Econ - Globalization and Trade vocab
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
specialization
a particular area which someone concentrates on/ is an expert on

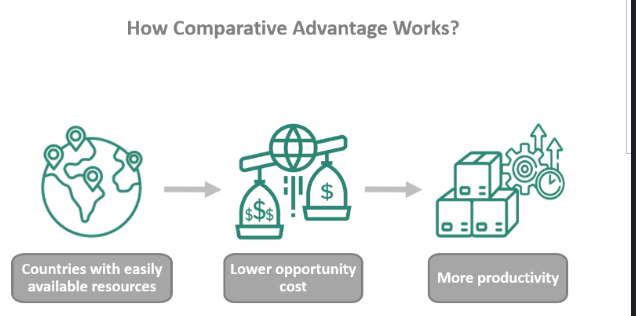
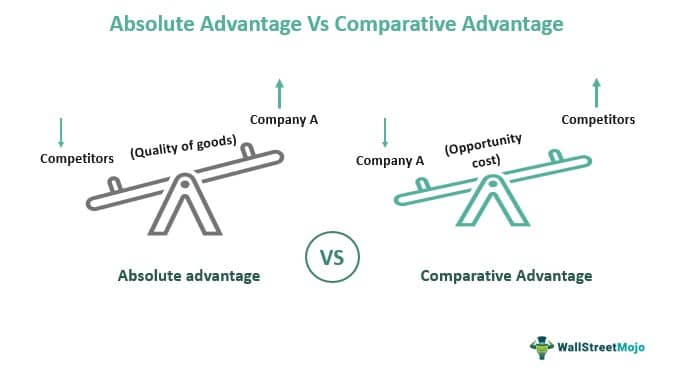
comparative advantage
when a country can produce a good at a lower opportunity cost
Absolute advantage
when a country can produce more of a good using the same quantity of resources
production possibilities curve
shows possible alternatives of production/ illustrates trade offs and opportunity costs
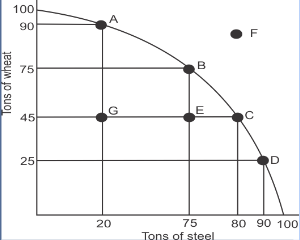
opportunity cost
the most valued alternative you give up when you make a choice

tariff
a tax on imports so they become more expensive - makes people want to buy from American companies rather than foreign companies
quota
a legal limit on the amount of a good that may be imported from other countries - meant to protect American companies from competition of other countries

embargo
a government order prohibiting the selling of goods to another country - usually because that country has bad/tyrannical/cruel leaders

world trade organization (WTO)
formed to help make trade agreements and settle trade disputes between countries
US-Mexico-Canada (USMCA)
A major free trade agreement was created that includes Canada, Mexico, and the United States. -Lowers trade restrictions between the countries to allow for better trading conditions.
exchange rate
the price of one country’s currency in terms of another country’s currency. (1 US dollar = 0.94 Euro)
trade deficit
negative balance of trade (imports greater than exports)
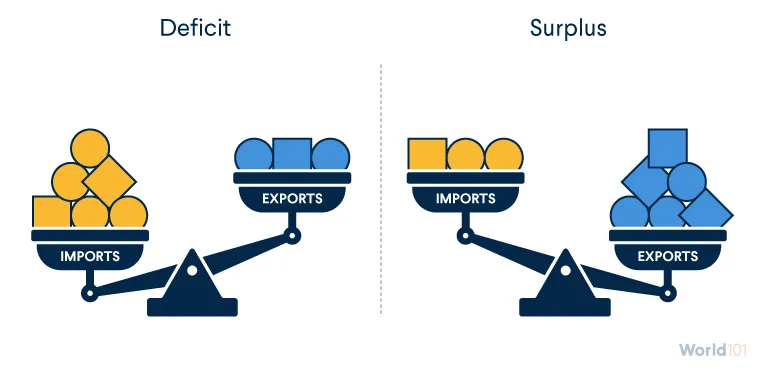
trade surplus
positive balance of trade (exports greater than imports)
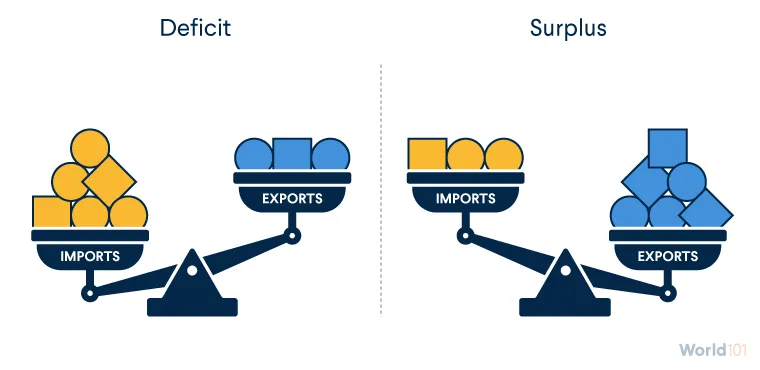
balance of trade
difference between a country’s exports and its imports.

globalization
the spread of the flow of financial products, goods, technology, information, and jobs across national borders and cultures.
outsourcing
to receive goods/services from an outside or foreign supplier.

European Union
a political and economic alliance of 27 countries located primarily in Europe
OPEC
an intergovernmental organization controlling most of the world’s oil supply