Aggregate demand and supply
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Aggregate Demand
the total demand for final goods and services in an economy domestically at a given time
aggregate demand curve
a curve that shows the quantity of goods and services that households, firms, the government, and customers abroad want to buy at each price level
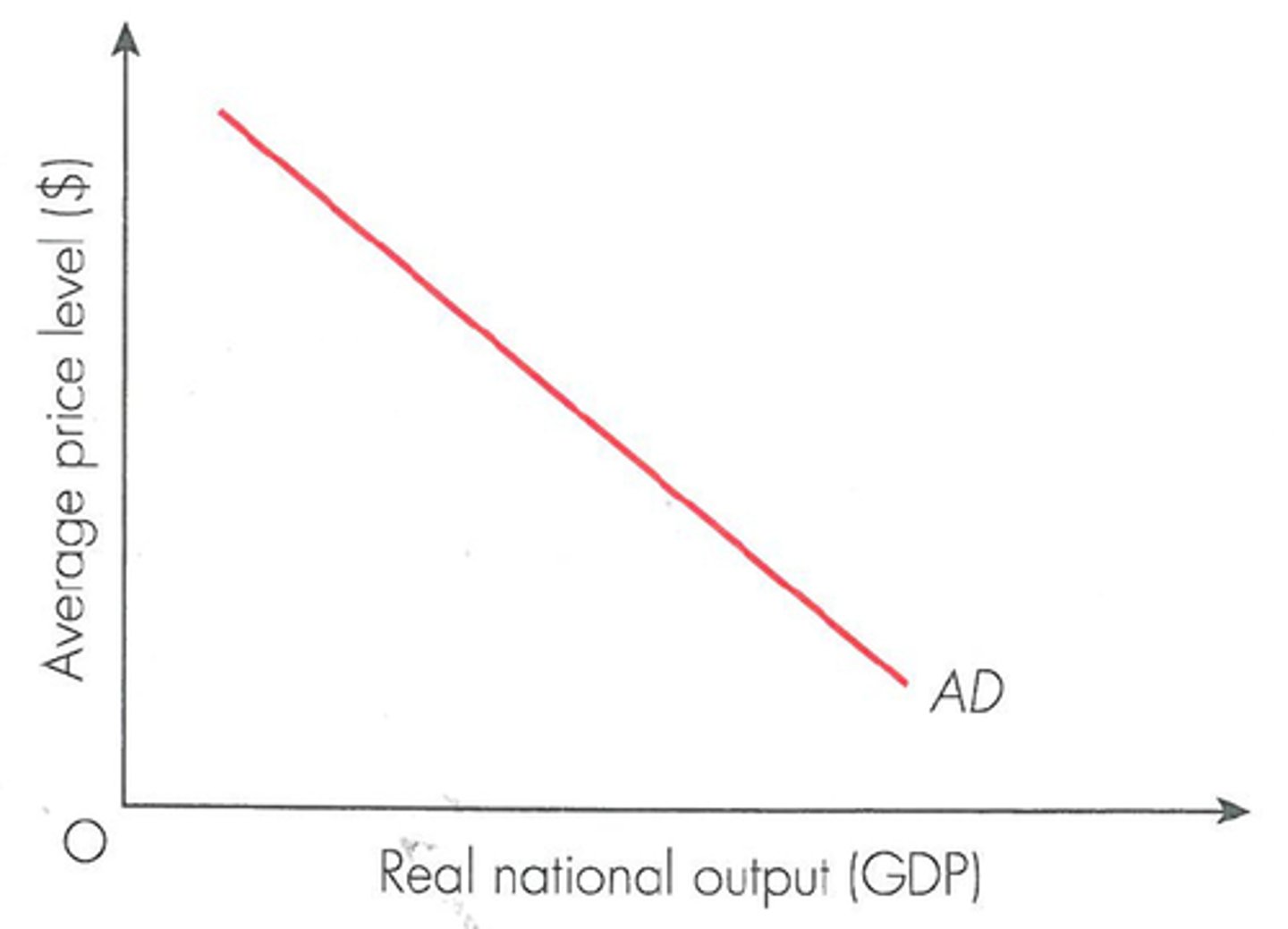
Shifts in Aggregate Demand
Wealth, Debt, confidence, taxes, interest rates
