Bot-Lec (Sem-1) - Chapter 10: Angiosperms
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
angiosperm
traditional name for flowering plants; large, diverse phylum of plants that form flowers for sexual reproduction and produce seeds enclosed in fruits
ovule
structure in the ovary that contains a female gametophyte and develops into a seed after fertilization; enclosed within ovaries in angiosperms
ovary
base of a carpel or fused carpels that contains ovules and develops into a fruit after fertilization
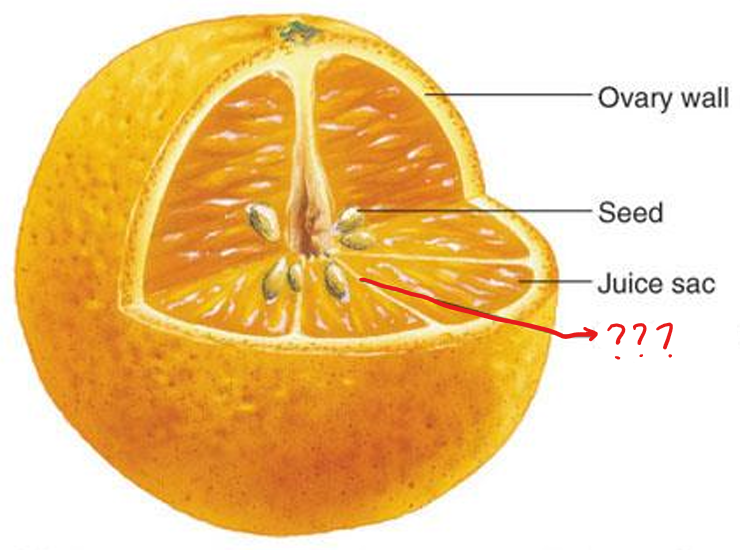
pericarp
the part of a fruit formed from the wall of the ripened ovary
exocarp; mesocarp; endocarp
parts of a pericarp
exocarp
skin/peel of the fruit
mesocarp
fleshy part of the fruit
endocarp
fleshy skin surrounding the seed of the fruit
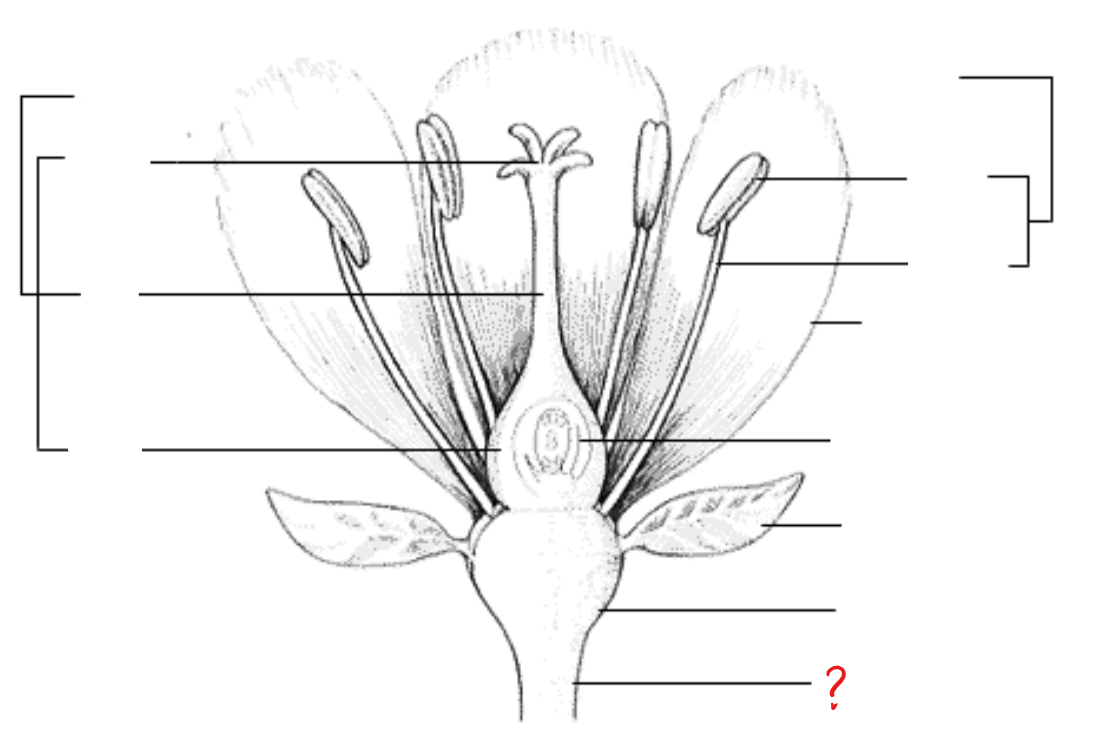
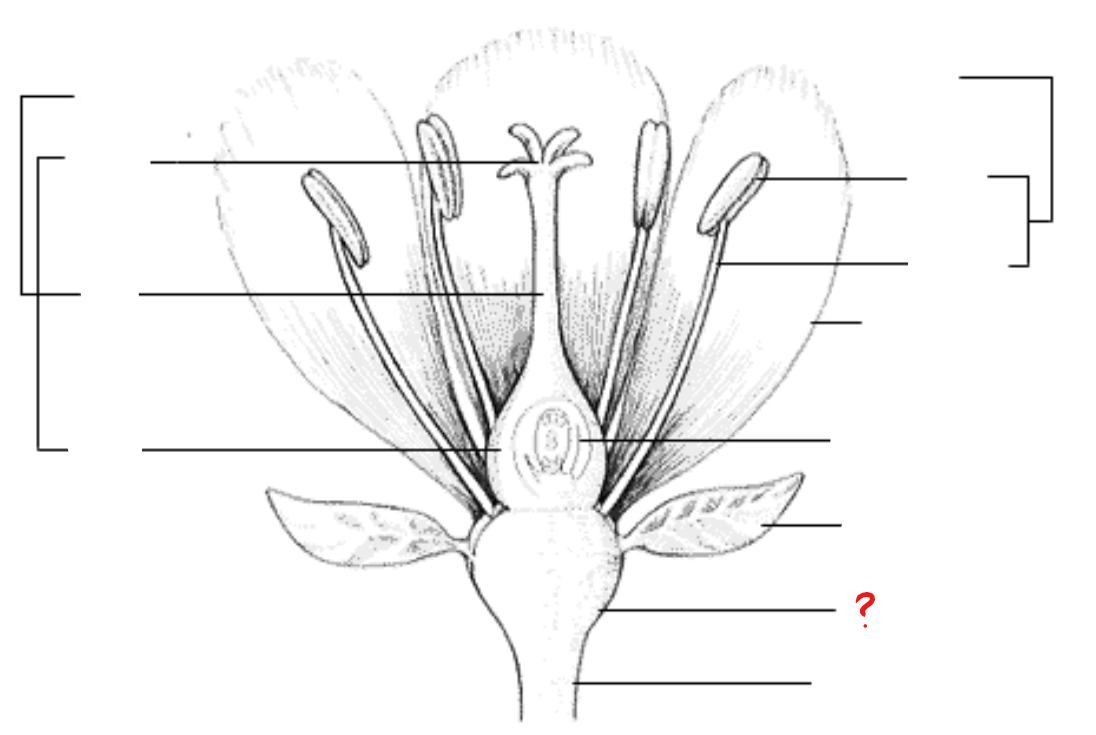
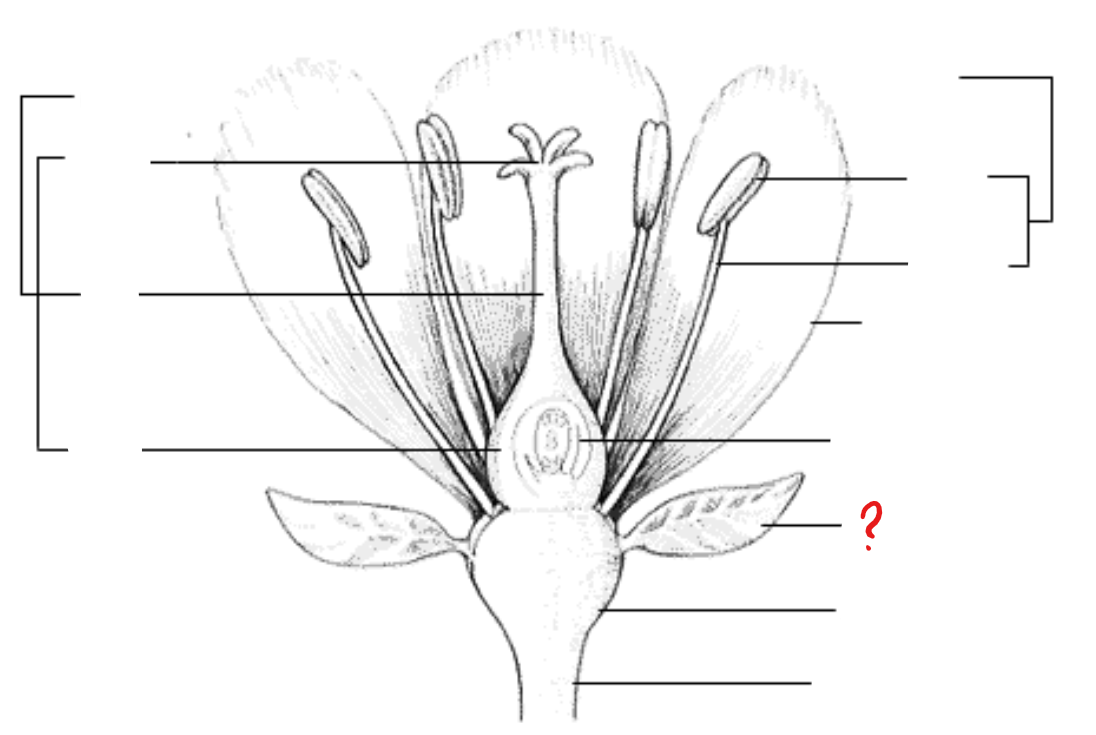
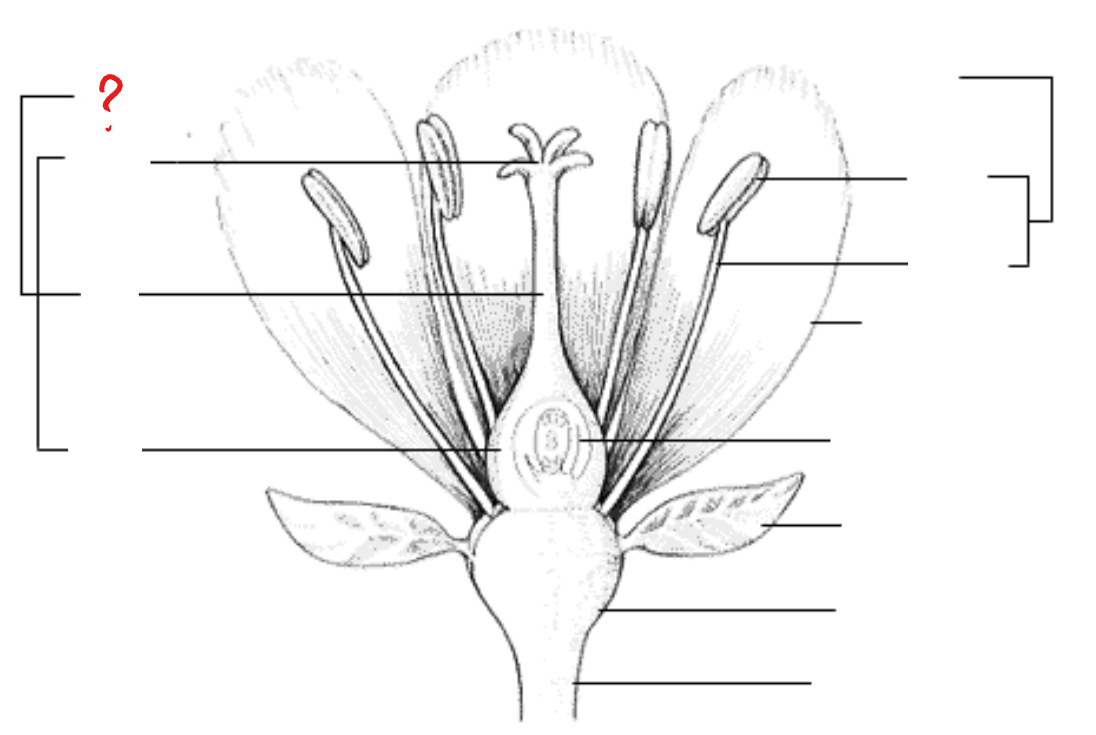
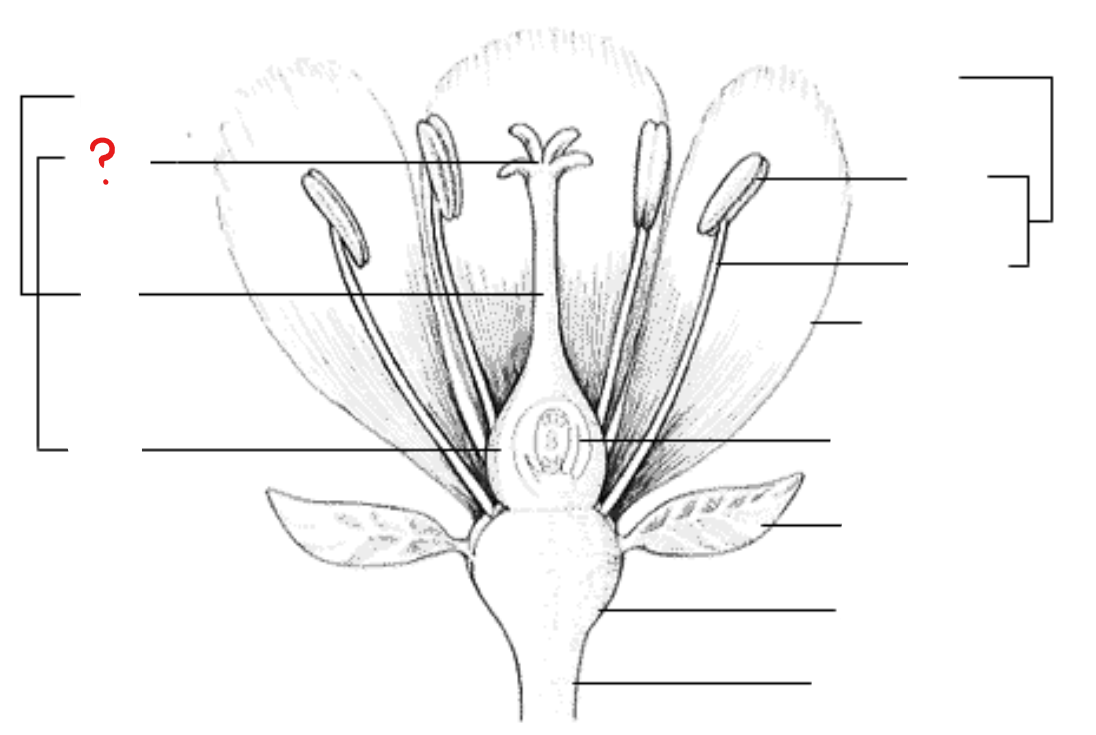
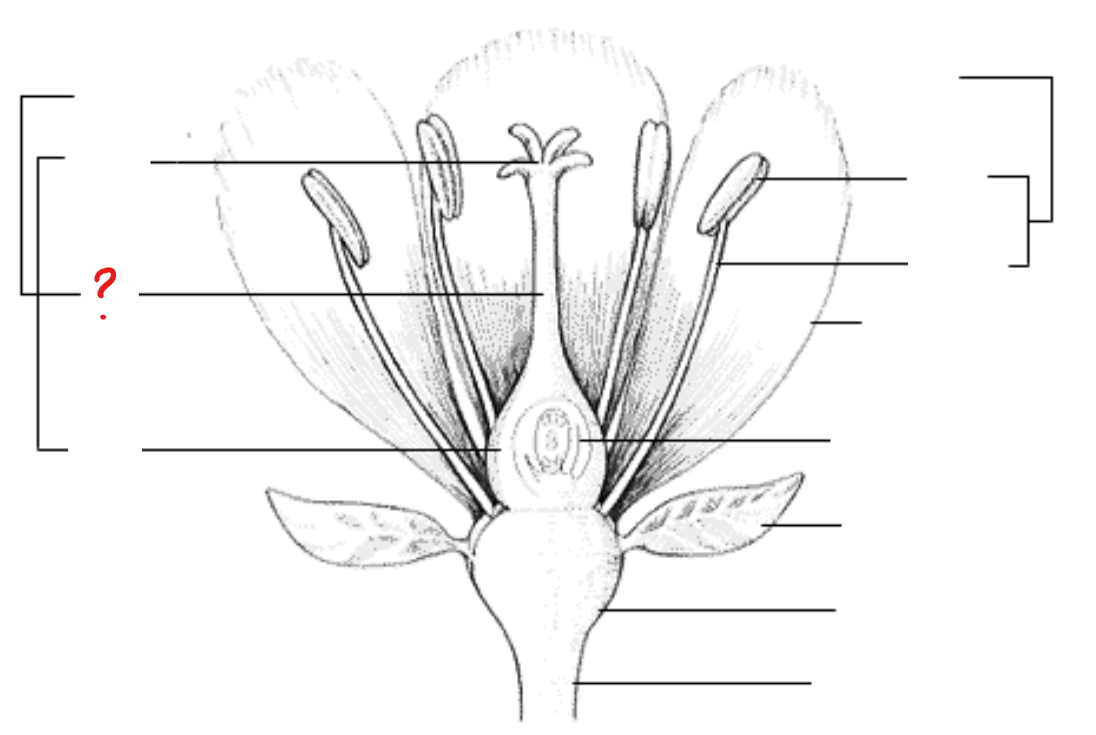
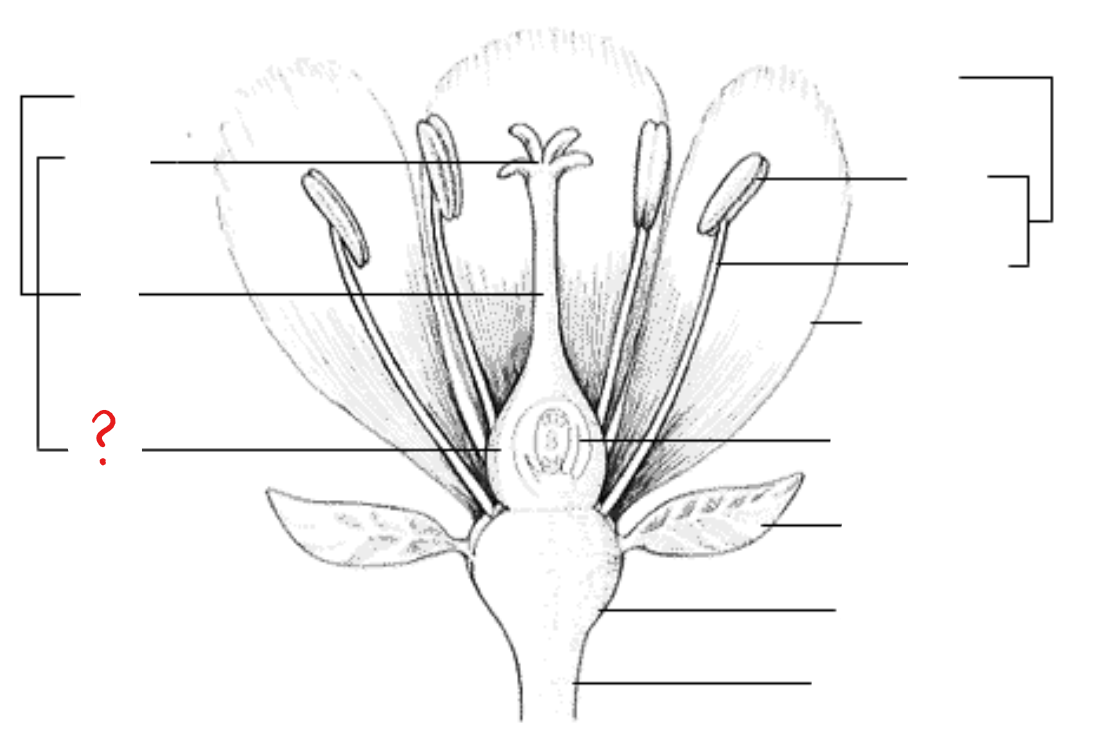
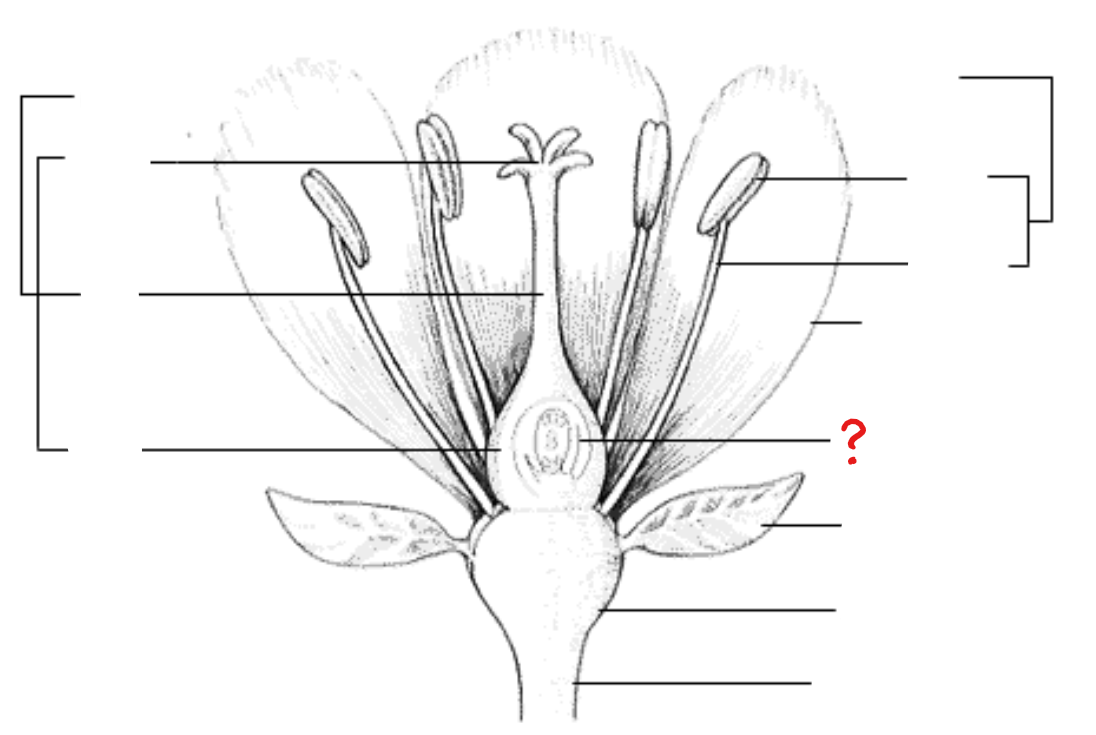
peduncle; receptacle; sepal; petal; stamen; anther; filament; pistil; stigma; style; ovary; ovule with embryo sac
parts of a flower
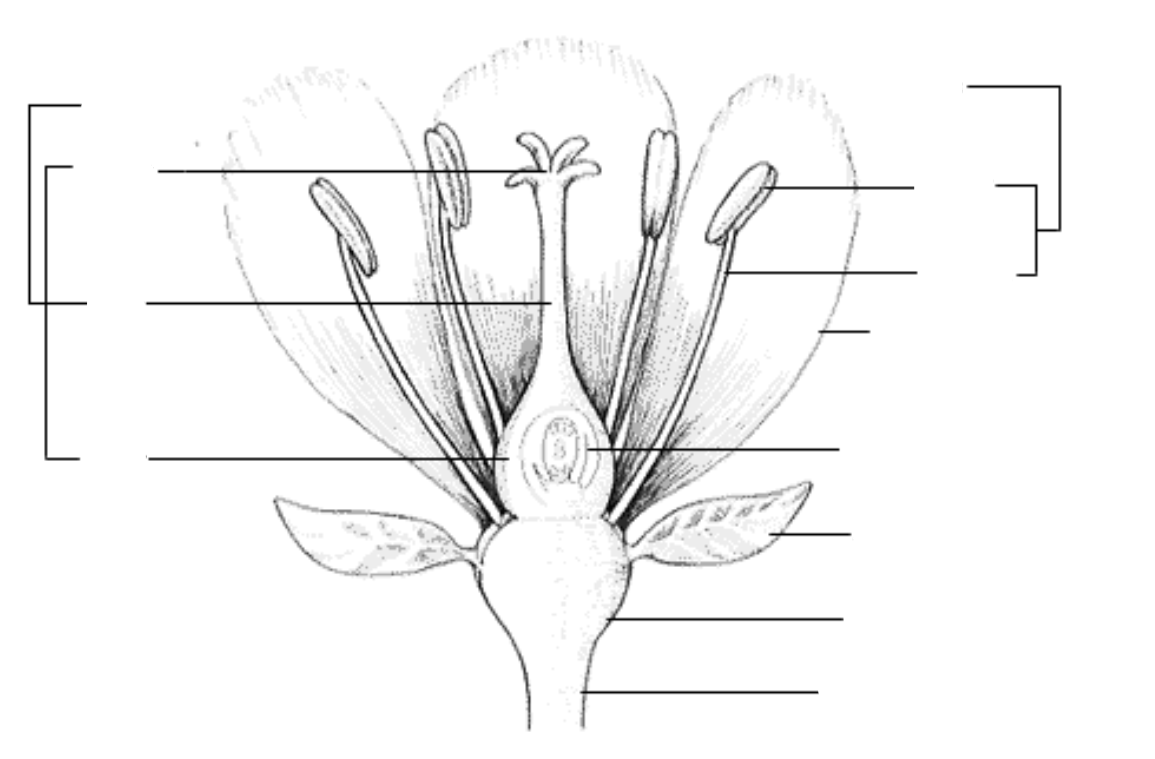
peduncle
identify the part labeled with a question mark; stalk of a flower
receptacle
identify the part labeled with a question mark; part of a flower stalk where the parts of the flower are attached
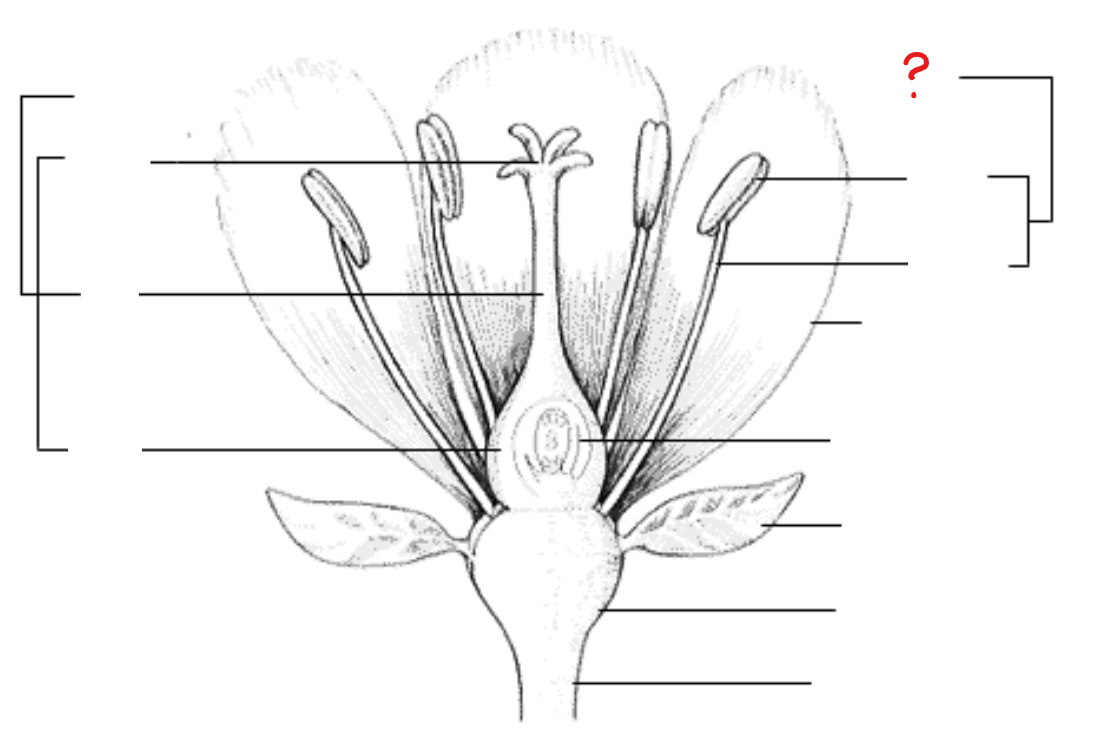
sepal
identify the part labeled with a question mark; outer parts of the flower (often green and leaf-like) that enclose a developing bud
