Wound closure and suture
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
45 Terms
Define “absorbable”.
Suture that loses its strength within 90 days and is capable of being broken down by tissue
Define “non-absorbable”.
Suture material that resists enzymatic digestion and absorption
What are the two classifications of suture material?
Monofilament
Multifilament
What are the advantages of monofilament sutures?
Does not harbor bacteria
Glides or passes through tissue more easily than braided suture
Causes less tissue damage
What are the disadvantages of monofilament sutures?
Does not hold knots as well as multifilament suture
More difficult to handle
What are the advantages of multifilament sutures?
Holds knots more securely than monofilament suture
Easier to handle
Greater tensile strength
More pliable and flexible
What are the disadvantages of multifilament sutures?
More likely to harbor bacteria between the "braids"
The braided suture can cause more tissue damage while passing through
Can be coated to enhance handling and reduce tissue damage
Name four multifilament types.
Silk (Braided, & non-absorbable)
Ethibond (non absorbable and similar to silk)
Vicryl (Braided, absorbable, & most common)
Fiberwire (ortho suture)
Monofilament suture types
Prolene
non absorbable. Has memory. Vascular suture)
Nylon (Monofilament, non-absorbable all specialities. Skin closure to allow drainage. Infection
Chromic (Fast absorbing. Soaked in alcohol solution. Made of animal products. Dental, plastics, ENT)
PDS (absorbable. Fascia in abdominal wound)
Monocryl (absorbable. Skin closure)
Natural suture material
-made out of naturally occurring substances such as cellulose, animal products, and animal tissue
Synthetic suture material
made of polymers of petroleum based products
Suture size refers to the
diameter or cause of the suture thread.
As the number of 0s increase in a suture,
the smaller the diameter of the suture
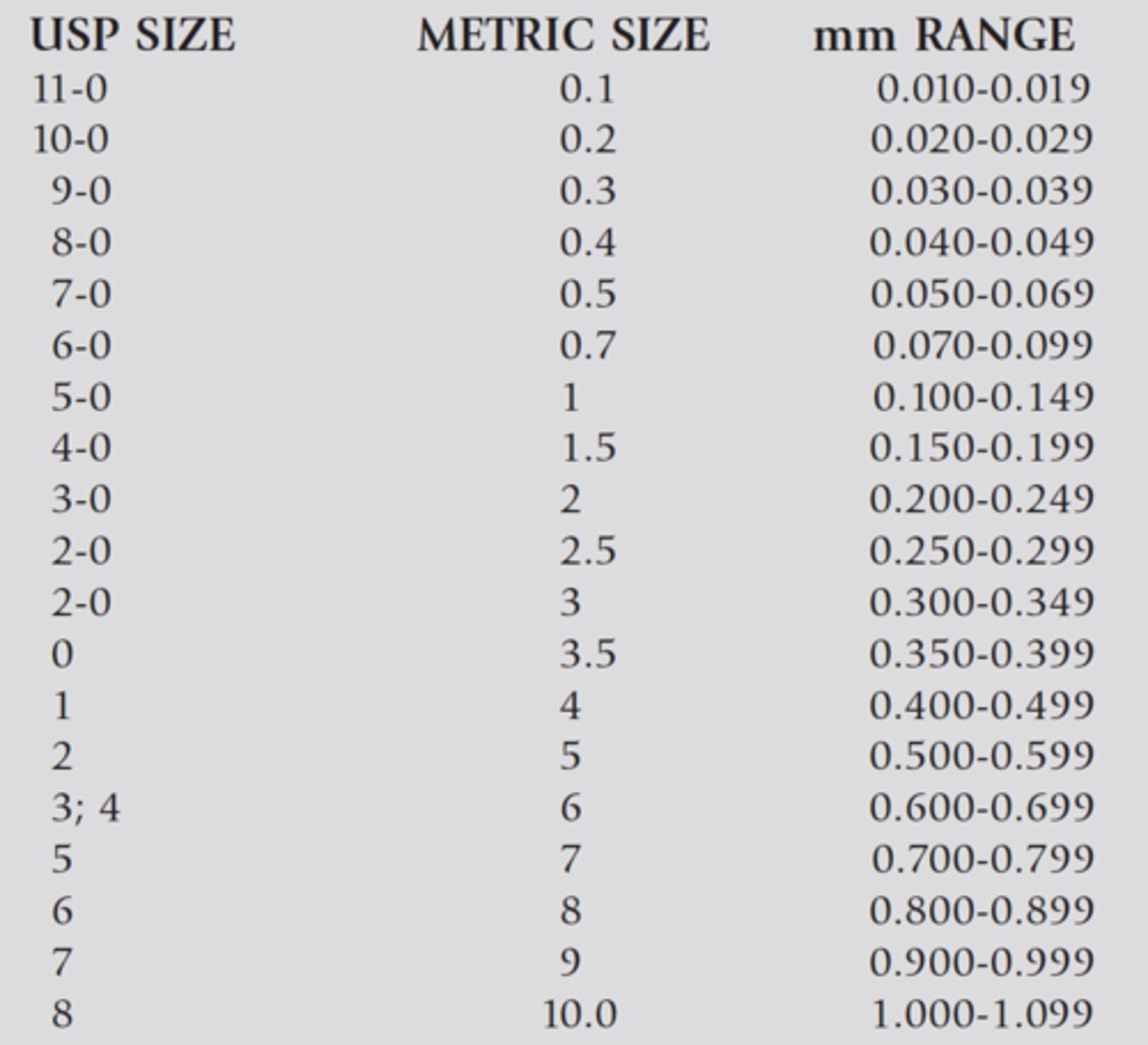
The surgeon will try to use the smallest diameter of suture
that will support the wound and tissue closure
The largest diameter suture available is a
5
The smallest diameter is a
11-0
Sizes _________ are the most commonly used sizes
1- 4- 0
Tensile strength of a suture is measure be the
force in pounds that the suture strands can withstand before it breaks
Tensile strength of the tissue being closed is what determines the
