Anatomy Final
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
What endocrine organ is larger in children than adults?
Thymus because it produces T cell for the immune system
What is the difference between an endocrine and an exocrine gland?
Endocrine glands are ductless and release hormones into the blood, exocrine glands have ducts and secrete substances like sweat.
What are the three sperm supporting glands?
Prostate, bulbourethral, and seminal vesicles.
What are the three meninges of the brain from superficial to deep?
Dura, arachnoid, pia.
What is the largest portion of the brain?
Cerebrum.
What type of epithelial tissue lines the renal pelvis?
Transitional epithelium.
What hormones are produced by the posterior pituitary gland?
none the posterior pituitary stores hormones
What hormones are produced by the anterior pituitary gland?
growth hormones, TSH, ACTH, FSH, LH, and prolactin
Why should the pituitary be considered two different glands?
Because the anterior pituitary makes hormones while the posterior pituitary stores hormones. Anterior is made of epithelial tissue and posterior is made of nervous tissue
What are secondary sex characteristics in males?
Deep voice, facial hair, and Adam's apple.
What are secondary sex characteristics in females?
breast, wide hips, high voice
What are the functions of the kidneys?
Filter blood, maintain electrolyte balance, blood volume and pressure, activate vitamin D, and produce erythropoietin.
Which muscle pulls the testes towards the body?
Cremaster muscle.
What hormone increases body heat production?
Thyroid hormones, T4 and T3.
What are the three mature bone cell types and their functions?
Osteoblasts build bone, osteoclasts break down bone, and osteocytes maintain bone.
What are the three parts of a neuron?
Dendrites, soma, and axon.
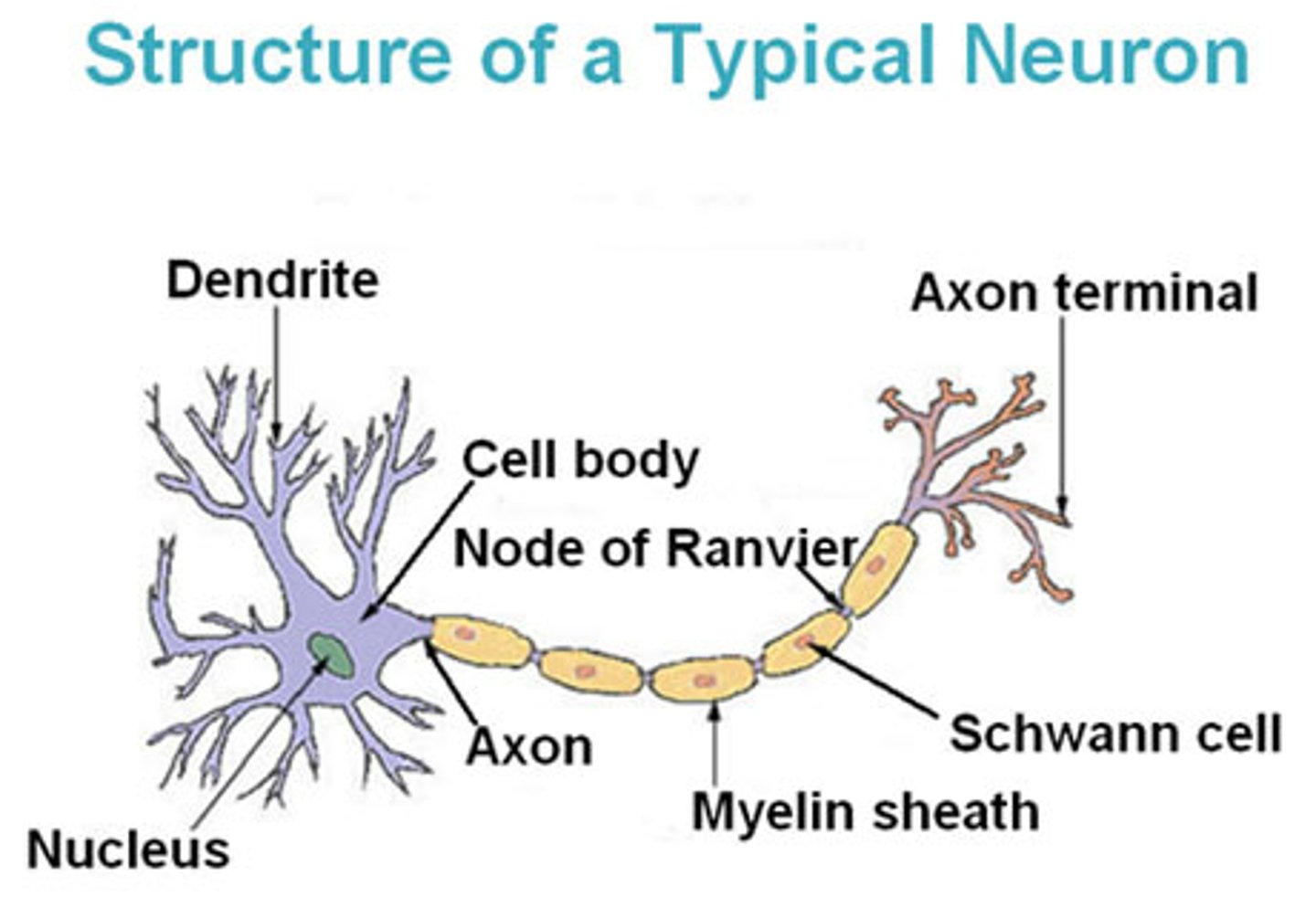
What are the rotator cuff muscles?
Supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis.
What are the layers of the epidermis from superficial to deep
Stratum corneum, lucidum, granulosum, spinosum, basale
How many floating ribs does the average human have?
4
What is the difference between spastic and flaccid paralysis?
spastic is muscle tightness and contraction flaccid is muscle weakness and inability to contract
Which bone of the forearm is lateral?
Radius.
Which tarsal bone is the largest?
Calcaneus.
What are the three types of muscle tissues?
Skeletal, cardiac, and smooth.
What are the four major tissue types?
Connective, muscle, nervous, and epithelial.
