ENGG2000 - Module 1
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Introduction to Humanitarian Settings
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
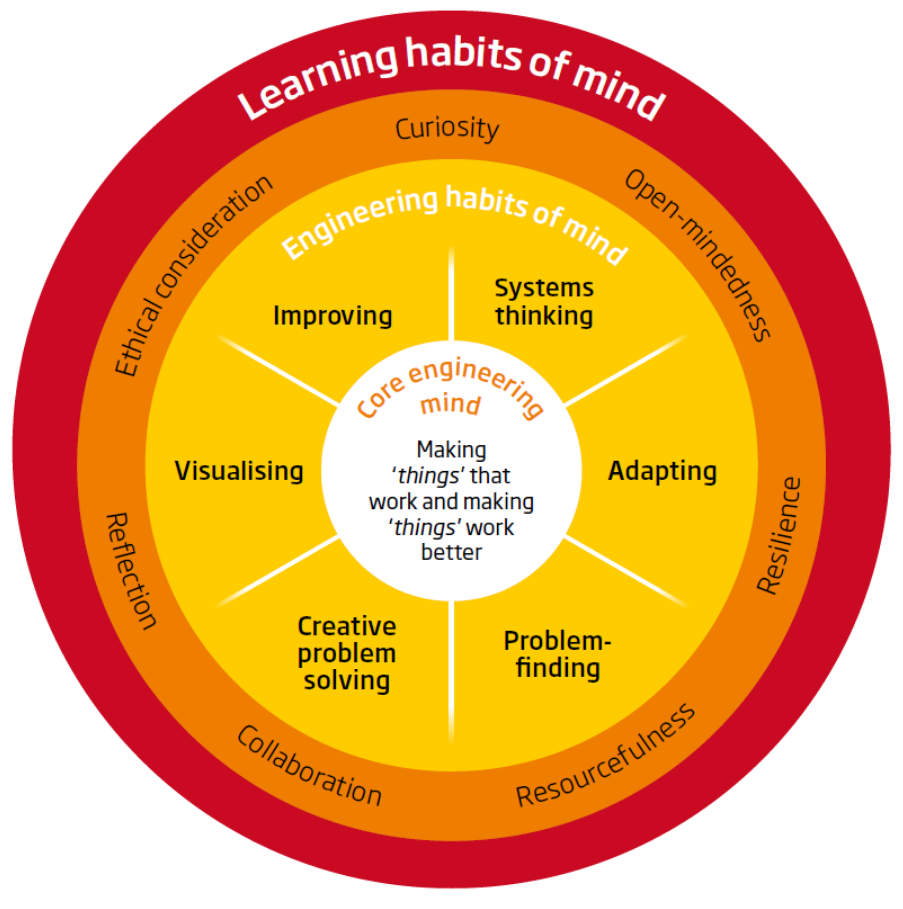
Learning habits of mind framework
Haiti Earthquake 2010 Issue
1.5 million homeless, 200,000 killed, 13 billion raised but only 48% actually reached Haiti and after a long time.
Engineer role in disaster
Optimize limited resources, construction of buildings/roads, help improve system.
Humanitarian Engineering Defintion
Application of engineering to develop affordable, culturally appropriate, sustainable solutions that improve social well-being.
Reason for humanitarian engineering
High poverty rates
Growing inequality
Rapid urbanisation
Climate change
Wars/natural disasters
HADE SPECTRUME
Humanitarian Action - response to external shock, short/medium term.
Development Engineering - response to ongoing vulnerability, long term.
Sustainable development goals
A global blueprint, created for every country to reach, giving a framework

Humanitarian crisis
When human/physics/environmental damage from events overwhelms communities capacity to cope. Can be man made, natural or complex (both).
4 Overarching humanitarian principles
Humanity: Protect life and dignity
Neutrality: Don’t take sides
Impartiality: Protect the most vulnerable
Operation independence: Preserve integrity of all decisions.
Core humanitarian standard
Nine commitments:
relevant
timely
strengthen locally
allow complaints
well coordinated
encourage feedback
treat staff fairly
ensure responsible service
encourage local communication
Most important sustainable development goals for engineers
water, sustainable energy and sustainable infrastructure and innovation are the three areas engineers can help the most
CEET
Global council of engineers, with purpose of reaching net zero by 2050.
Humanitarian vs Traditional engineering
Humanitarian engineering is more circular/human centered, looking for constant improvements and feedback. Done “with” communities instead of for, to empower and reach long term solutions.

MDGs
Millennium Development Goals - old goals with focus on improving impoverished, developing nations, now the SDGs, which apply to all nations.
EWBA
Engineers without borders Australia - Creates change across borders through engineering, have implemented solar power in Australia, Biogas and alternative fuels in Cambodia.
Tragedy of the commons and examples
Situation in which when individuals/public have access to a recourse, act in own interest and deplete recourse and damage society.
Coffee - Farms now take up too much land
Over fishing - Species face extinction
Fast Fashion - Produces waste and sweatshops
Traffic Congestion - Fossil fuels, dangerous and congestion
Groundwater - Decreasing faster then can be replenished
Unfairness statistic in current engineering
90% of engineering seeks to benefit top 10% of civilization.
SDG 6 and engineers role
Clean water and sanitation - manage wastewater and provide clean drinking water, expanding washing/cleaning services, removing cholera (SDG 3 - health)
SDG 7 and engineers role
Affordable and clean energy - innovate with low cost, renewable solutions, especially storage is important in places such as Africa.
SDG 9 and engineers role
Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure - Engineers are responsible for roads and infrastructure and maintenance. Furthermore, are often leading in industry as well.
UNESCO statement on engineering
Engineering knowledge underpins sustainable social and economic development, and can be considered the engine for global development. (UNESCO - United Nations Education Science Cultural Organization)