Skeletal System
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
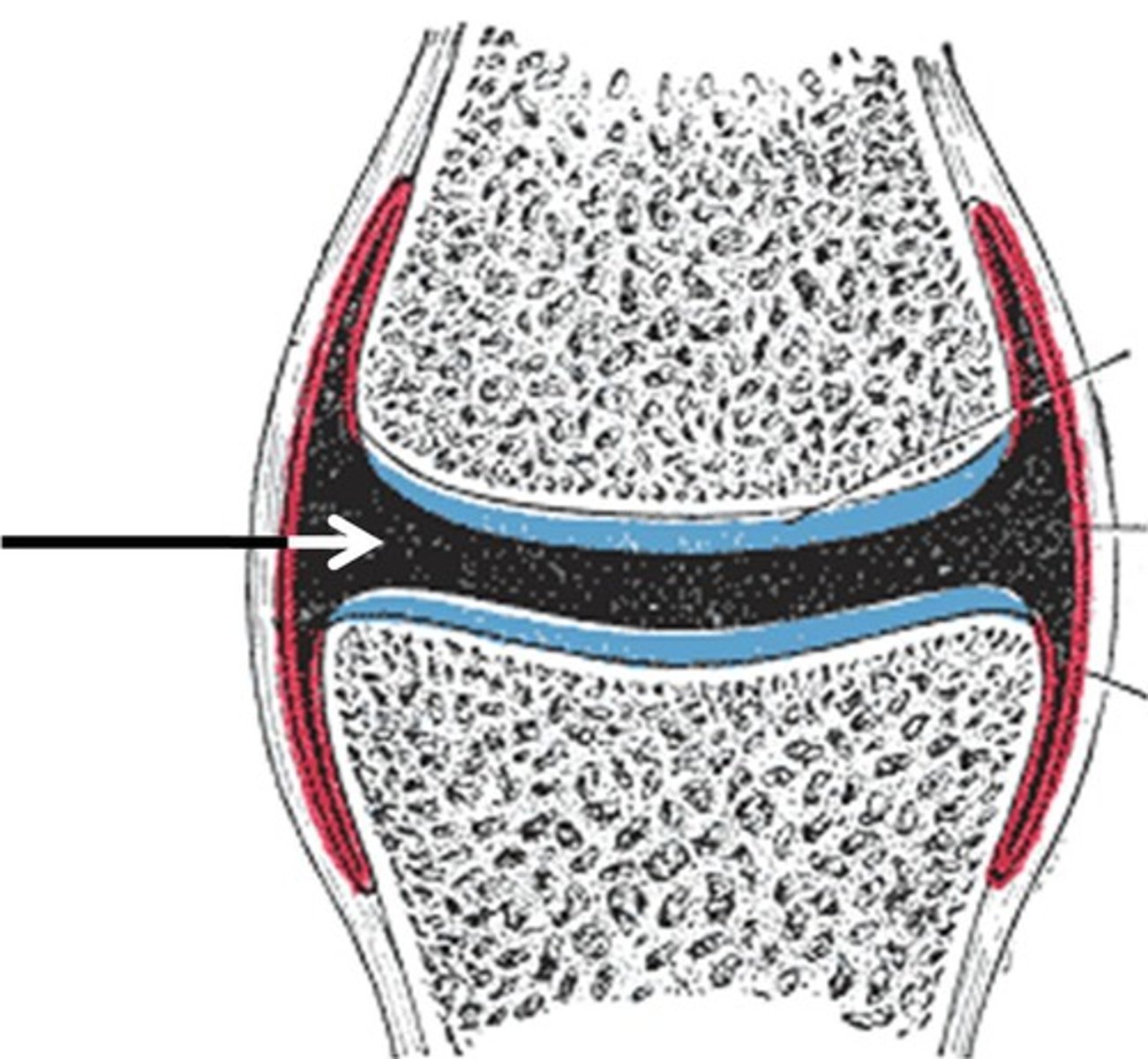
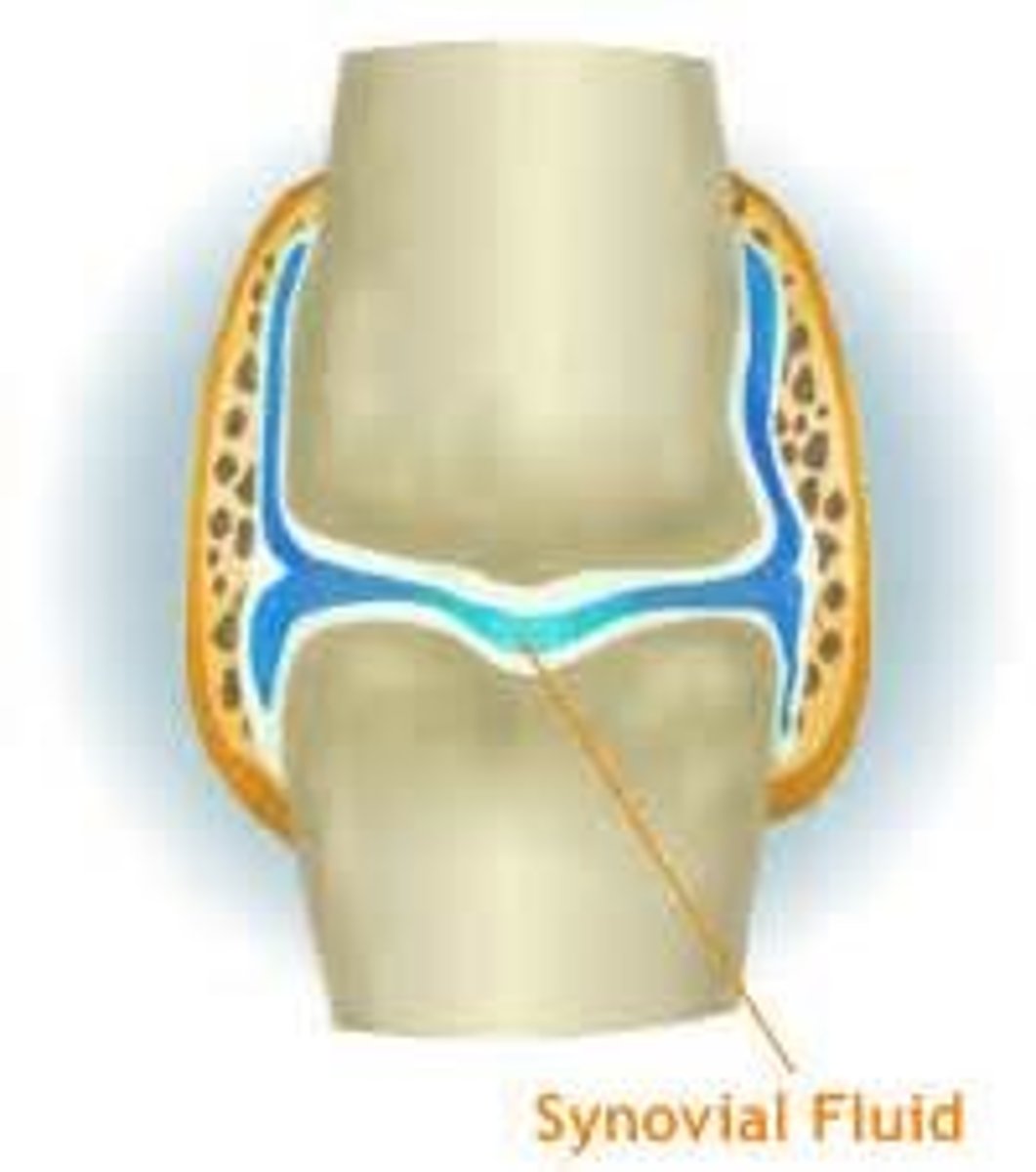
synovial cavity
contains the synovial fluid
synovial fluid
lubricates the articular surfaces of the opposing bones
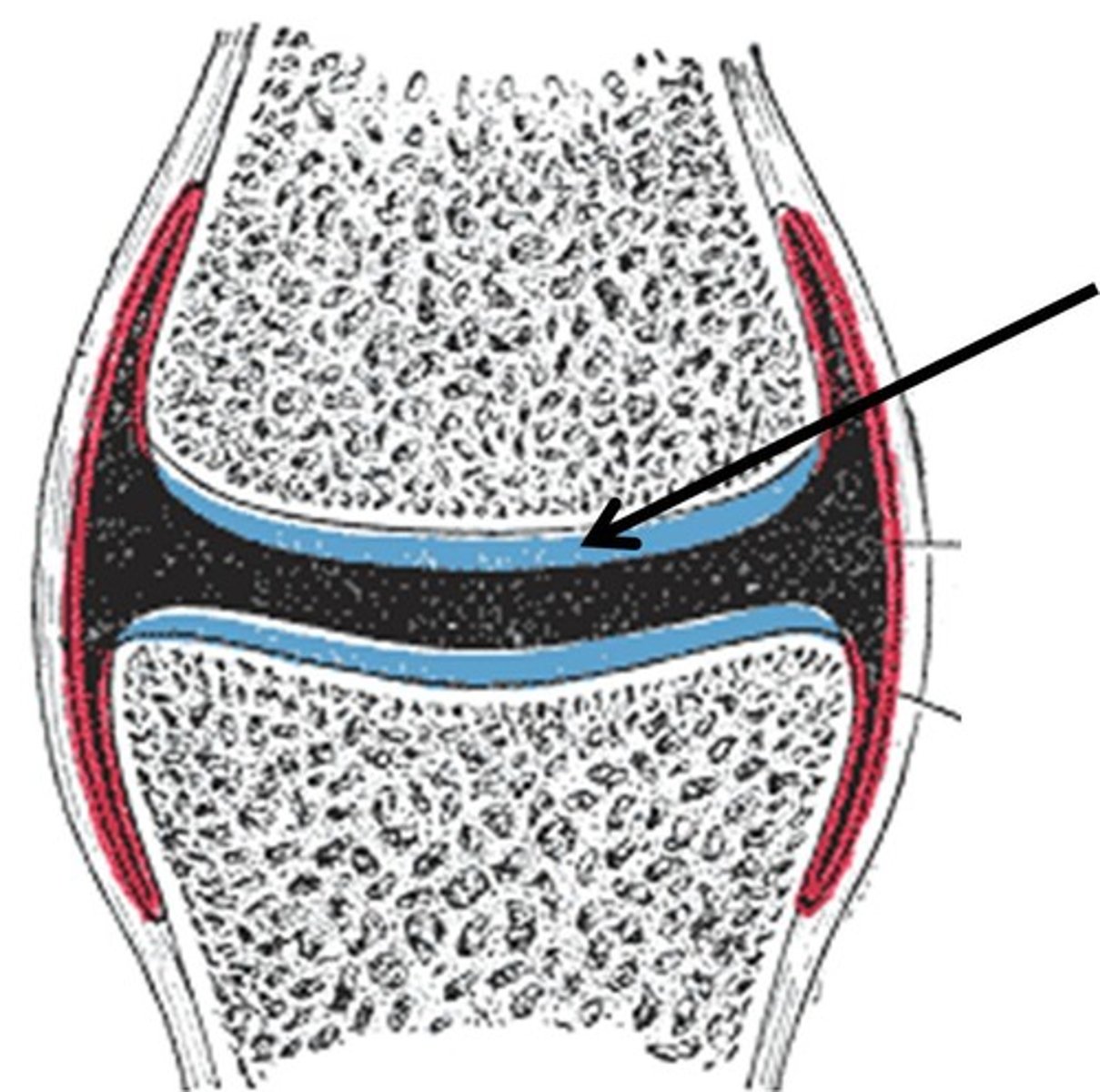
articular cartilage
a layer of hyaline cartilage that create a smooth surface to reduce friction
flexion movement
decrease in the angle between bones
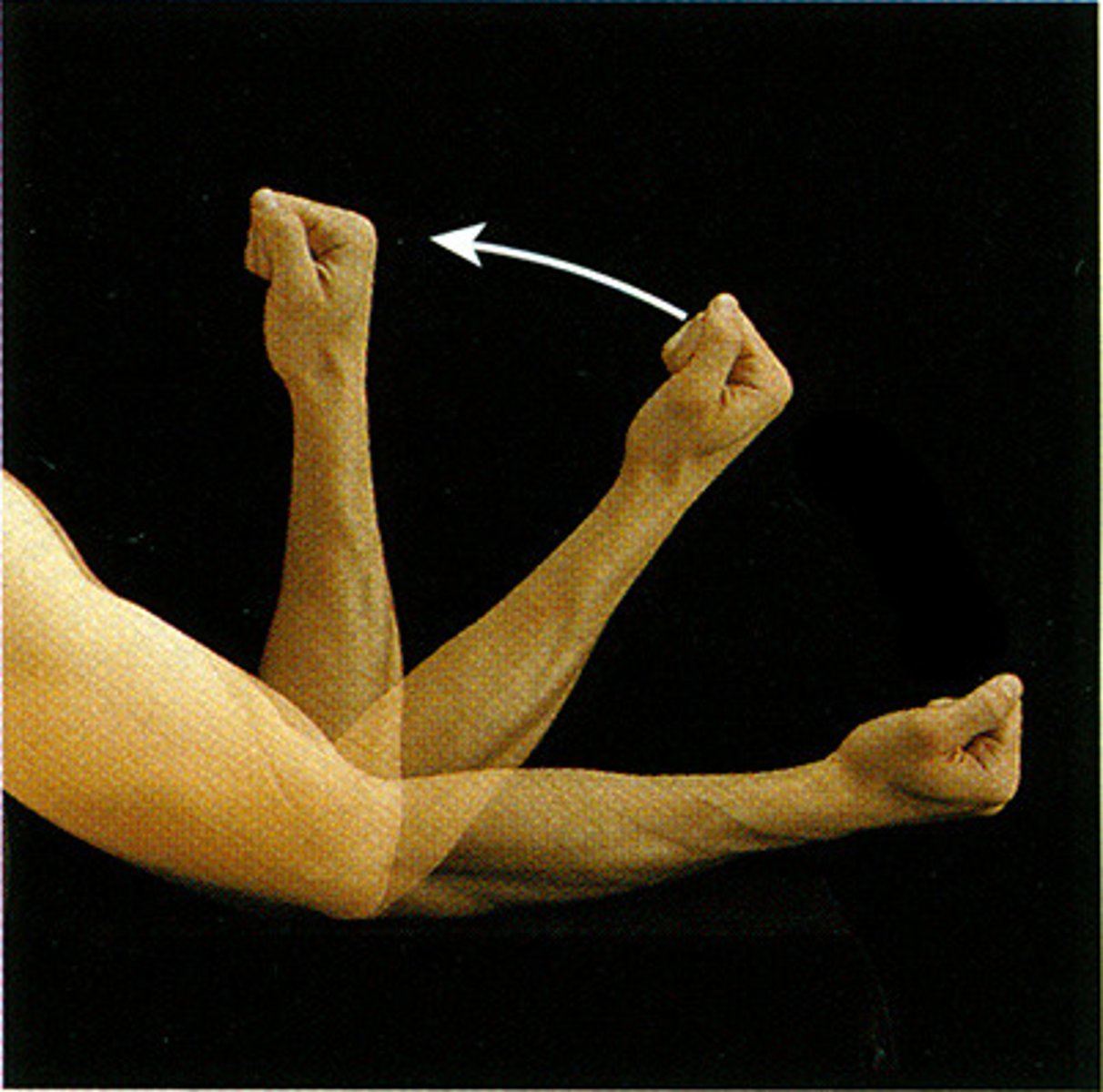
extension movement
