Genitourinary Radiology
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What are the five retroperitoneal spaces?
Anterior Pararenal
→ contains the duodenum, ascending and descending colon, as well as the pancreas
Perinephric
→ contains the kidneys and proximal ureters
Posterior Pararenal
→ contains fat as well as Gerota and Transversalis Fascia
Vascular Compartment
→ Aorta and IVC
Muscular Compartment
→ psoas major and iliacus
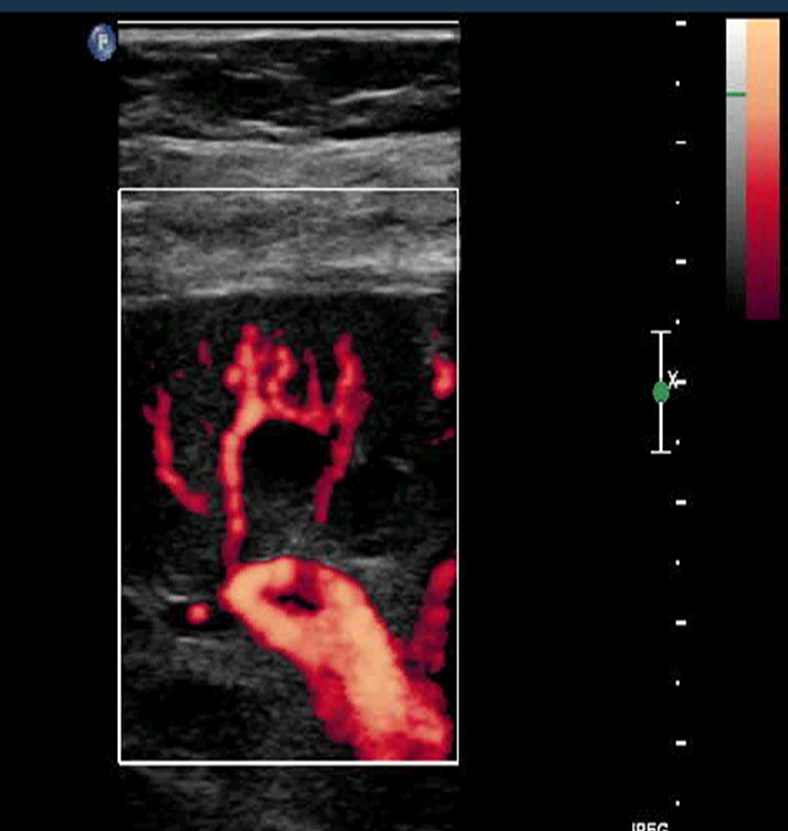
What is this?
This is an color doppler ultrasound depicting the renal anatomy based on the vessels
→ the very top portion of the kidney is marked by the cortex which will move down into the renal pyramids and eventual sinus fat
→ identifiable are also the arteries
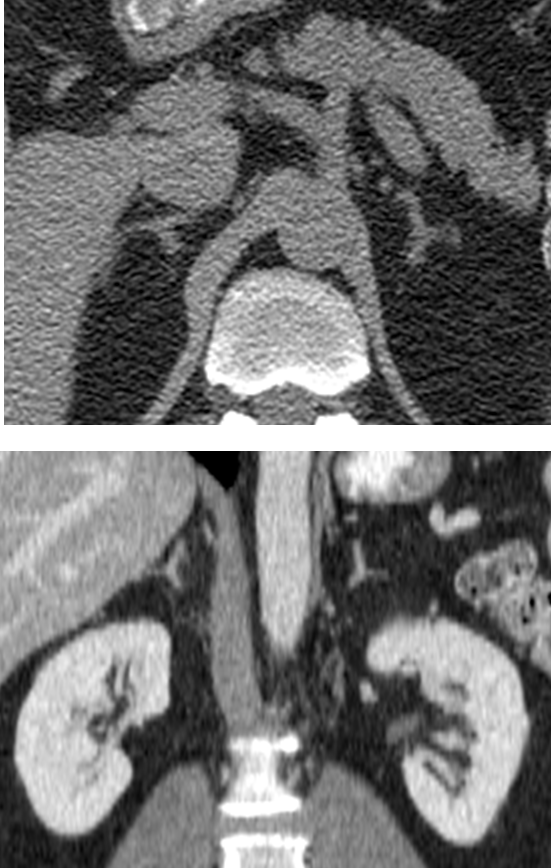
Where are the adrenal glands identifiable on this image?