4 changes in aggregate demand
Consumer spending, Investments spending, Govt spending, Xnet exports
Increase in demand
a rightward shift of the demand curve
Decrease in demand
a leftward shift of the demand curve
Consumer spending
more wealth=more spending
less wealth=less spending
Investment spending
spending on productive physical capital
Higher expectations=more investments
lower expectations=lower investments
Government spending
more government spending=increase in AD
less govt spending=lower investment
Net Exports (NX)
stronger $= more imports, less exports=decrease in AD
Aggregate Supply
the total value of all goods and services that all firms would produce in a specific period of time at various price levels
short-run aggregate supply curve
a curve that shows the relationship in the short run between the price level and the quantity of real GDP supplied by firms

Short Run Aggregate Supply
At least one resource is fixed and cannot produce more than what is available
sticky wages
wages are fixed
Changes in Aggregate Supply
Political or environmental, Input prices, Productivity/technology, Expected inflation, Government
Increase in SRAS
rightward shift
Decrease in SRAS
leftward shift
Long Run Aggregate Supply
Wages and resource prices are flexible and WILL change as price levels change. Resources are also variable
Aggregate Equilibrium
AD=SRAS
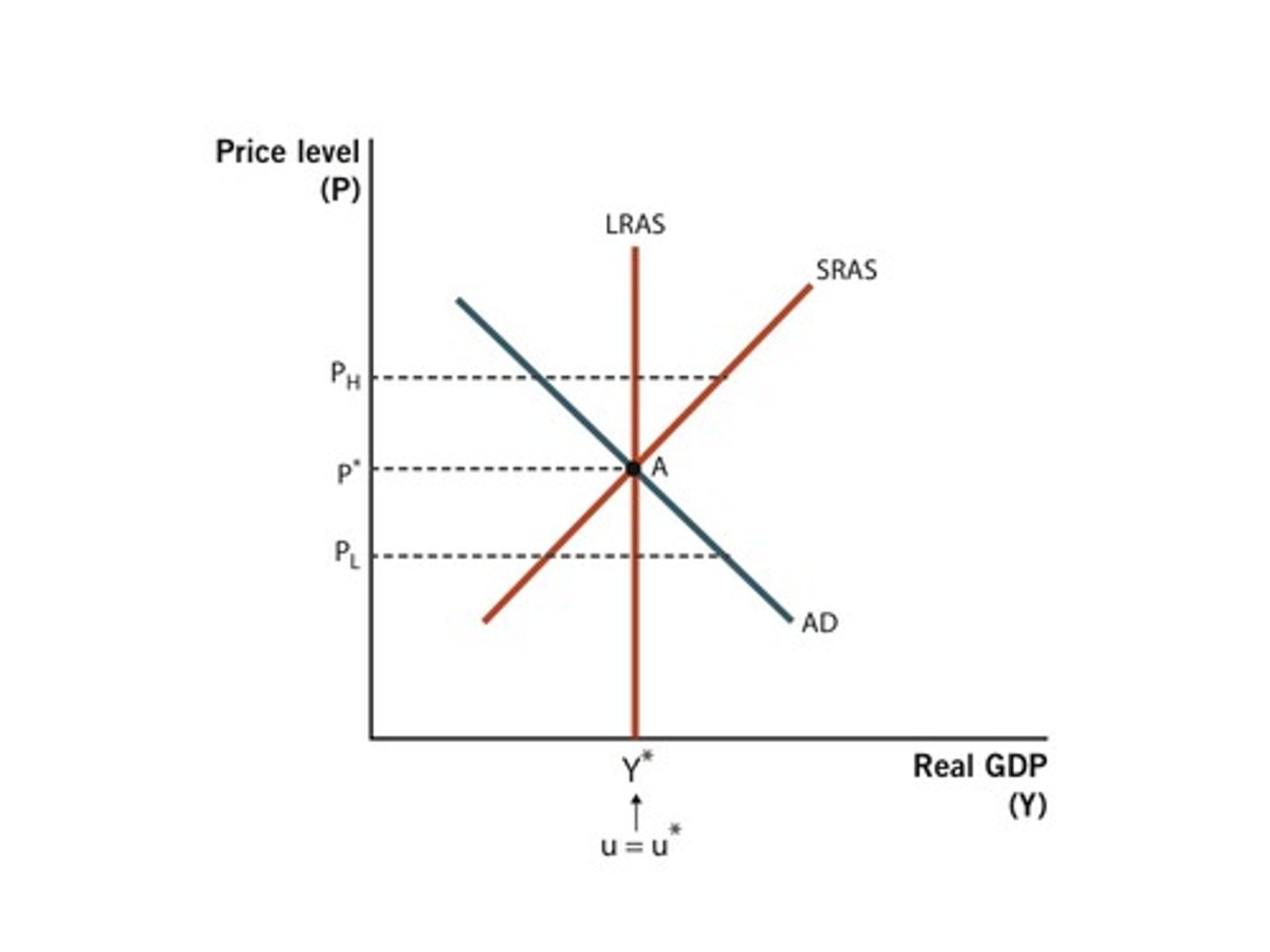
QF
quantity at full employment
