Selection and Breeding
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
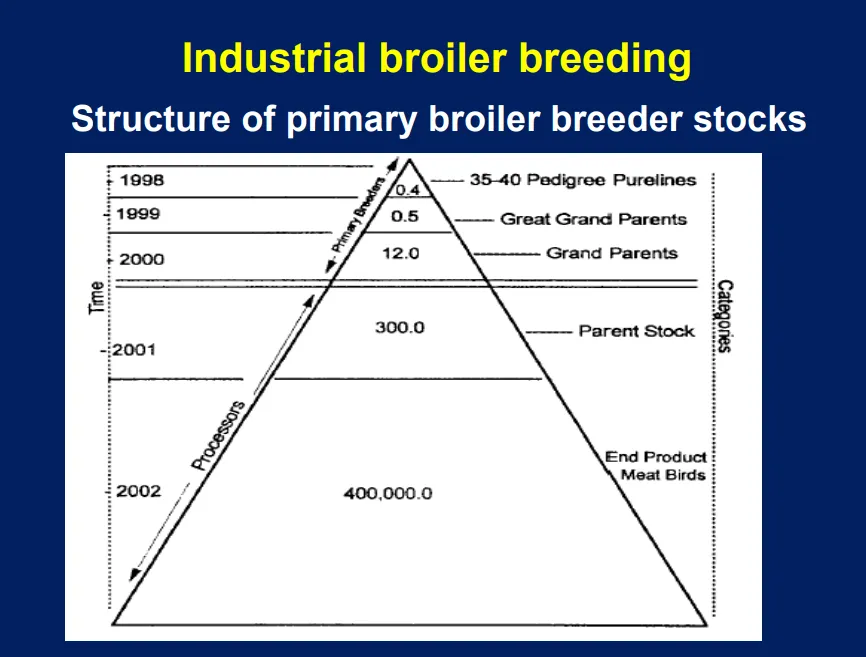
Structure of primary broiler breeder stocks has how many pedigree pure line birds at the top?
0.4 million pedigree birds from 35 to 40 pure lines
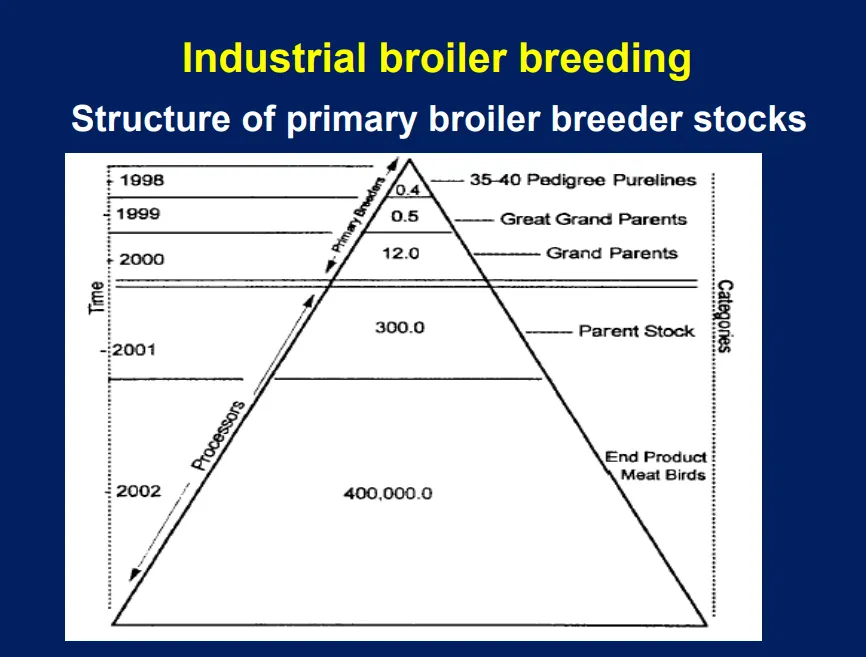
Structure of primary broiler breeder stocks has how many end product meat birds at bottom?