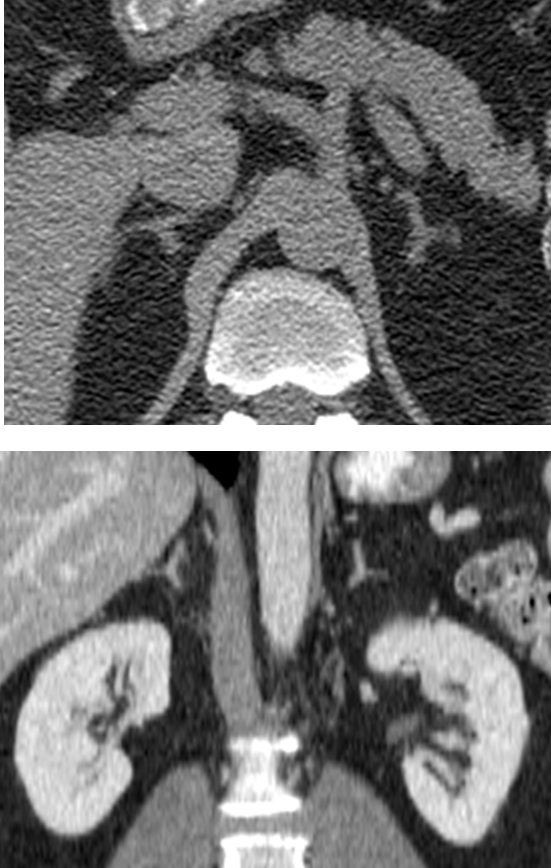
Adrenal glands can be seen in the retroperitoneal space within Gerota’s Fascia
→ identifiable on CT making a inverted Y or V shaped
→ the adrenal glands can be discoid or linear if the kidneys have not developed
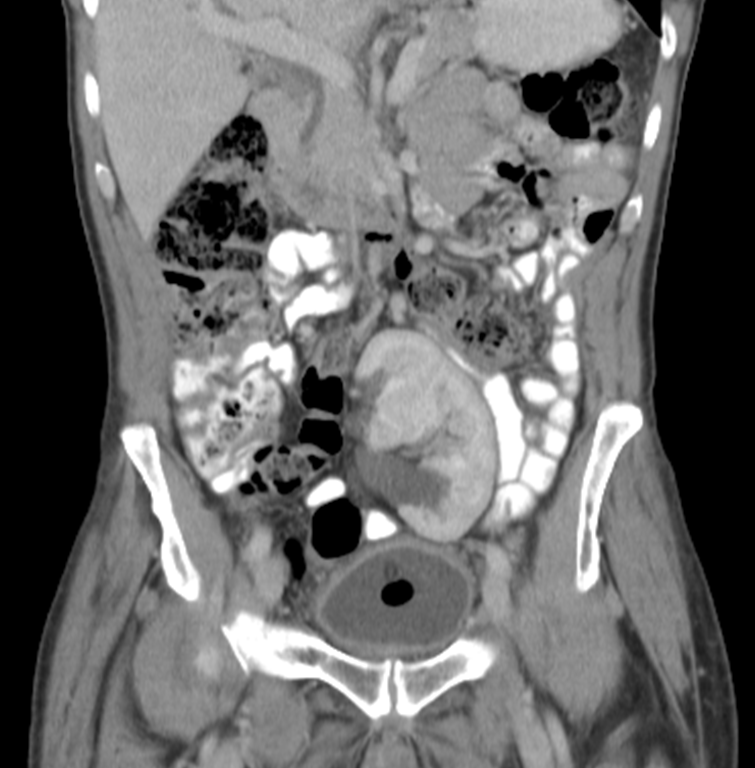
What is this?
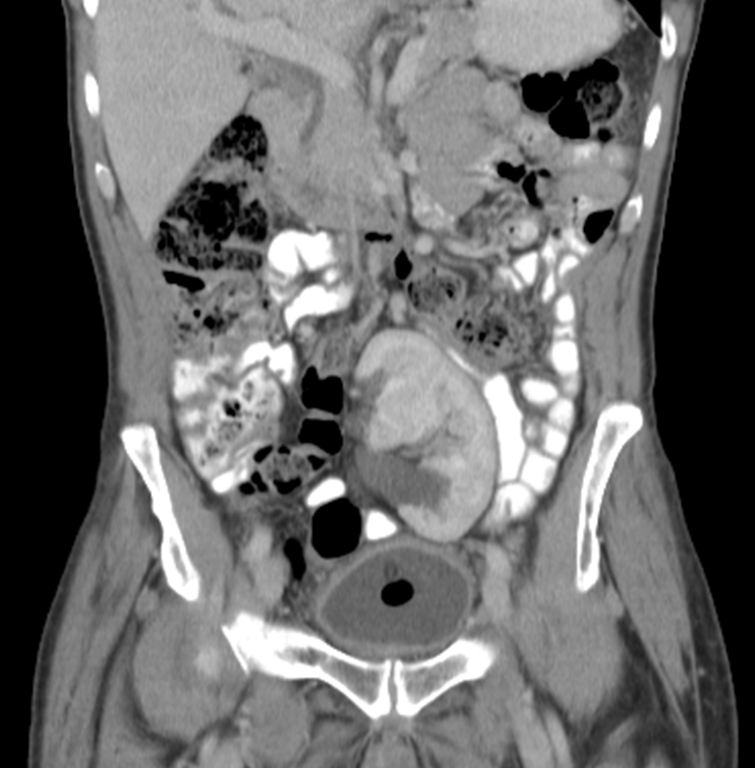
Pelvic Kidney
→ kidney located in the pelvis and is the most common renal ectopia or congenital condition where kidneys are abnormally placed
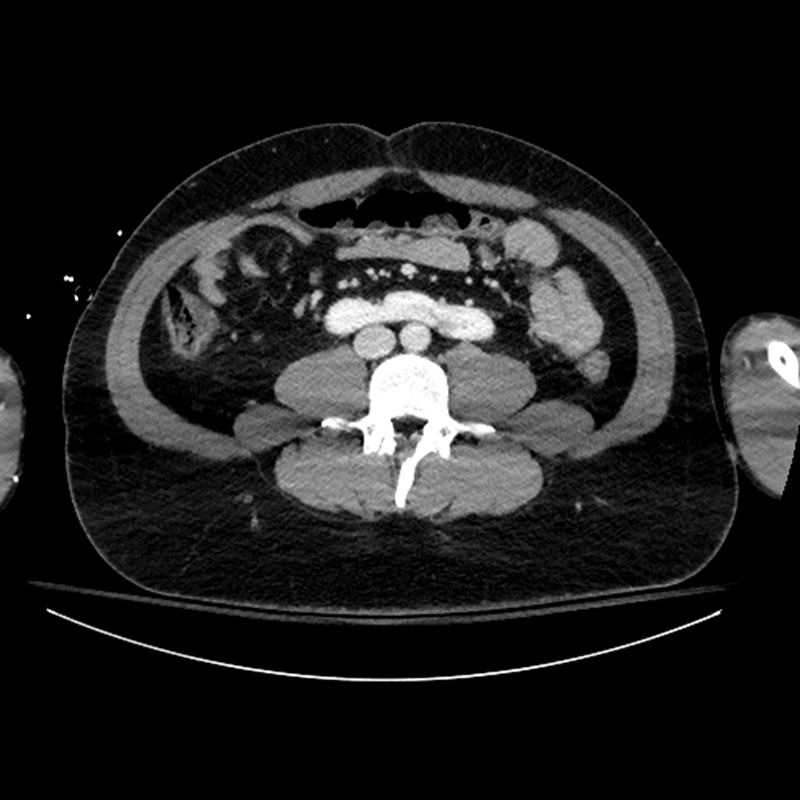
What is this?