increase in the angle between bones
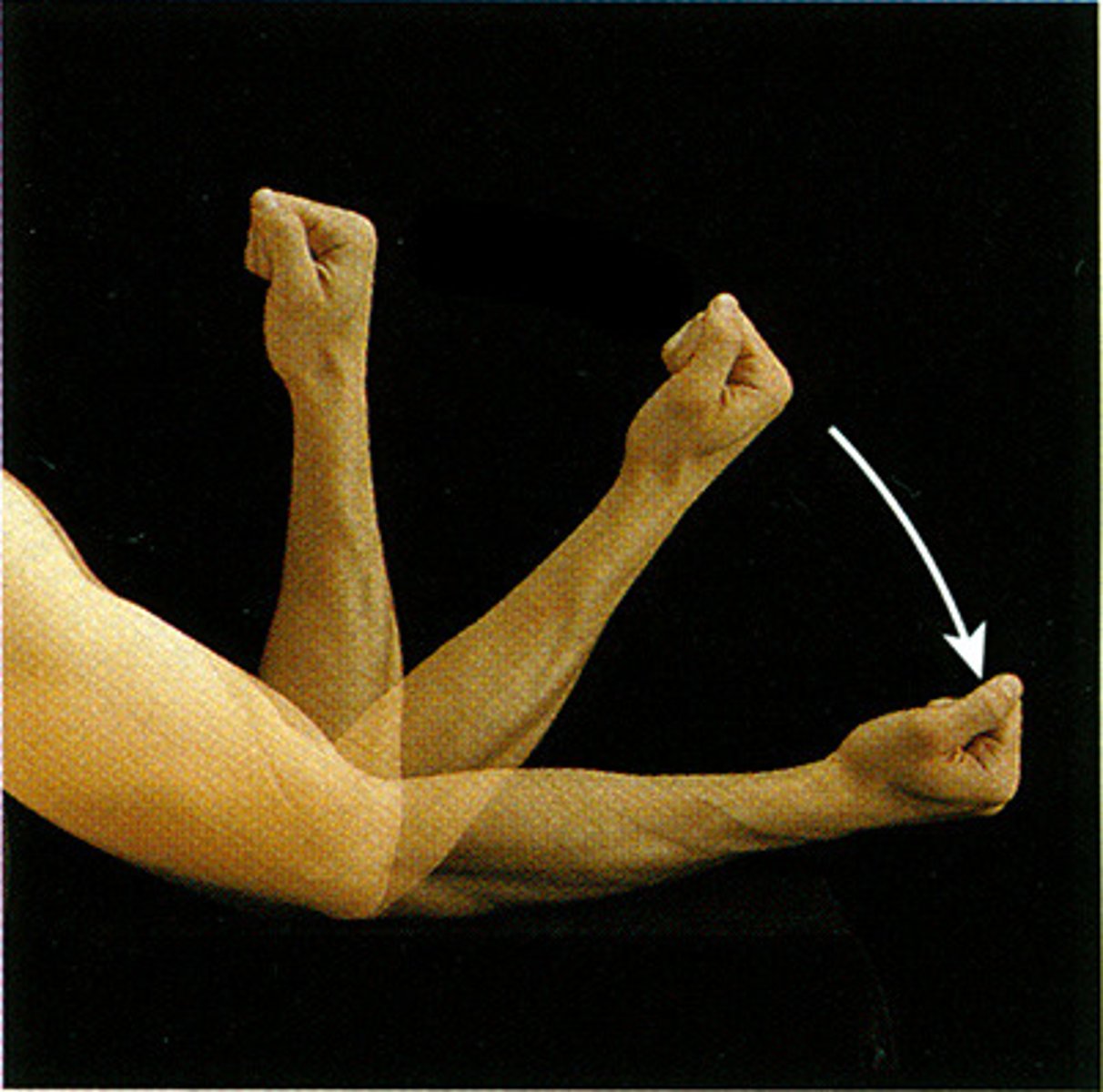
abduction movement
movement away from the body midline
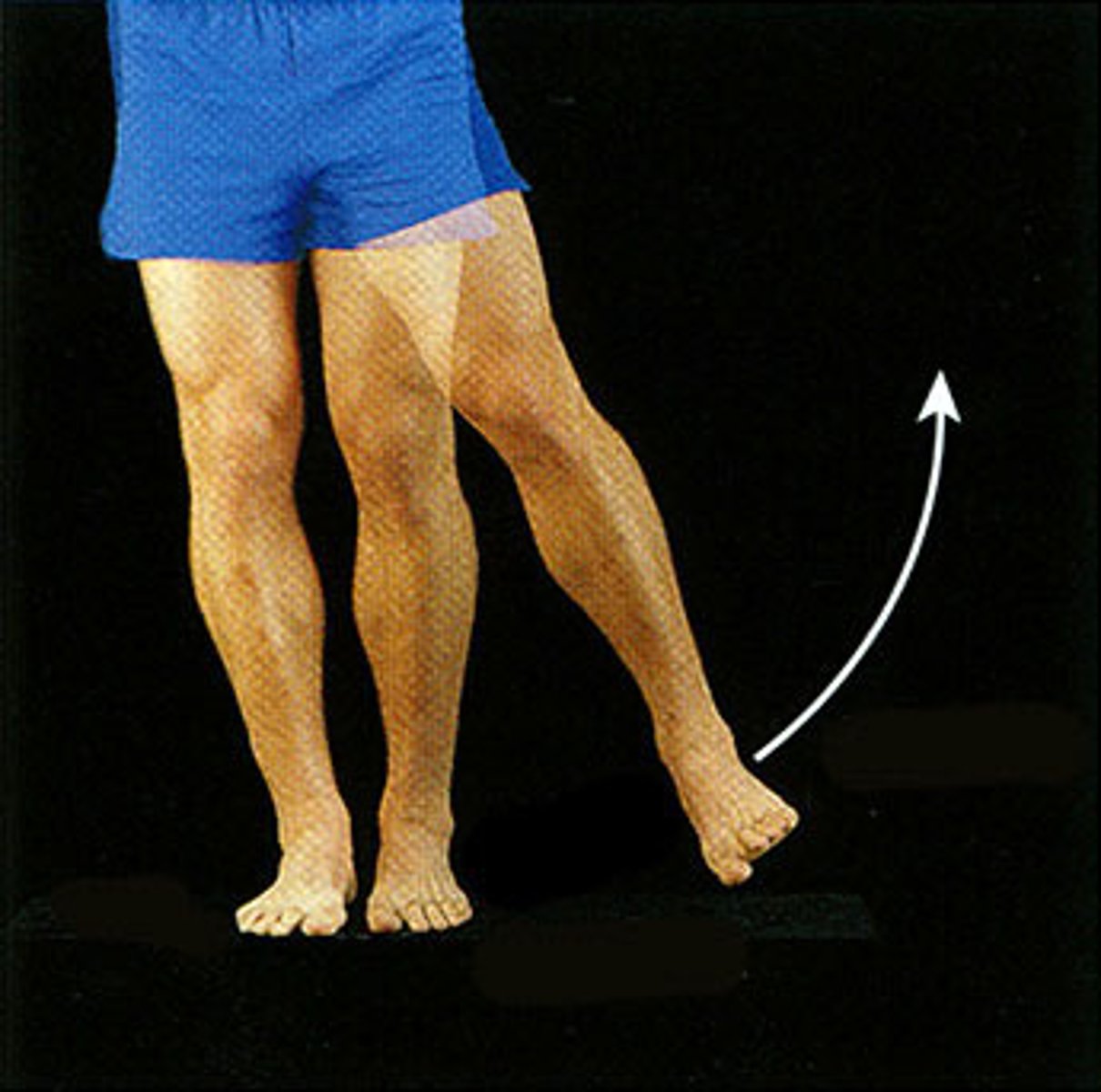
adduction movement
movement toward the body midline
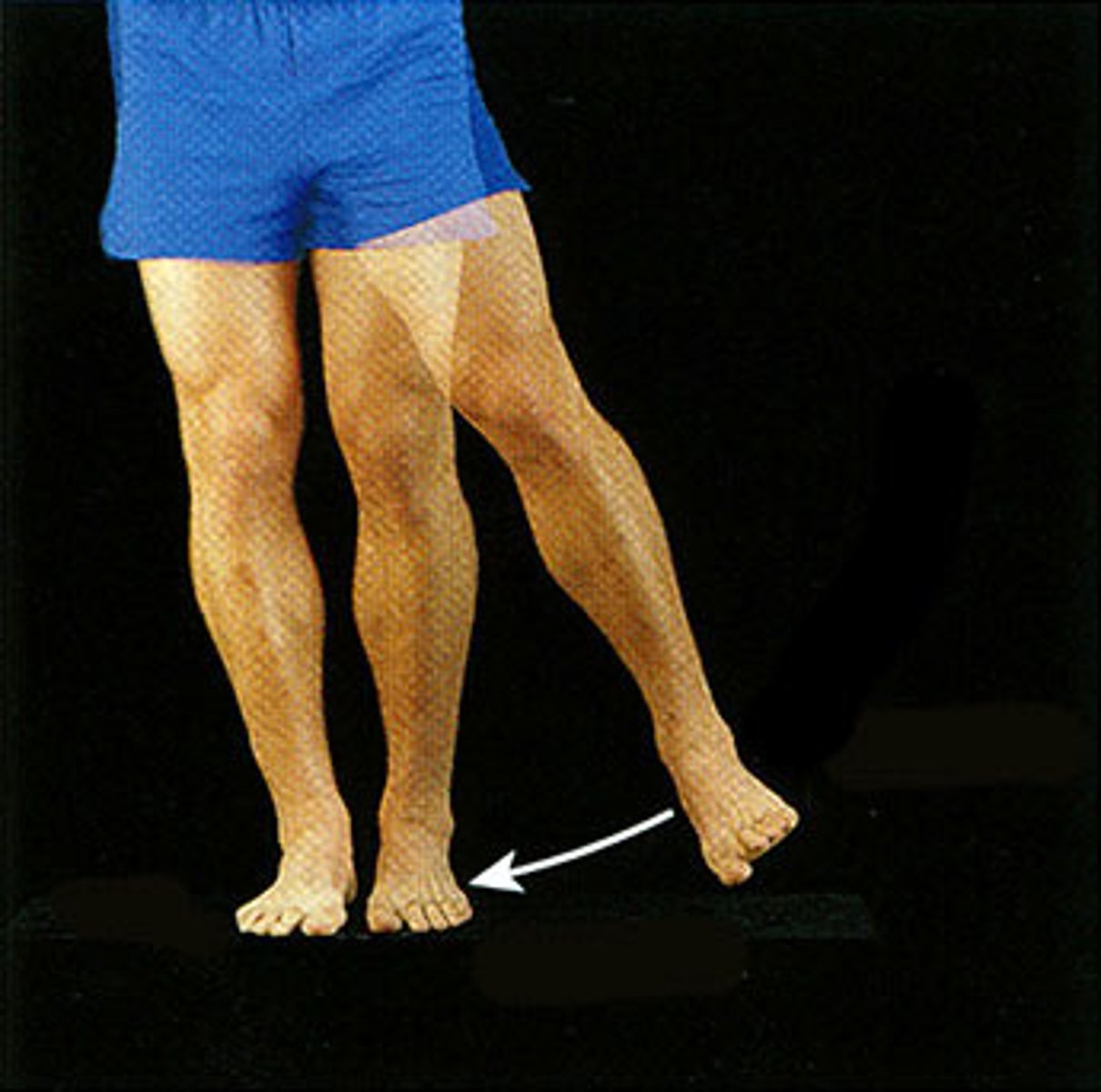
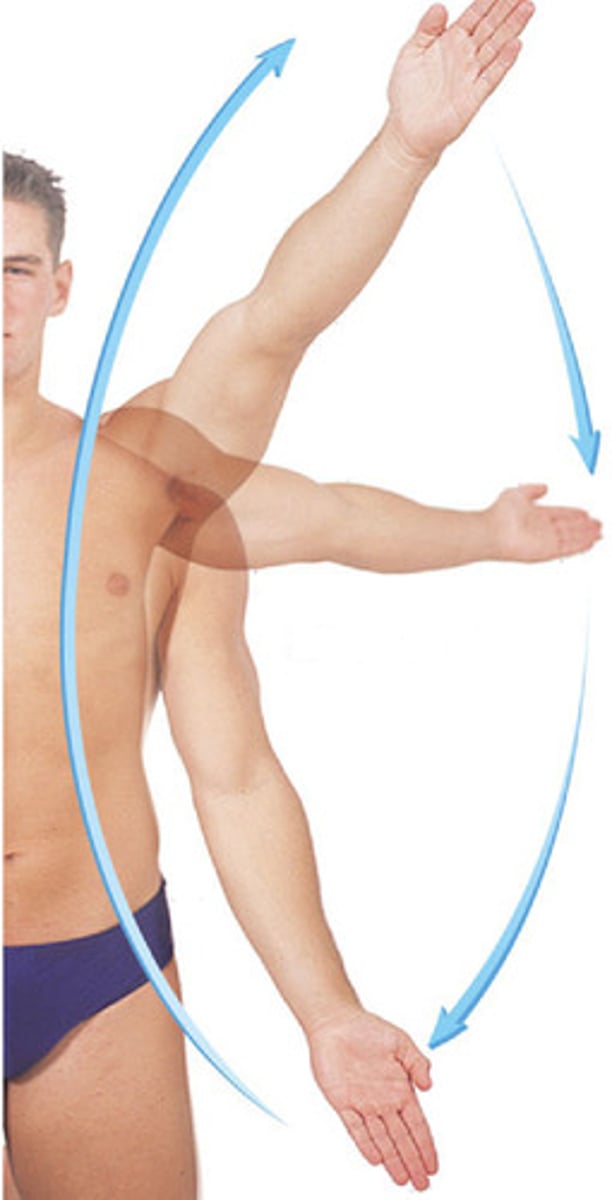
circumduction movement
movement of a distal part in a circular motion
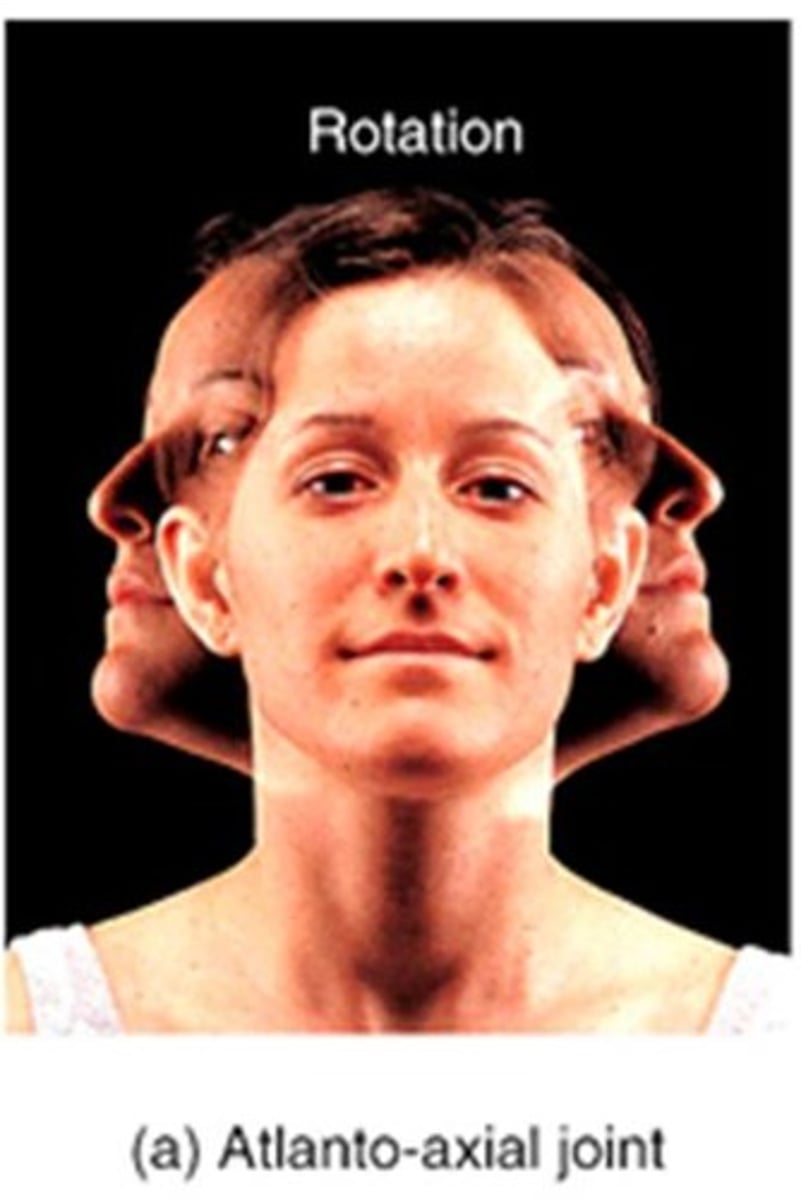
rotation movement
movement on a pivot in a circular motion
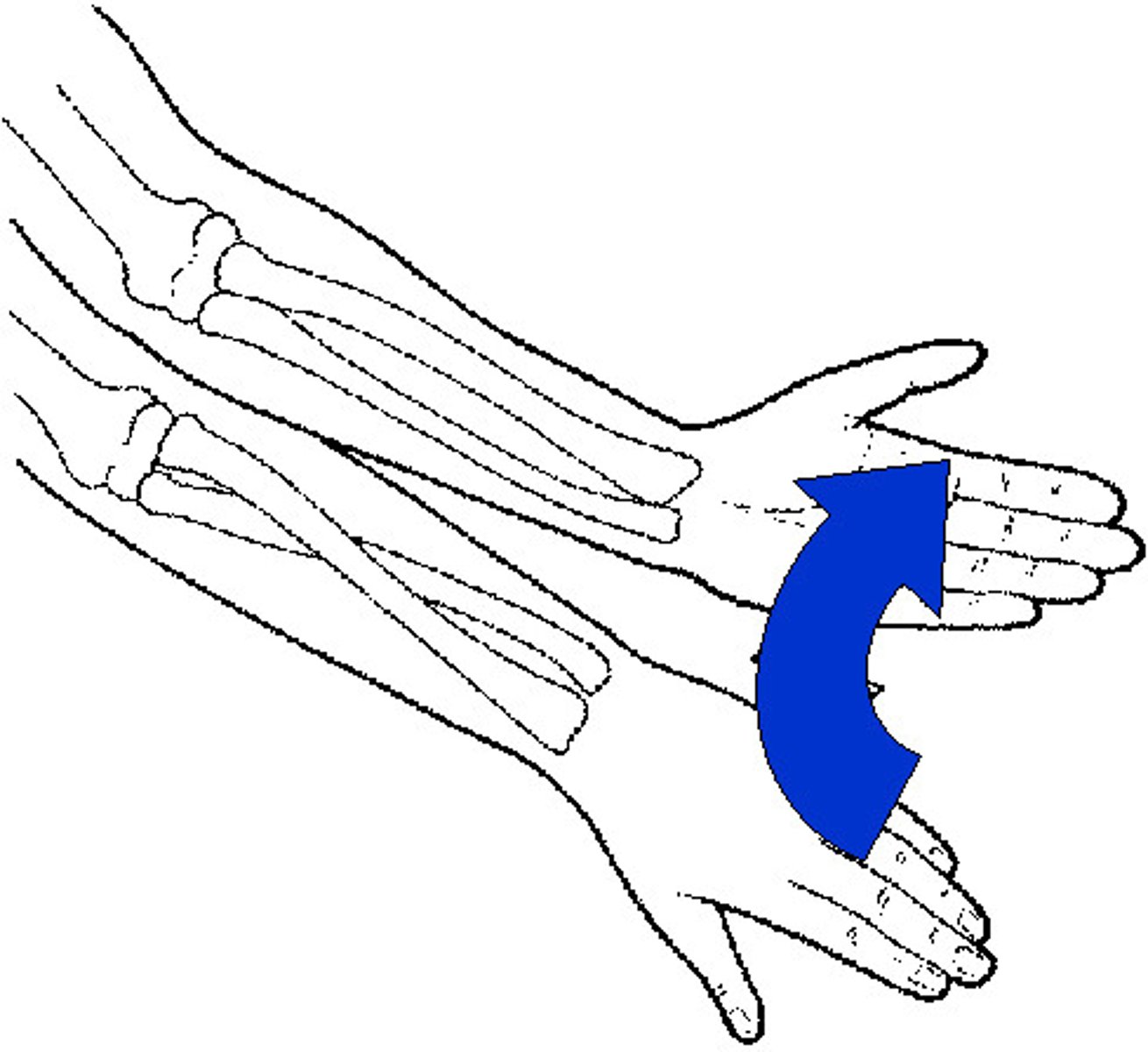