petal
identify the part labeled with a question mark; parts of a flower that are often conspicuously colored; used to attract pollinators
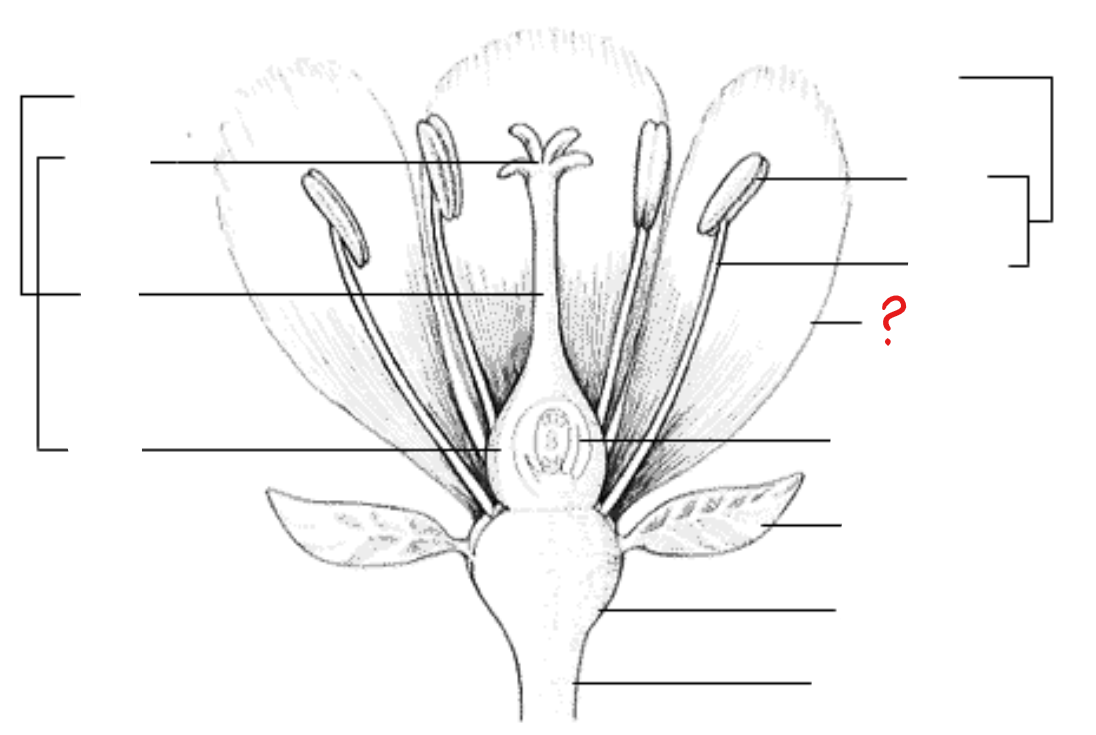
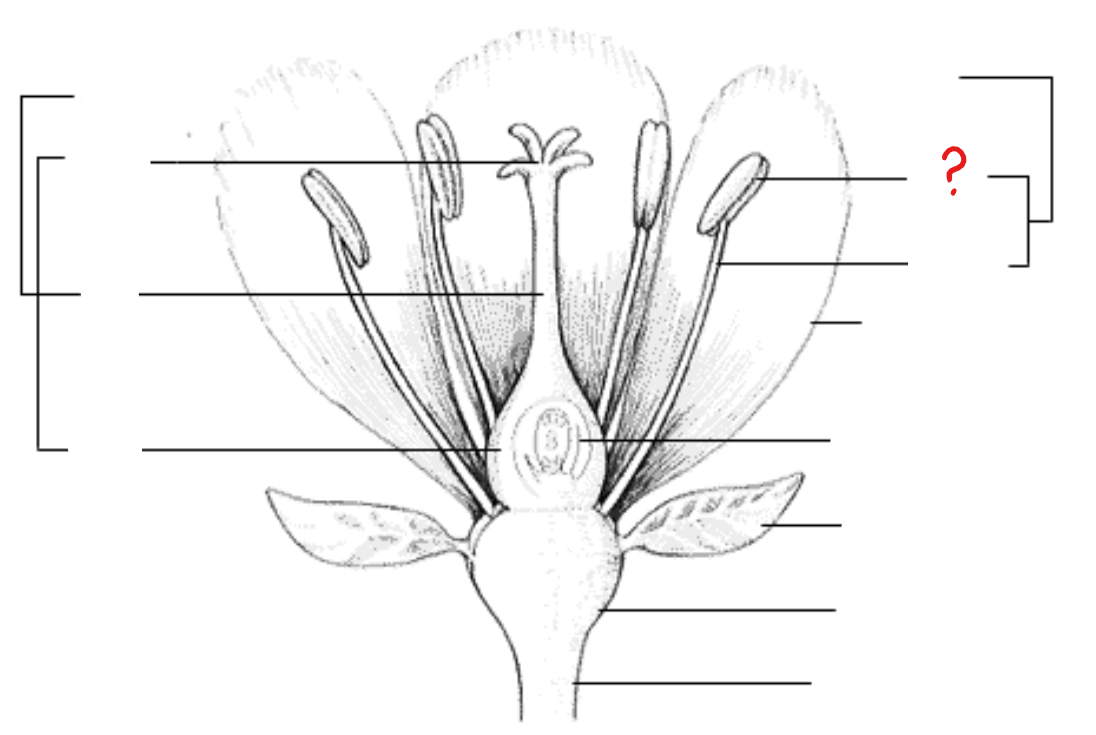
stamen
identify the part labeled with a question mark; pollen producing part of a flower, usually with a slender filament supporting the anther
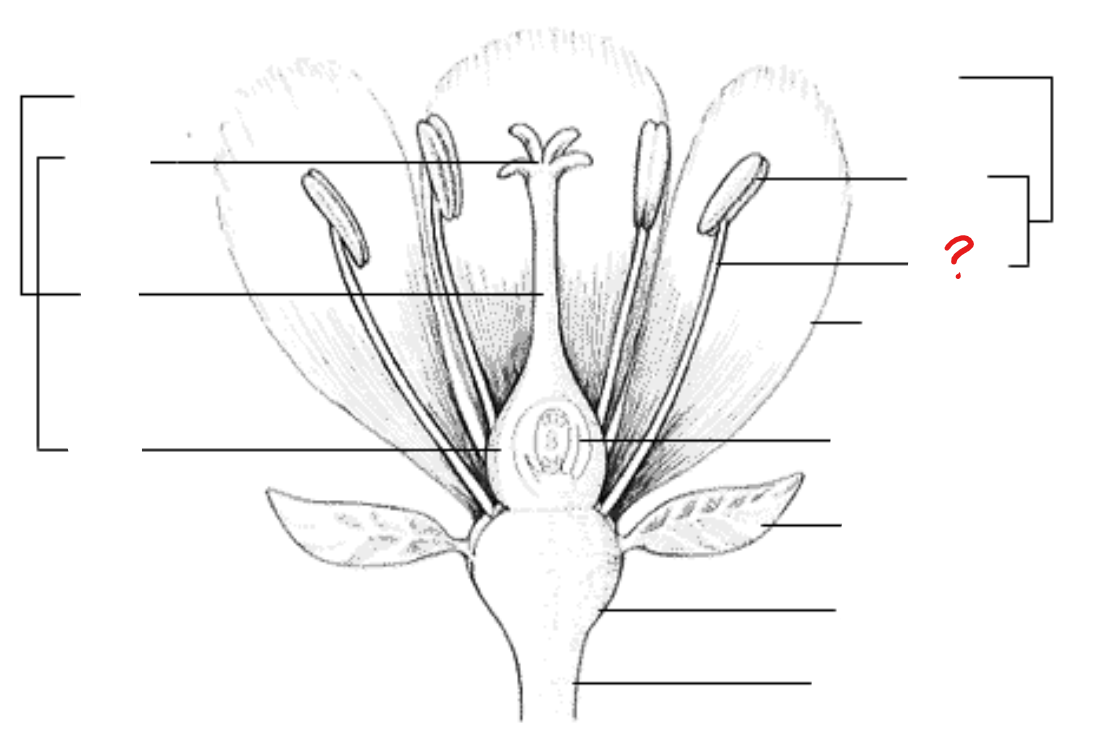
anther
identify the part labeled with a question mark; part of the stamen where pollen is produced
filament
identify the part labeled with a question mark; a stalk-like structure that attaches to the base of the flower and supports the anther
pistil
identify the part labeled with a question mark; ovule producing part of a flower; ovary often supports a long style, topped by a stigma; mature ovary is a fruit, and the mature ovule is a seed
stigma
identify the part labeled with a question mark; part of the pistil where pollen germinates
style
identify the part labeled with a question mark; the stalk that supports the stigma and connects it to the ovary
ovary
identify the part labeled with a question mark; enlarged basal portion of the pistil where ovules are produced
ovule with embryo sac
identify the part labeled with a question mark; female gametophyte or embryo sac, which at maturity contains the gametes, develops within a specialized structure, the ovule
corolla
all of the petals of a flower
calyx
all of the sepals of a flower
perianth
all of the petals and sepals of a flower
Citrus sinensis
eudicot; orange; a tangy and sweet citrus fruit
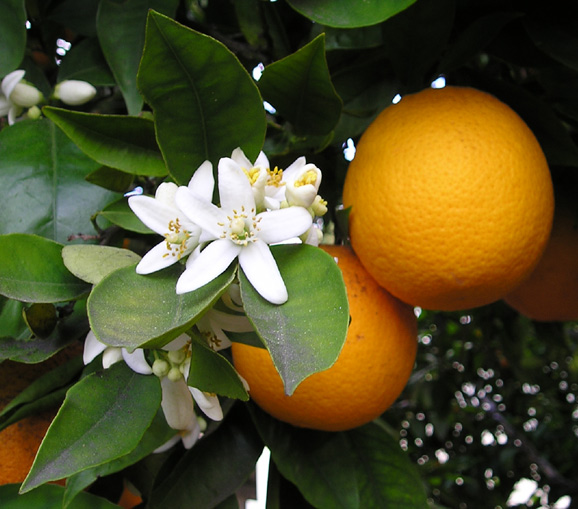

