α&β Adrenergic Receptor Agonists & Antagonists
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Dr. Rose
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Direct-Acting Mixed-Acting α & β Agonists
MOA
Clinical Use
Adverse effects
Norepinephrine (Levophed)
Equal affinity for α1 & α2 but β1>>>β2
↑HR↑Na+ &fluid retention, ↑Peripheral vasoconstriction
Used in IV to treat SHOCK
Adverse effects are hypertension, reflex bradycardia, cardiac arrhythmias
Droxidopa (Northera)
NE oral pro-drug converted to NE outside CNS by DOPA
Used for symptomatic neurogenic orthostatic hypotension in those with primary autonomic failure or dopamine β-hydroxylase deficiency
Adverse effects include headache and hypertension
Epinephrine (Adrenalin)
Equal affinity for α1=α2 and β1=β2; more potent for β2 than NE
Low doses vasodilate and high doses vasoconstrict peripherally and divert blood to
↑HR↑Na+&fluid retention
@β2 Bronchodilation, glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis
Clinical use: stop bleeding, increase potency of lidocaine in dental treatments, asthma, CPR, anaphylactic shock
Ephedrine - “mini epi”
Similar to Epinephrine but partial agonist, so not as strong
Only use is for induced hypotension during anesthesia
Adverse effects include insomnia, hypertension, palpitations and ventricular tachyarrhythmias
Dopamine (D) Hydrochloride (Intropin)
D1>>β>>α
Low doses ↑RBF, vasodilates
Medium doses ↑CO
High doses ↑BP
Adverse effects include cardiac arrythmias, local extravasation causes necrosis
Indirect-Acting Sympathomimetics (α&β Agonists)
Drugs
MOA
Adverse effects (all the same)
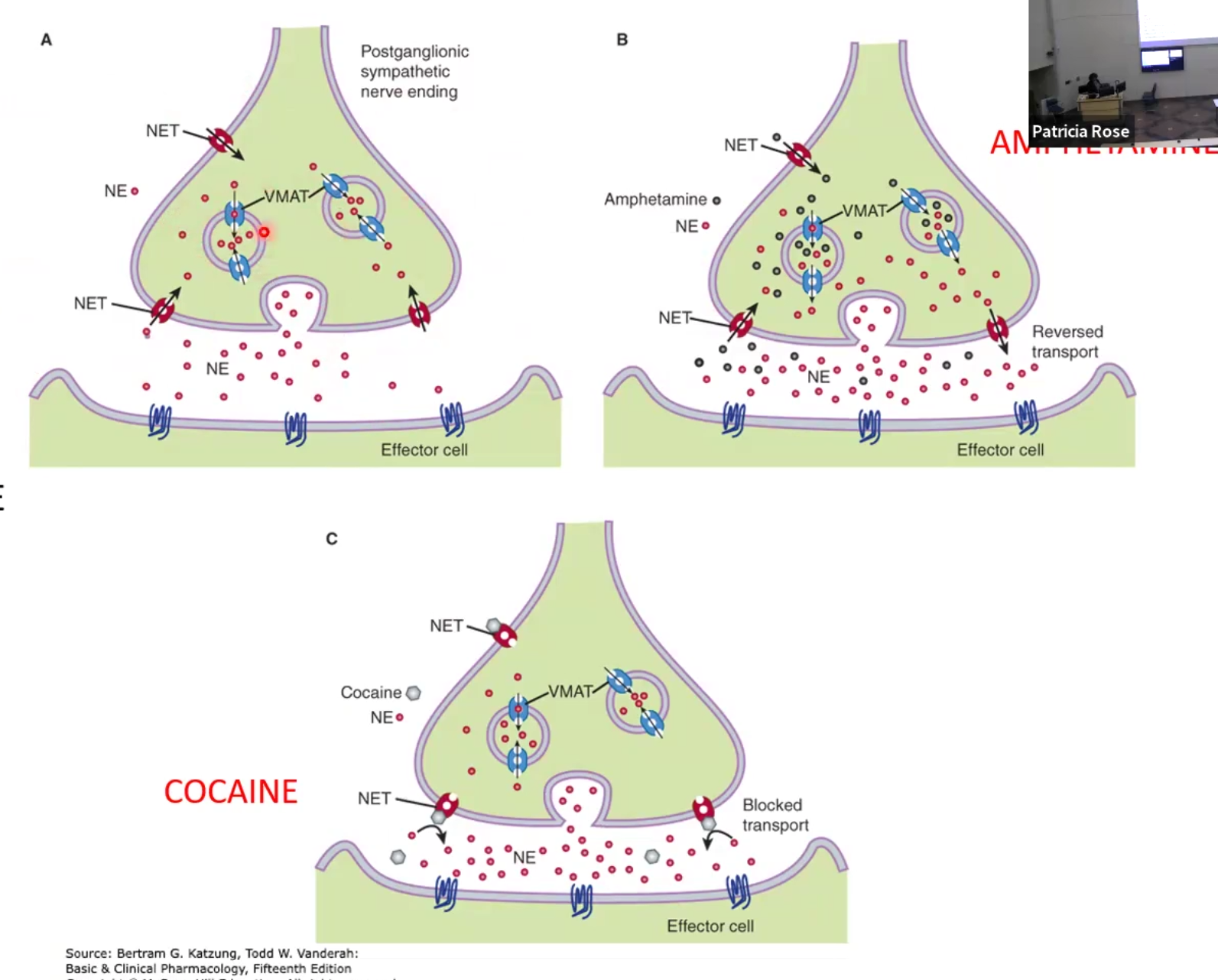
Amphetamine: increase NE release by displacing it from storage or via reverse transport NET
Tyramine-containing foods like wine and cheese also displace NE, primarily dangerous when on MAO inhibitor drugs (antidepressants)
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCA’s), SNRI’s and Cocaine: block NET transporter and increase NE in synapse
Adverse effects are ↑BP and HR
Reserpine: depletes NE and makes indirect-acting sympathomimetics lose effect
Selective α1 Agonists
Phenylephrine (Neosynephrine) PROTOTYPE
↑Ca+, Vasoconstriction, ↑BP
Used for hypotension and shock, mydriasis, nasal decongestant
