Space Science Learning Experience 1
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
Astronomy is what two types of sciences?
Historical science and observational science
Light-year
The distance light travels in one year / 5.8 × 1012 miles
How does nature reveal itself?
observations, experiments, models, and testing
What are the most common elements in the universe?
hydrogen and helium
Aristotle’s evidence for the Earth being round?
The shadow on the moon is always round, and not everyone sees the same stars overhead.
parallax
shift in direction of an object due to the observer moving
stellar parallax
shift in apparent direction of a star due to Earth’s orbit
What did Eratothenes discover?
He calculated the Earth’s circumference and discovered that the Earth is round by using 2 wells in Alexandria and Syene, and observing the shadows (or lack of shadows)
What did Hipparchus do?
He measured the position of objects in the sky and calculated the brightest and dimmest stars, as well as developed a system with celestial coordinates. He also hypothesized precession.
precession
The slight “wobble” of the Earth; the slow circular motion of Earth’s axis rotation
What is precession caused by?
The gravitational pole of the moon and sun
How many years does it take for the North Star to change due to precession?
Approximately 26,000 years
What did Ptolemy discover?
He created a method that predicted the positions of the sun, moon, and planets in the sky
What is the Epicycle/Ptolemaic Theory?
“wheels within wheels” or “circles within circles”
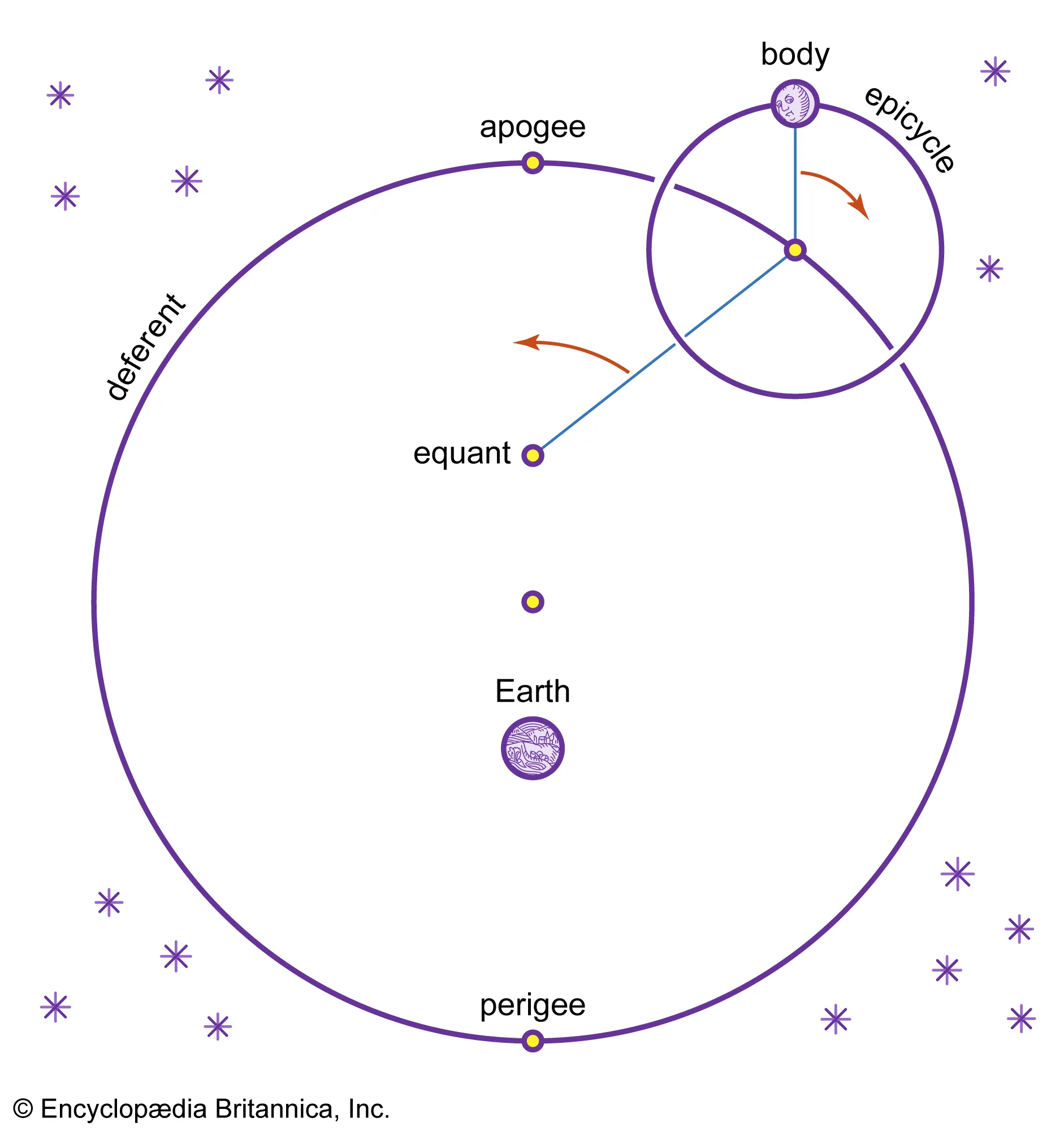
retrograde motion
the apparent motion when planets seem to go backwards, and then speed up
What were the two major flaws that set Ptolemy back?