nectary
a flower organ that secretes nectar; observed in orange blossoms
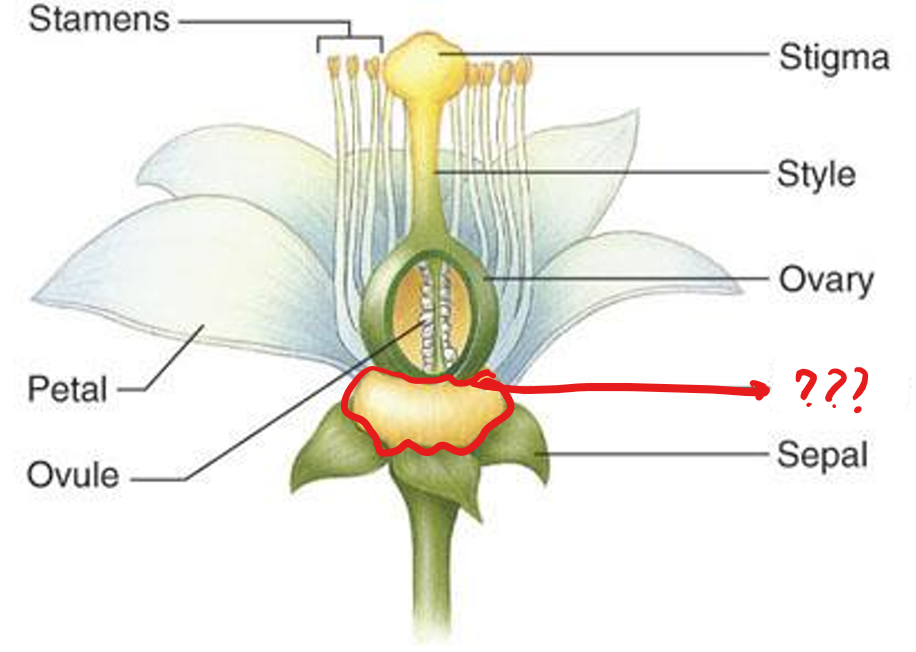
carpel wall
the wall of each section of an organ
cork; rubber; tobacco; coffee; chocolate; aromatic oils for perfumes; lumber; fibers; medicines
products derived from angiosperms
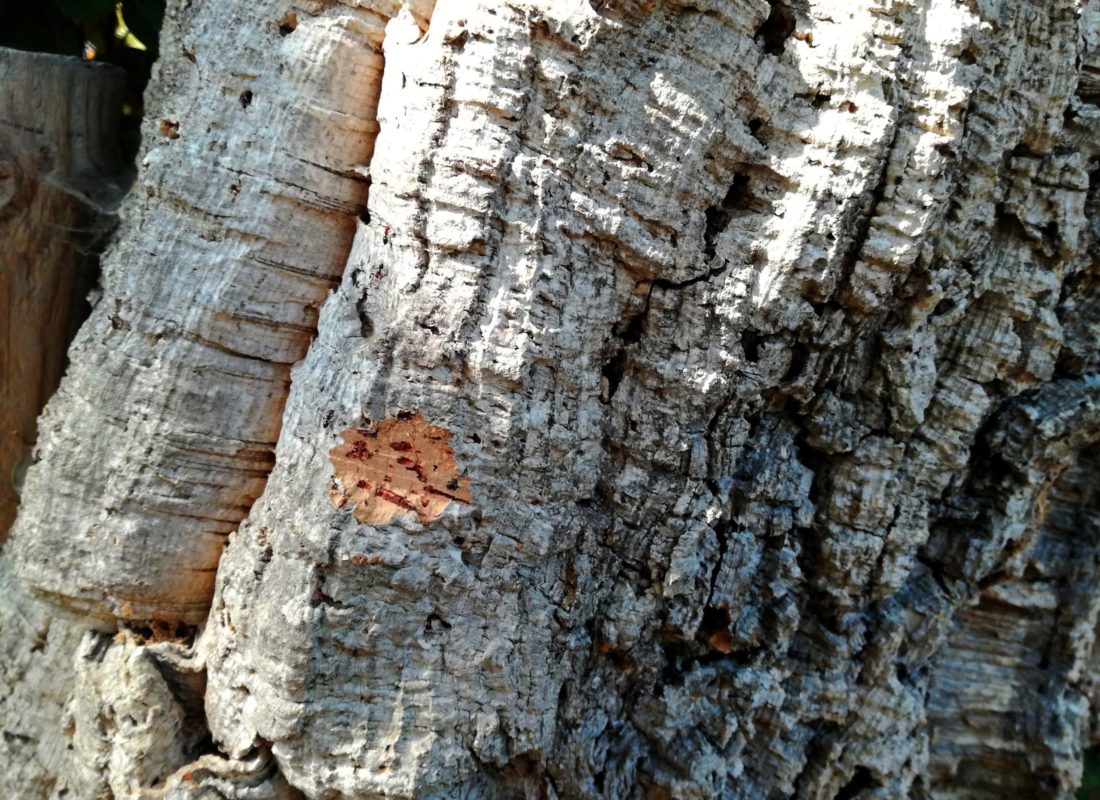
Quercus suber
eudicot; cork oak; primary source of cork