Midodrine (Pro-Amatine)
Same MOA, oral only, pro-drug
Used for symptomatic orthostatic hypotension and maintaining BP during hemodialysis
Adverse effects: hypertension, rebound congestion, reflex bradycardia, urinary retention, goosebumps
Selective α2 Agonists
Clonidine (Catapres)
Stimulates α2 receptor in the brain (NO BARORECEPTORS), in high doses also acts on α1
Used for severe hypertension, ADHD and epidural, opioid withdrawal
Guanfacine (Tenex, Intuniv)
Same as clonidine
Hypertension and ADHD
Tizanidine (Zanaflex)
Related to clonidine, central acting on SK, no CV effect
Used as a muscle relaxant
Drug interaction with ciprofloxacin
α-Methyldopa (Aldomet)
Same as Clonidine but is a pro-drug
Antihypertensive, crosses placental barrier
Dexmedetomidine (Precedex/Igalmi)
Related to clonidine as well, used as sedative for ICU patents, schizophrenic and bipolar
Apraclonidine (Iopidine)
Clonidine derivative, ↓cAMP and increases production of aqueous humor; does not cross BBB
↓IOP for glaucoma
Brimonidine (Alphagan)
Same MOA and clinical use as Apraclonidine but may cross BBB
NOT USED AS GEL bc it can cause orthostatic hypotension
Adverse effects: severe hypotension, xerostomia, sedation; for eye ones blurred vision
Selective α1 Blockers/Antagonists
The “-SINS”
Prazosin (Minipress) & Terazosin (Hytrin): block α1a,α1b,α1c
↓vasoconstriction & BP
Treat hypertension
Doxazosin (Cardura): for BPH and hypertension comorbidity
Tamsulosin (Flomax): selective α1a blocker specifically for BPH and causes less orthostatic hypotension
Non-Selective α1 & α2 Blockers/Antagonists
Phentolamine (Oraverse)
Competitive antagonist
Used as local injection to prevent necrosis due to α agonist extravasation; used to reverse EPI when it is used with lidocaine for oral anesthesia, vasodilation
Contraindication for angina, worsens tachycardia
If combined with epi, it can decrease BP even more
Phenoxybenzamine
Irreversible Non-competitive antagonist
Used for hypertension and localized sweating in pheochromocytoma
Contraindications: history of ischemic heart disease
Selective α2 Blockers/Antagonists
Yohimbe (Yohimbine)
Increases NE release
No longer used, causes nervousness, tremors, hypertension, pancreatic insulin release
Direct Acting β1 Agonists