The belief that the Earth is the most important, and thus in the center, and that everything is in a perfect circle
zenith
the point directly above your head when you look up and the sky looks like a dome
astrology
the thought that the positions of the bodies among the stars are thought to hold the key to understanding life
What did Nicolaus Copernicus discover?
He developed a sun centered (heliocentric) model of the solar system, and a picture of where all the planets belong.
What did Galileo Galilei discover?
He studied motion and the action of forces on bodies, and created the first telescope
mean solar day
interval when the sun is at the celestial median from one day to the next due to Earth’s rotation; takes 4 minutes longer to return to the median
sideral
interval when the stars are at the celestial median from one day to the next (star time)
What did Aristotle believe?
that the universe was symmetrical, spherical, and finite with the earth at the center
How fast does light travel?
9.46 × 1012 kilometers per second
How many planets are currently in our solar system?
8
The smallest piece of an element that still has all the properties of the element is called?
an atom
The south celestial pole and the north celestial pole lie in the sky directly above what?
the earth’s axis
On the celestial sphere, halfway between the celestial pole lies what?
celestial equator
The star that is currently closest to the North Celestial Pole is what?
Polaris
Within a constellation, a smaller, recognizable pattern of stars is often called what?
an asterism
Astronomers divide the whole sky into 88 sections called what?
constellations
What are the steps of the scientific method?
Define the problem, gather data, hypothesis, test the hypothesis, retest, conclusions
How many tests does it take to prove a hypothesis false?
1 or 2
How many tests does it take to prove a hypothesis true?
infinite
What is the order of the solar system?
Sun, Mercury, Venus, Earth, Mars, asteroid belt, Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, Neptune
speed of light
c = 3×108 m/s = 300,000 km/s
age of the Earth
4.5 billion years
age of the universe
13.8 billion years
Structure of the universe / smallest to biggest
atoms, molecules, meteors, comets, planets, sun, solar system, Milky Way galaxy, clusters of galaxies, universe
Which direction do planets travel when looking at the solar system from above?
counterclockwise
Which direction do the sun, moon, and planets travel from earth?
Rise in the east, set in the west - move eastward in our sky
right ascension
longitude of the sky (west and east), counted in hours/minutes/seconds
declination
how far above or below the celestial equator (north and south), measured in degrees
If you are standing at the equator, where is Polaris?
the northern horizon
If you are standing at the North Pole, where is Polaris?
directly overhead at the zenith
altitude
angle height above the horizon
azimuth
compass direction is the left/right angular measure with respect to the horizon (North = 0 or 360; East = 90; South = 180; West = 270)
What is the angular size of the sun and moon from earth?
½ degree
How quickly does the earth rotate?
¼ degree per minute, 15 degrees per hour
How many degrees does earth move around the sun per day/that the sun seems to move in our sky?
1 degree
The same side of the moon always faces the earth
True
Pythagoras
used mathematics to describe natural phenomena, proposed earth is spherical and revolved around a distant center, studied phases of the moon, lunar eclipses (saw the shadow on the moon was curved)
Aristotle
proposed the earth was spherical, believed the universe was symmetrical, spherical, and finite with earth at the center, the circle was the perfect shape
Aristarchus
first proposed heliocentrism (wasn't taken seriously), estimated size of the moon, estimated earth-moon distance using mathematics/lunar eclipses
Copernicus
founded the heliocentric model of the solar system, explained the position of planets around the sun
Hipparchus
magnitudes of the stars, precession
Galileo
used a telescope to discover the phases of Venus and Jupiter’s moons; provided compelling evidence for the heliocentric model
What causes seasons?