supination movement
palm movement from posterior to anterior
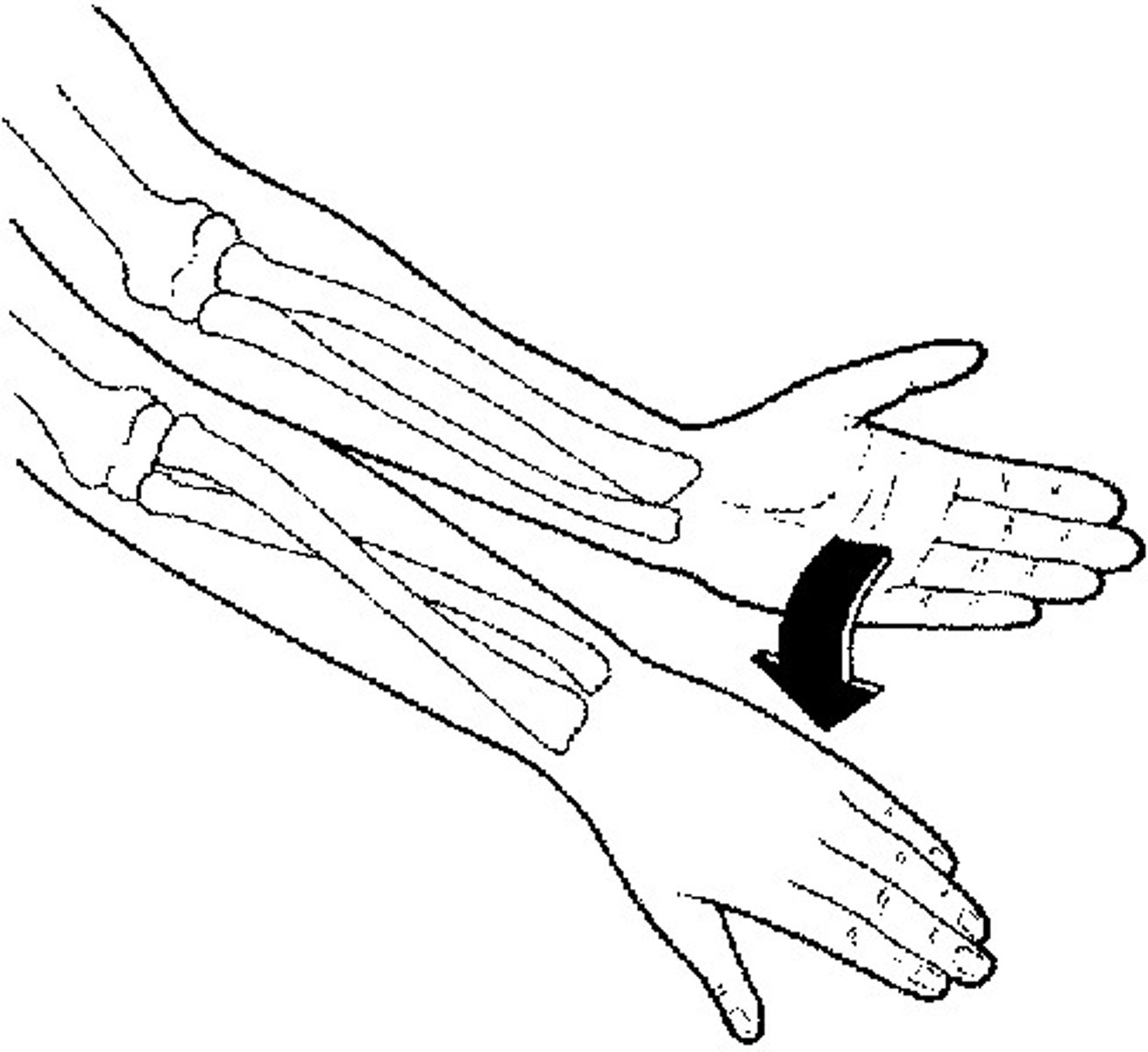
pronation movement
palm movement from anterior to posterior
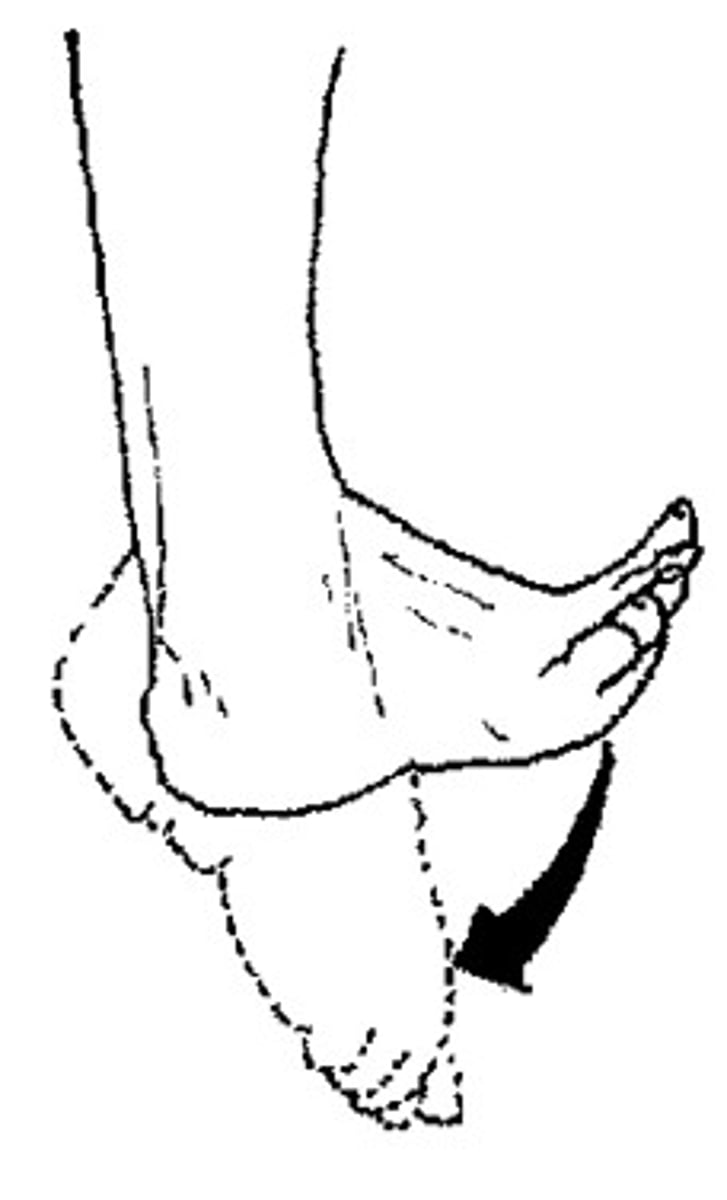
inversion movement
sole movement in a medial direction
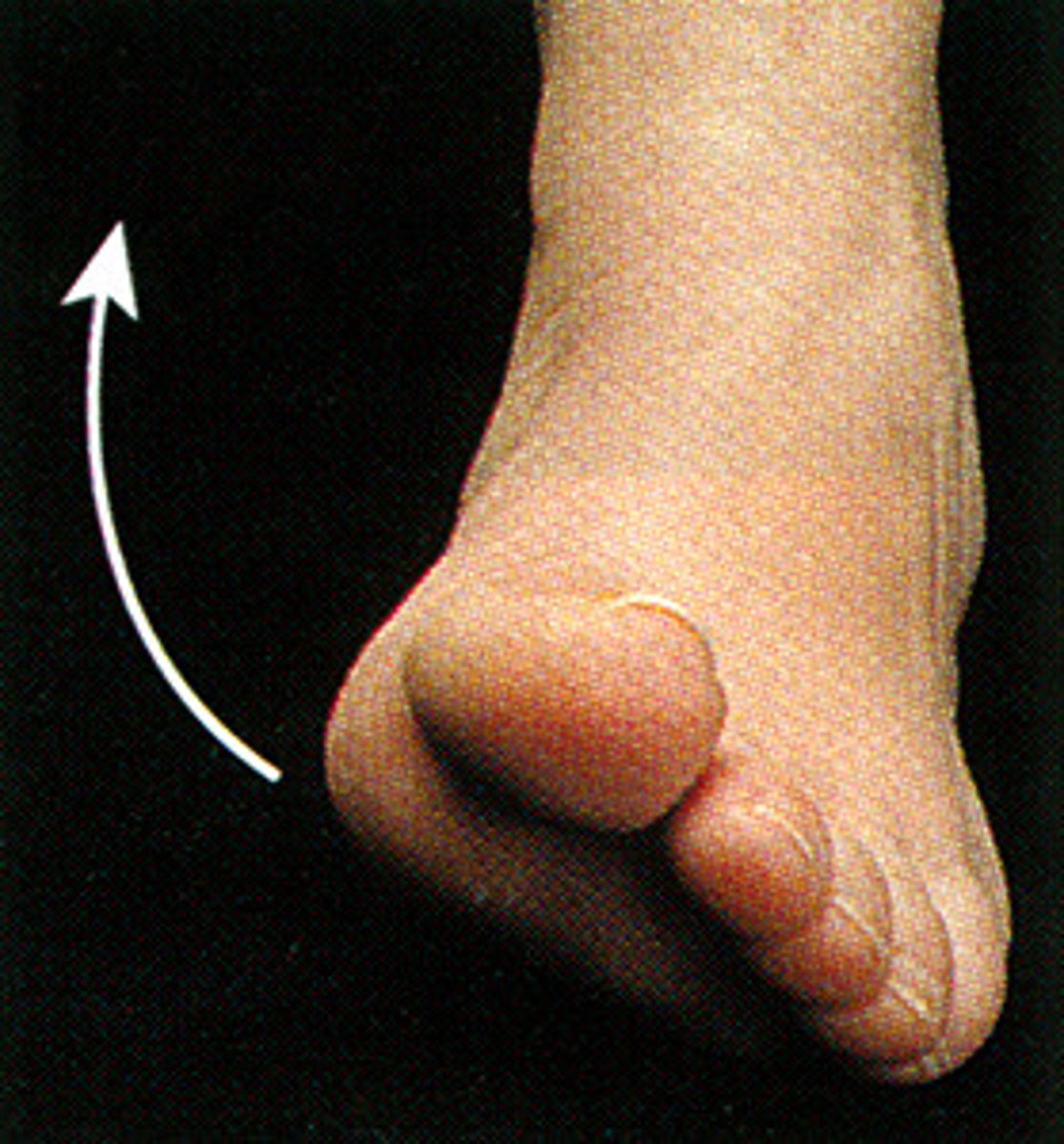
eversion movement
sole movement in a lateral direction
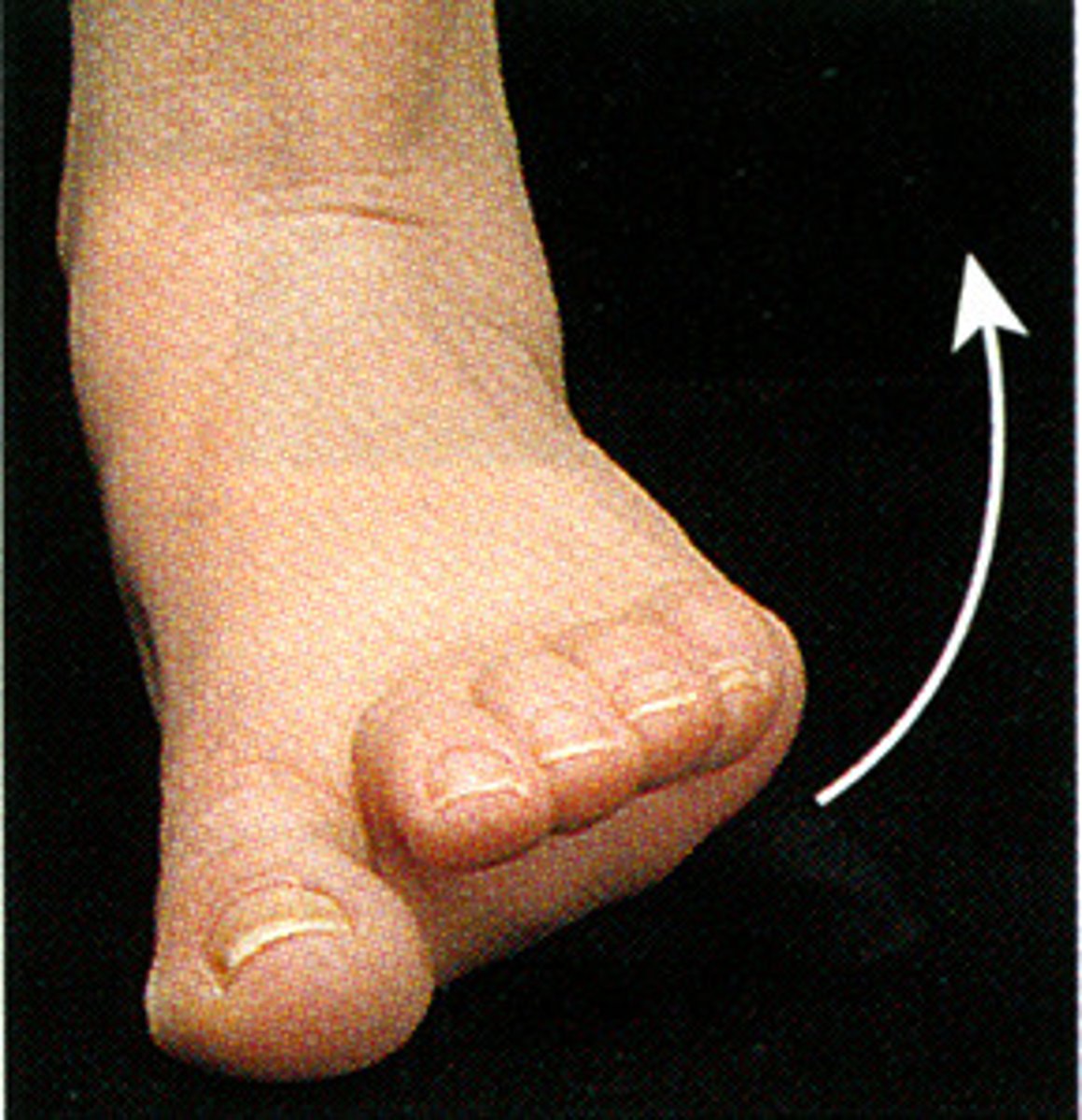
dorsiflexion movement
movement of the foot dorsally (point toes up)
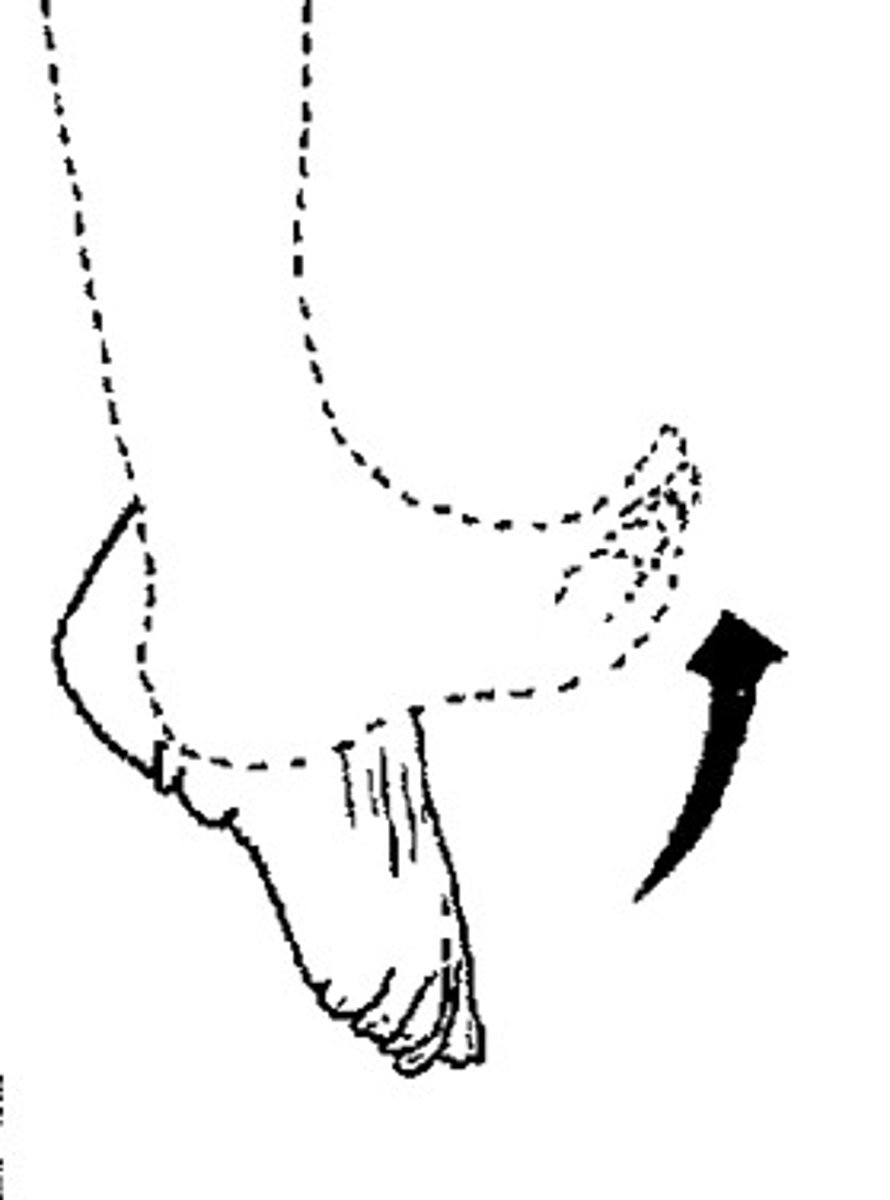