tensile strength of the suture being used
strength of the tissue and strength of the suture should be
equal
suture information on package
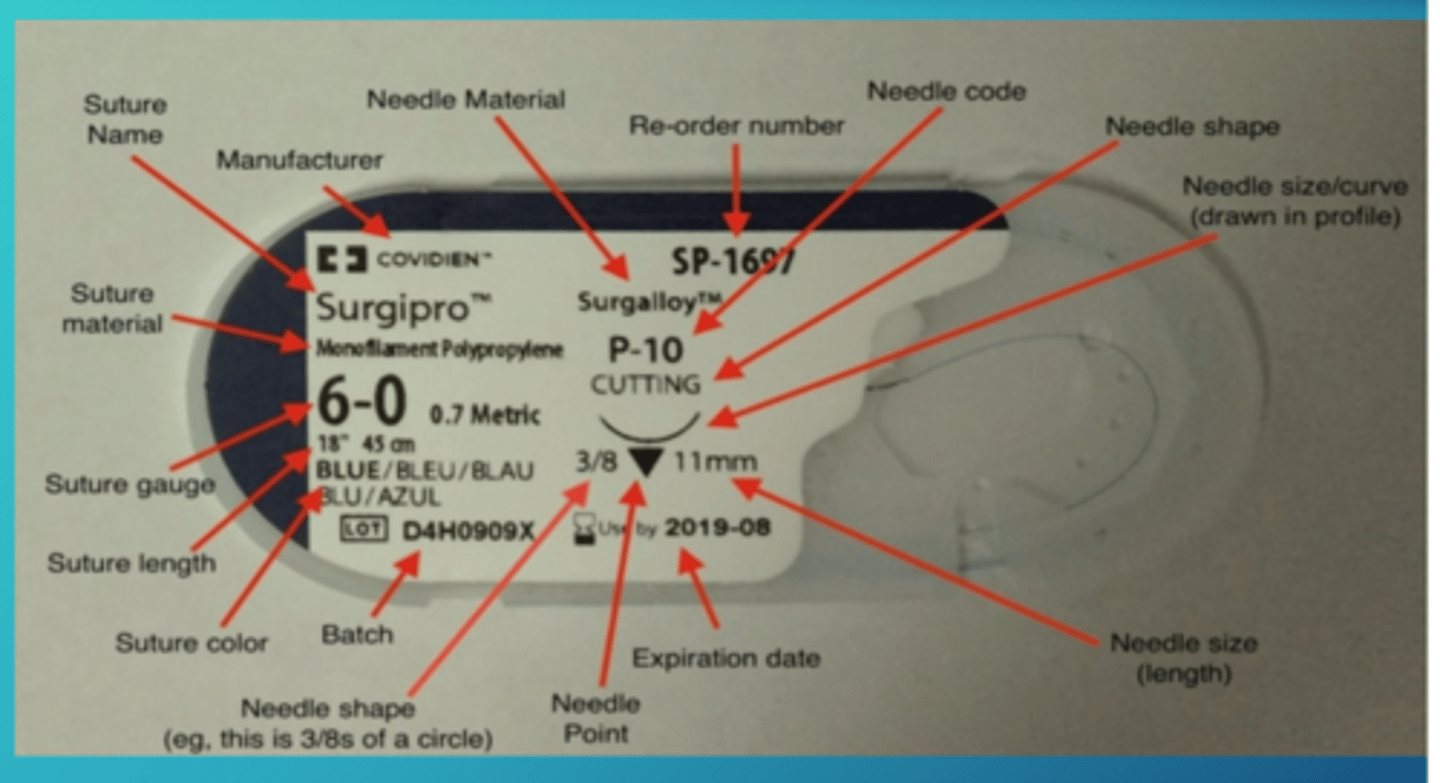
suture color coding packages

Ligatures are used to
occlude vessels for bleeding control
Deep bleeding vessels require
a longer strand
superficial bleeding vessels require
a shorter strand
Free tie
-single strand tie
-NOT on a reel
-NOT loaded onto an instrument
-Single strand of suture placed into the open hand of the surgeon
Ligature reel
-continous suture strand wound around a reel
-surgical tech should unhook the suture strand and pull out 2-3 inches for surgeon to grasp
-usually used for superficial bleeding vessels
-plastic portion is x-ray detectable
Tie on a pass
-a single strand of suture placed on an instrument/ clamp (usually on a tonsil, right angle, curved hemostat or mixter)
-used in hard to reach, deep bleeding vessels
Stick tie
-strands of suture that are swaged on (attached to) on a traumatic NEEDLE
-Loaded onto a needle driver
-used to occlude large bleeding vessels to prevent slippage and prevent uncontrolled hemorrhage
-Tie is passed directly through the vessel.