The way the Earth tilts on its axis; causes light to hit more directly and heat more effectively, and effects the amount of daylight
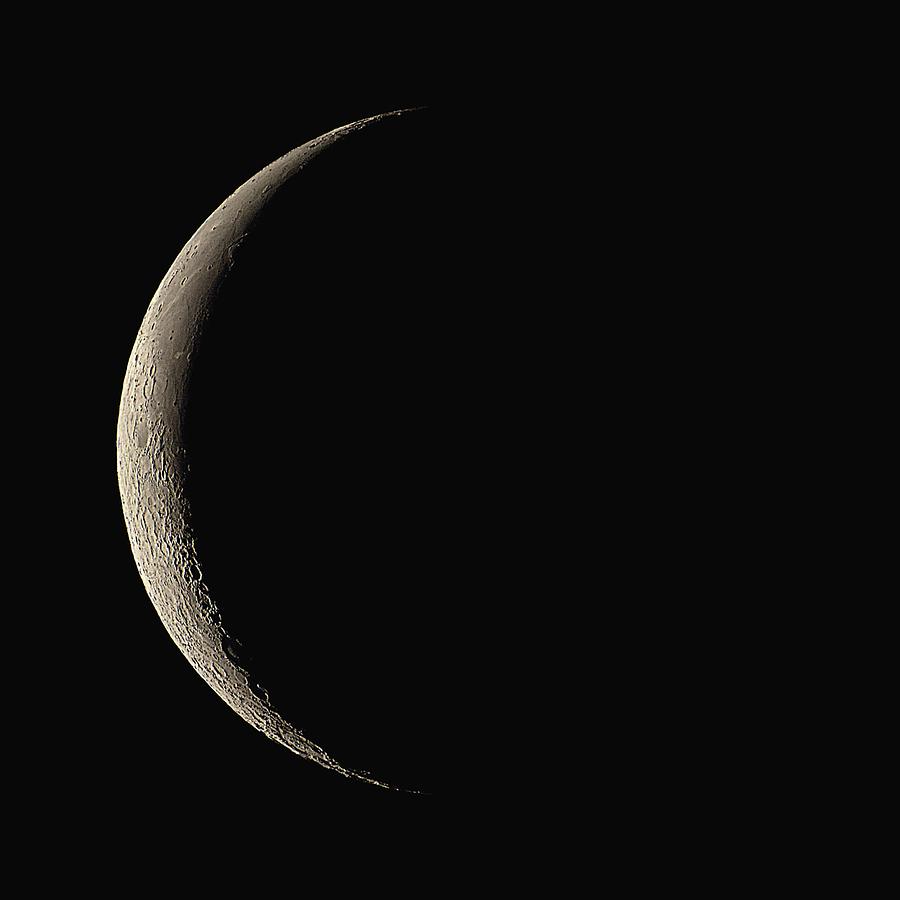

What phase of the moon is this?
waning crescent
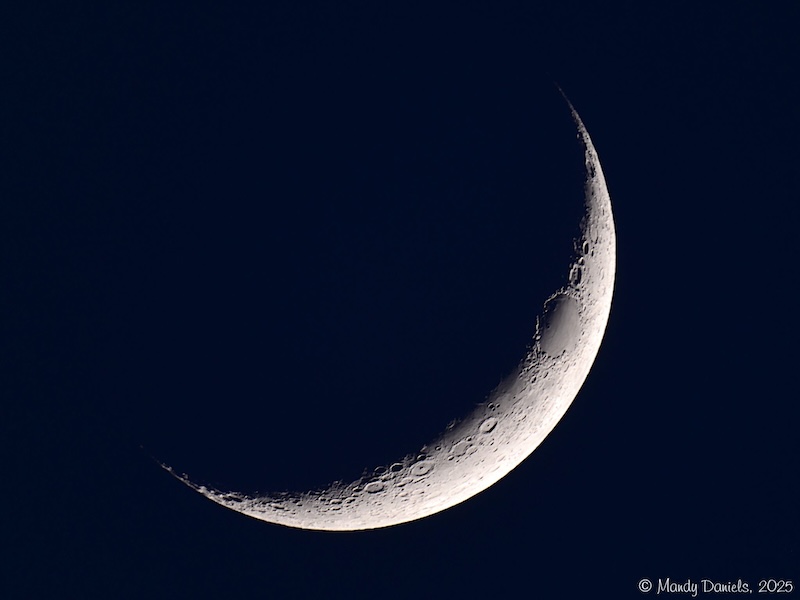

What phase of the moon is this?
waxing crescent

What phase of the moon is this?
