits fluorescent inner surface - produces visible light
27
New cards
How do you make light using electric discharge?
passing an electric current through a gas → causes gas to GLOW
(ex. neon sign)
(ex. neon sign)
28
New cards
What si luminous and non-luminous light
29
New cards
Drawing Ray Diagrams for Concave Mirrors (diagrams)
(1): Locate the **Principal Axis** \n (2): Locate the Centre of Curvature "**C**" \n (3): Locate the **Vertex** \n (4): Locate the Focal Point/Focus (**F**) - half the distance of the radius, half way __between the Centre of Curvature and the Vertex.__ \n (5): Determine the Focal __length__ (**f**) - distance between the vertex and the focal point
30
New cards
what does SALT stand for (give examples)
S- size (small,large,same)
A- attitude (up,invert)
L- location (behind mirror, betwn C-F, etc)
T- type (virtual, real)
A- attitude (up,invert)
L- location (behind mirror, betwn C-F, etc)
T- type (virtual, real)
31
New cards
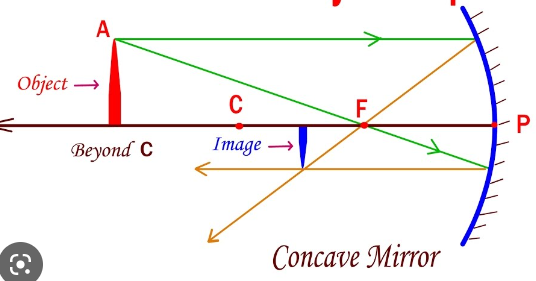
(Concave mirrors-SALT) How do you describe an object when it is
\-BEYOND C
\-BEYOND C
S- Smaller
A- Inverted
L - Between C & F
T - Real
A- Inverted
L - Between C & F
T - Real
32
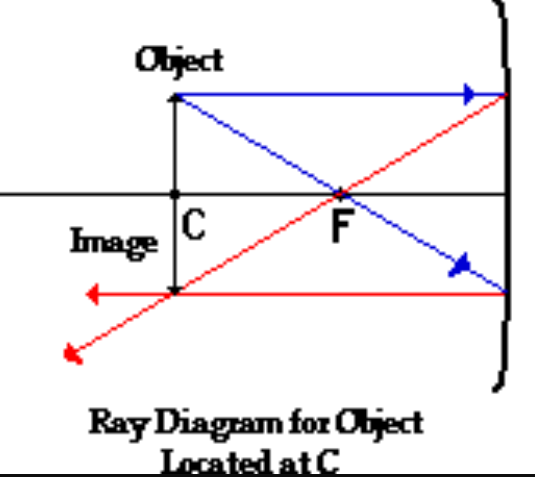
New cards
(Concave mirrors-SALT) How do you describe an object when it is
\-On C
\-On C
S- Same size
A- Inverted
L - on C
T - Real
A- Inverted
L - on C
T - Real
33
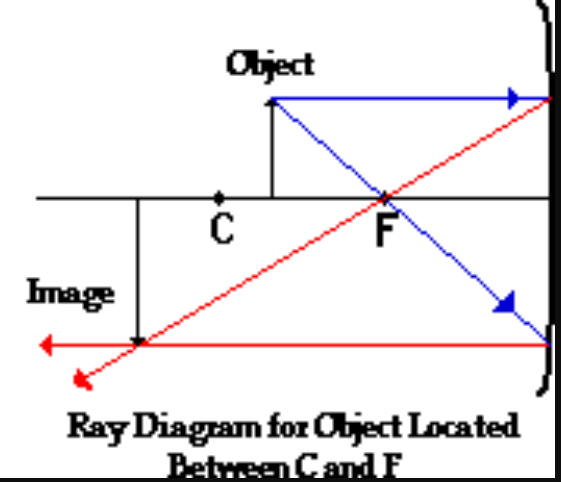
New cards