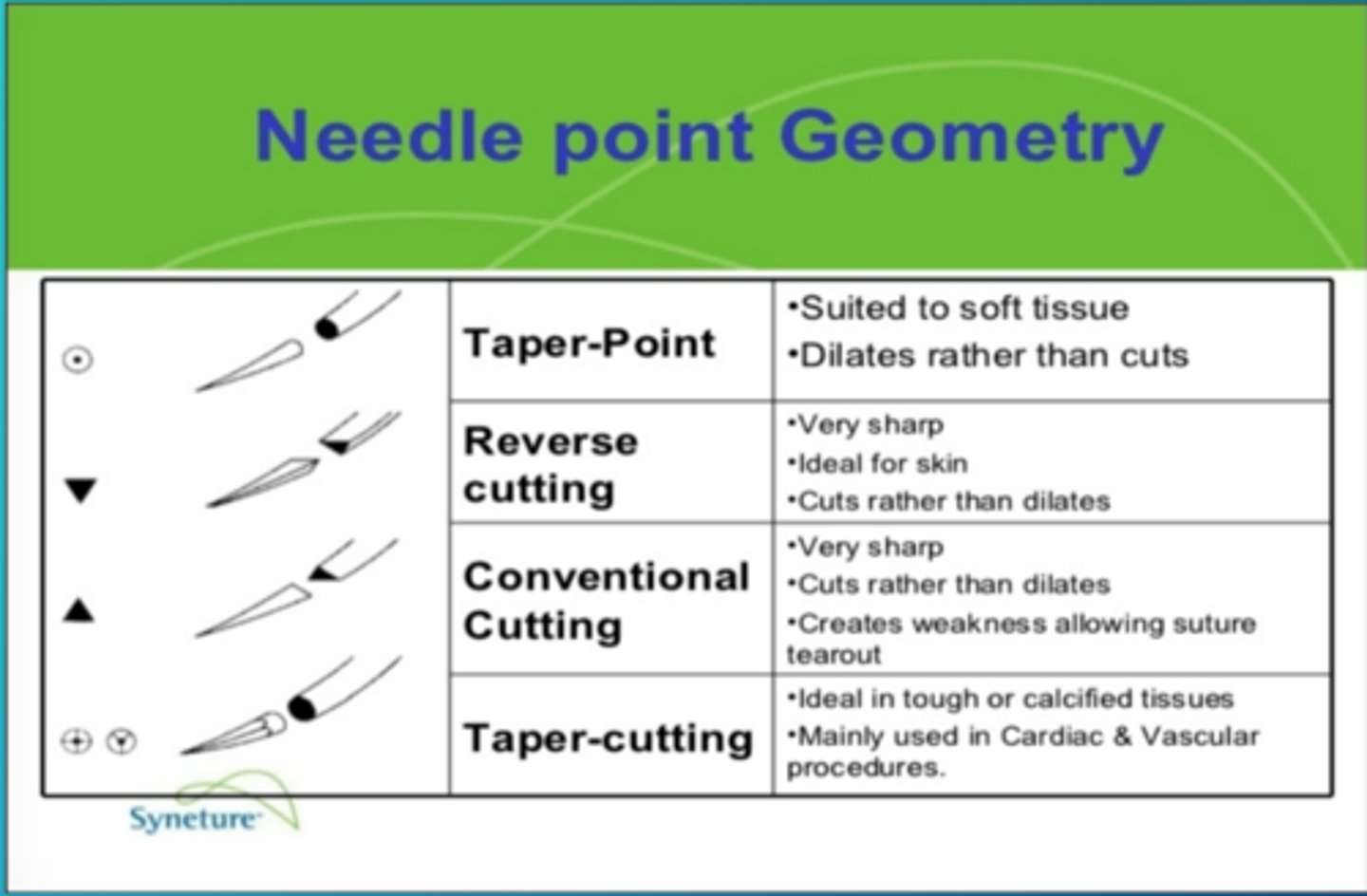
Surgical needle points:
Cutting
-used for tough tissue that is difficult to penitrate
-sharp edges of the needle actually cut the tissue as it passes through
-sclera, tendons, skin
Surgical needle points:
Tapered
-rounded shaft without a cutting edge (only sharp at the tip)
-for delicate tissue
-Tapered cut
_cutting tip that makes smaller holes in the tissue than regular cutting needles
Surgical needle points:
Blunt
-Rounded shaft that ends in a blunt tip
-for Fribale, delicate, weak tissue
cutting needles:
Conventional cutting
-3 cutting edges along inner curve of needle
-makes a small cut in the direction of the suture pull
Cutting needles:
Reverse cutting
-cutting edges in a triangular formation along the entire length of the needle shaft.