Horseshoe kidney where the kidneys are fused together and stuck below the IMA. It is the most common fused ectopia
1) Horseshoe kidney has abnormal collecting systems that causes urine stasis leading to infection, stones and tumor development
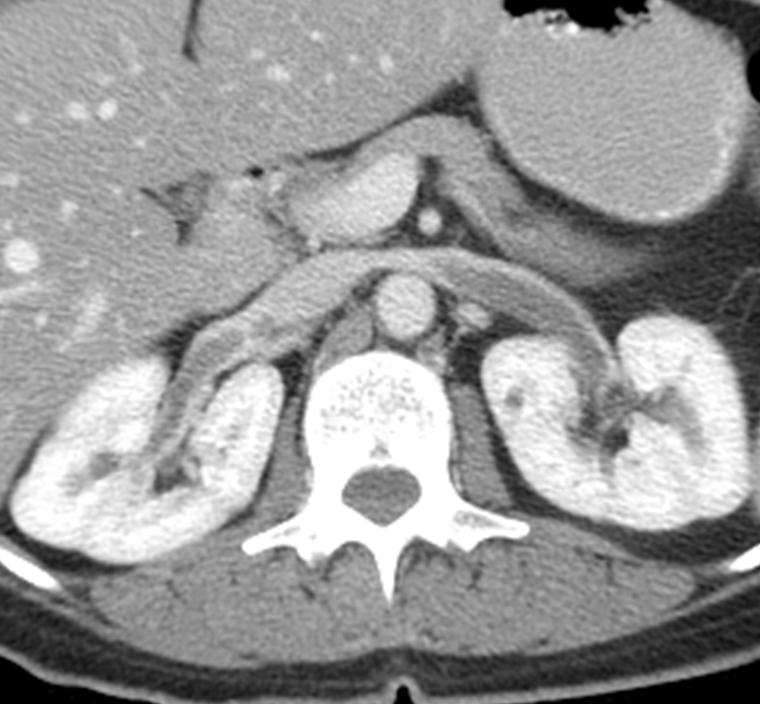
What is this?
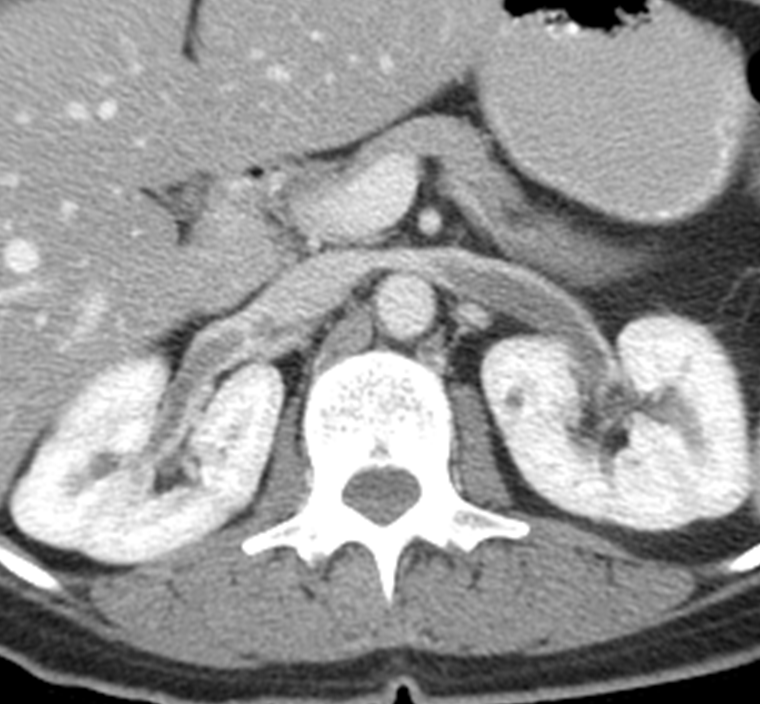
Renal Vein Thrombosis where the renal vein entering into the IVC has a blood clot form
1) often seen in patients that are in hypercoagulable states or some other condition like cancer
→ renal cancers can track through the lumen of the renal vein creating an obstruction
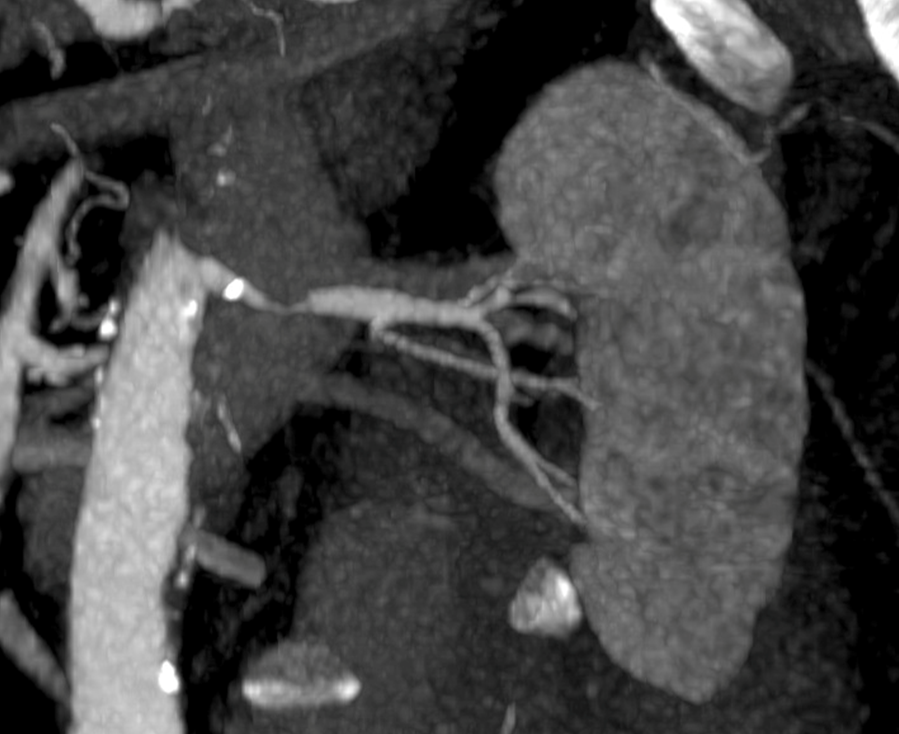
What is this?