waning gibbous
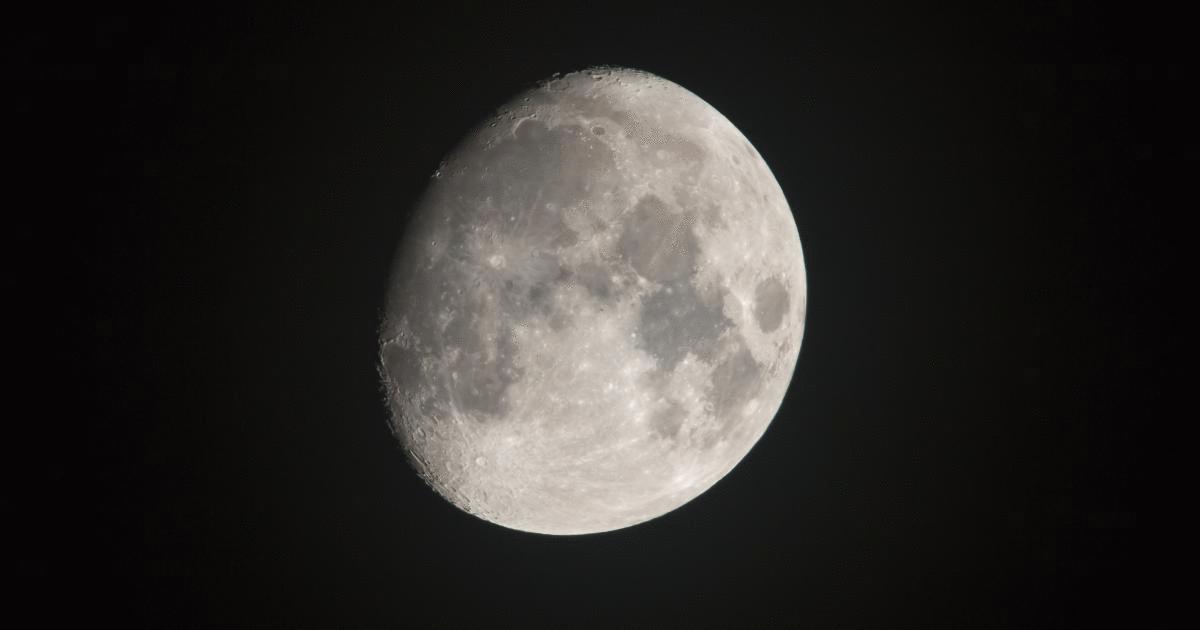

What phase of the moon is this?
waxing gibbous
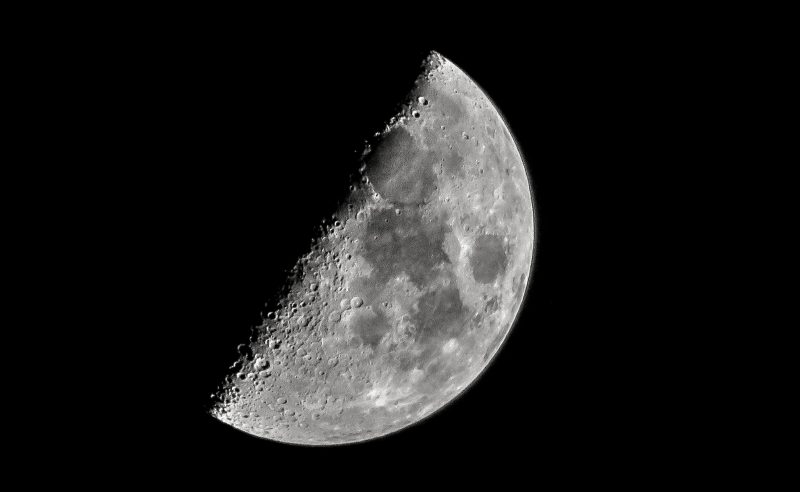

What phase of the moon is this?
first quarter
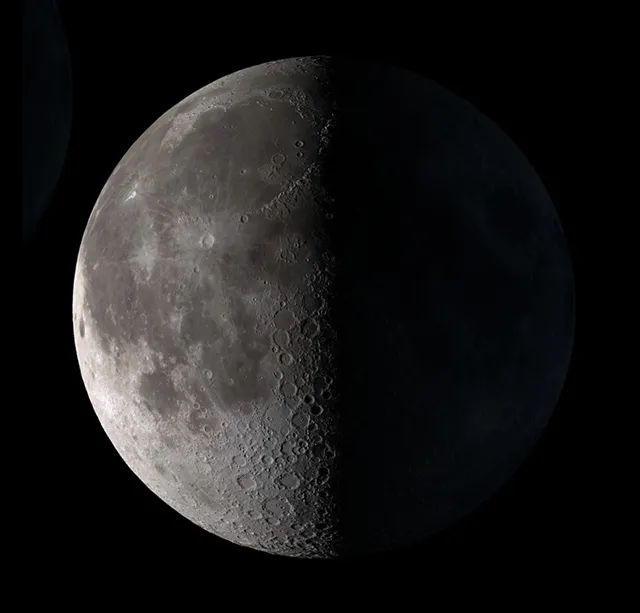

What phase of the moon is this?
third/last quarter
synodic period
29.5 days, new moon to new moon
lunar sidereal period
27.3 days, period for the moon to make a complete orbit around earth
aphelion
the point when the earth is farthest away from the sun (94.5 million miles, July 4th)
perihelion
the point when the earth is closest to the sun (91.4 million miles, January 3)
perigee
when the moon is closest from the earth
apogee
when the moon is farthest from the earth