plantar flexion movement
movement of the foot inferiorly (stand on toes)
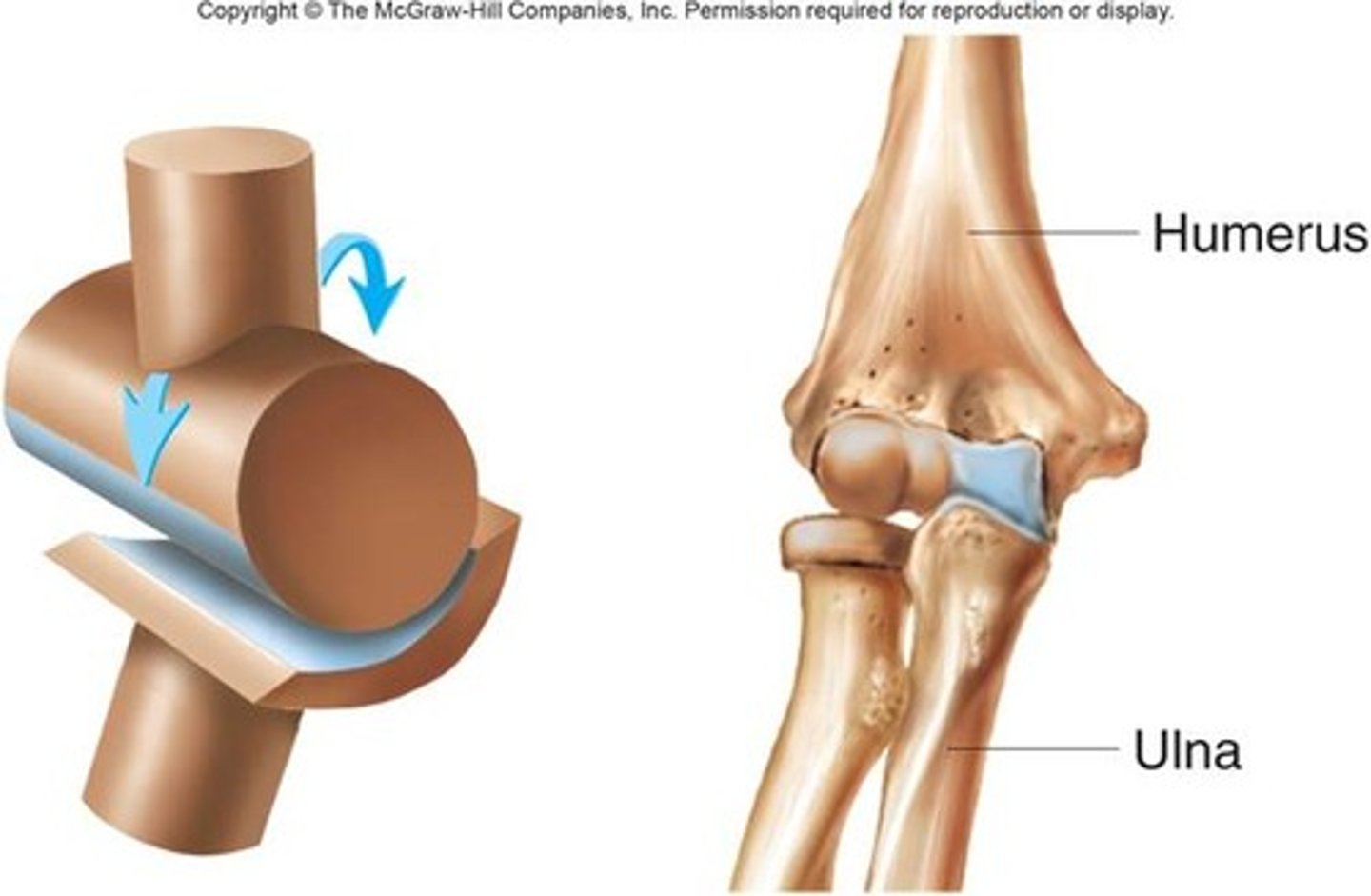
hinge joint
rounded bone fits into concave bone; flexion and extension (elbow joint)
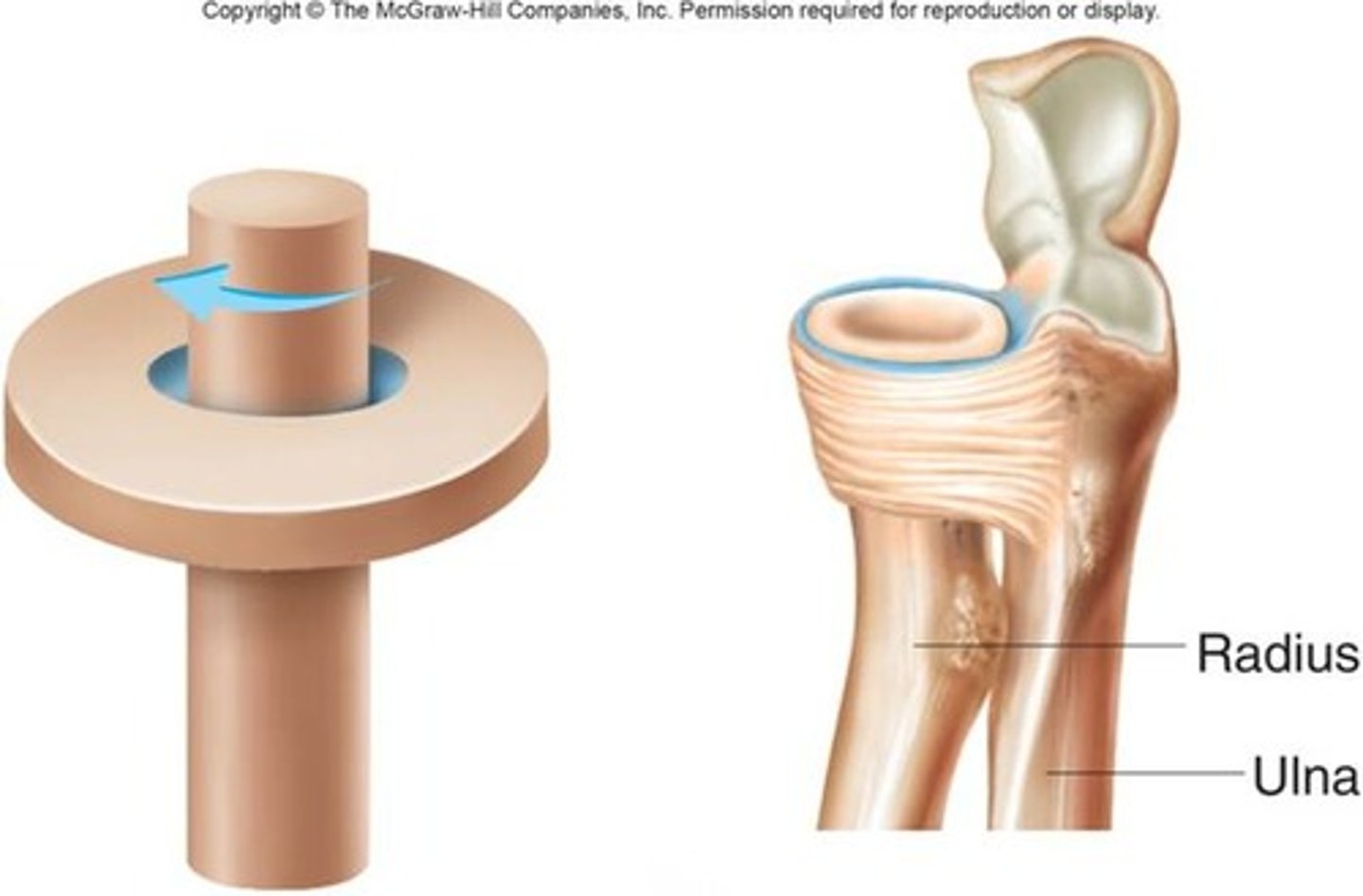
pivot joint
rounded bone fits into depression; rotation and supination/pronation
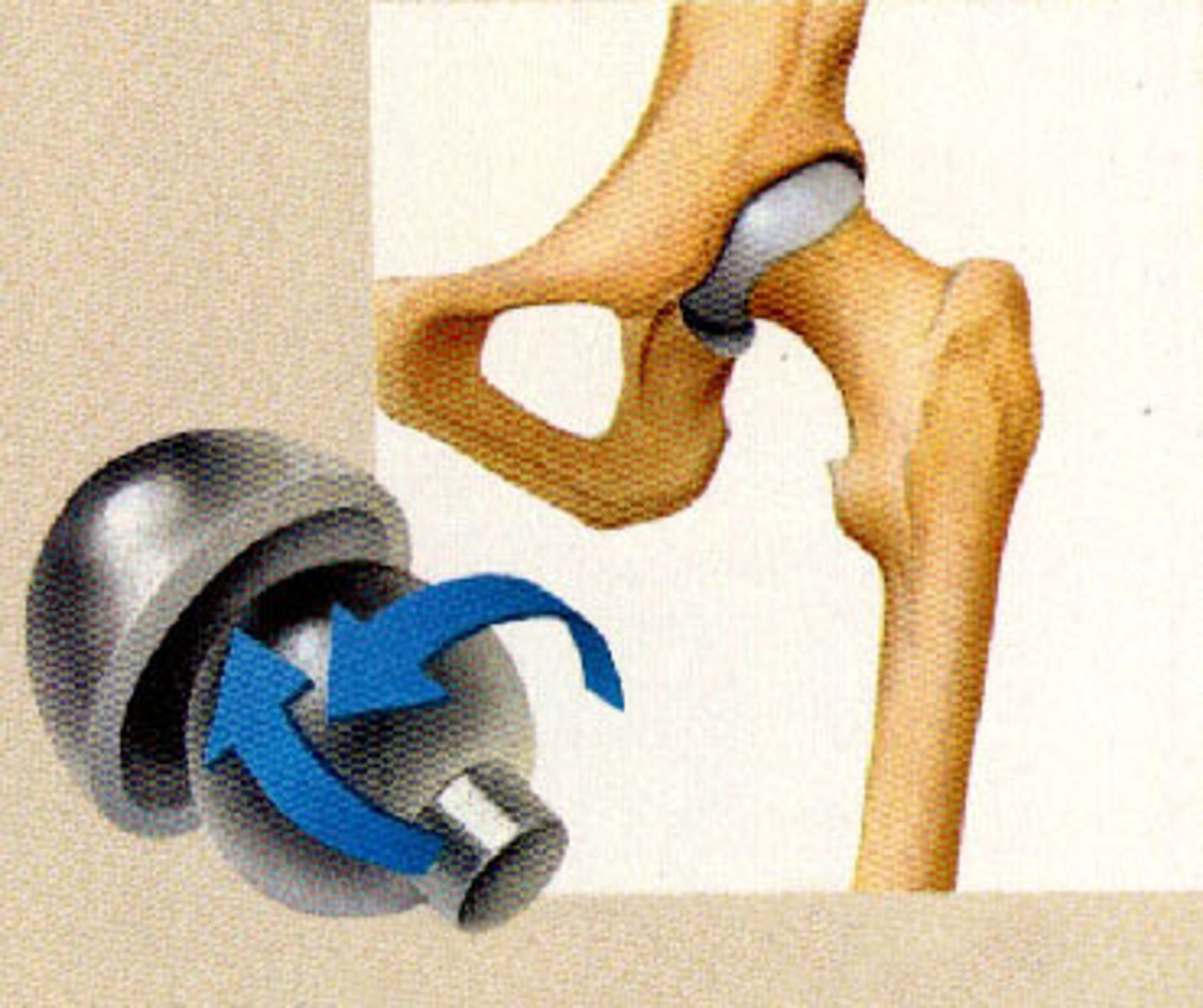
ball and socket joint
ball-shaped head fits into cup-like depression; all angular movements and rotation