Renal Artery Stenosis
→ narrowing of one or both of the renal arteries, leading to reduced blood flow to the kidney
→ can cause necrosis due to ischemia
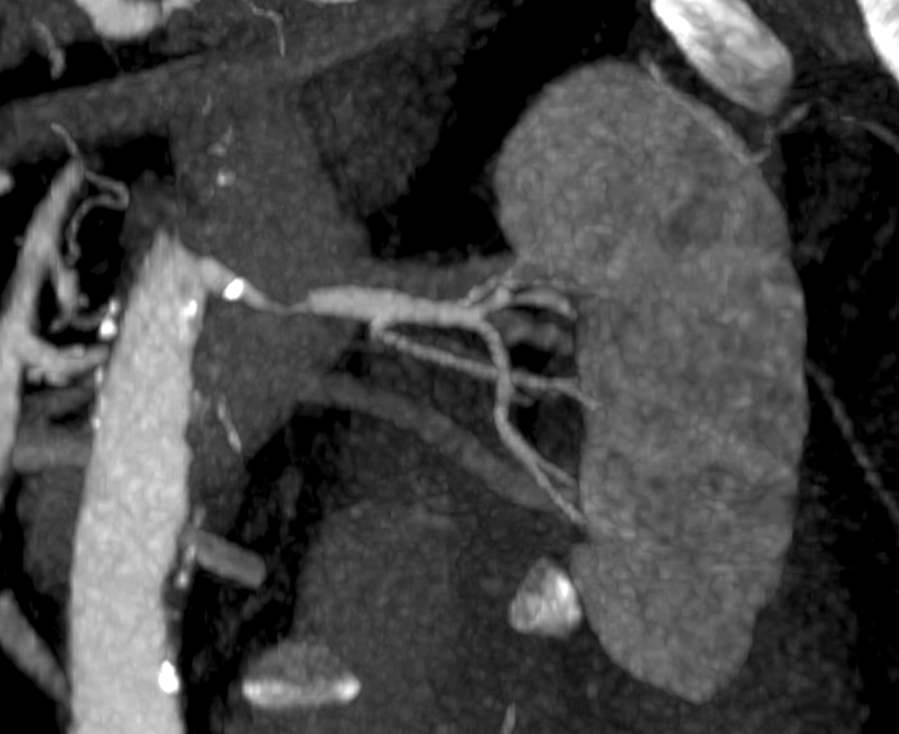
What is this?
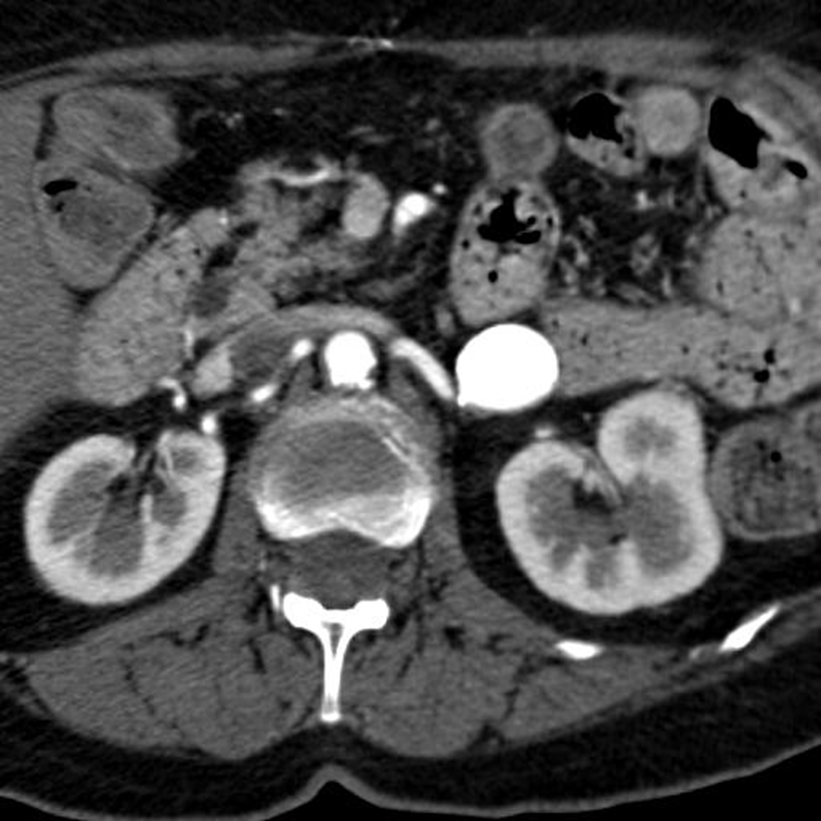
Renal Artery Aneurysm
→ bulging of the wall of the renal artery that can potentially rupture
→ often occurs at branching points
What is Laceration of the Kidneys? Shattered Kidney
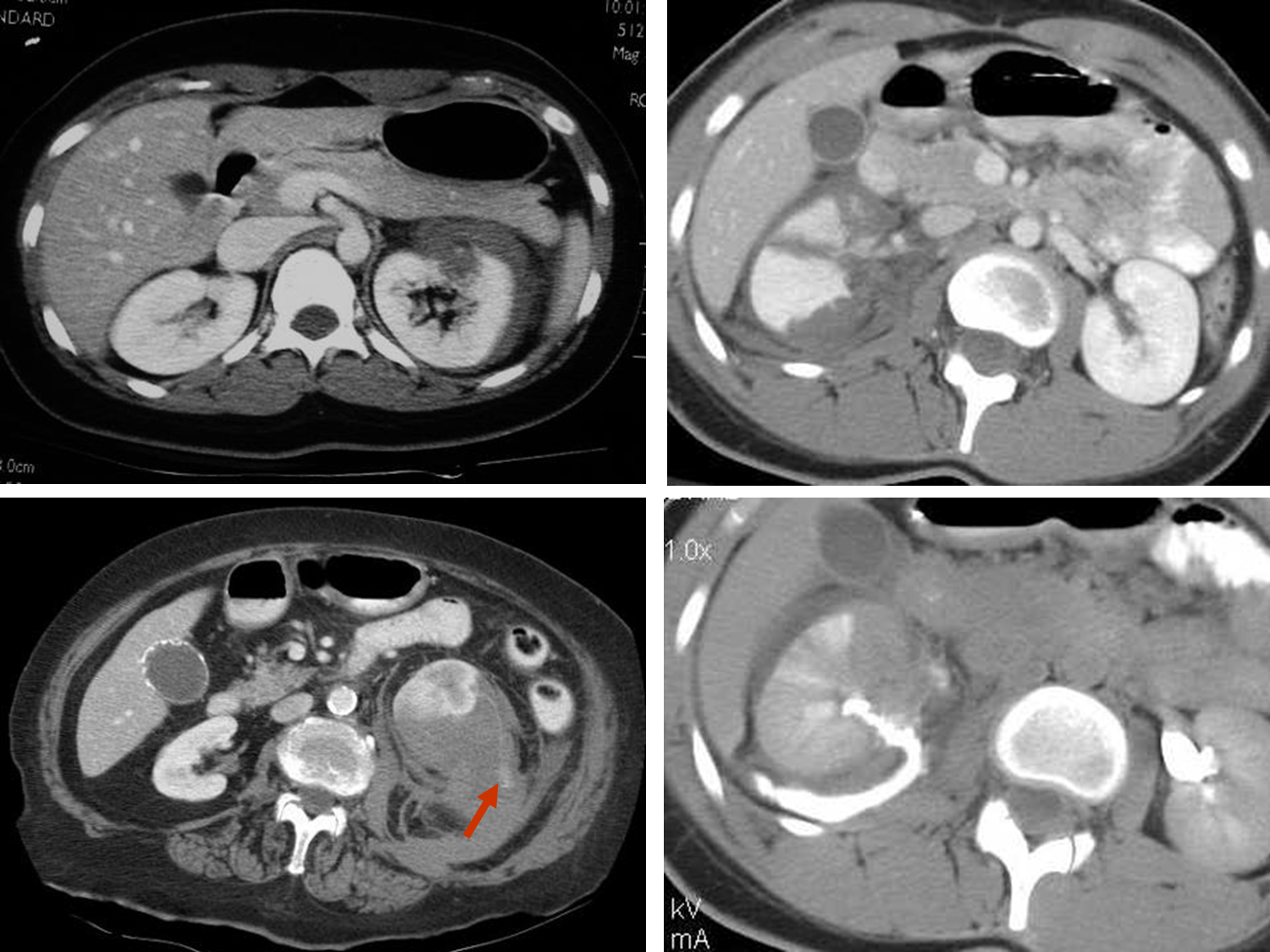
Laceration of the kidneys or a cut of the kidney is often have different outcomes depending on the location of the laceration