-flat edge in the direction of the suture pull reduce tissue tearing
-skin
cutting needles
side cutting
-mostly used in ophthalmic procedures procedures because they will not cut into deeper tissue
-for eyes
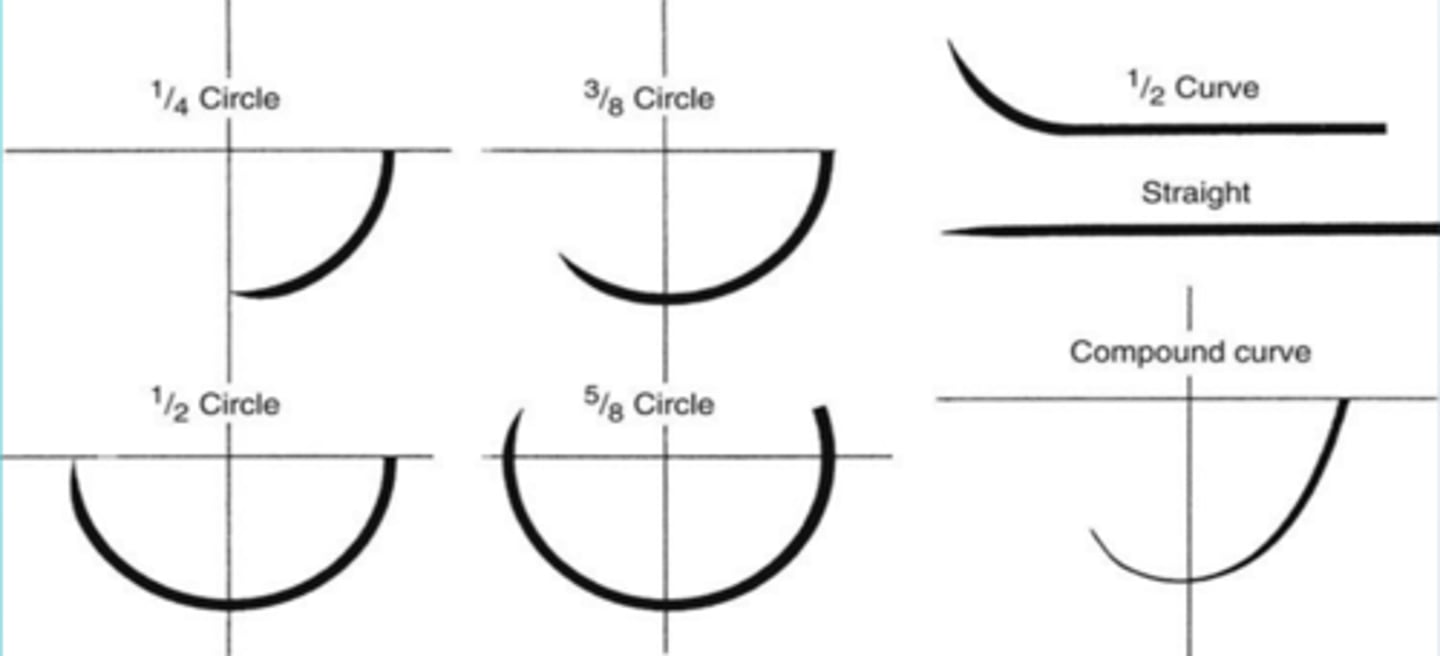
Needle point geometry
needle curves
Pop offs / controlled release
-come in packs of 8
-Needle releases from suture strand very easily with a gentle pull
-used when multiple interrupted stitches are placed
Runner
-needle does not release from suture with out cutting it off
-1 suture per pack
-used when one continuous suture is going to be placed
closure of an abdominal wound
1. peritoneum (thin membrane lining the abdominal cavity under the posterior fascia 3-0 absorbable suture frequently used)
2. Fascia (Layer through connective tissue that covers muscle. Primary support layer of soft tissue. Must be closed securely)
-heals slowly
-Heavy gauge (1, 0) non-absorbable suture is ideal
3. muscle layer
-typically is not closed with the suture
-muscle does not tolerate suture well
-muscles are normally split and reattached rather than incised so the need for suture is rarely present.