central, vertical axis of the body, including the skull, vertebral column, and thoracic cage
axial skeleton
all bones of the upper and lower limbs, plus the girdle bones that attach each limb to the axial skeleton
appendicular skeleton
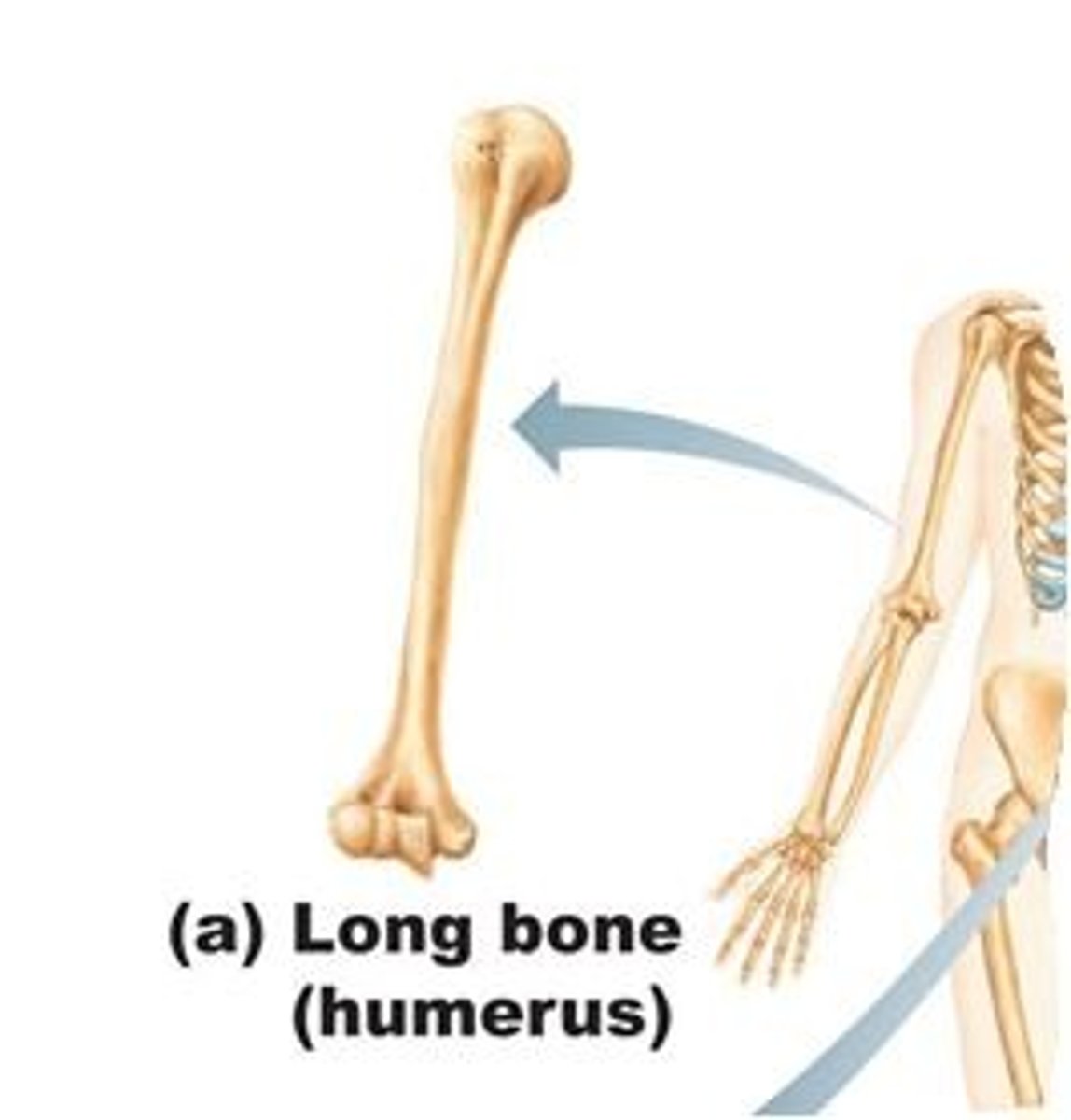
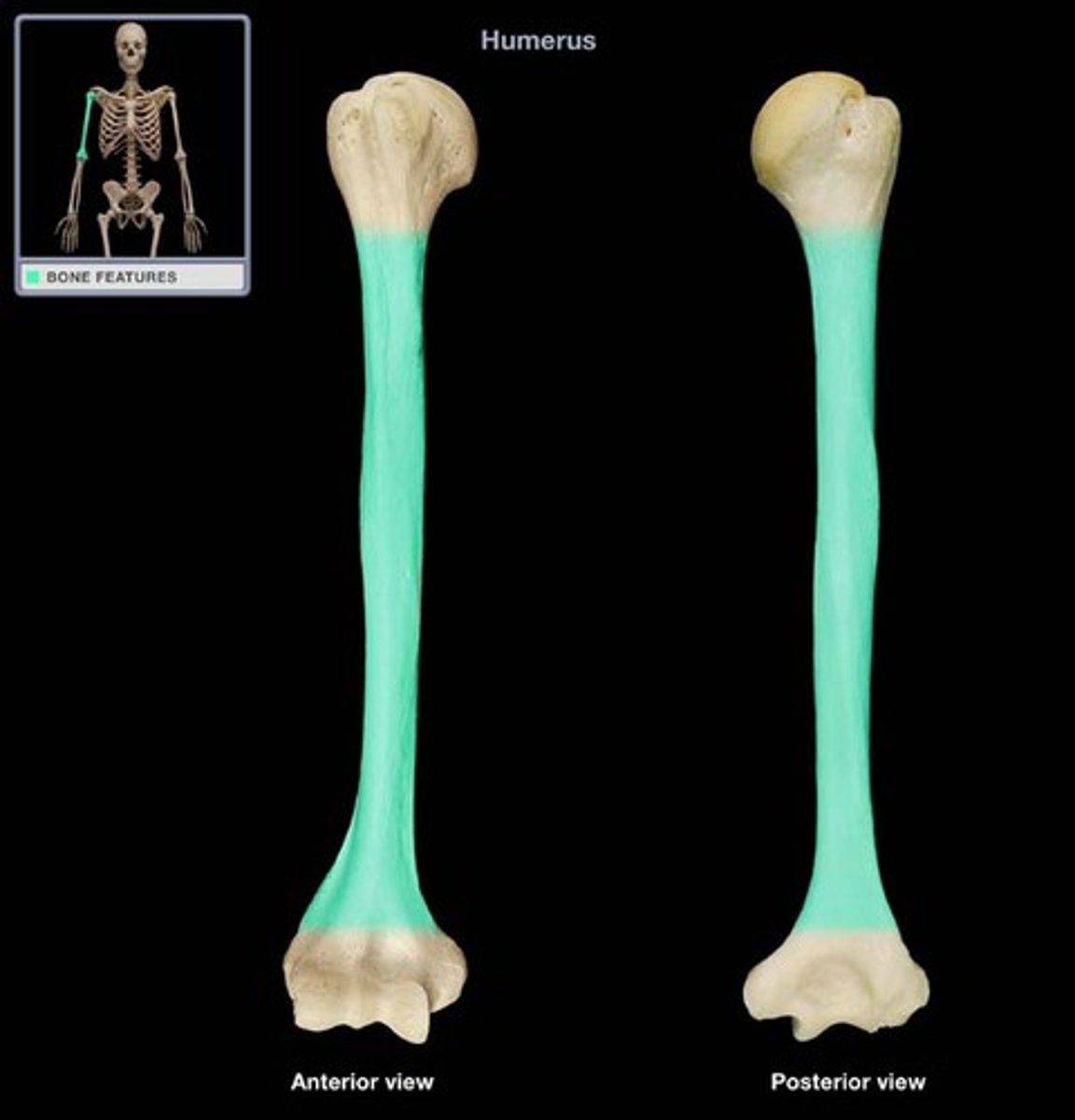
long bone
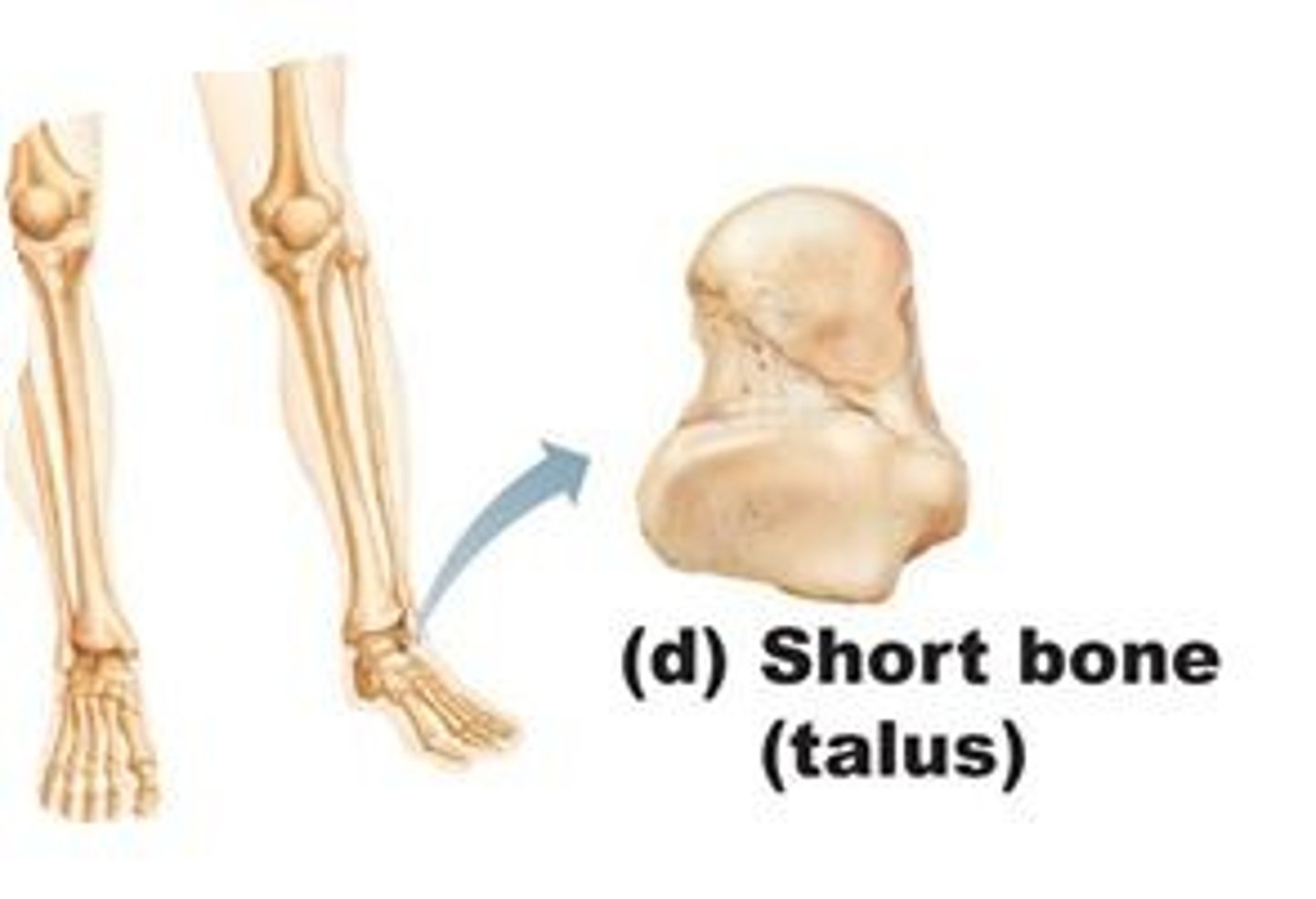
short bone
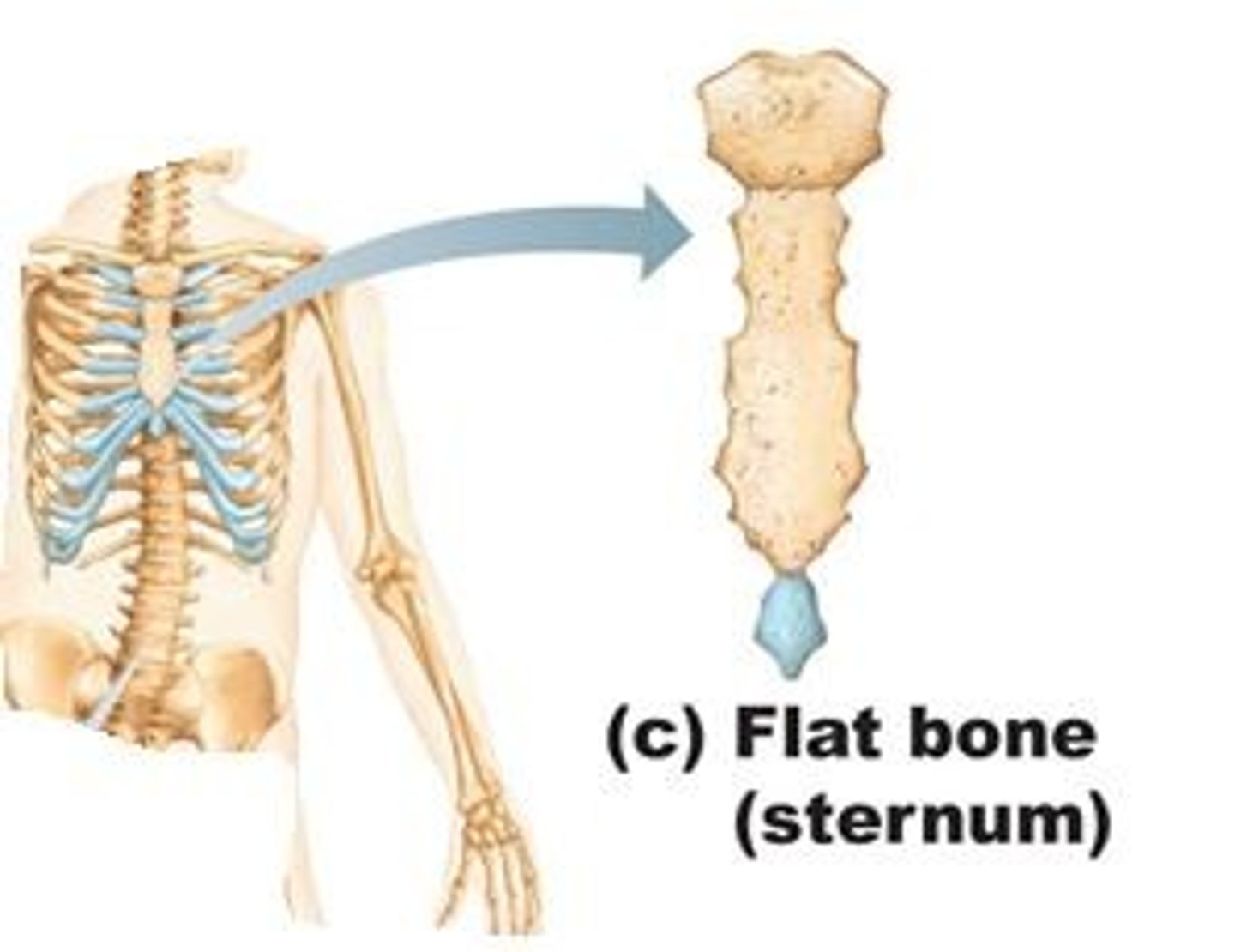
flat bone
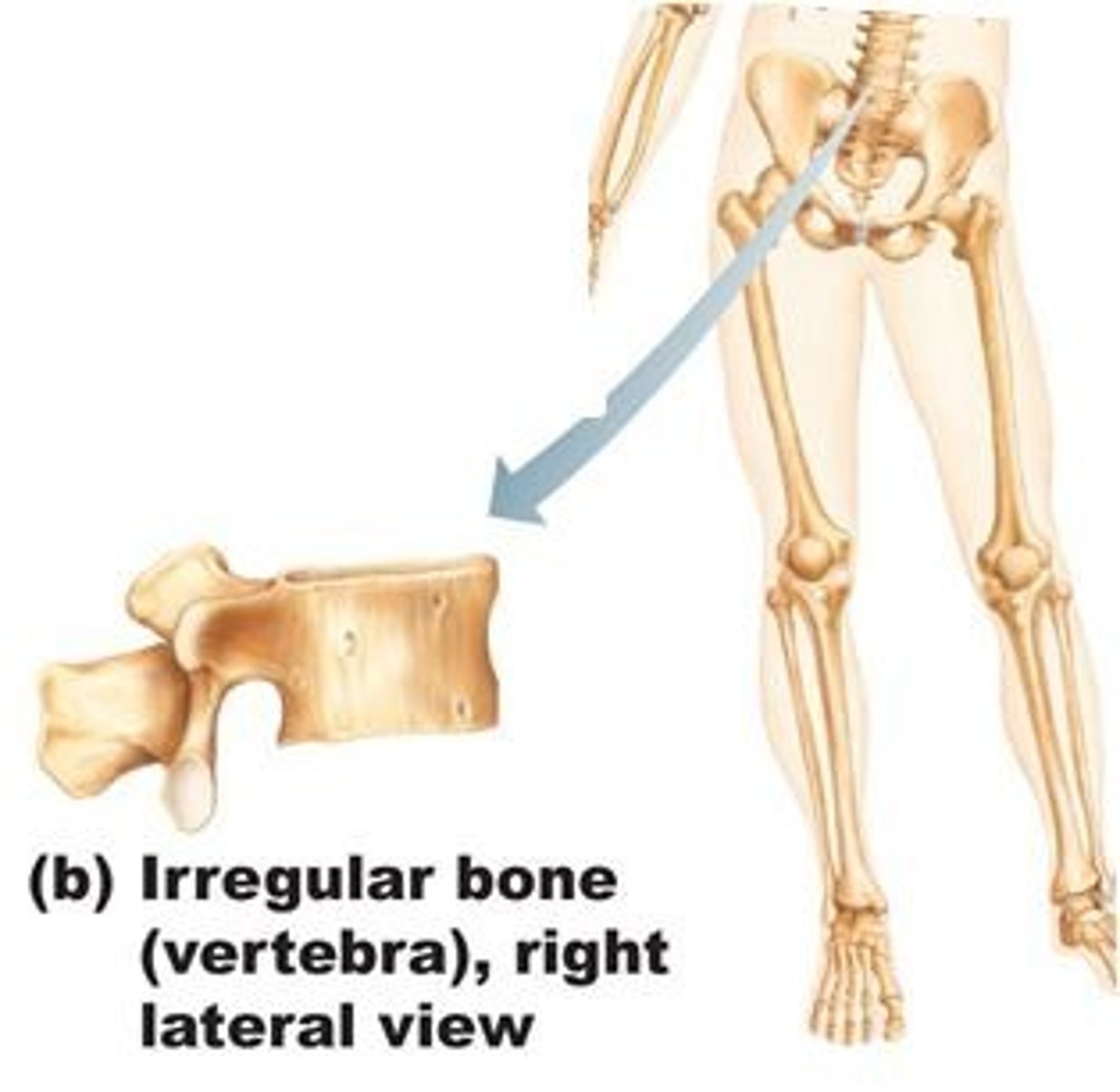
irregular bone
functions of skeletal system
