Grade 10 Bio Microscope Quiz
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
How a Microscope Works
Bending Light: The objective (bottom) convex lens magnifies and focuses (bends) the image inside the body tube and the ocular convex (top) lens of a microscope magnifies it (again).
The Parts of a Light Microscope
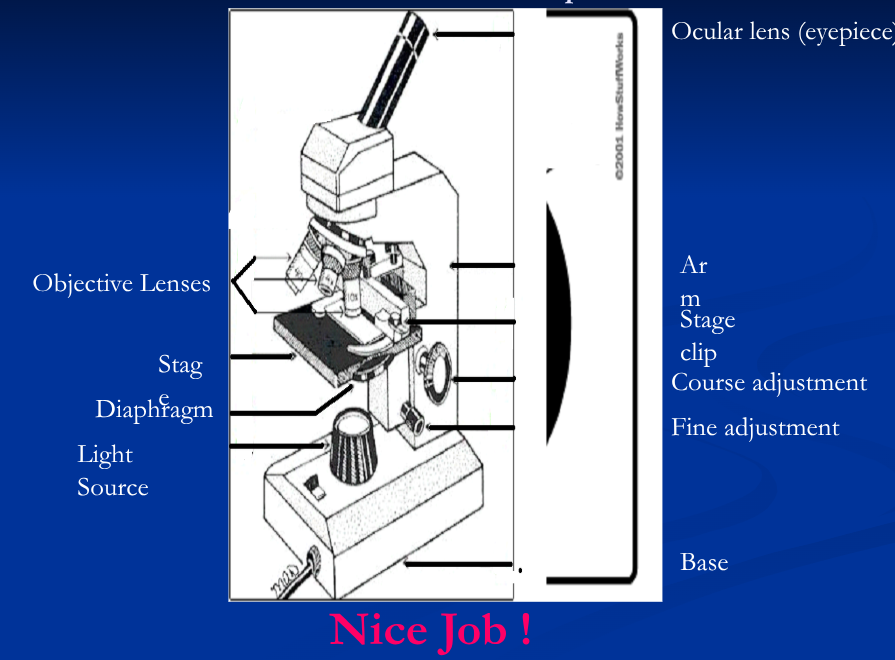
Light source
Could be a mirror, but most likely it is a bulb built into the base
Diaphragm
Adjusts the amount of light striking an object
Ocular lens
Gathers light and magnifies image. Usually 10X.
Objective lens
Magnifies objects (4X, 10X, 40X) and focuses light to your eye.
Stage
Holds slide. Can be moved using the coarse or fine adjustment knobs to bring the object into focus.
Stage clips
Hold slide in place
Base and arm
Structural support for the microscope
Resolution
the ability to distinguish between two objects that are very close together
Electron versus light microscopes
Light microscopes are limited by their resolution.
Light microscopes cannot produce clear images of objects smaller than 0.2 micrometers (1 mm = 1000 μm)
Electron microscopes use beams of electrons, rather than light, to produce images
Electron microscopes can view objects as small as the diameter of an atom
Types of Electron Microscopes
Specimens from electron microscopy must be preserved and dehydrated, so living cells cannot be viewed
Transmission electron microscopes (TEMs) pass a beam of electron through a thin specimen
Scanning electron microscopes (SEMs) scan a beam of electrons over the surface of a specimen
Caring for a Microscope
Clean only with a soft cloth/tissue
Make sure it’s on a flat surface
Don’t bang it
Carry it with 2 HANDS…one on the arm and the other on the base
Using a Microscope
Start on the lowest magnification
Don’t use the coarse adjustment knob on high magnification…you’ll break the slide!!!
Place slide on stage and lock clips
Adjust light source
Use fine adjustment to focus
Magnification
To determine your magnification…you just multiply the ocular lens by the objective lens
Ocular 10x Objective 40x: 10 x 40 = 400
So the object is 400 times “larger”
Total Magnification
Total Magnification : ocular (10x) times the objective lens
Low power : 10x * 4x = 40x
Medium power : 10x * 10x = 100x
High power : 10x * 40x = 400x
Field Diameter
distance across the field of view
note: 1 mm = 1000 μm
Low power [40x] = 4.5 mm = 4 500 μm
Medium power [100x] = 1.8 mm = 1 800 μm
High power [400x] = 0.45 mm = 450 μm
Finding Field Diameter
If you find field diameter on a low power magnification, you can use this to calculate the field diameter at higher magnifications
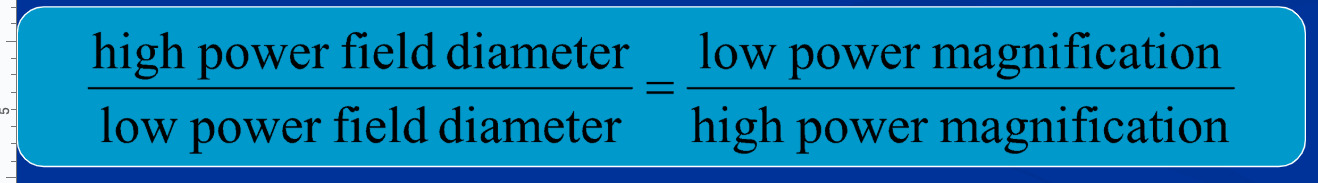
Field of View
whole circular area that you see when you look through the microscope
Calculating Estimated Actual Size of a Specimen
Field diameter
Determine by evaluating which objective lens was used to view specimen
Ensure units are μm
# of specimens fitting across field diameter
Estimate how many specimens fit across the field diameter width wise