1) Deep into the collecting system
→ lacerations like this will often heal on their own
2) Extravasation or leaking into the surroundings such as the fascia will form a hematoma and heal on its own
3) for blunt trauma management for as long as possible, penetrating trauma reparable - this is only relevant as long as the blood remains in the retroperitoneal
→ if blood enters the peritoneal cavity, you have to do surgery or they will die
→ blood entering into the peritoneal cavity from a kidney laceration is known as a shattered kidney
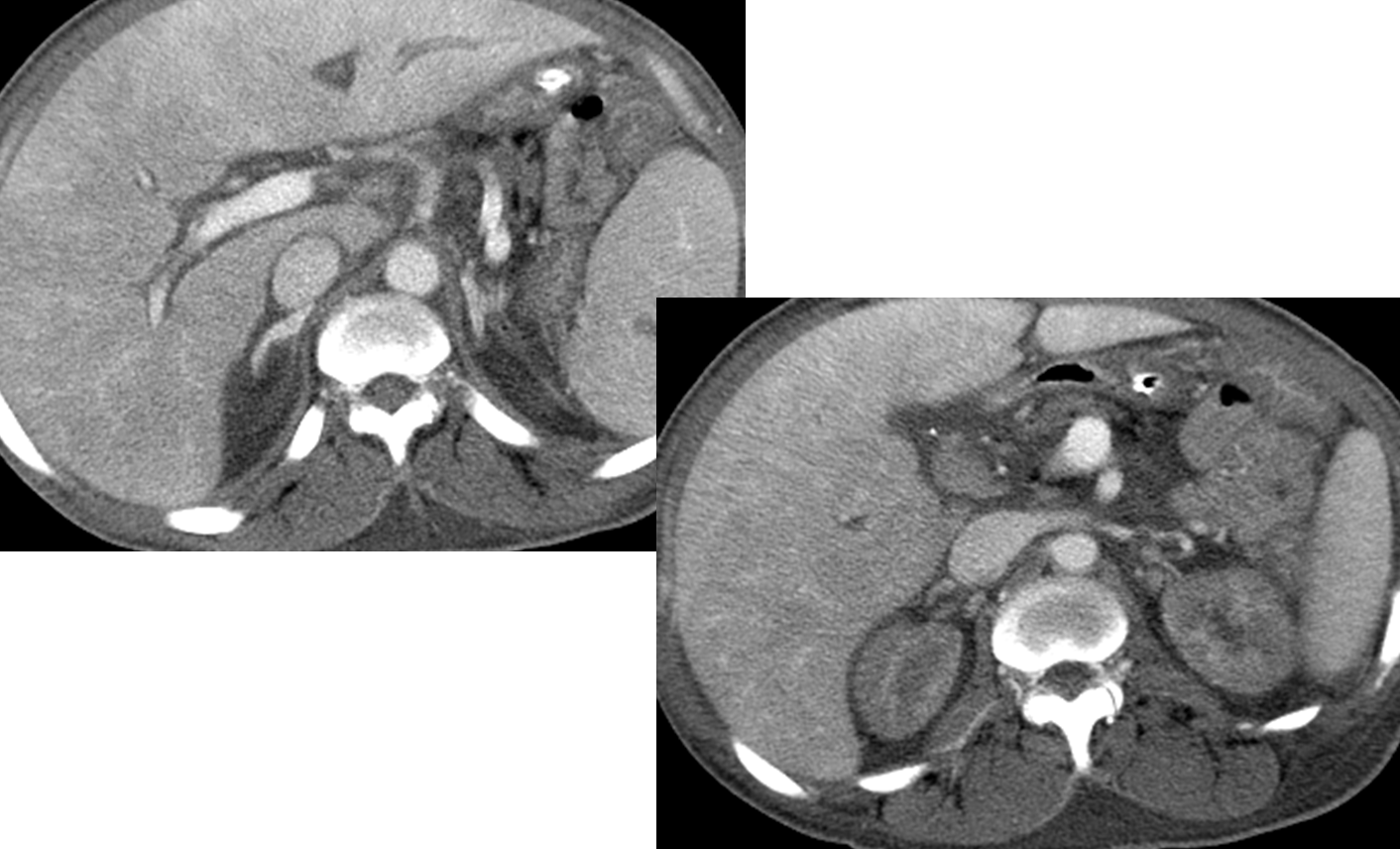
What is this?