Dobutamine (Dobutrex)
Used for cardiogenic shock and acute heart failure
Adverse effects include tachycardia, be careful with angina (coronary heart disease) patients
Selectivity lost at high doses; starts to hit the other receptors as well
Direct Acting β1&β2 Agonists
Iosoproterenol (Isuprel)
↑HR ↑vasodilation ↓Peripheral resistance
Used as a bronchodilator but may cause arrythmias
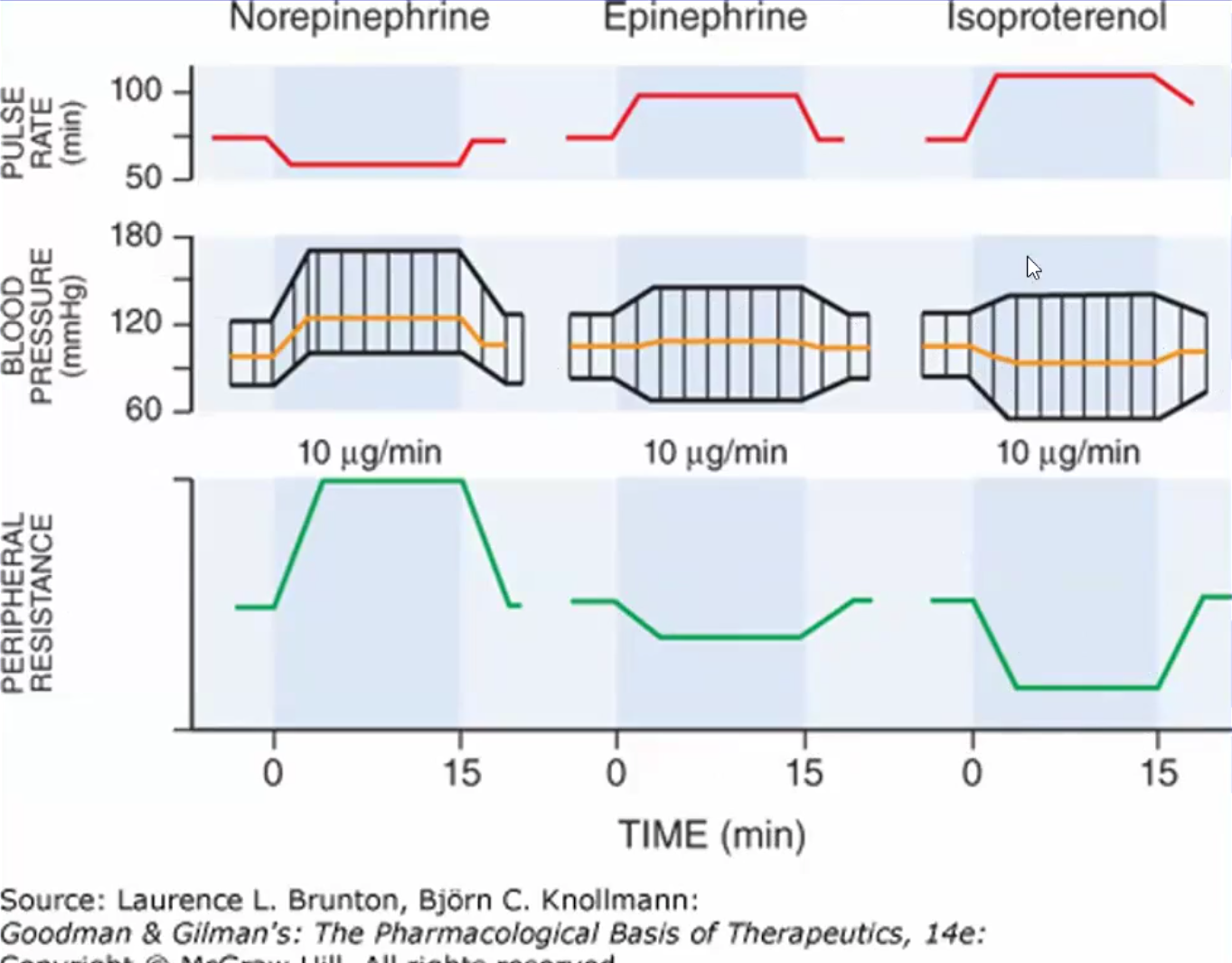
Effects of NE, Isoproterenol and EPI on BP, HR and PVR
NE: ↑PVR↑BP↓Initial pulse rate due to reflex bradycardia
EPI: ↓PVR~same BP ↑Pulse rate
Isoproterenol: ↓PVR ↓BP↑Pulse rate due to reflex tachycardia
Selective β2 Agonists
All bronchodilators
Albuterol & Levalbuterol: for oral inhalation; emergency rescue inhalers bc lasts 2-6hrs
Salmeterol &Formoterol: even more selective for β2; not for emergency rescue bc they last 12-24hrs
Terbutaline: uterine smooth muscle relaxant, not used anymore
Side effects: tachycardia, palpitations
Selective β3 Agonists
Mirabegron (Myrbetriq)
Used to relax bladder walls and calm overactive bladder, allow filling
Can cause hypertension, do not give to pt with urinary/bladder obstruction
Non-Selective β Blockers/Antagonists
Propranolol (PROTOTYPE), Nadolodol, Timolol
Crosses BBB, anesthetic effects so cannot be used as eye drops
Used for hypertension, angina, arrhythmias, migraines
May cause bradycardia, cardiac depression, sedation, hypoglycemia (do not give to diabetics), may worsen peripheral vascular disease
If combined with EPI, alpha receptors are unopposed=more vasoconstriction
Pindolol: same but is a partial agonist (ISA)
Cardioselective (and kidney) β1 Blockers/Antagonists
Atenolol (Tenormin):Same effect as non-selective but safer for asthmatics, diabetics and PVD
Less sedative effects than non-selective β
Risk for rebound phenomenon if abruptly discontinued (becomes extremely tachycardic)
Metoprolol (Troprol XL): same but approved for heart failure and post MI
Acebutolol (Sectral): partial agonist (ISA), less risk for rebound phenomenon and side effects
Mixed β & α Blockers/Antagonists
Carvediol (Coreg): Blocks RAAS in HF
Labetalol (Normodyne): used for hypertensive crises in stroke patients, hypertension with clampsia or pre-clampsia, pheochromocytoma