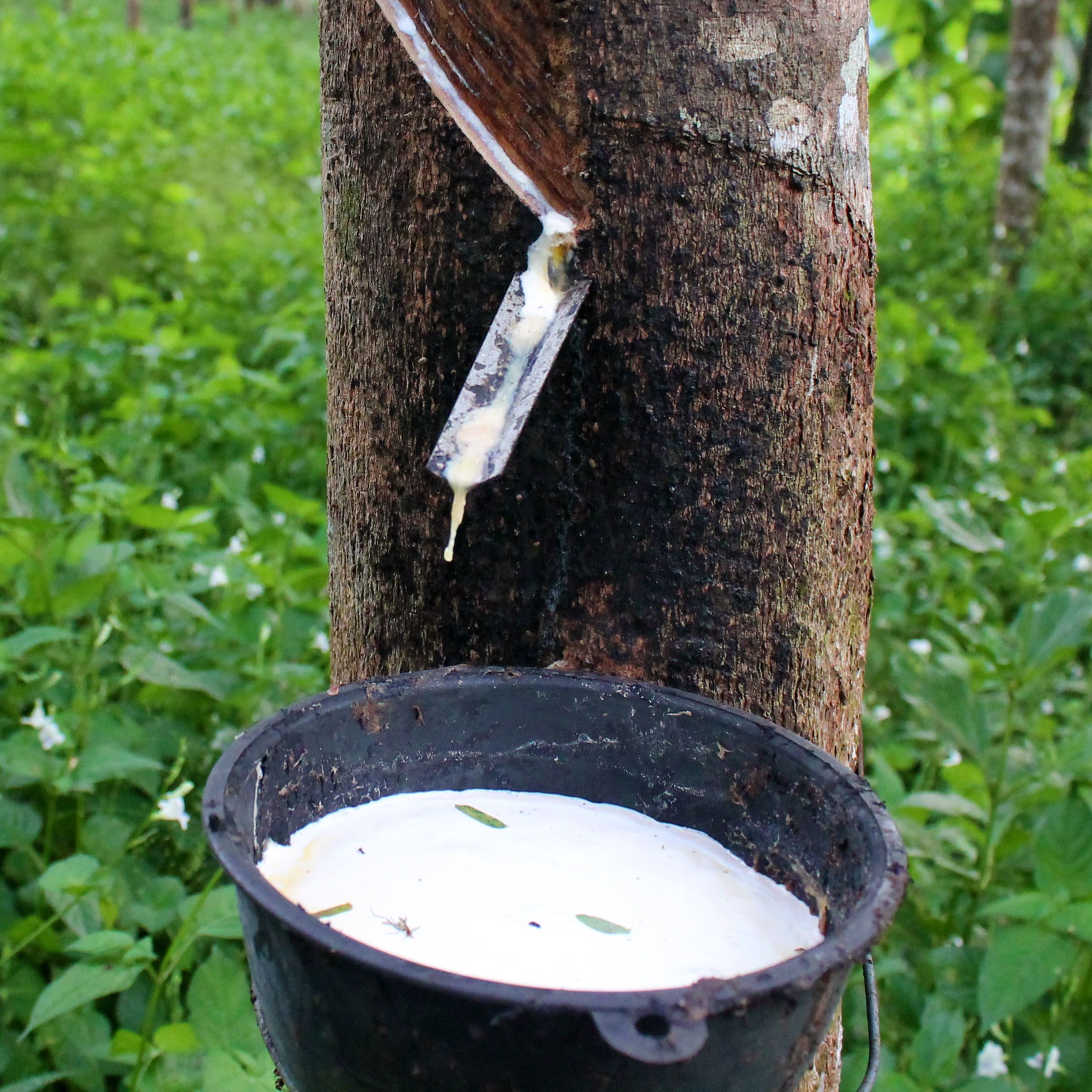
Hevea brasiliensis
eudicot; rubber tree/plant; native to the Amazonian basin; primary source of rubber