(Concave mirrors-SALT) How do you describe an object when it is
\-Between C and F
\-Between C and F
S- bigger
A- Inverted
L - beyond C
T - Real
A- Inverted
L - beyond C
T - Real
34
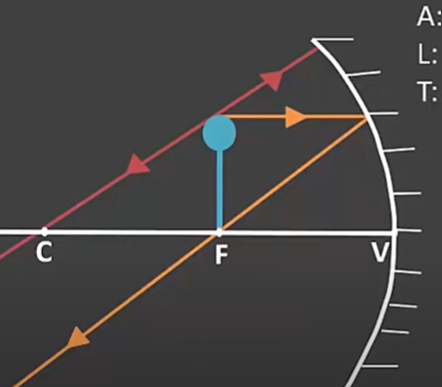
New cards
(Concave mirrors-SALT) How do you describe an object when it is
\-on the FOCAL POINT
\-on the FOCAL POINT
NO IMAGE
35
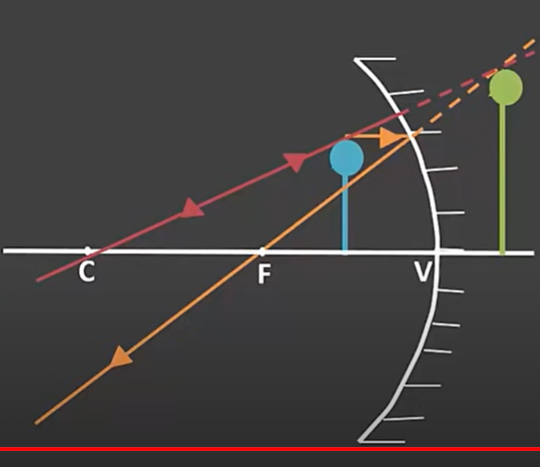
New cards
(Concave mirrors-SALT) How do you describe an object when it is
\-Object between F and MIRROR
\-Object between F and MIRROR
S- bigger
A- upright
L - behind the mirror
T - Virtual
A- upright
L - behind the mirror
T - Virtual
36
New cards
(concave) What happens with the light rays when the object is Beyond C, At C, or between C-F
1 - **incident rays** that travel perpendicular to the principal axis reflect off mirror - reflective rays go through **FOCUS**
2- __incident ray__ travel __through focus__ - __reflective rays__ parallel to principal axis
\-all real all inverted
2- __incident ray__ travel __through focus__ - __reflective rays__ parallel to principal axis
\-all real all inverted
37
New cards
(concave) What happens with the light rays when the object is AT **F**
NO IMG
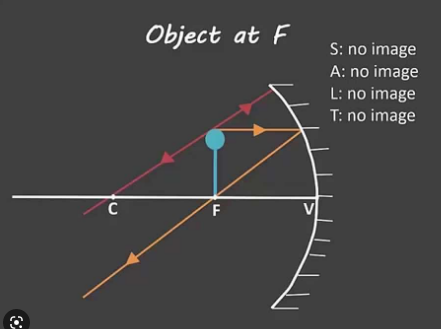
38
New cards
(concave) What happens with the light rays when the object is betwn F and Mirror
S- bigger
A- upright
L - behind the mirror
T - Virtual
A- upright
L - behind the mirror
T - Virtual
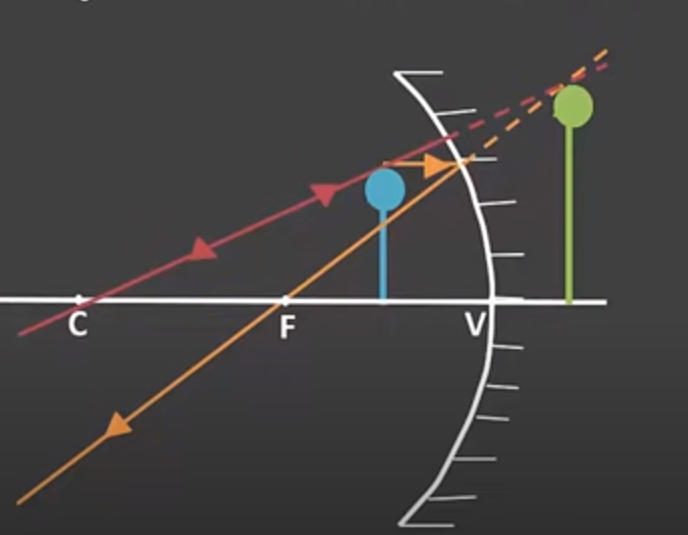
39