GDP surplus
producing more than it is consuming
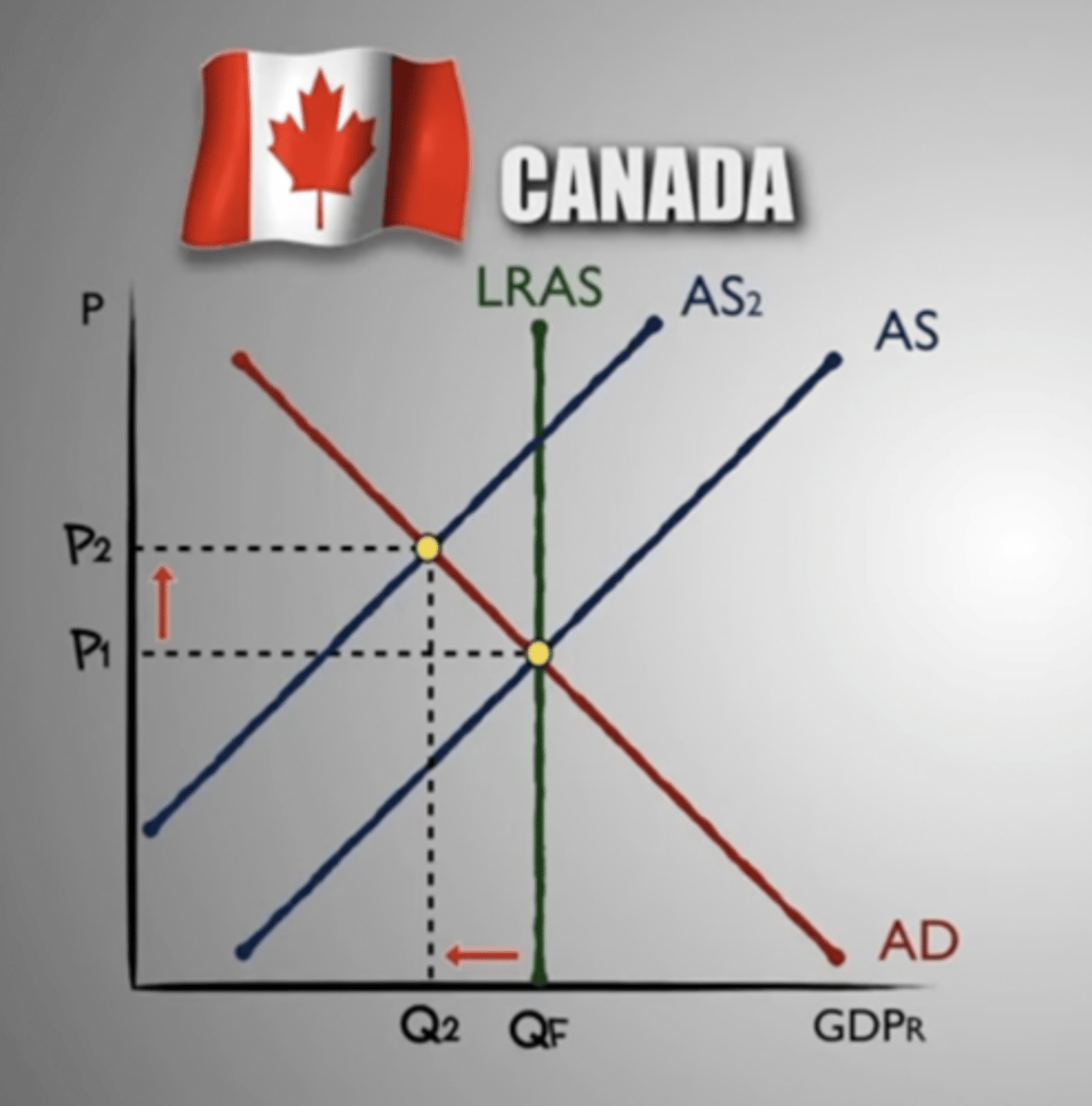
GDP shortage
AD>AS
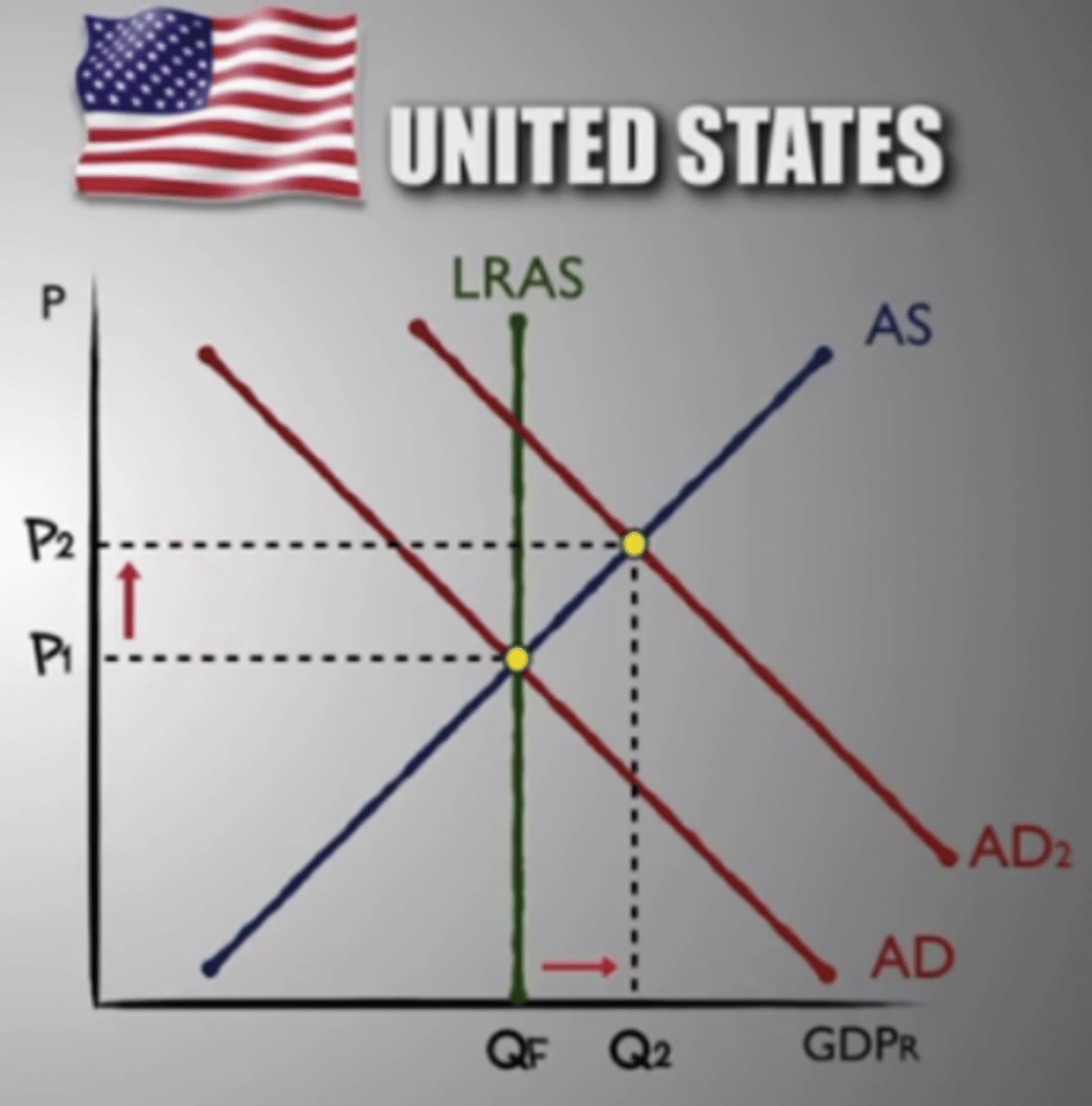
inflationary gap (expansionary)
when aggregate output is above potential output
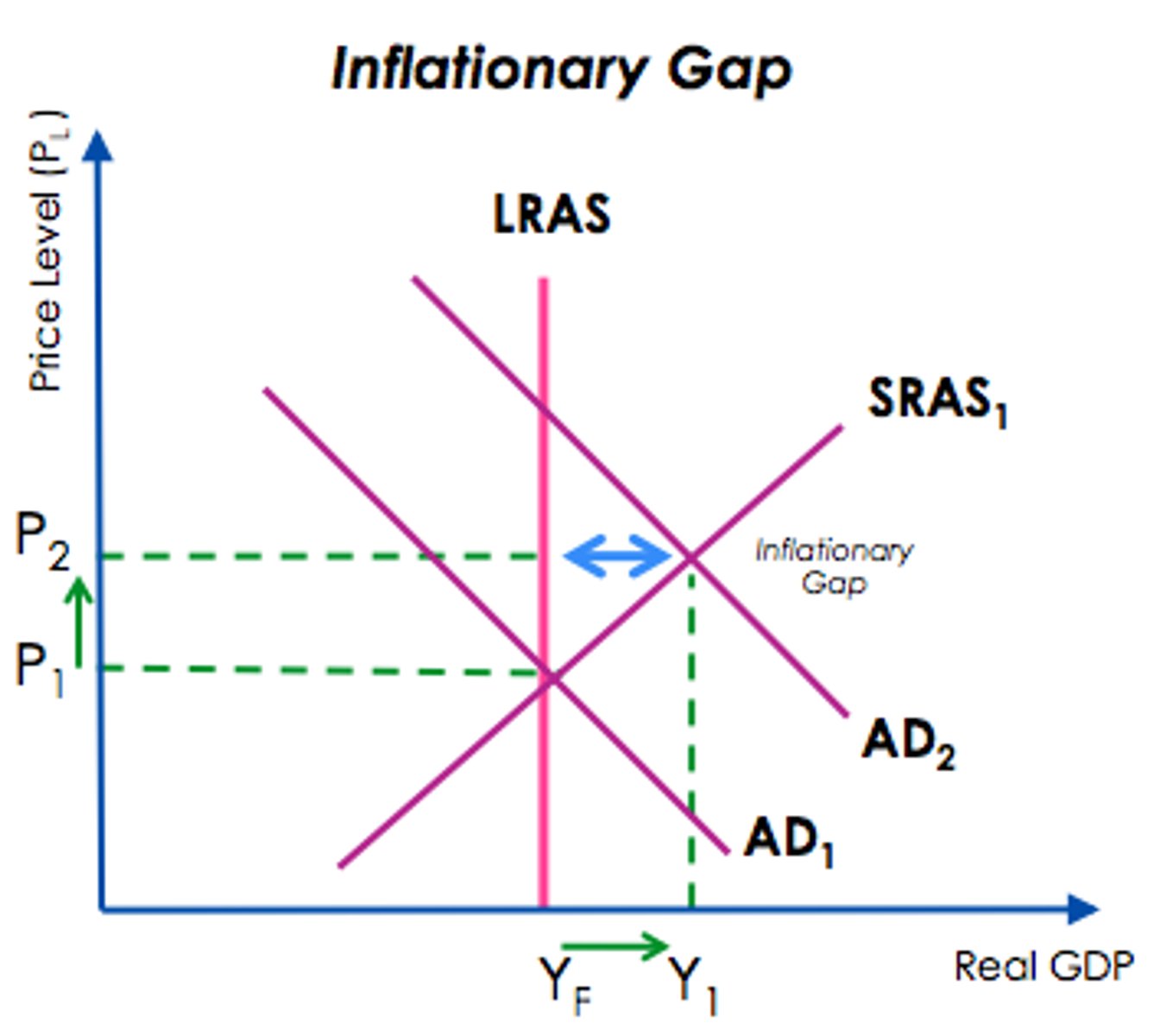
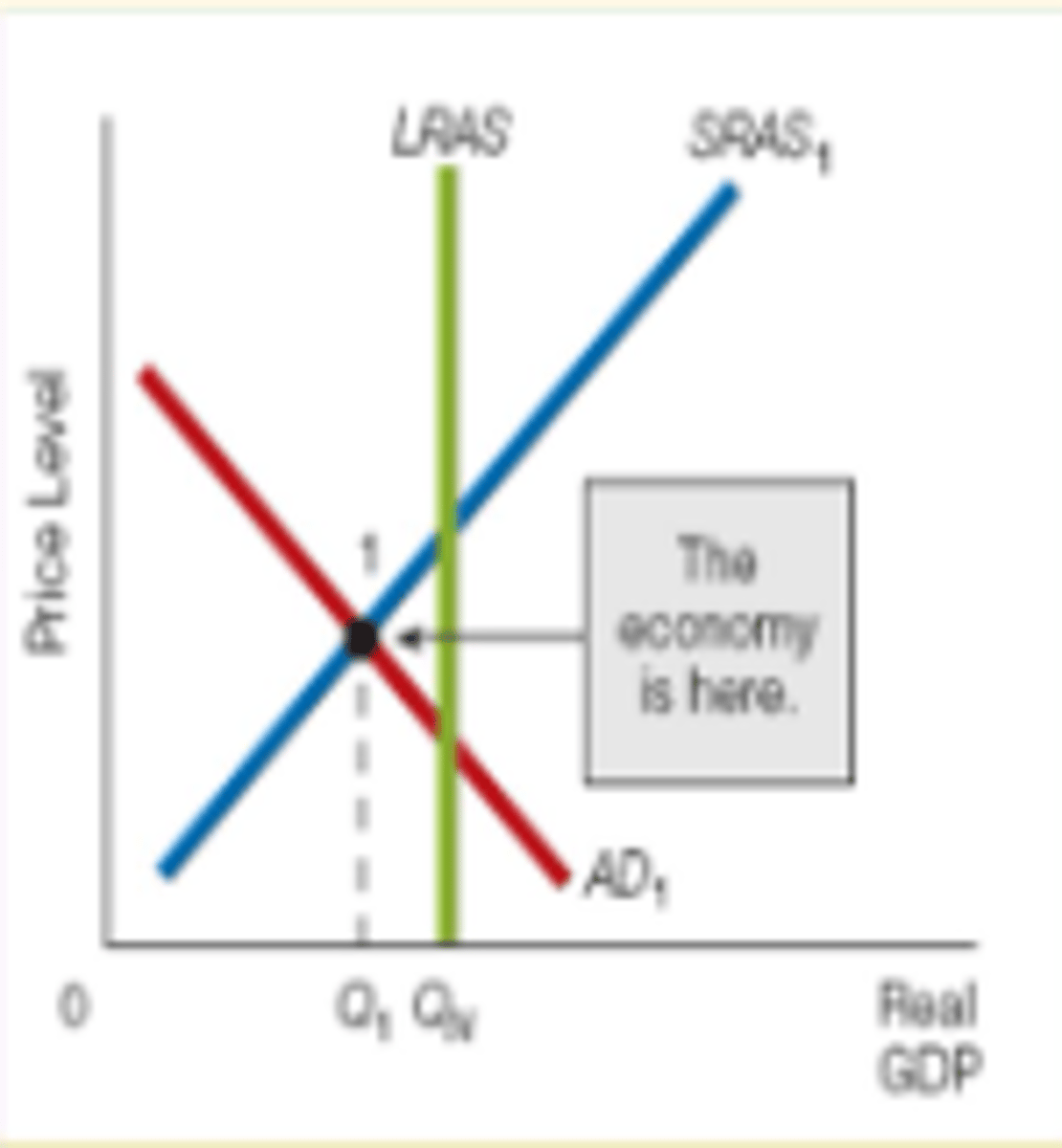
recessionary gap (contractionary)
Short-run GDP behind long-run aggregate supply
Disinflation in aggregate equilibrium
increase in supply
stag inflation