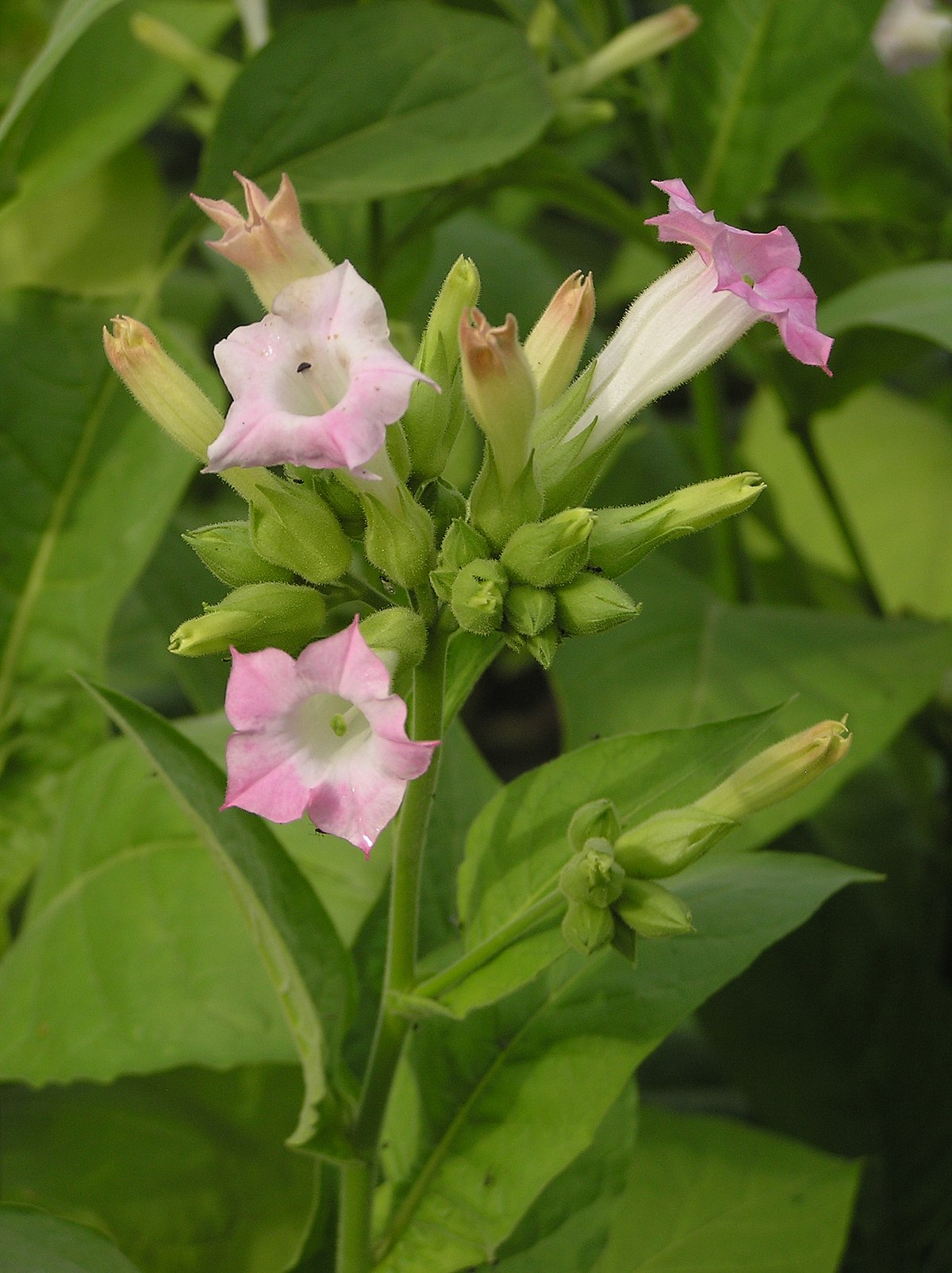
Nicotiana tabacum
eudicot; tobacco; nicotine