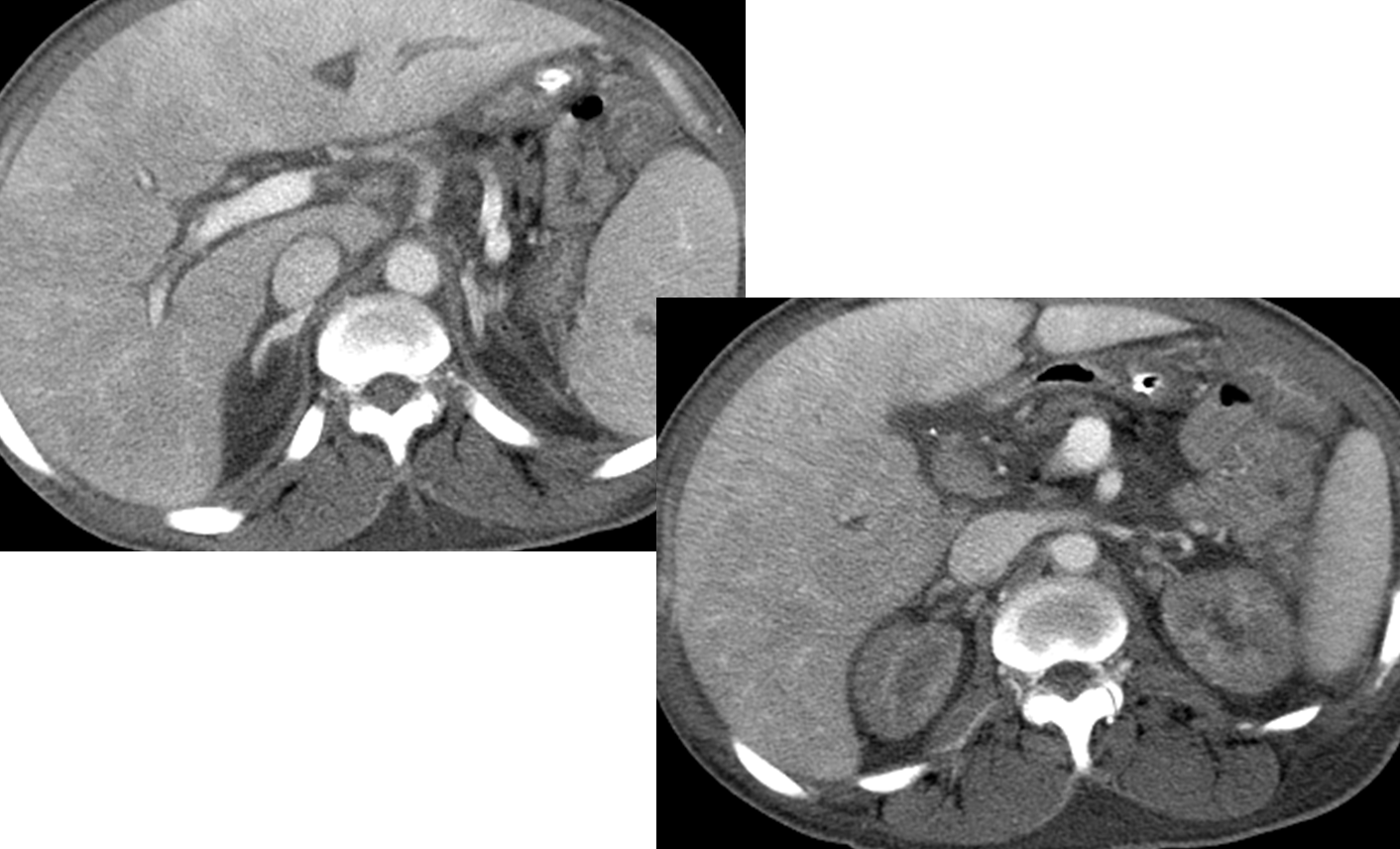
Shock Kidneys and Adrenals
→ when the body has lost lots of blood, the blood in venous circulation will begin to pool - done in order to preserve flow to the brain
→ blood in the renal veins will not flow out well
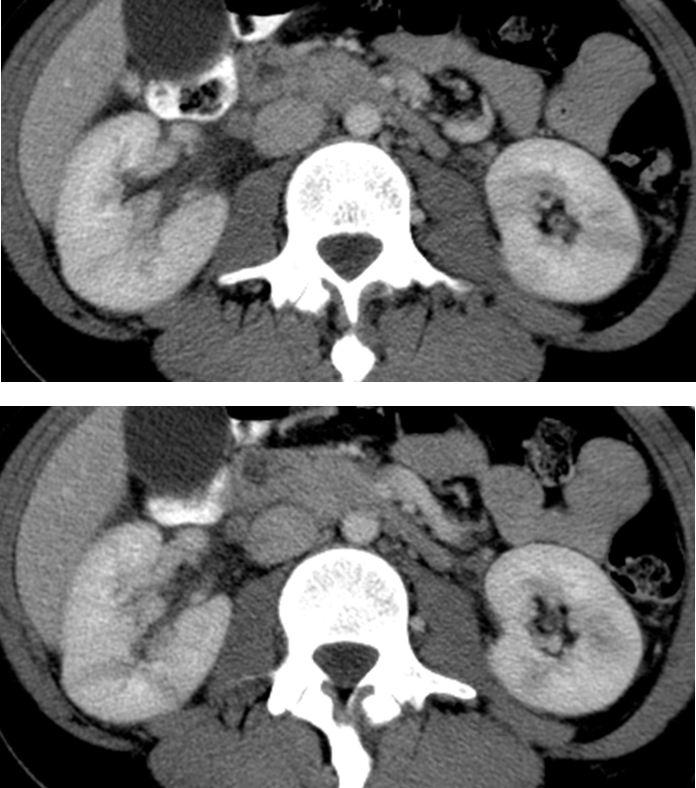
What is this?