high unemployment and high inflation(decrease in supply)
fiscal policy
govt tools that can be used to fight inflation or unemployment
2 ways to fix it
Taxes and government spending
Taxes
Decrease disposable income, Decrease consumer spending
Government spend
government purchases, transfer payments
expansionary fiscal policy
fiscal policy that increases spending and or decrease taxes
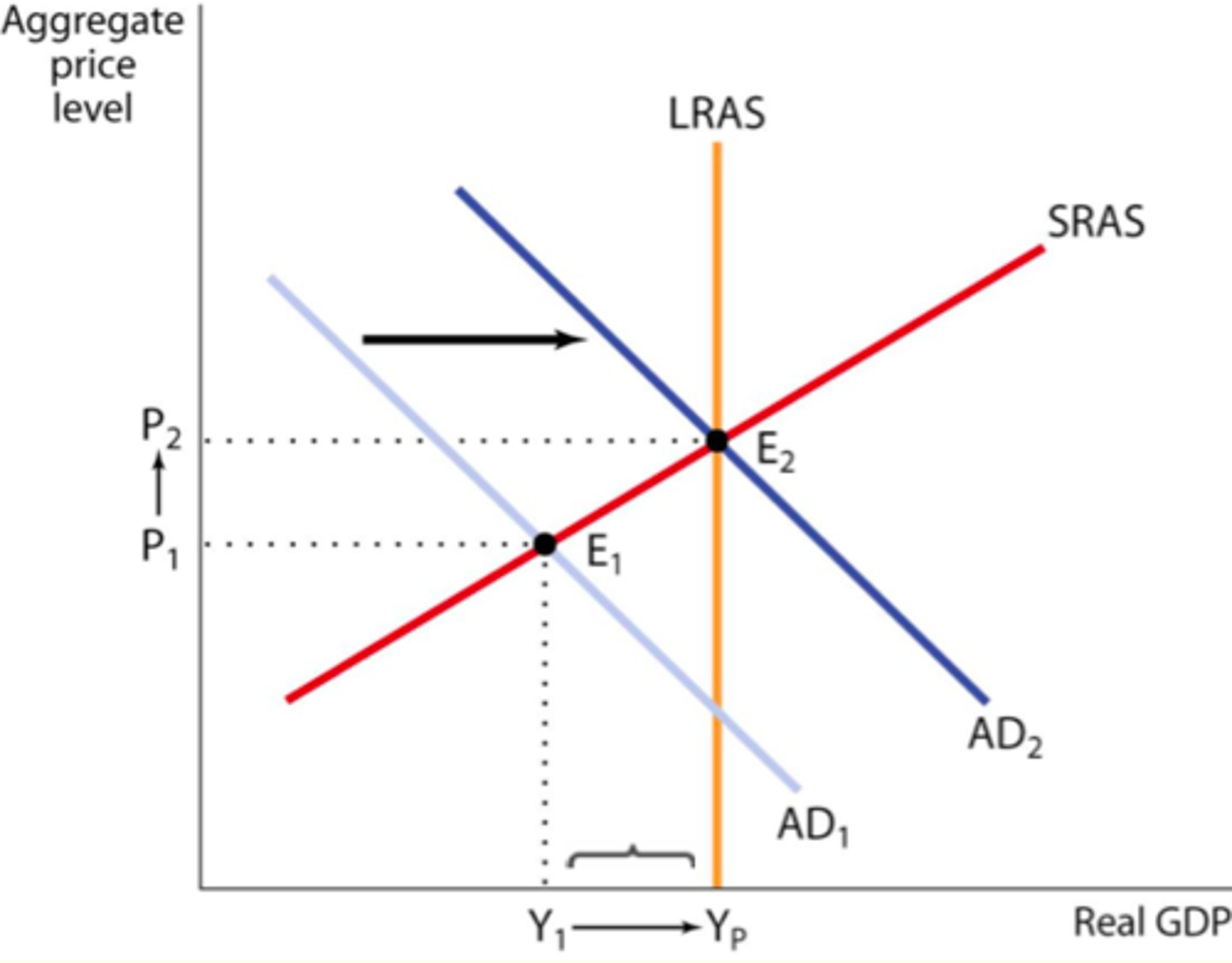
contractionary fiscal policy
decreasing govt spending and/or increasing taxes
