Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What is the relative mass and relative charge for protons?
1, +1
What is the relative mass and relative charge for neutrons?
1, 0
What is the relative mass and relative charge for electrons?
0, -1
Isotopes
Atoms of the same number of protons but different number of neutrons (same atomic number but different atomic mass)
Molecule
Fixed number of atoms bonded together
What happens when atoms become charged?
An ion is formed
Compound
Two or more elements chemically bonded in fixed proportions.
Fixed proportions
Same ratio of the elements to each other throughout.
Mixture
Different elements that are not chemically bonded.
What is the sum for relative atomic mass (Ar)?
relative atomic mass (Ar) = sum of (isotope x isotope abundance number)/sum of abundances of all the isotopes
Electronic structure
how the electrons are arranged in an atom of that element
What did J.J Thompson discover?
Plum pudding model in 1904, electron in 1897
What is the concept of the plum pudding model?
An atom is a ball of positive charge with negative electrons embedded in it.
What experiment was conducted in 1905 that lead to the nucleus model and by who?
The alpha particle scattering experiment A.K.A the Gold Foil Experiment by Ernest Rutherford and his student Ernest Marsden
What happened in the Gold Foil Experiment?
To their surprise, it resulted in some particles being deflected, some being deflected backwards by the nucleus, and most of the particles passing through empty space.
What did Rutherford come up with based on the results of his experiment?
The mass of the atom is concentrated in the nucleus, the nucleus was positively charged, proved the atom was not a solid, the mass was only in the centre, indicated that the charge was in the centre.