-if suture is needed it should bd sewn back together loosely with absorbable suture.
4. Subcutaneous tissue
-does not tolerate suture well
-fatty layer (fat is difficult to suture)
5. subcuticular layer
-area of tough connective tissue just beneath the skin
-closure of this layer minimizes scarring
-small gauge, absorbable sutures are preferred (3, 0)
6. Skin (final)
-this layer may be closed with absorbable or non-absorbable sutures
-can be continuous running suture or interrupted suture technique
-can also be closed using staples
suturing techniques
continous (runner)
-a single strand of suture placed as a serious or sticks down the length of the incision
-not ideal for wounds under tension
-tied at each end of the incision
-various types of techniques
-if any portion of the stick breaks, the entire closure is jeopardized
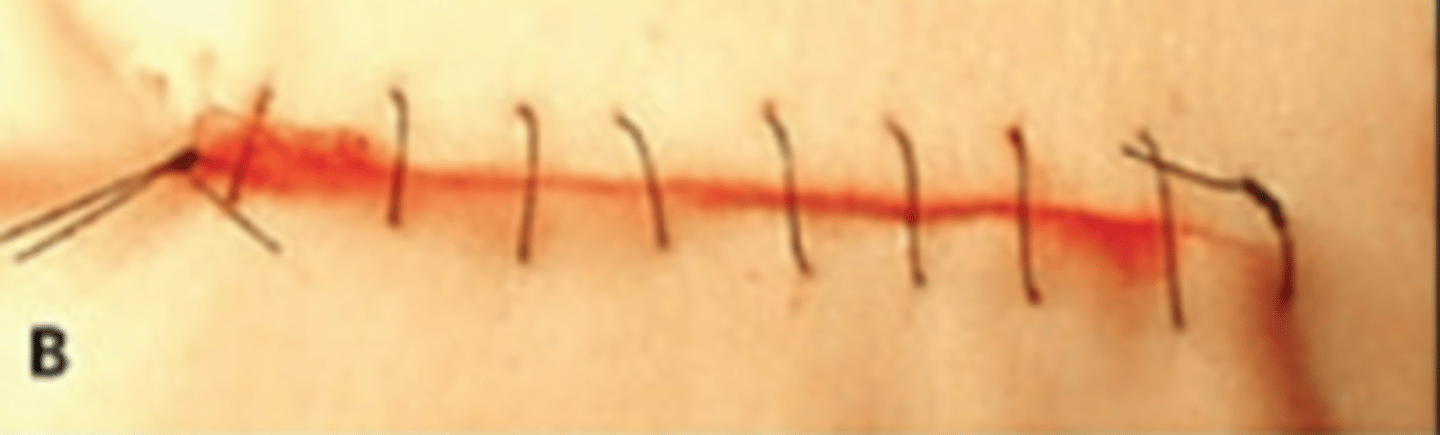

suturing techniques
interrupted
-ideal for wounds under tension
-infected wounds
-fascia
-each stitch is individually placed, tied, and cut down the entire length of the incision
-various types of techniques
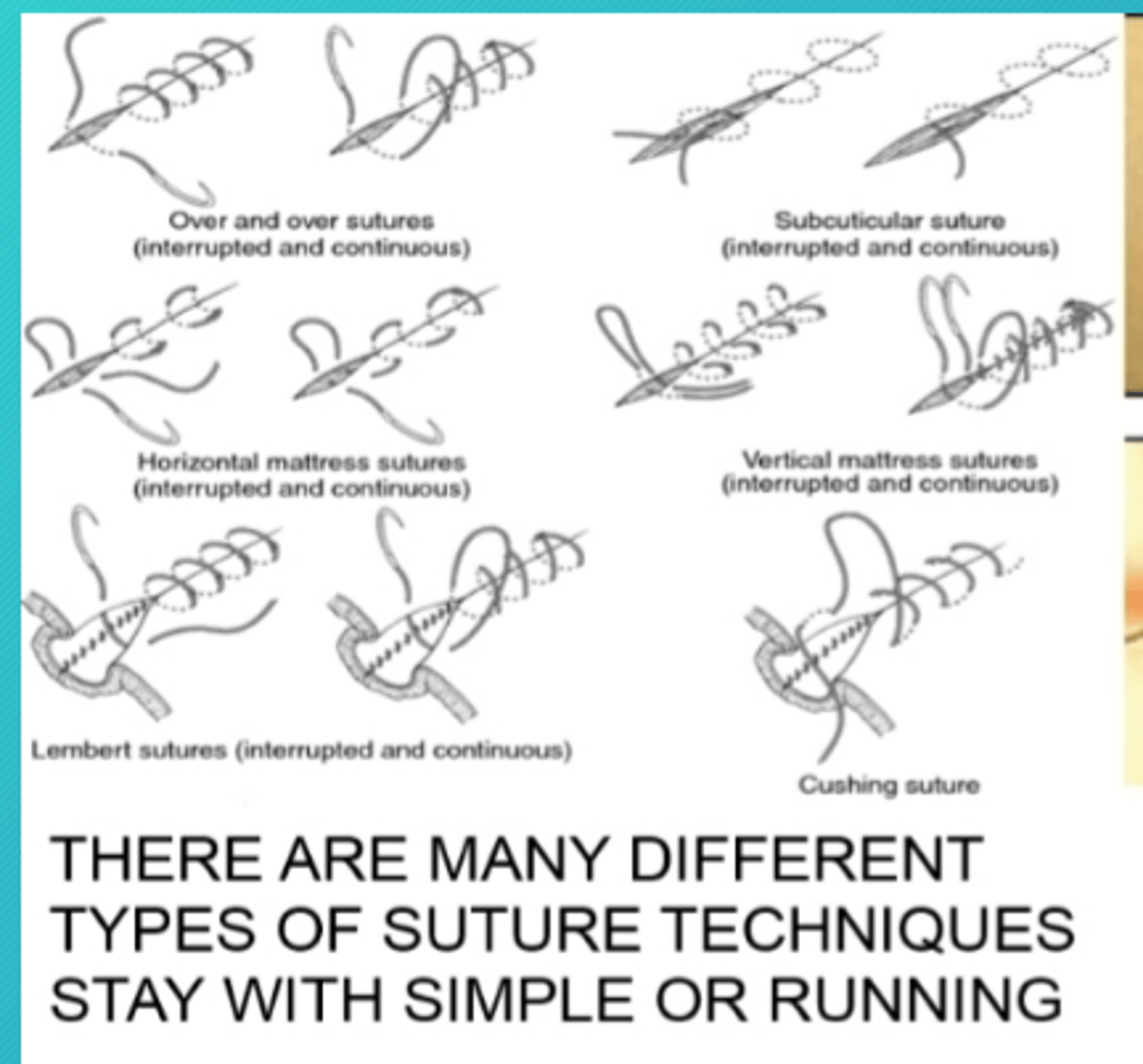
Types of suture techniques
-continuous running stitch (simple continuous)
-continous running, interlocking stitch (baseball stitch)
-subcuticular (continous)
-purse string stitch (drawstring) to close off an opening (appendix)
-simple interrupted
-horozontal mattress( interrupted)