Coffea arabica
eudicot; coffee plant; major source of caffeine

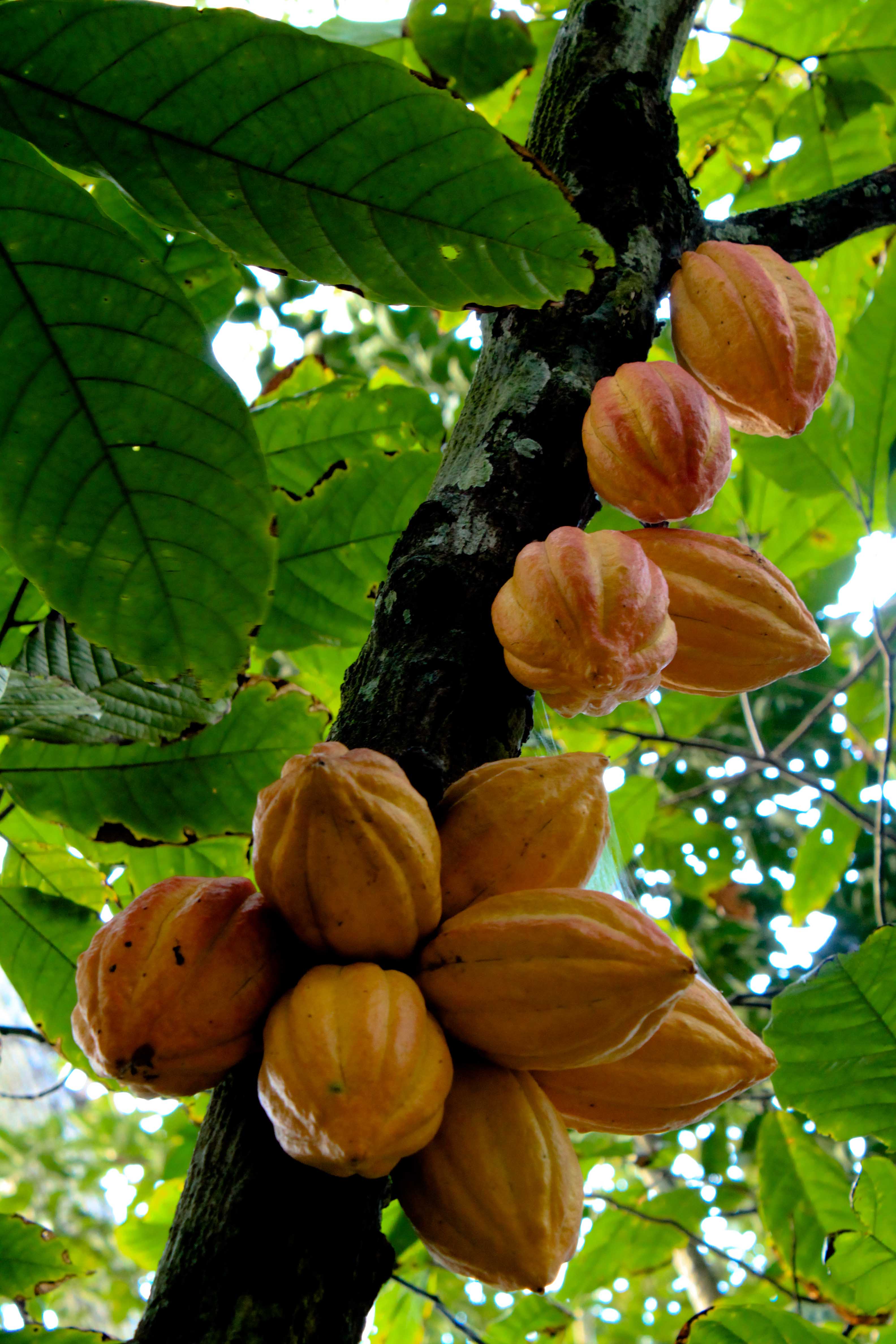
Theobroma cacao
eudicot; cocoa; seeds are used to produce chocolate

cotyledon
seed leaf of a plant embryo, which may contain food stored for germination
monocot
group of flowering plants with a single cotyledon; floral parts in threes; include grasses, orchids, irises, onions, lilies, and palms
Trillium cernuum
monocot; nodding trillium

Adonidia merrillii
monocot; Arecaceae; Manila palm (native to Palawan)/Christmas palm (in the US, specifically Florida);

Arecaceae
palm family
Miscanthus sinensis
monocot; Poaceae; eulalia/Chinese silver grass; prominent flowers

Poaceae
grass family
Ophrys apifera
monocot; Orchidaceae; bee orchid; an example of sexually deceptive pollination and floral mimicry, a highly selective and highly evolved plant–pollinator relationship
Orchidaceae
orchid family
Allium cepa
monocot; Amaryllidaceae; onion; widely cultivated species of vegetable

Amaryllidaceae
amaryllis family; perennial and bulbous flowering plants
Iris reticulata
monocot; Iridaceae; netted iris; characterised by a fibrous net surrounding the bulb

Iridaceae
iris family
Lilium lancifolium
monocot; Liliaceae; tiger lily; Asian species of lily
Liliaceae
lily family
eudicot
two main classes of flowering plants; contain two cotyledons; floral parts in fours or fives; include oaks, roses, mustards, cacti, blueberries, sunflowers
Tacitus bellus
eudicot; chihuahua flower

Quercus alba
eudicot; Fagaceae; white oak; one of the preeminent hardwoods of eastern and central North America

Fagaceae
beech family (beeches, chestnuts, and oaks)
Rosa chinensis
eudicot; Rosaceae; Chinese rose;
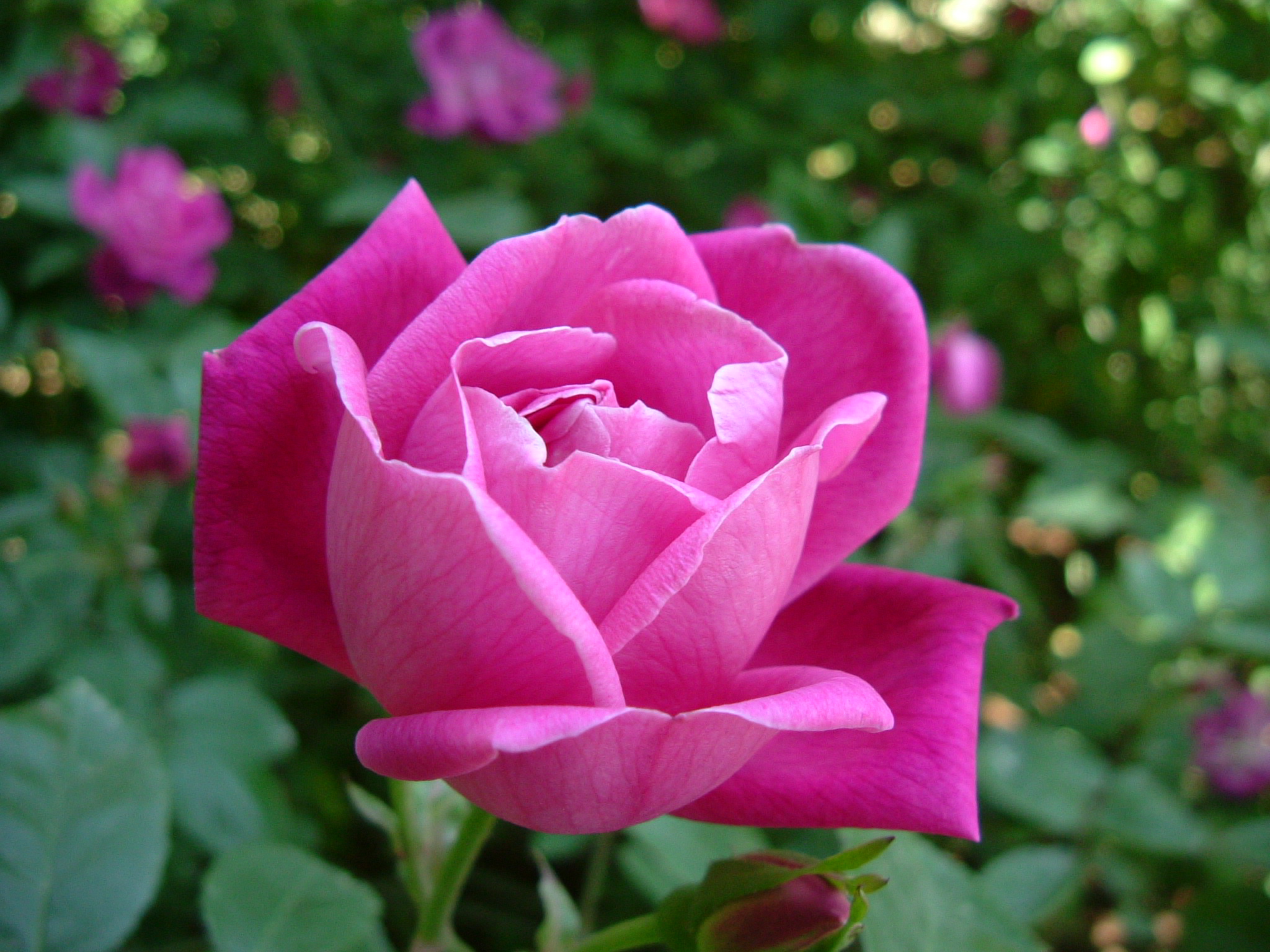