Who revised Rutherford’s nuclear model in 1913?
Niels Bohr
How did Bohr adapt the nuclear model?
He suggested that electrons orbit the nucleus in specific distances (shells), and his theoretical calculations agreed with his experimental calculations.
What conclusion did Rutherford’s further experimentation give?
The positive charge of the nucleus could be divided into smaller particles, discovering the proton which had to be a whole number and all have the same amount of positive charge.
Who proved the existence of neutrons in 1932?
James Chadwick
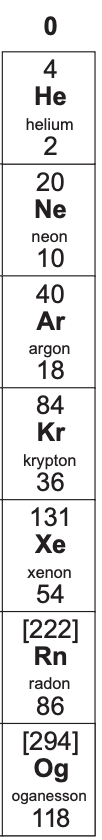
What is group 0/8 known as?
noble gases
Why are group 0 elements generally stable and unreactive?
They have a full outer shell of electrons.
What are some of the properties of group 0 elements?
non-flammable
all exist as single atoms
colourless gases at room temperature
Bp increases as you go down the group (because number of electrons+shells increase so greater intermolecular forces need more energy to break them)
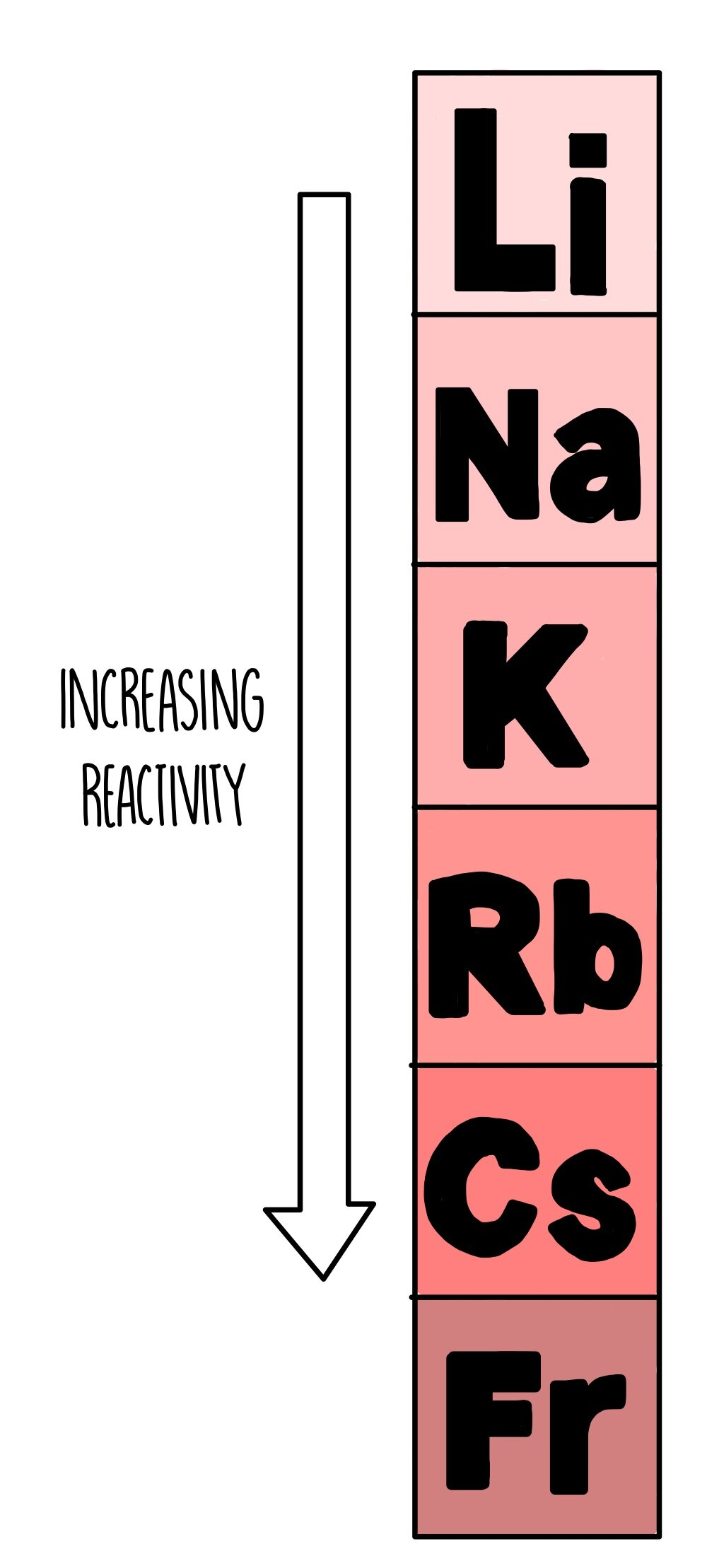
What are group 1 elements also known as?
Alkali metals
What are some of the properties of group 1 elements?
silvery solids that must be stored in oil (they oxidise quickly)
have low densities (Li, Na, K less dense than water)
react with water releasing hydrogen
form hydroxides that dissolve in water to give alkaline solutions
react with non-metals to form ionic compounds where they form ions with a +1 charge
Bp and Mp decrease down the group
reactivity increase down the group
When alkali metals react with water, what happens?
produces a metal hydroxide + hydrogen gas
hydroxides formed will dissolve in water to form alkali
When alkali metals react with oxygen, what happens?
They make metal oxides
When alkali metals react with chlorine, what happens?