Pyelonephritis is an infection of the kidney and renal pelvis
→ causes the kidney to have stranding and striated nephrograms or a pattern of alternating linear bands
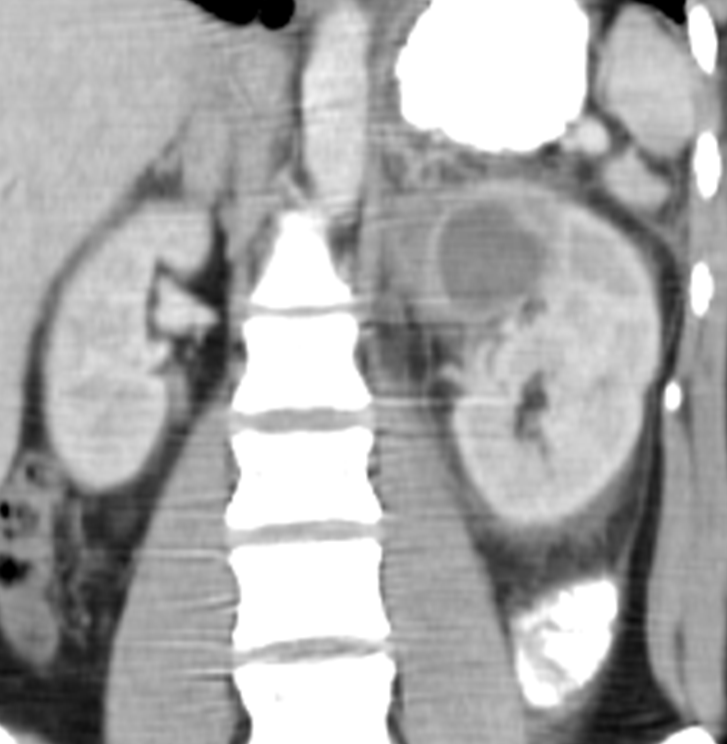
What is this?
Renal Abscess is a complication of untreated pyelonephritis
→ shows as a dark spot on the kidney
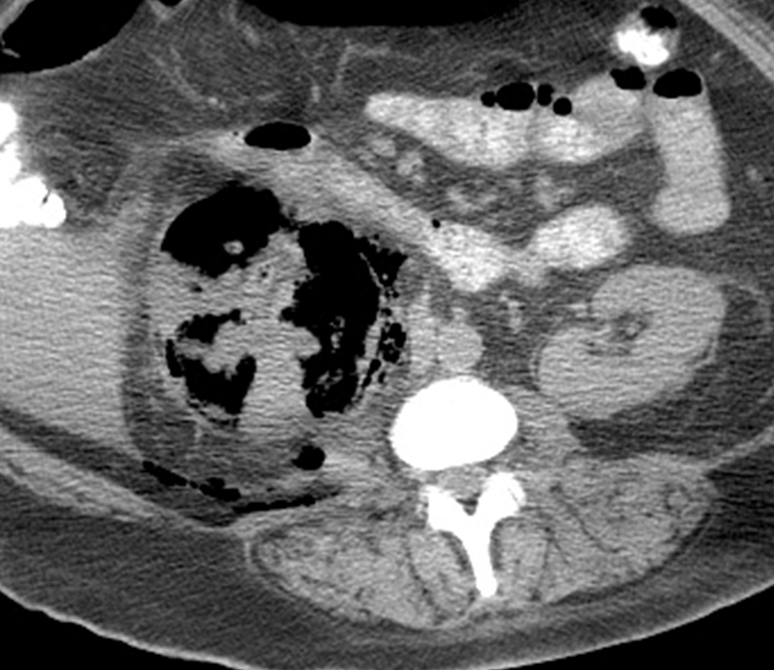
What is this?
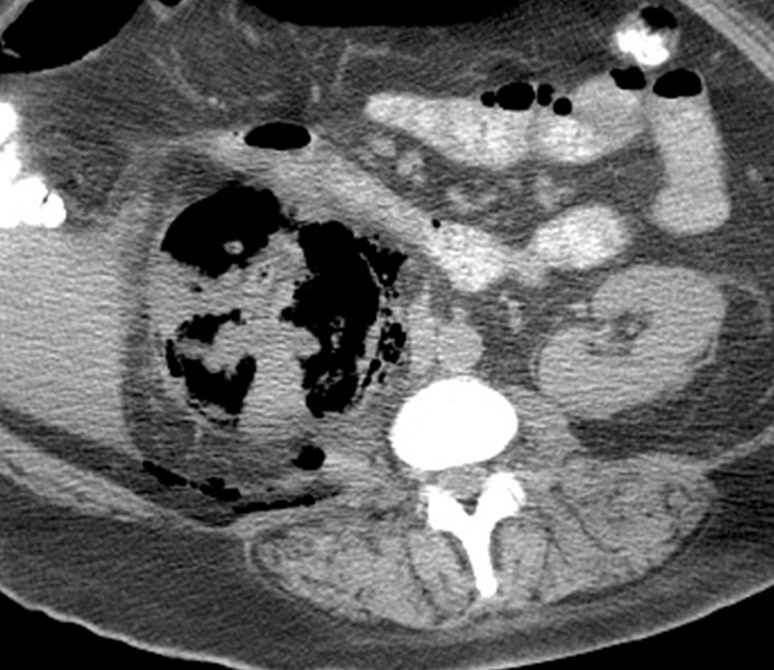
Emphysematous Pyelonephritis
→ caused by gram negative rods that create gas in the kidney leading to dark space throughout the kidney
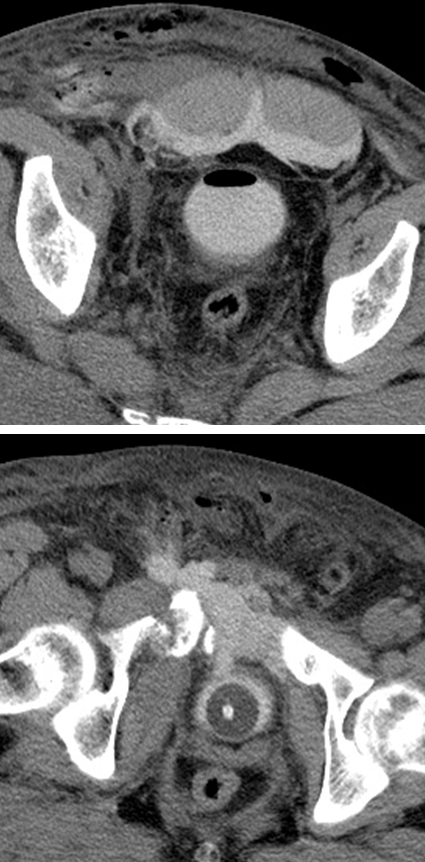
What is this?