New cards
what is the relationship between TYPE and ATTITUDE of an image
**Real** - Inverted
**Virtual** - Upright
**Virtual** - Upright
40
New cards
what is the difference between PLANE, CONCAVE and CONVEX mirrors
PLANE: - virtual imgs - reflected image same size
CONCAVE: - reflective rays converge on a point - reflected image magnified
CONVEX: - light rays DIVERGE - virtual imgs - reflected image smaller
CONCAVE: - reflective rays converge on a point - reflected image magnified
CONVEX: - light rays DIVERGE - virtual imgs - reflected image smaller
41
New cards
list these electromagnetic waves from **lowest to highest energy :**
microwaves, gamma rays, infrared light, visible (white) light, radio waves, X-ray
microwaves, gamma rays, infrared light, visible (white) light, radio waves, X-ray
radio waves < microwaves < infrared < visible (white) < ultraviolet < x-ray < gamma ray
42
New cards
SALT for Plane mirrors
S - same size
A - inverted
L - behind mirror
T - virtual
A - inverted
L - behind mirror
T - virtual
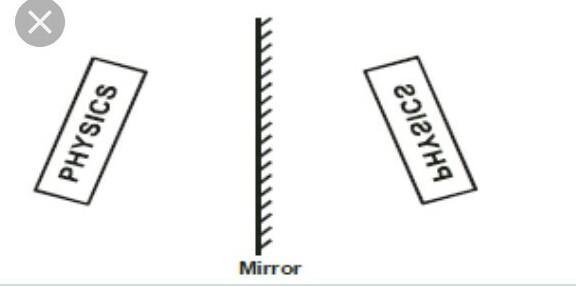
43
New cards
ray diagram for convex mirror (and attributes)
S- smaller
A- upright
L- between F-V(mirror)
T- virtual
A- upright
L- between F-V(mirror)
T- virtual
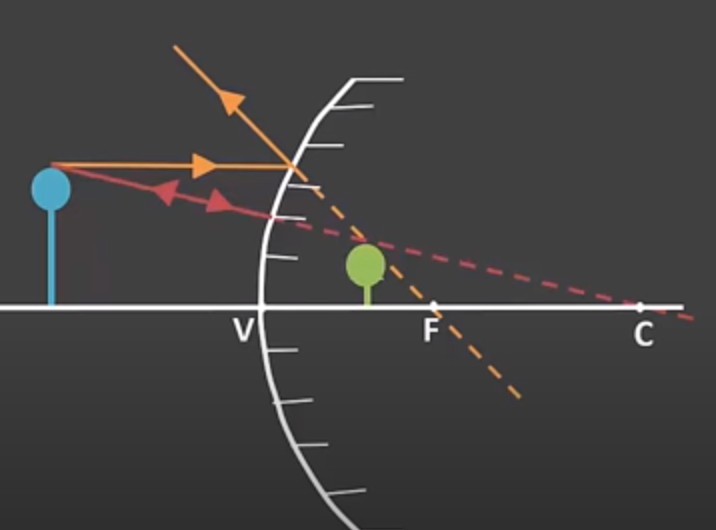
44
New cards
\
7 distinct colours in order of lowest to highest energy
7 distinct colours in order of lowest to highest energy
Red \n Orange \n Yellow \n Green \n Blue \n Indigo \n Violet