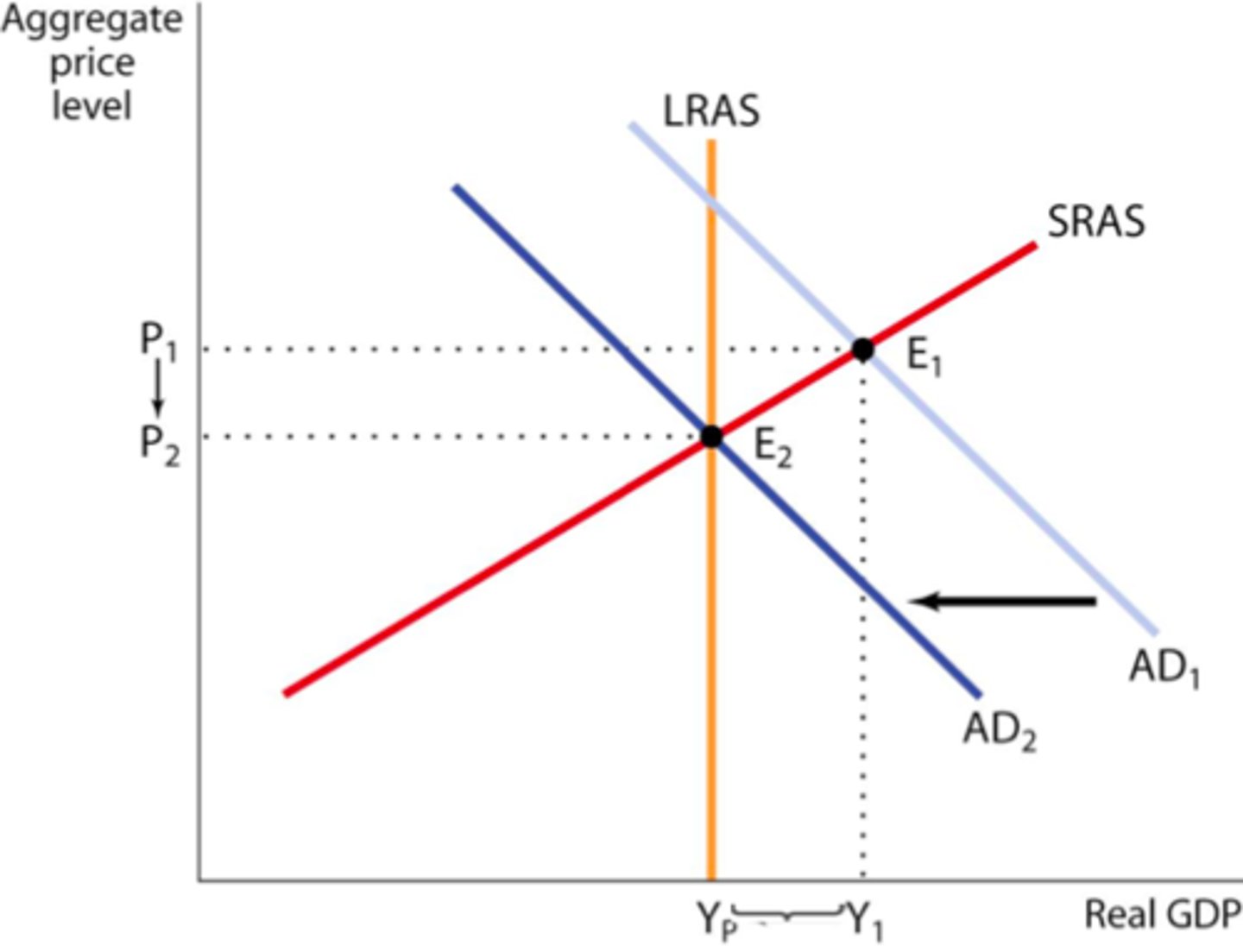
crowding out
increased government spending leads to a decreased private spending as higher interest rates make borrowing more expensive.
crowding in
the phenomenon where increased government spending leads to an increase in private sector investment, often due to lower interest rates or improved economic conditions.
Cost push
inflation caused by rising production costs, leading to decreased supply.
Demand pull
inflation caused by increased consumer demand, leading to higher prices.
positive shock
a sudden and unexpected event that significantly affects the economy, often leading to changes in supply or demand.
automatic stabilizers
mechanisms that automatically adjust government spending and taxes in response to economic changes, helping to stabilize the economy. (taxes, unemployment)
Autonomous
Investments that are not dependent on economic conditions, like GDP or income changes