support the body, protect soft organs, facilitate movement, store minerals and fats, blood cell formation
bone markings
surface features of bones, sites for muscle, tendon, and ligament attachment, passage for nerve and blood cells
projections
grow out from the bone surface
depressions
indentation
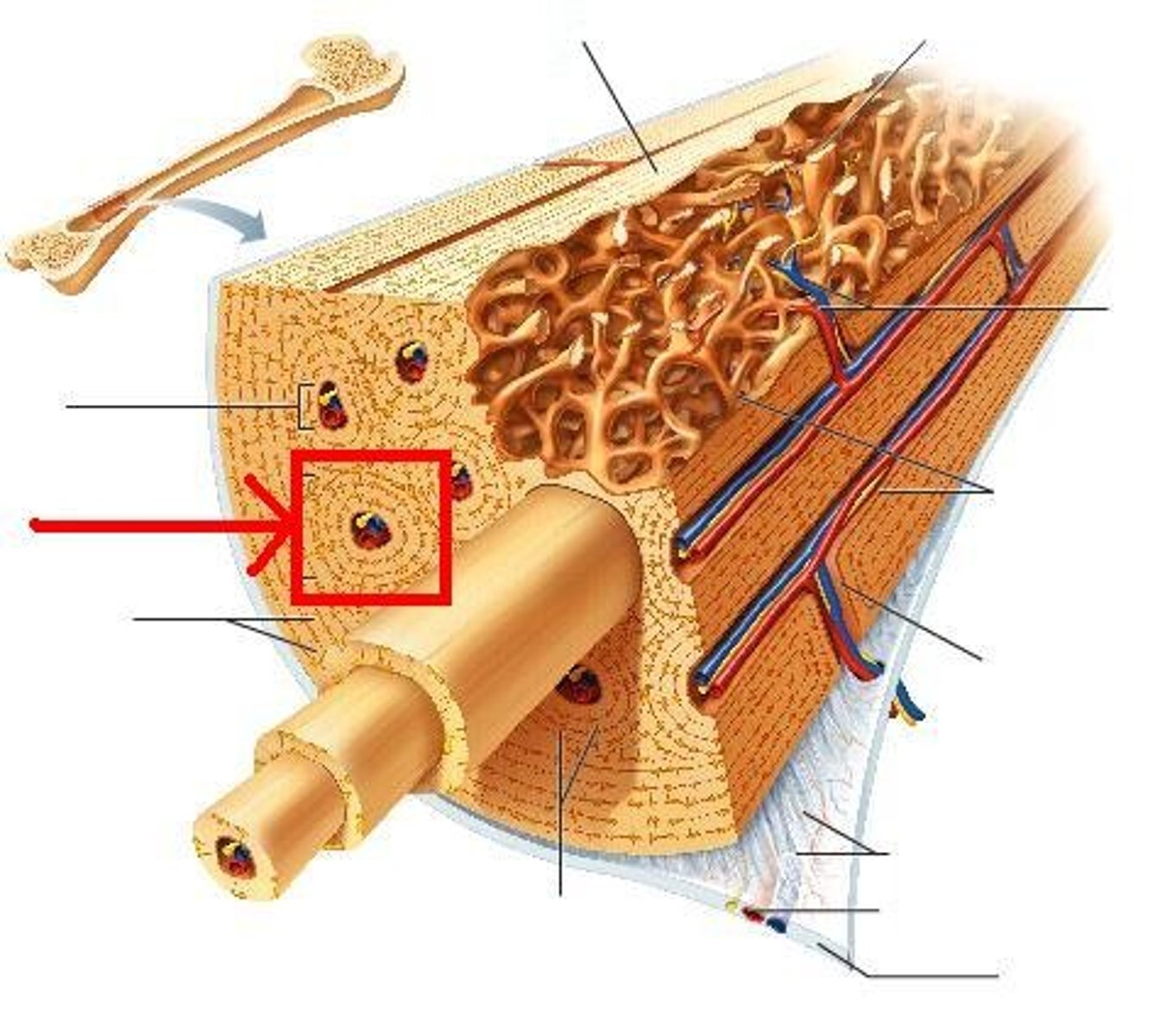
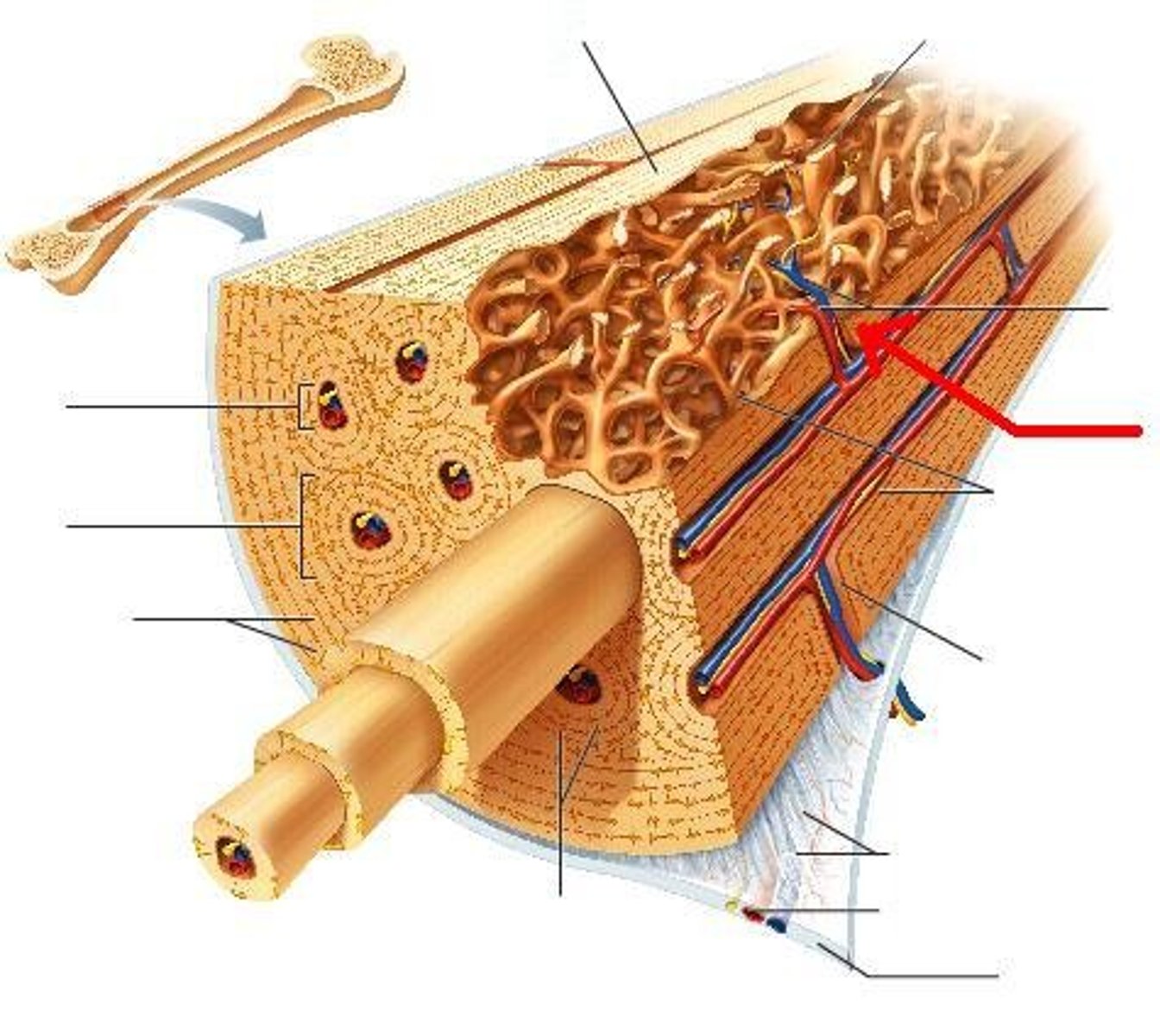
bone that surrounds yellow marrow
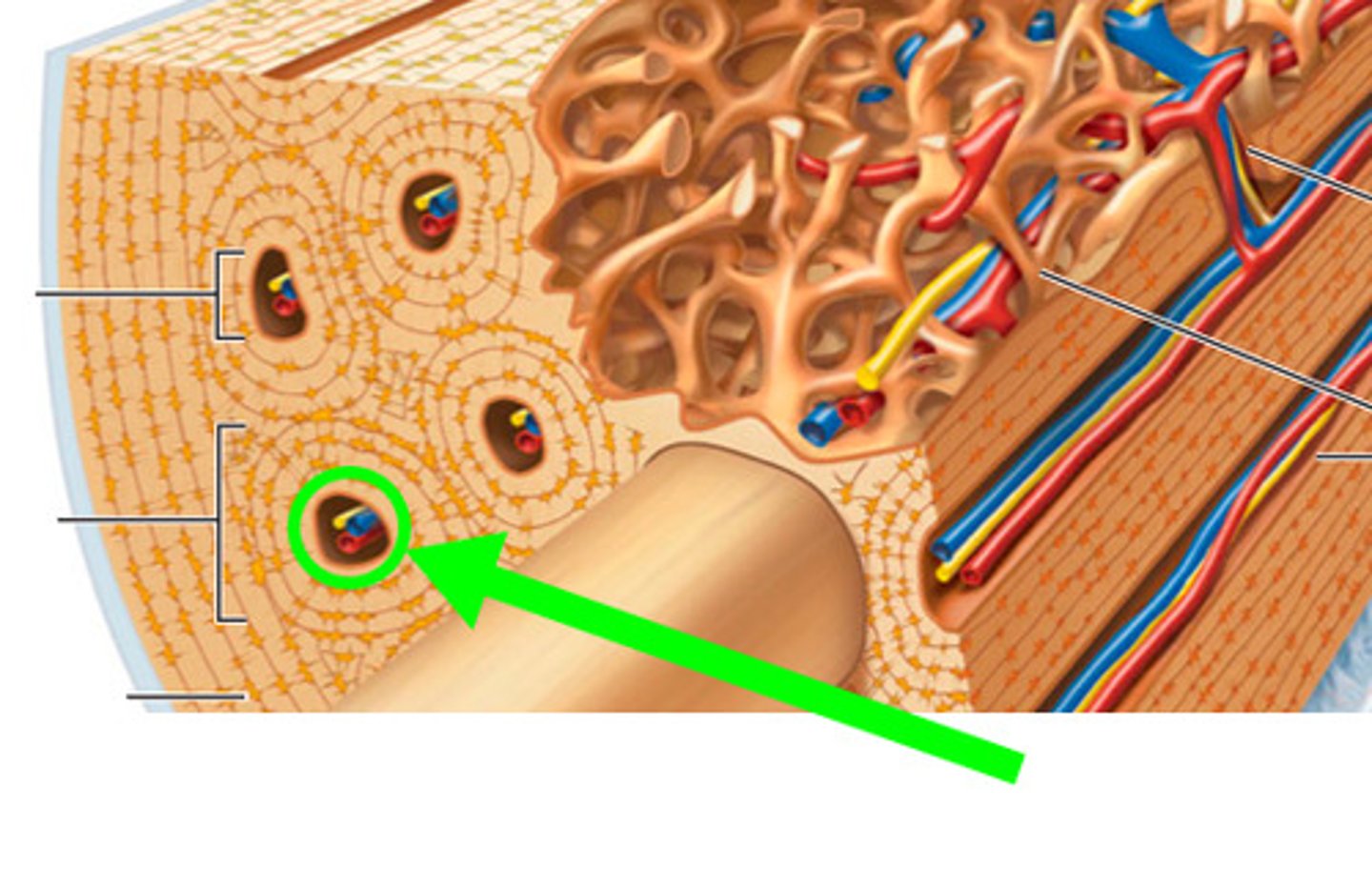
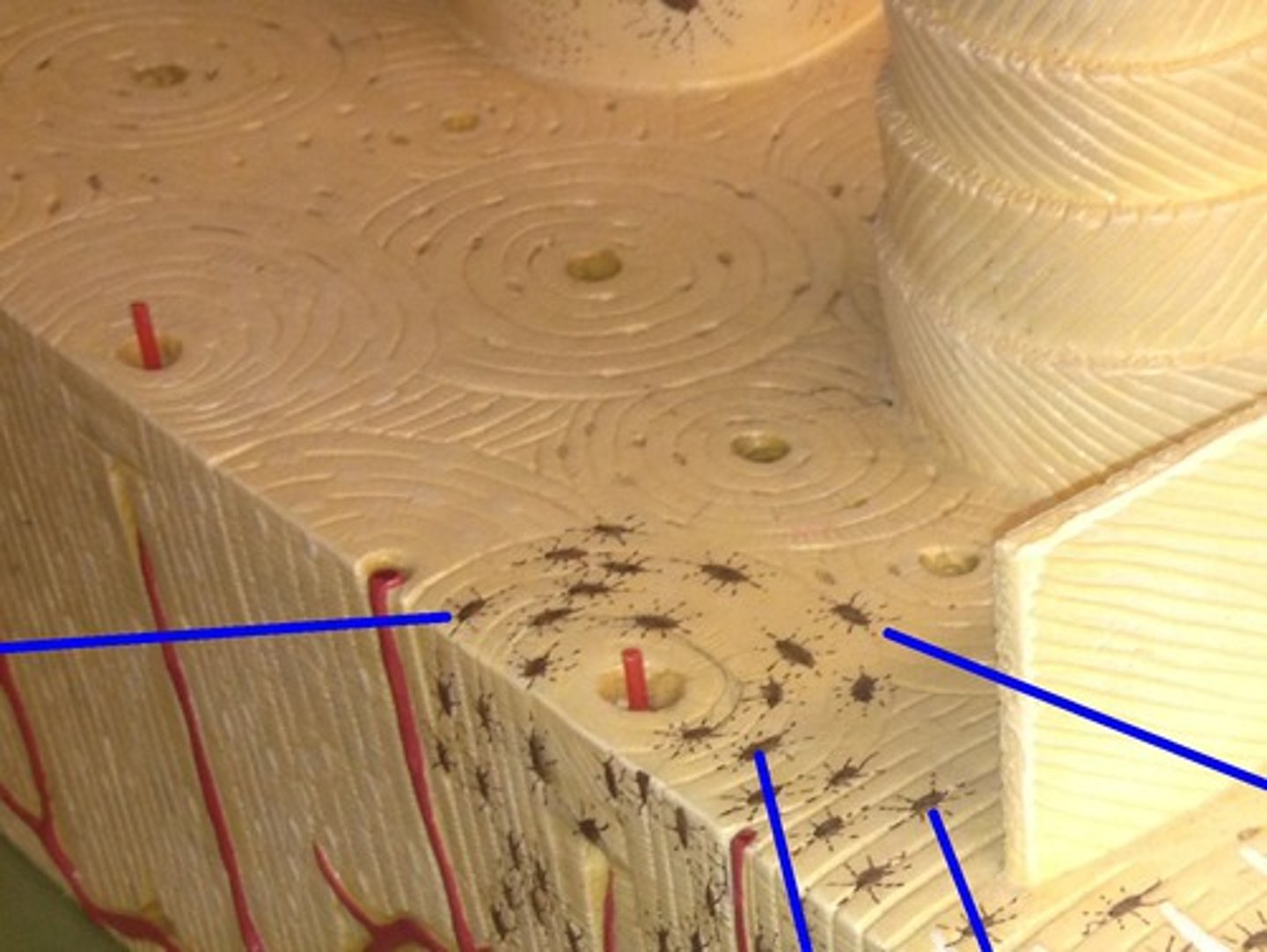
compact bone