produce chlorides
at room temperature chlorides are white solids
dissolve in water to form colourless solutions
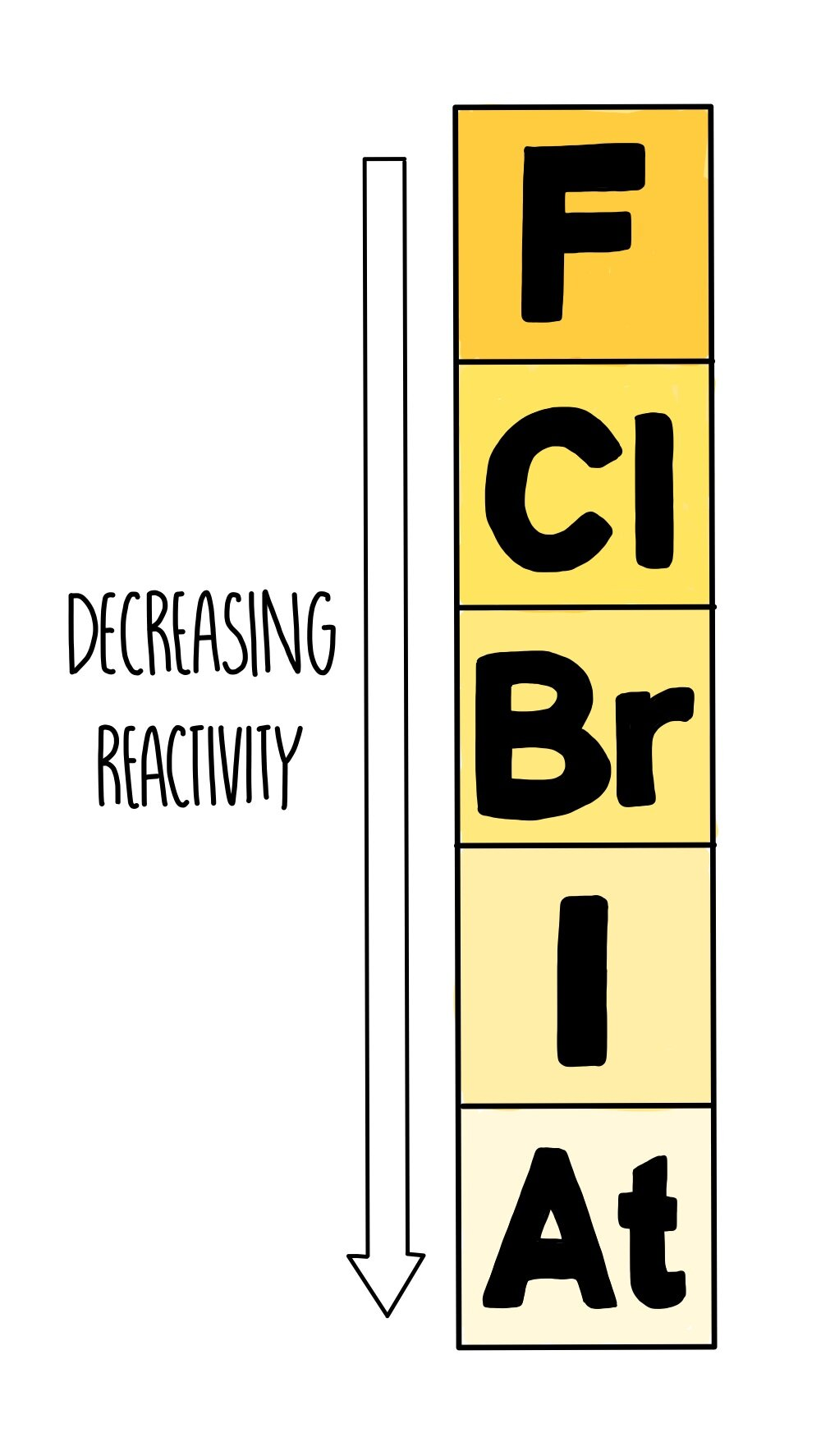
What are group 7 elements known as?
Halogens, which are non-metal elements that exist as molecules made of pairs of atoms (diatomic molecules)
What are some of the properties of group 7 elements?
coloured vapours
form molecular compounds with other non-metallic elements
react with metals to form ionic compounds where they form halide ions with a -1 charge
react with non-metals by sharing electrons to form covalent bonds
What are the trends in group 7?
bond between atoms in molecule are strong, but forces of attraction between molecules are weak
Mp and Bp increase down the group because molecules get larger, intermolecular forces become stronger and more energy is needed to overcome these forces
reactivity decreases as you go down the group (atoms get larger, more distance between the outer shell and the nucleus, forces of attraction between nucleus and the outer shell decreases)
When halogens react with metals, what do they form?
metal halides (salts)
What are the properties of transition metals?
excellent thermal and electrical conductors
dense, strong and shiny
their compounds make good catalysts
can form positive ions with different charges
Compare the properties of transition metals with properties of alkali metals
both shiny
good conductors of heat and electricity
transition metals are less reactive
transition metals are denser, stronger and harder
transition metals have higher melting points and boiling points