What are the four body systems for excretion and what do they expel?
urinary for nitrogenous waste, respiratory for CO2, digestive for feces, integumentary for sweat in urea
What are the types of fibers in connective tissue?
Collagenous, elastic, and reticular fibers.
What are the signs of melanoma?
asymmetry, border, color, diameter greater than ¼ in, evolution
Do babies retch?
No they typically projectile vomit.
What are the five stages of digestion in order?
Ingestion, digestion, absorption, compaction, defecation.
What is the anatomical position?
Standing upright with palms facing forward.
What are the ways to name skeletal muscles?
location, shape and size, origin and insertion, and movement.
What is the difference between origin and insertion in muscles?
Origin is the attachment point that does not move, while insertion is the attachment point that moves.
What muscle is perpendicular to the internal obliques?
external oblique
What is the blood flow through the kidney?
Renal artery, segmental arteries, interlobar arteries, arcuate arteries, interlobular arteries, afferent arterioles, glomeruli, efferent arterioles, peritubular capillaries, venules, renal vein.
What muscle is known as the kissing muscle?
Orbicularis oris.
How many heads does the gastrocnemius muscle have?
2
skeletal muscle
striated, multinucleated, voluntary
smooth muscle
nonstriated, mononucleated, involuntary
cardiac muscle
striated, mononucleated, involuntary
white blood cell types in order of most abundant to least
neutrophils, lymphocytes, monocytes, eosinophils, basophils
what blood vessles lead to the kidney
renal arteries
burn only the epidermis with redness
1st degree
burns that blister
2nd degree
burns that destroy the layers of the epidermis and dermis
3rd degree
3 meniges of the brain superficial to deep
dura, arachnoid, pi
why should the pituitary be considered two different glands
anterior makes hormones and is made of epithelial cells, posterior stores hormones and is made of nervous tissue
what is the difference between the CNS and the PNS
CNS: brain and spinal cord
PNS: everything else
olfactory nerve
I
optic nerve
II
oculomotor nerve
III
trochlear nerve
IV
trigeminal nerve
V
abducens nerve
VI
facial nerve
VII
vestibulocochlear nerve
VIII
glossopharyngeal nerve
IX
vagus nerve
X
accessory nerve
XI
hypoglosssal nerve
XII
what lobe of the brain is important for memory
temporal lobe
two things that cause spastic paralysis
cerebral palsy and MS
two things that cause flaccid paralysis
botox and ALS