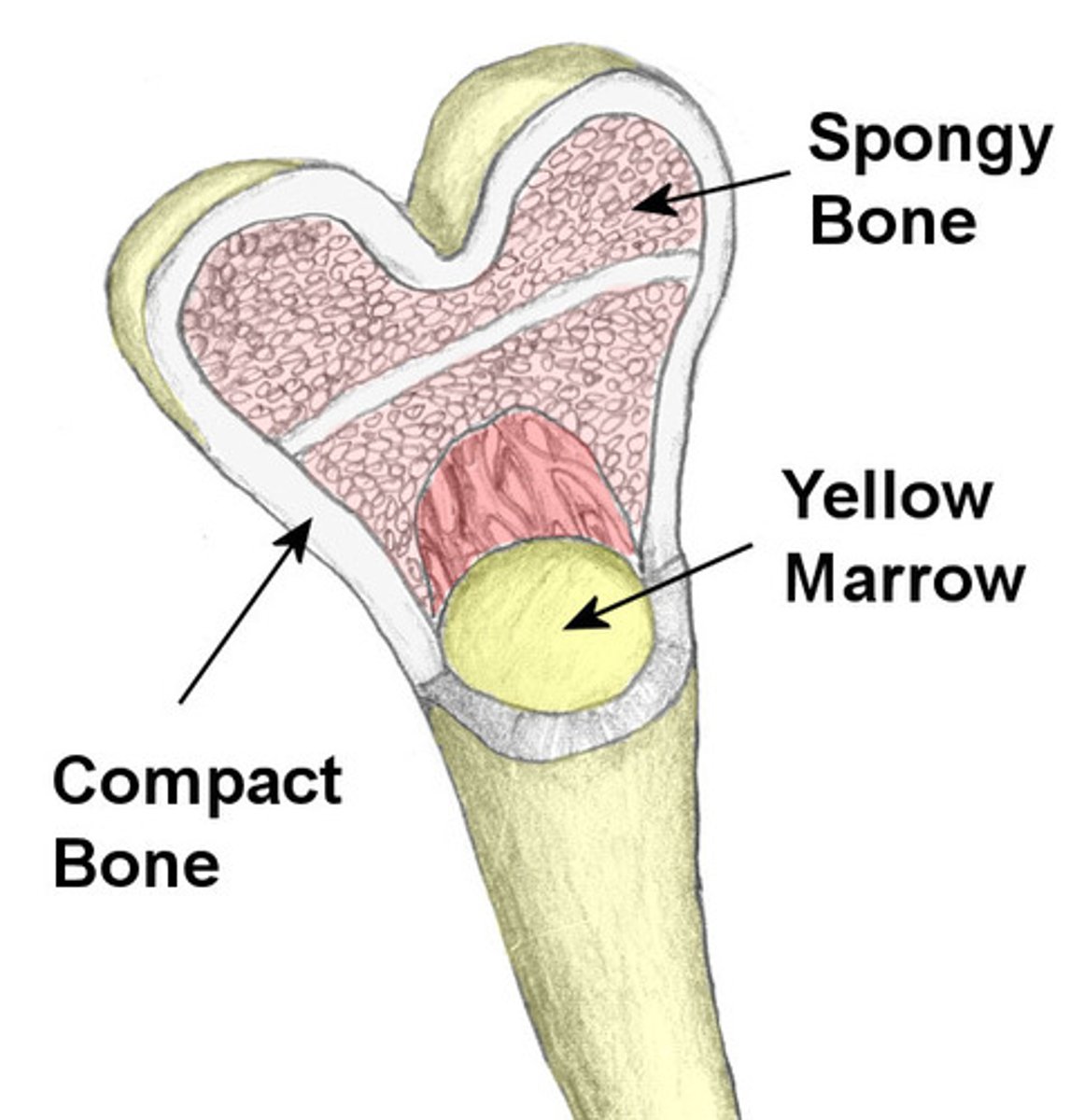
trabeculae (small needle like pieces of bone) with many open spaces, holds red marrow
spongy bone
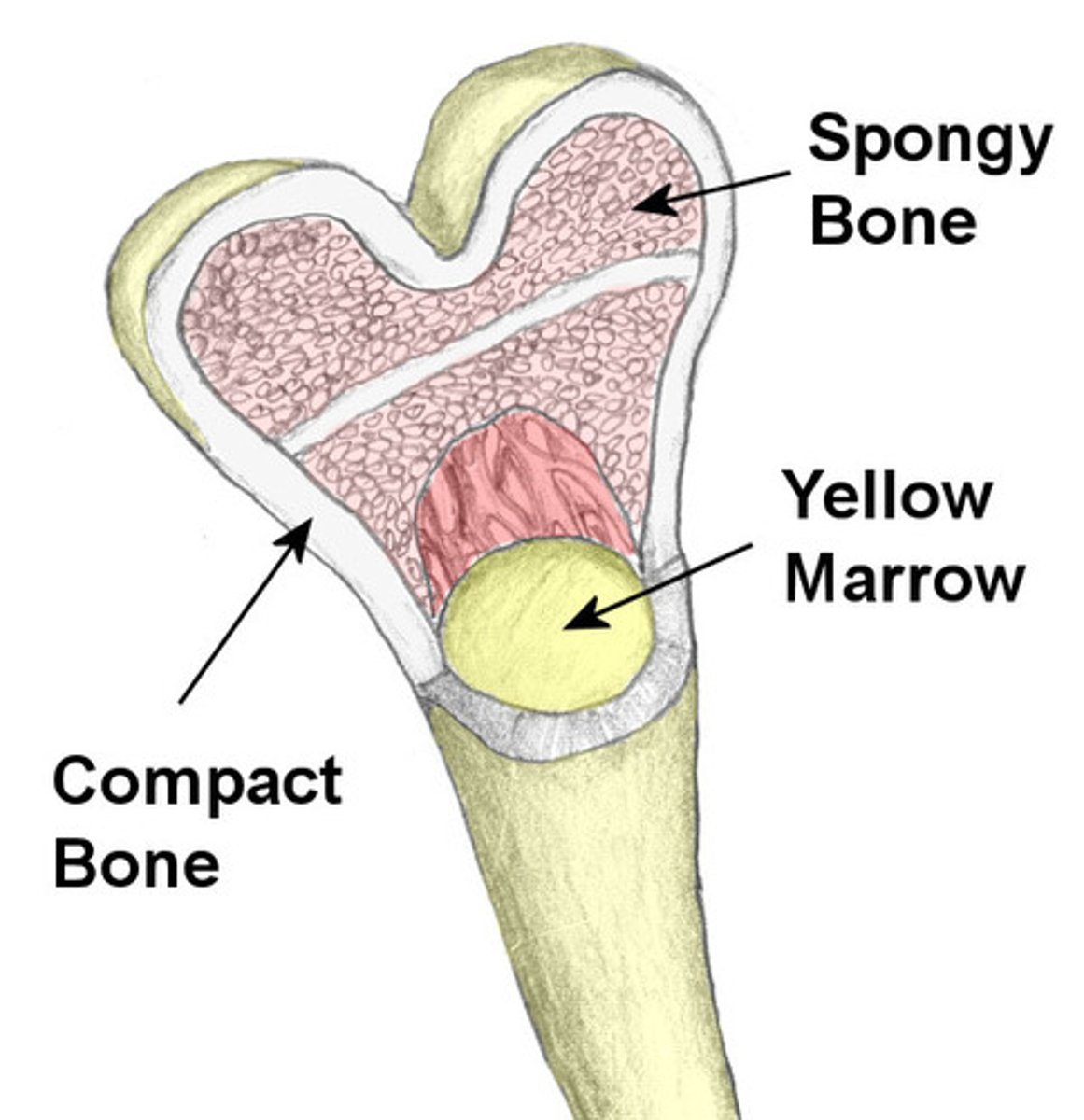
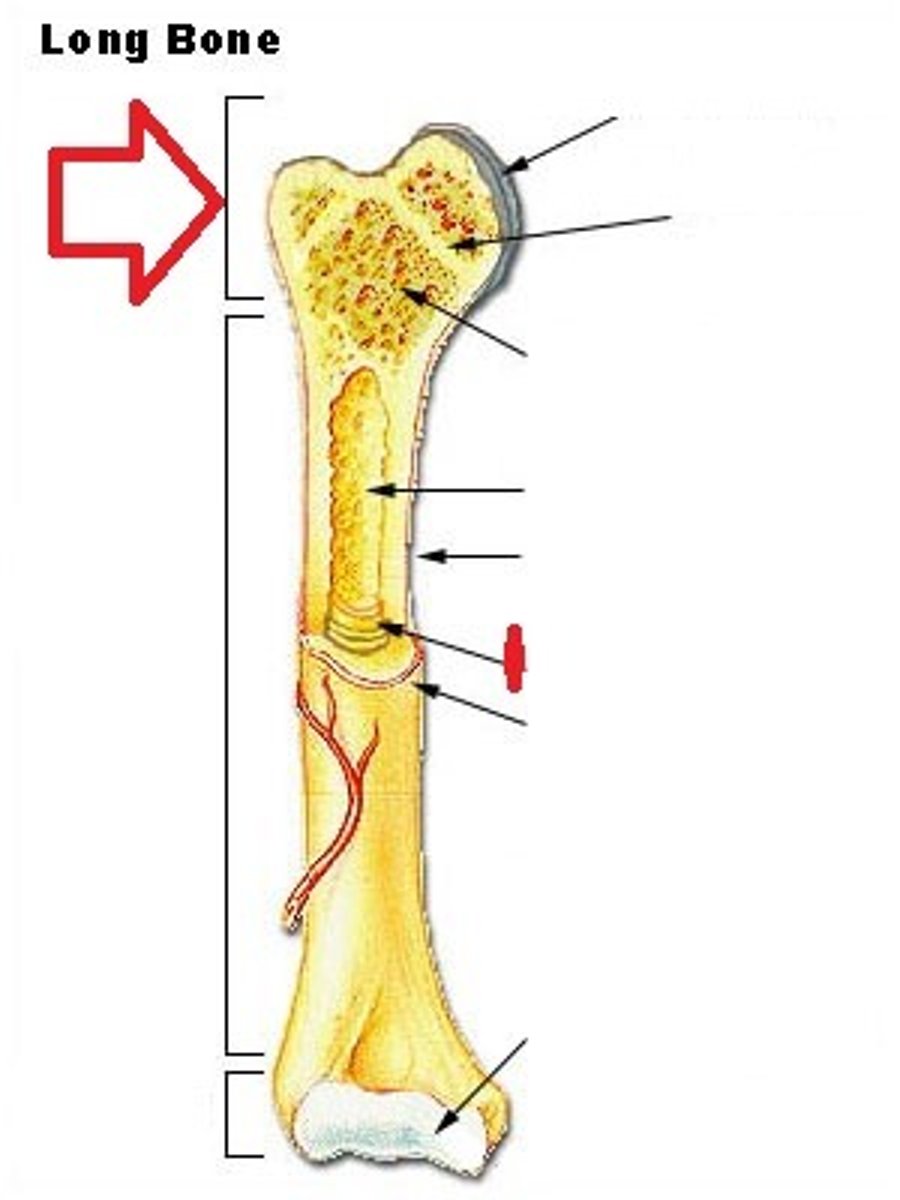
hemapoptosis takes place
red marrow
fat is stored
yellow marrow
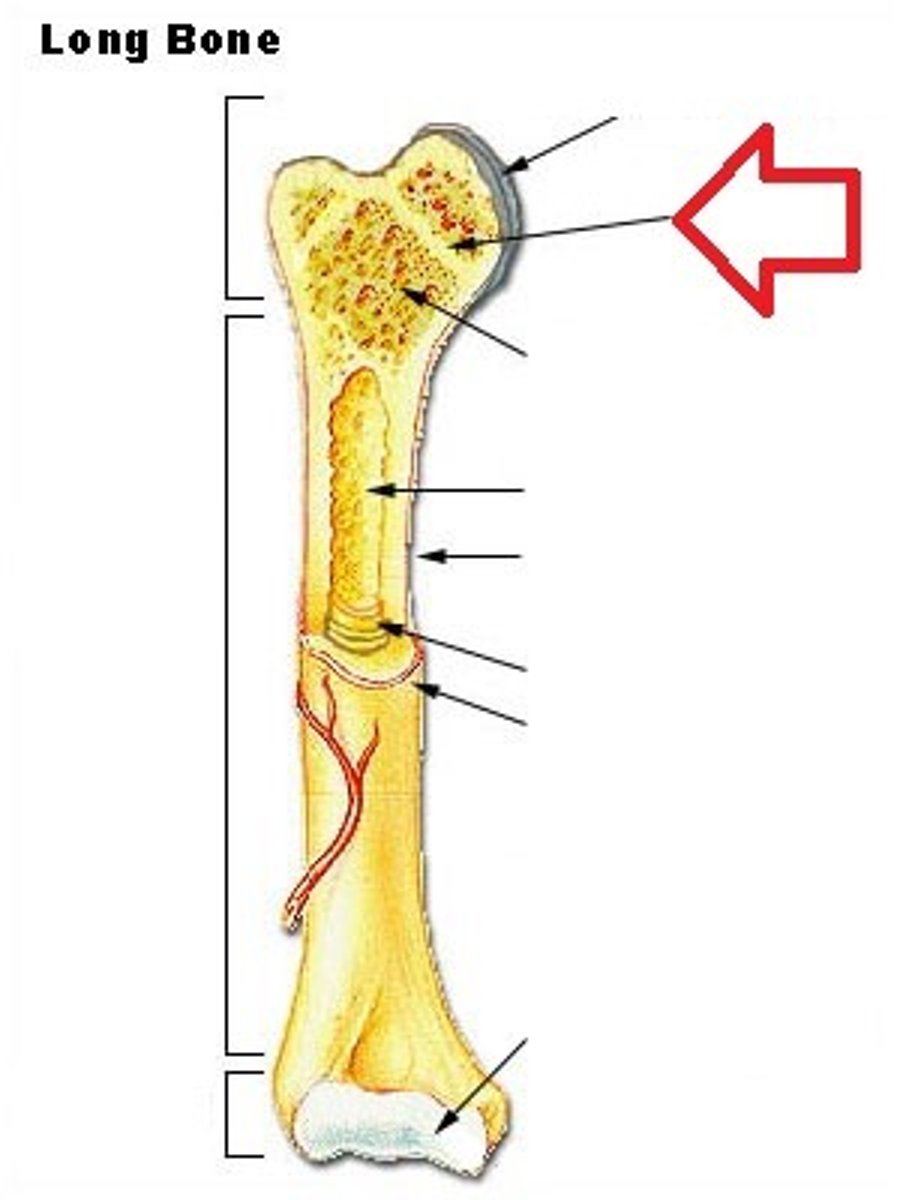
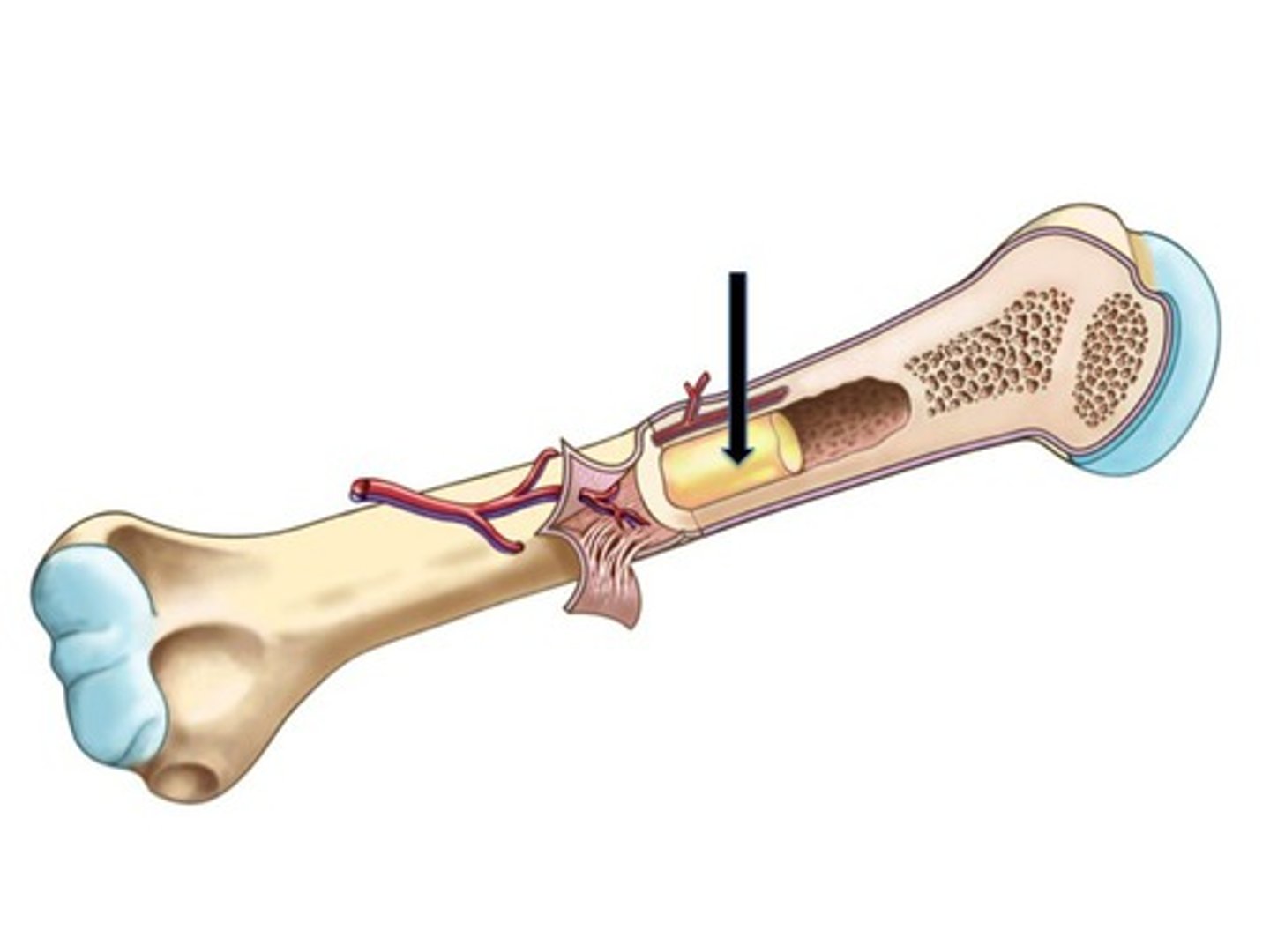
wide section at each end of a long bone; filled with spongy bone
epiphysis
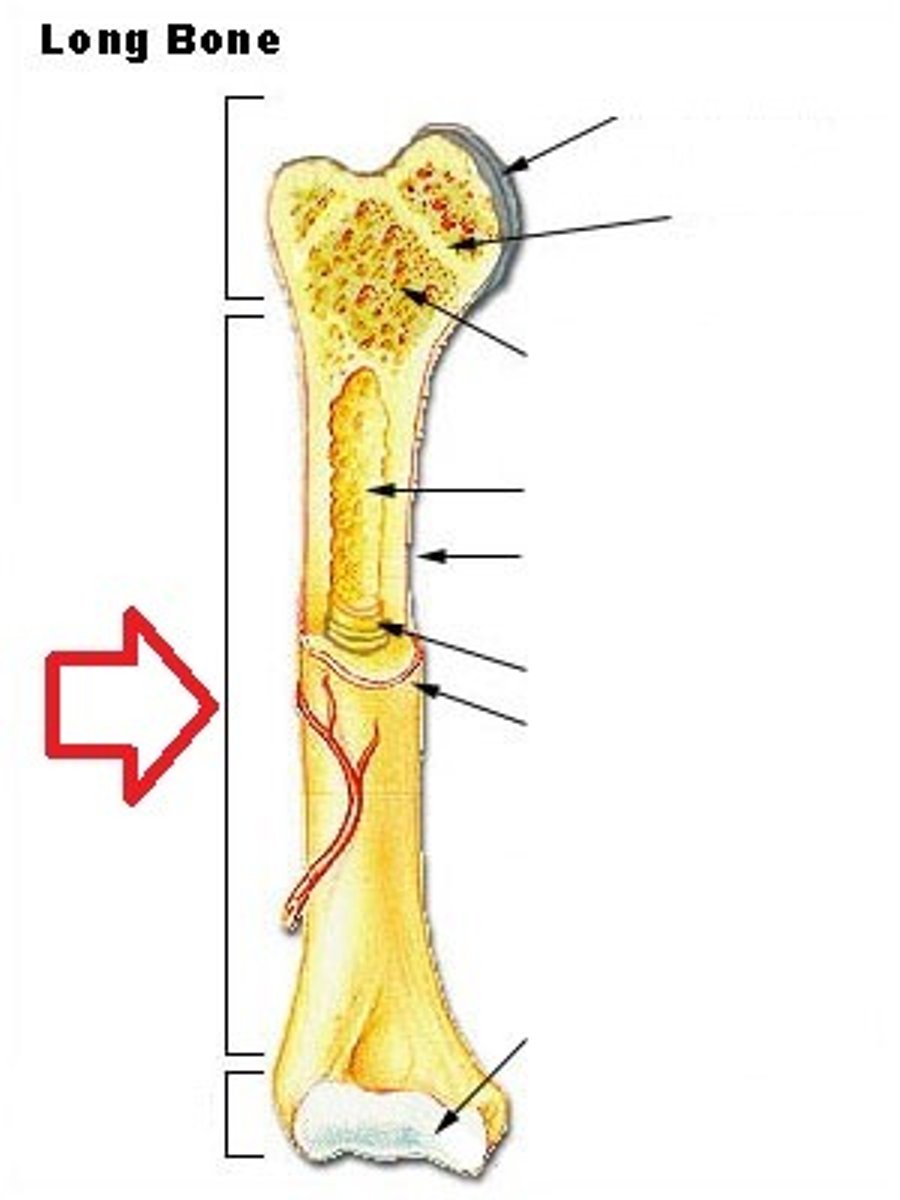
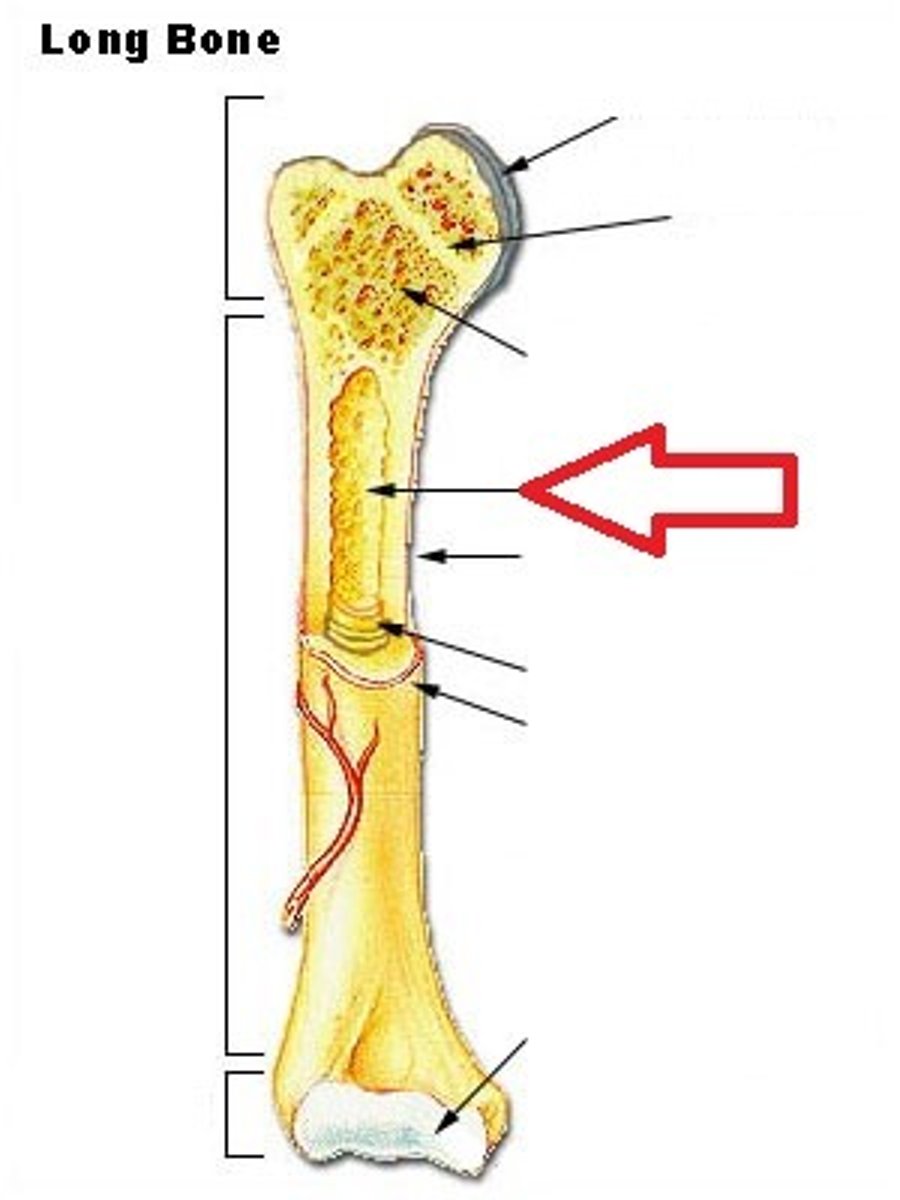