Rosaceae
rose family
Brassica oleracea
eudicot; Brassicaceae; cauliflower; composed of a white inflorescence meristem
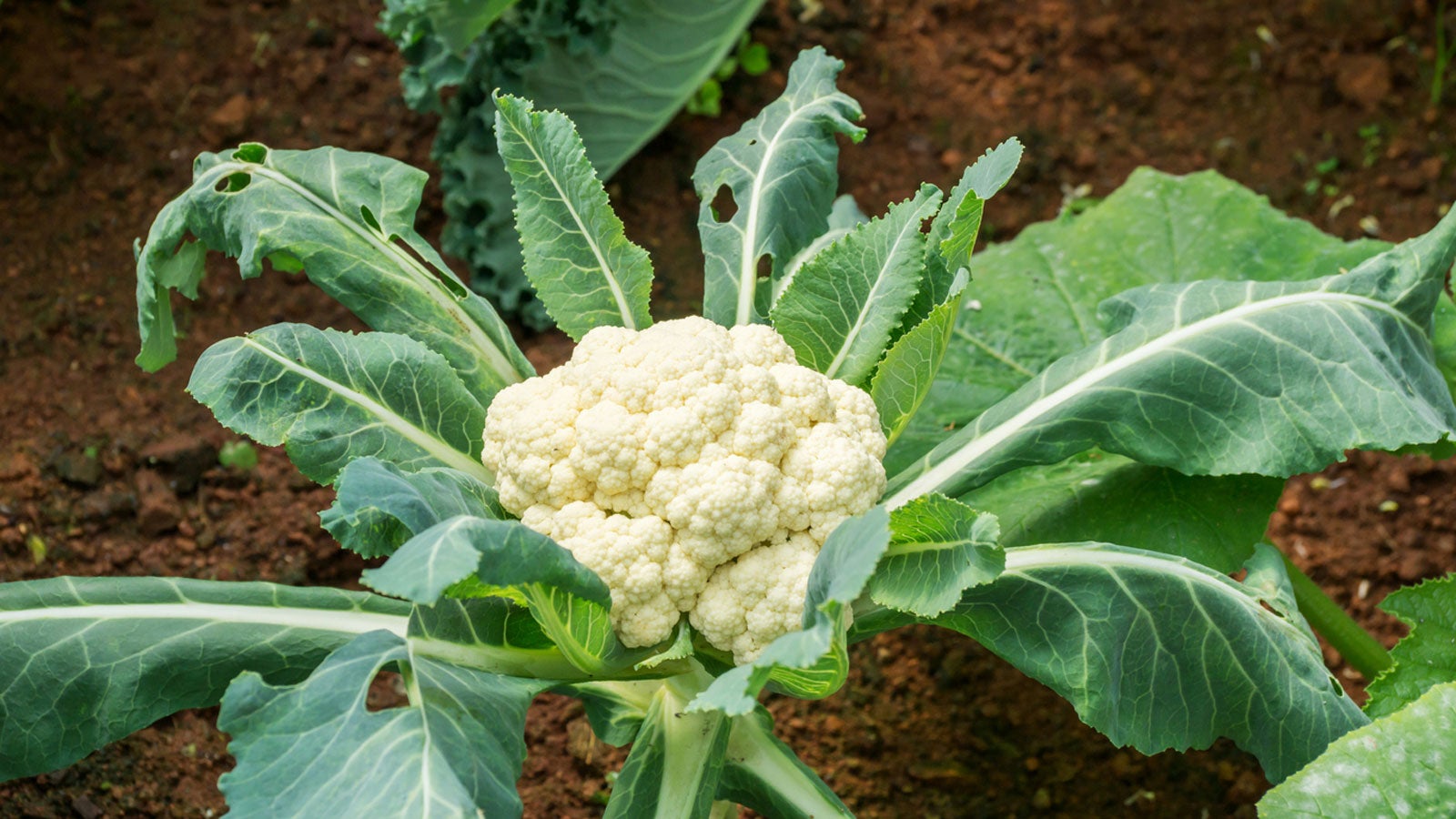

Brassicaceae
mustard family
Ferocactus acanthodes
eudicot; Cactaceae; barrel cactus
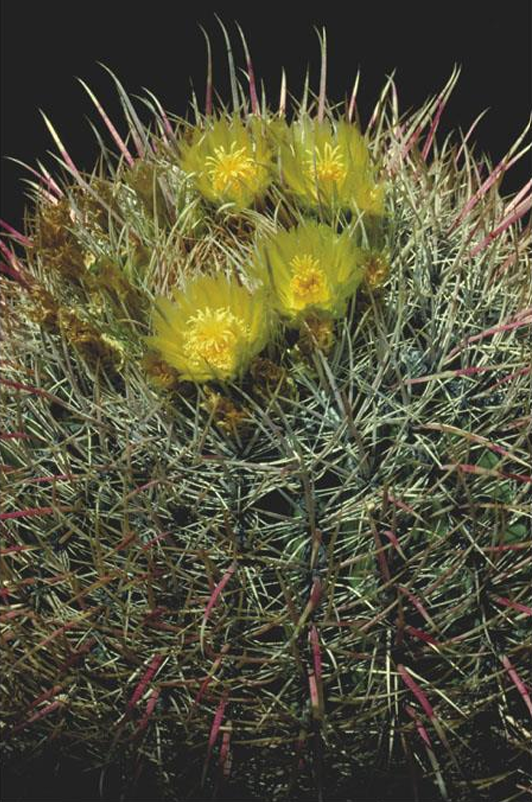

Cactaceae
cactus family
Vaccinium angustifolium
eudicot; Ericaceae; lowbush blueberry
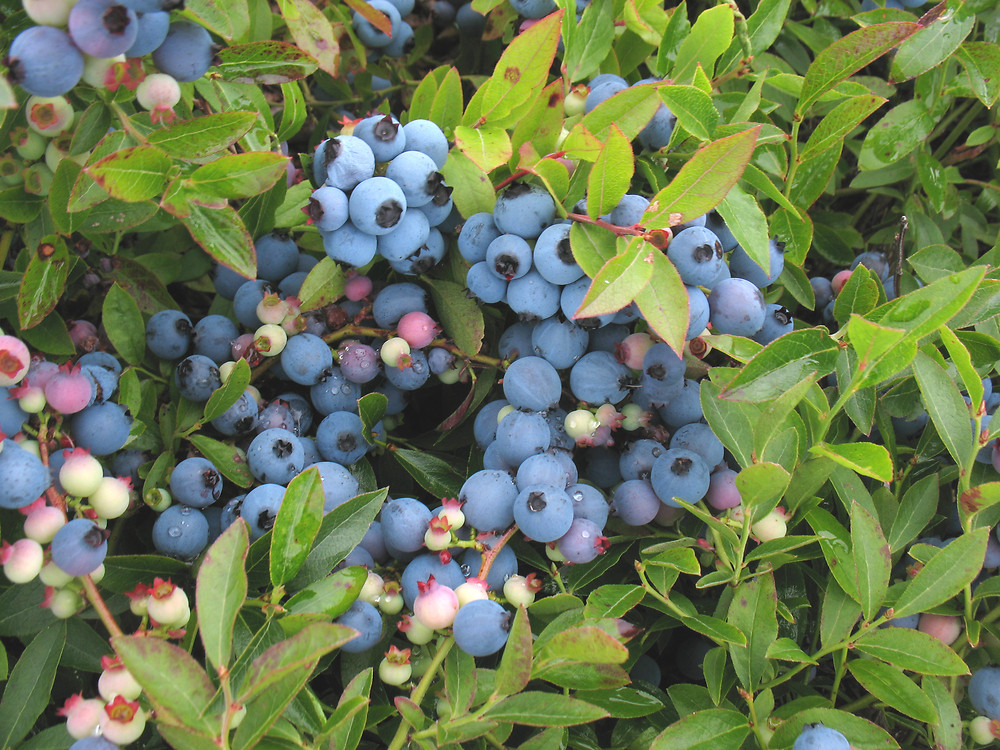