-vertical mattress (interrupted)
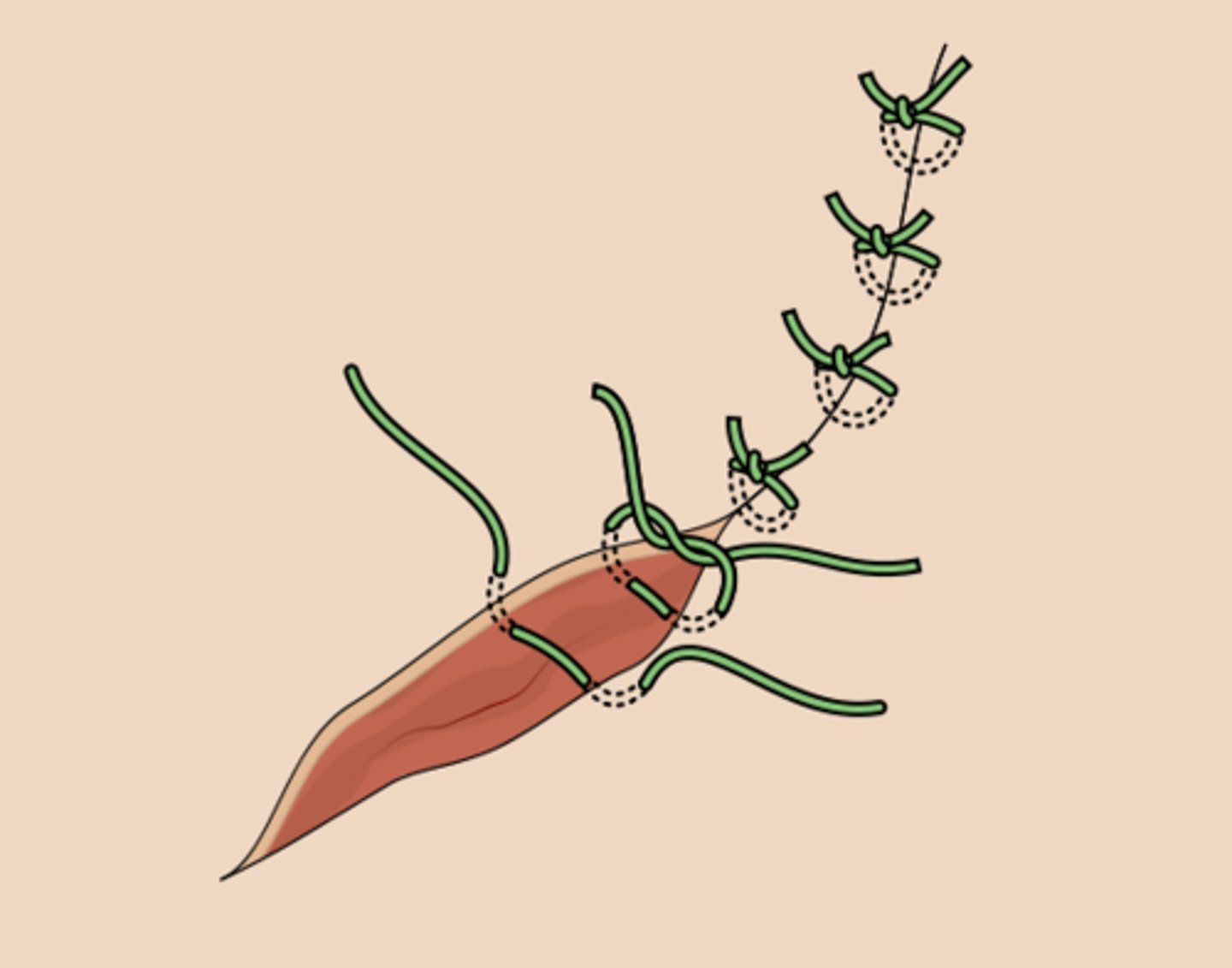
traction sutures
-used to retract tissue or sutures that are not well controlled with an instrument retractor
-non-absorbable sutures are placed in the suture and the ends are clamped with a hemostat and pulled to the side of the operative site
-examples: skin flaps, sclera of the eye, myocardium of the heart, tongue
skin stapler
-used to approximate wound edges for skin closure
-disposable devise that dispenses a single staple during each pull of the trigger
-can be wide, regular or small with
-use adson forceps with teeth during skin stapling to assist in edge approximation
-can also be used to close fascia