Chemistry Final
4.9(8)
Card Sorting
1/46
Last updated 12:24 AM on 12/9/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
47 Terms
1
New cards
atom
the smallest particle of an atom that still has the properties of that atom
2
New cards
What makes an atom neutral?
if there is the same number of protons and electrons
3
New cards
electron cloud
the space around the nucleus where the electrons orbit
4
New cards
electrons
negatively charged subatomic particles that help make up an atom
5
New cards
What determines which element an atom is?
the number of protons
6
New cards
neutrons
subatomic particles that do not have a charge
7
New cards
atomic number
the number of protons in an atom
8
New cards
mass number
the atomic mass of an atom (protons + neutrons)
9
New cards
1 amu =
1/12 of a carbon-12 atom
10
New cards
hyphen notation
name of the element - mass number of element
11
New cards
How are cations formed?
The atom loses electrons creating a positive charge
12
New cards
How are anions formed?
An atom gains electrons, creating a negative charge
13
New cards
What type of element generally forms cations?
Metals
14
New cards
What is the formula for atomic mass?
AMU= (mass A x A%) + (mass B x B%)
15
New cards
billard ball model
created by Democritius, the proposition that atoms existed

16
New cards
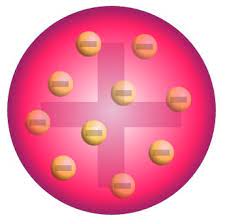
plum pudding model
created by jj thompson, discovered electrons
17
New cards
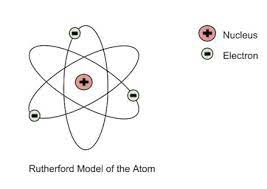
rutherford model
created by ernest rutherford, discovered that the middle of an atom was made up of a nucleus
18
New cards
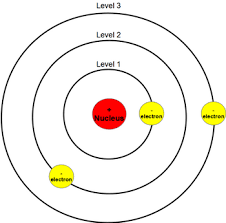
Bohrs/Planetary Model
created by niels bohr, discovered electrons could jump between atoms by gaining or losing energy
19
New cards
The Quantum Mechanical model
created by multiple people, discovered the electrons moved in a fuzzy cloud and less of exact orbits
20
New cards
Who is attributed with the idea of arranging the known elements of his time into a model based on their chemical and physical properties?
Dmitri Mendelev
21
New cards
Who arranged the periodic table of elements by atomic number?
Henry Mosely
22
New cards
The periodic law states there is a periodic repetition of physical and chemical properties of the elements...
when they are arranged in order of increasing atomic number
23
New cards
valence electrons
electrons on the outer shell of an atom
24
New cards
What are the horizontal rows of the periodic table called?
periods
25
New cards
What do elements in the same periodic group have in common?
same valence configuration, same number of valence electrons, similar chemical properties
26
New cards
What do elements in the same periodic periods have in common?
same number of electron shells
27
New cards
What does PEL stand for?
Principal energy levels
28
New cards
How many elements are in the 2nd and 3rd rows of the periodic table?
eight
29
New cards
How many valence electrons do atoms in group 17 have?
7 or 17
30
New cards
What are the three classes of elements?
Metals, metalliods, non-metal
31
New cards
What elements are metalliods?
B, Si, As, Te, Ge, Sb
32
New cards
Which class of elements is dull, brittle, gains electrons, and are not good conductors?
non-metals
33
New cards
Which class of elements lose electrons, malleable, ductile, and are good conductors?
metals
34
New cards
most reactive group of nonmetals
17- halogens
35
New cards
completely unreactive periodic group
18- noble gases
36
New cards
which rows contain the transition metals?
3-12
37
New cards
most reactive group of metals
1- alkali metals
38
New cards
first row of the f-block elements
lathinides
39
New cards
class of elements that have both metal and nonmetal properties
metalliods
40
New cards
What is the periodic trend for atomic radius?
increases from left to right, increases down the group
41
New cards
What is the periodic trend for ionization energy?
increases from right to left across, increases up the group
42
New cards
What is the periodic trend for electronegativity?
increases from right to left across until the noble gases, increases up the group
43
New cards
what is ionization?
the amount of energy it takes to remove an electron from an atom
44
New cards
what is electronegativity?
the amount of attraction an element has to gaining electrons
45
New cards
Do metals have high or low electronegativity?
low
46
New cards
What element is most electronegative?
fluorine
47
New cards