Ericaceae
heath/heather family
Helianthus annuus
eudicot; Asteraceae; common sunflower
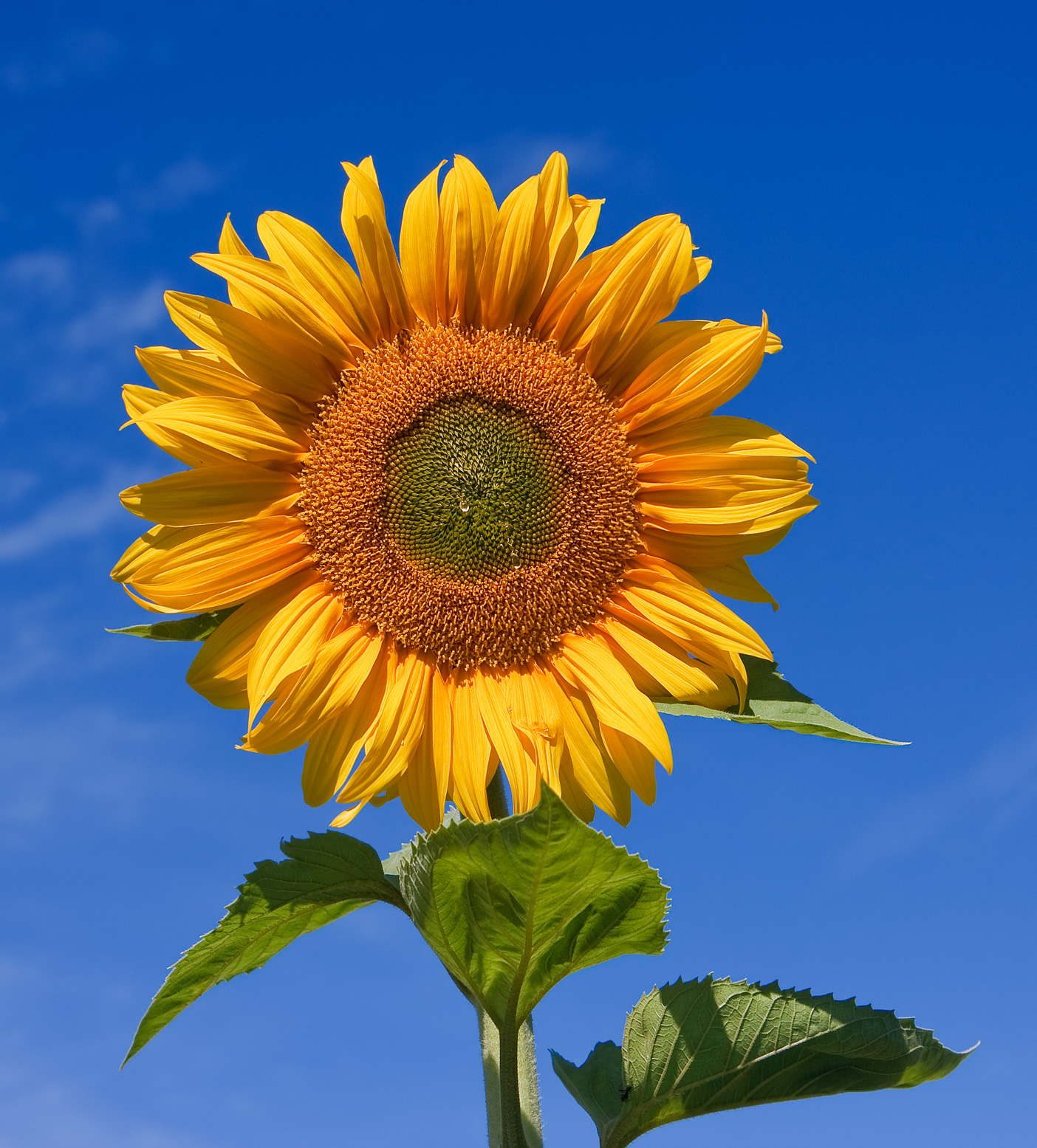

Asteraceae
daisy family
sporophyte generation
larger and nutritionally independent
gametophyte generation
reduced to only a few microscopic cells
double fertilization
process in the flowering plant life cycle in which there are two fertilizations; one results in a zygote and the second results in an endosperm
antipodal cells
three haploid cells; situated at the opposite end to the micropyle; provide nourishment to the egg cell; rich in lipid content; form the basis of endosperm production
polar nuclei
either of two female haploid nuclei, in the embryo sac of flowers, that fuse to produce a diploid nucleus, which combines with a male nucleus to form the endosperm
synergids
two specialized cells that lie adjacent to the egg cell in the female gametophyte of angiosperms and play an essential role in pollen tube guidance and function
endosperm
3 n nutritive tissue formed at some point in the development of all angiosperm seeds
vessel elements
water-conducting feature in the xylem
sieve-tube elements
carbohydrate-conducting feature in the phloem; specialized cells that function in the conduction of sugars
apomixis
type of reproduction in which fruits and seeds are formed asexually
Drimys piperita

Archaefructus
oldest known fossil angiosperm (125 million years old from northeastern China)

Archaeanthus linnenbergeri
100 mya; scars on reproductive axis (receptacle

Amborella trichopoda
Amborellales; most basal angiosperm
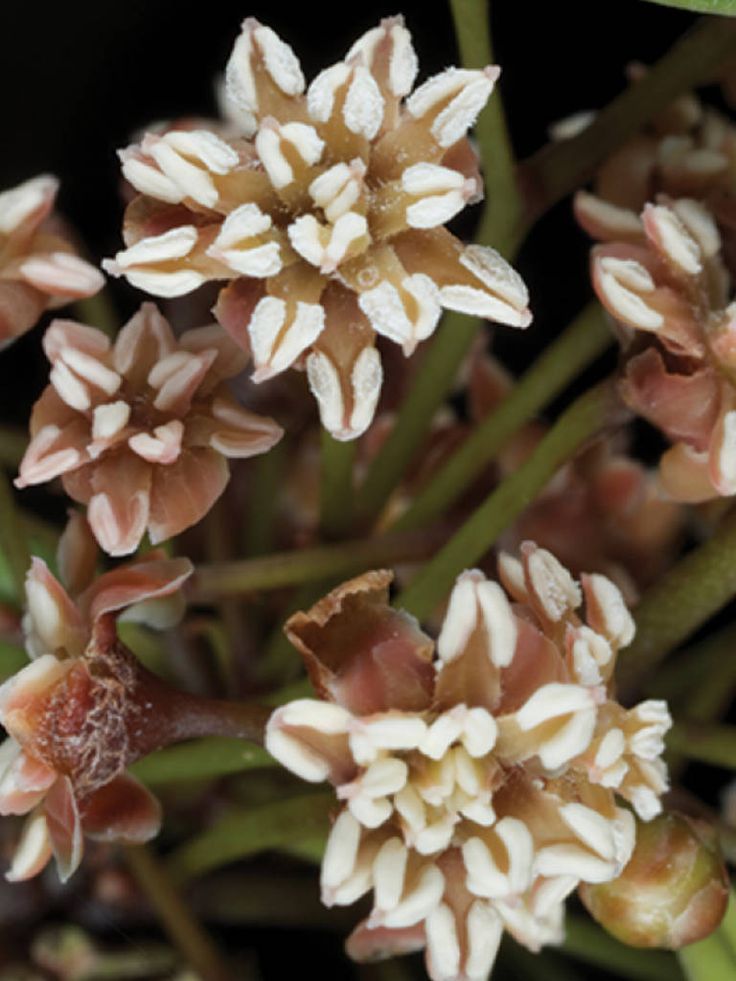

Nymphea odorata
basal angiosperm; Nymphaeales; water lily

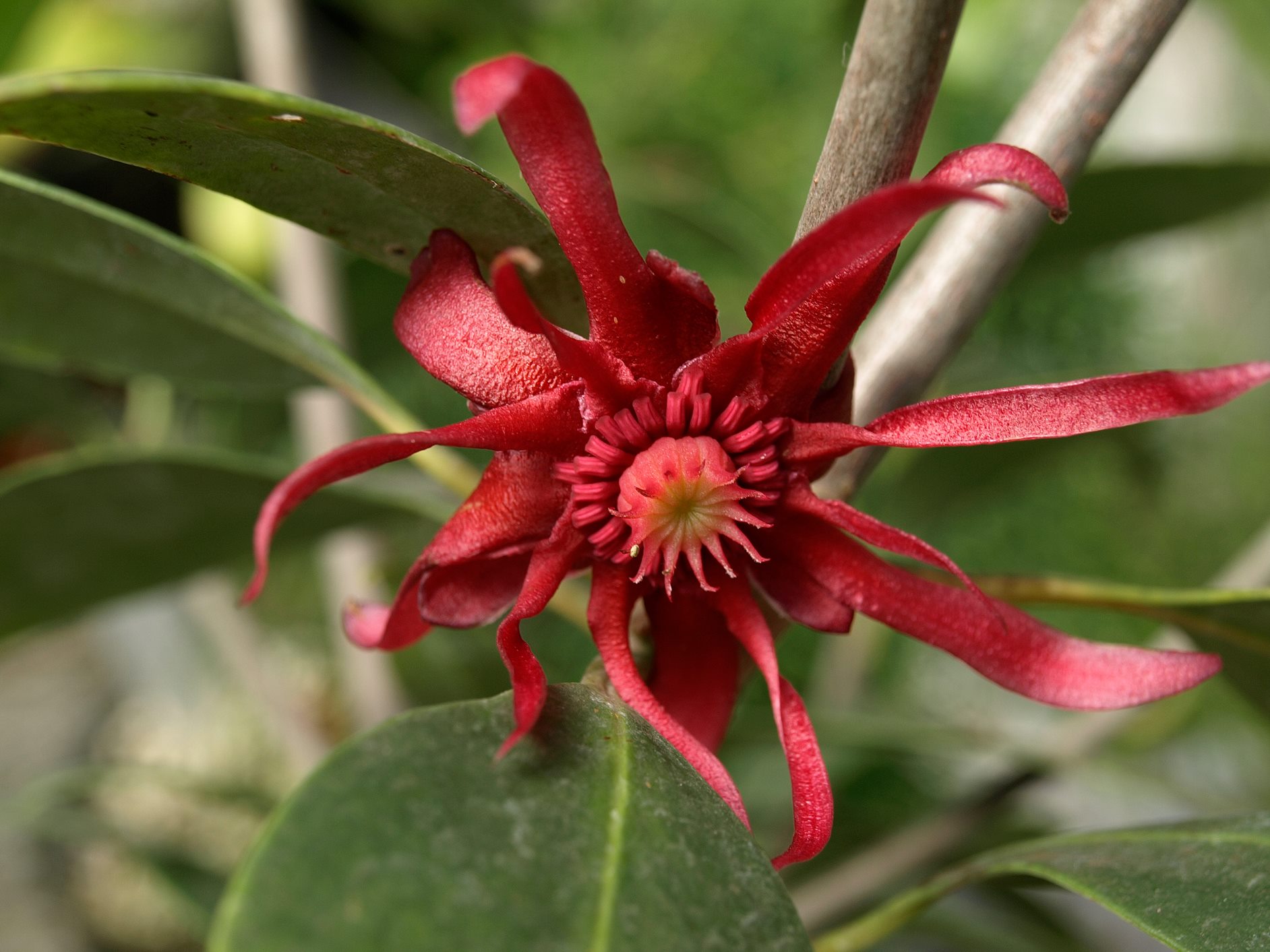
Illicium verum
basal angiosperm; Illiciales; star anise

Magnolia grandiflora
magnoliid; core angiosperm

basal angiosperm
one of three groups of angiosperms thought to be ancestral to all other flowering plants
core angiosperm
group including most angiosperm species; divided into three subgroups: magnoliids, monocots, and eudicots
magnoliid
one of the groups of flowering plants; core angiosperms once classified as “dicots,” but molecular evidence indicates they are neither eudicots nor monocots; includes species in magnolia, laurel, and black pepper families, several related families