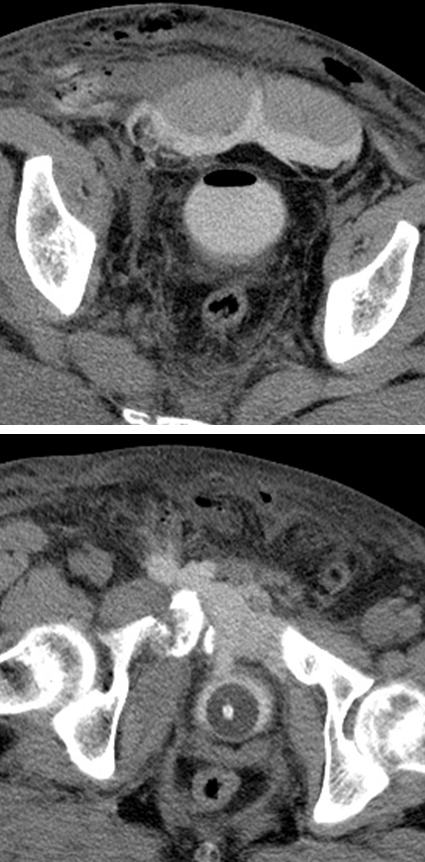
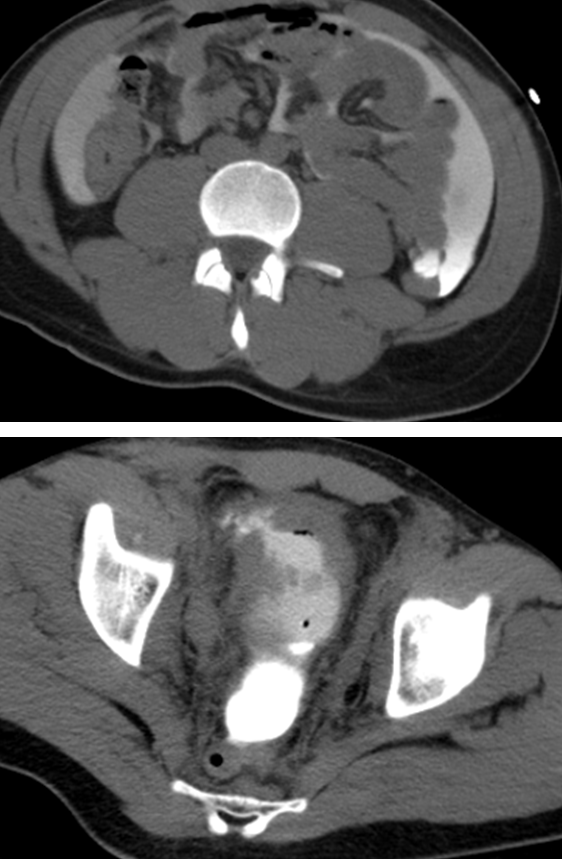
Extraperitoneal Rupture
→ most common rupture of the bladder, seen anterior or lateral bladder wall
→ urine leaks into the retropubic or perivesical space
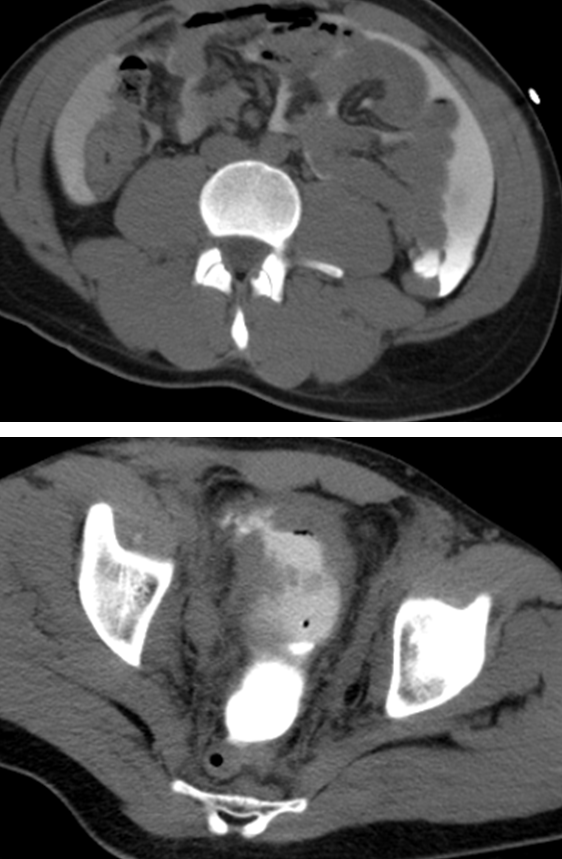
What is this?
Intraperitoneal Rupture
→ rupture of the superior part of the bladder covered by peritoneum
→ the urine leaks into the peritoneal cavity, more serious than extraperitoneal