400,000
Sire Lines (male lines)
broiler lines selected primarily for performance of males
males from crosses of these lines used as fathers to produce production offspring
Dam lines (female lines)
broiler lines selected primarily for performance of females
females from the crosses of theses lines sold as mothers to produce production offspring
What stock can be sold?
grand parent, parental, commercial product (EP)
bottom three in chart
What stock cannot be sold?
pedigree foundation, great grand parents
Grand parents will sell
female and male but only one from each like
male 1, female 2, male 3, female 4
Parental stock will sell
only male lines 1 and 2, female lines 3 and 4
Commercial stock will sell
male and female
Primary broiler breeder company structure is shaped like a
pyramid
How many purelines?
35-40 purelines
Purelines undergo
genetic selection for improvement in major economic traits
Male lines improve
growth rate, edible meat yield, feed conversion
Female lines improve
egg production, but also have good growth rate and repro traits
Genetic improvement made in pedigree lines is passed down thorugh
multiplication process
How long does multiplication process take?
4 years, and genetic improvement is diluted since selection is minimized or does not exist
genetic comp in an individual changes during meiosis
Some steps of multiplication can be skipped if
populations are large enough
Broilers of pedigree pure lines will serve as
great grand parents to produce grand parents
In reproduction of pure lines and great grandparents what mating technique is used?
artificial insemination
Grandparents are crossed to grandparents from other lines to
generate parent stocks that are commercially available
What stocks are actual broilers used in broiler prod?
offspring of parent stock (EP or commercial stock)
The efficiency of energy retention in broilers peaks when?
Early in life
Does efficiency of energy retention continuously go up throughout a broiler’s lifetime?
No, it will decrease over time
constant for first 1/3 of growth period
What are the two main components of metabolizable energy in broilers?
Heat production and energy retained
Heritability for reproductive traits is high or low?
low
What is performed regularly to identify superior crosses?
test crosses
Which term describes the deviation observed between reciprocal crosses?
Reciprocal effect
What is the heritability estimate for egg production typically considered to be?
Low (<0.3)
Is reciprocal recurrent selection is more applicable to broiler or layer selection?
Layer selection
Which of the following traits is typically negatively correlated with egg production?
Body weight
What is an advantage of line crosses and pyramidal structure?
they take advantage of heterosis (hybrid vigor)
Growth associated traits are:
live body weight
body weight gain
growth rate (g/day)
meat comp and yield
feed consumption and efficiency
fat content
Energy retain is mostly for
protein and fat
Growth requires that metabolizable energy is larger or smaller than heat production?
larger
What happens to the ratio of protein to fat as animals mature?
It decreases
animals have more energy go to protein when young
Is more energy required to grow lean meat or fat?
Fat
Is genetic effect sex-linked?
Partially sex-linked
Is genetic effect polygenic (influenced by multiple genes)?
Yes
What is the growth curve?
an accelerating growth phase, decelerating growth phase, limiting mature weight
Does heterosis in growth exist?
Yes
Does growth respond to genetic selection?
Yes. Heritability ranges from 0.3-0.7
Agemax is
the age when maximum rate of weight gain is reached
Broiler body weight and weight gain are pos or neg correlated w/feed consumption?
positively
Broiler body weight and weight gain are pos or neg correlated w/feed conversion?
negatively
Live body weight is pos or neg correlated w/abdominal fat?
positively
Weight gain is pos or neg correlated w/abdominal fat?
negatively
Do faster or slower growers show better conformation of carcass?
Faster growers
Do fast or slow growing broilers have higher mortality rate?
Fast growing
Indoor vs Outdoor living affecting protein distribution is an env or genetic effect?
environmental
Fast vs slow growing chickens relates to env or genetic effects?
Genetic
Selection for growth traits is one or multiple stages?
multiple
What kinds of selection is used for growth traits?
Mass selection and index selection
Age of first egg refers to
when layers reach sexual maturity and are able to lay eggs
Heritability for egg production is additive or non additive genetic effect?
non-additive genetic effect
Is viability a factor for survivor egg prod measurement?
no
Within line selection is used to
maintain and select several pure lines and use pure lines for three and four way cross to produce high performance offspring for prod purposes
Line cross is used to
select parents that produce higher heterosis that results from epistasis and dominant effect (non additive genetic effect)
Reciprocal recurrent selection is a form of family selection based on what effect?
Reciprocal effect
the lines that serves better as females are called dam/female line, line serves better as males called sire/male lines
Reciprocal effect is the
deviation between line crosses of two parental lines in which their roles as female or male parents are reversed
The purpose of the reciprocal effect approach is to
select parents that prod higher heterosis, which is considered more in layers than broilers