tubular shaft that runs between the proximal and distal ends of a long bone
diaphysis
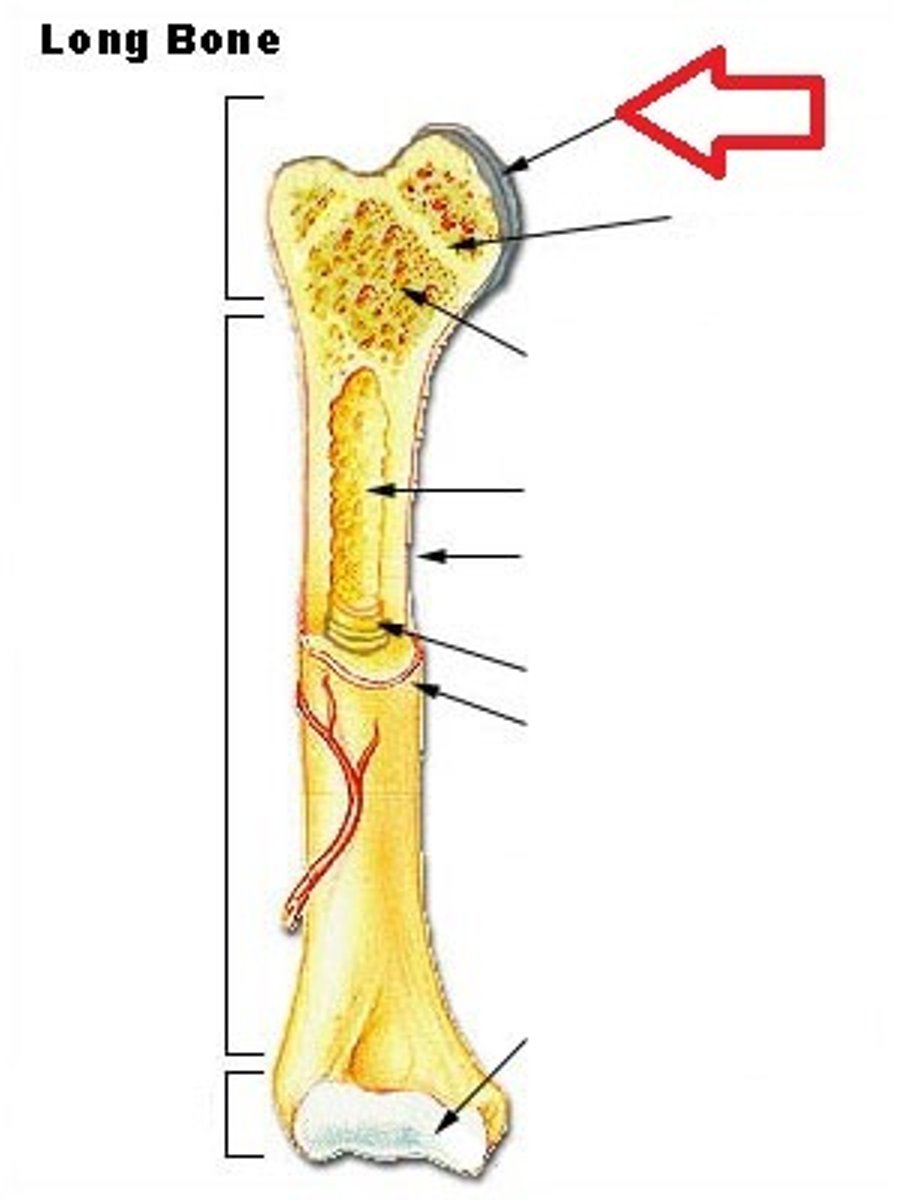
thin layer of cartilage covering an epiphysis; reduces friction and acts as a shock absorber
articular cartilage
fibrous membrane covering the outer surface of bone and continuous with ligaments
periosteum
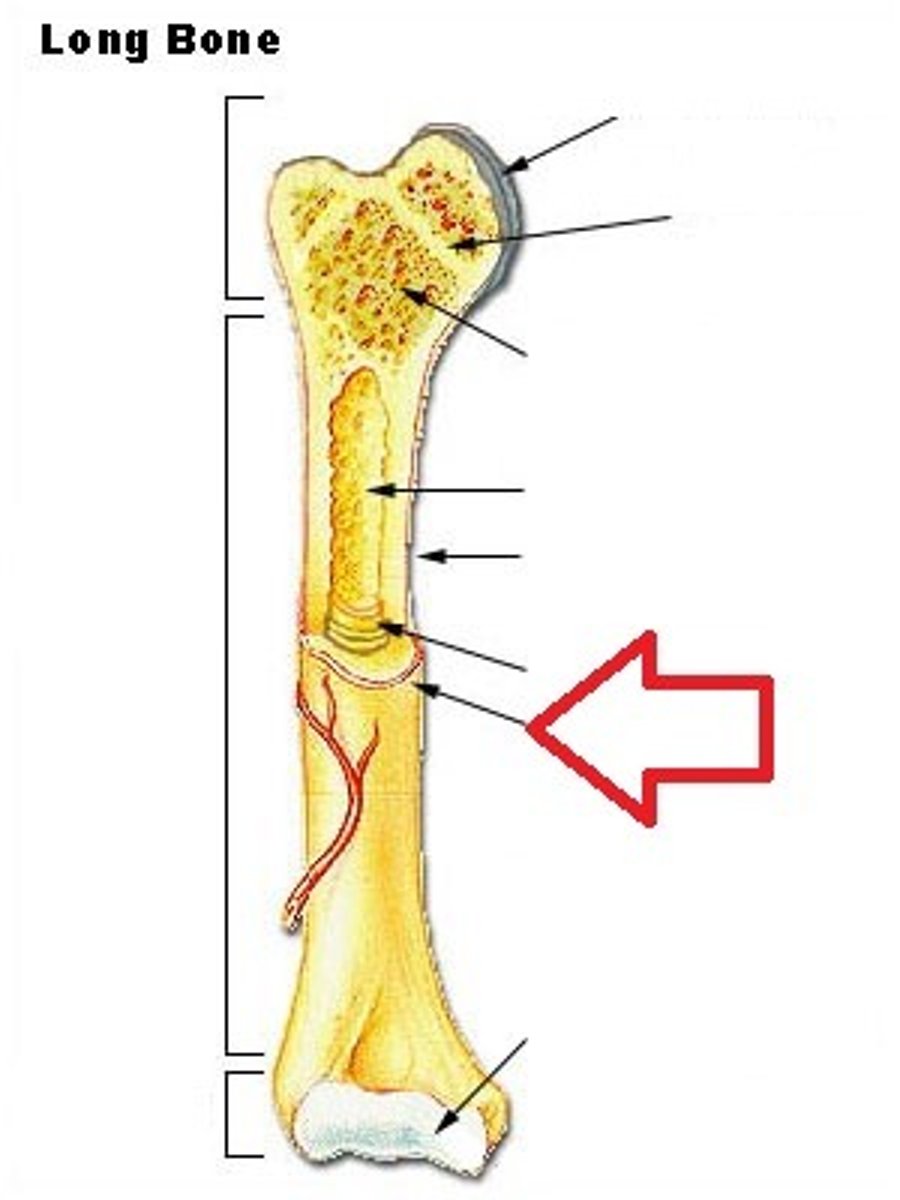
completely ossified remnant of the epiphyseal plate
epiphyseal line
hollow region of diaphysis; filled with yellow marrow
medullary cavity
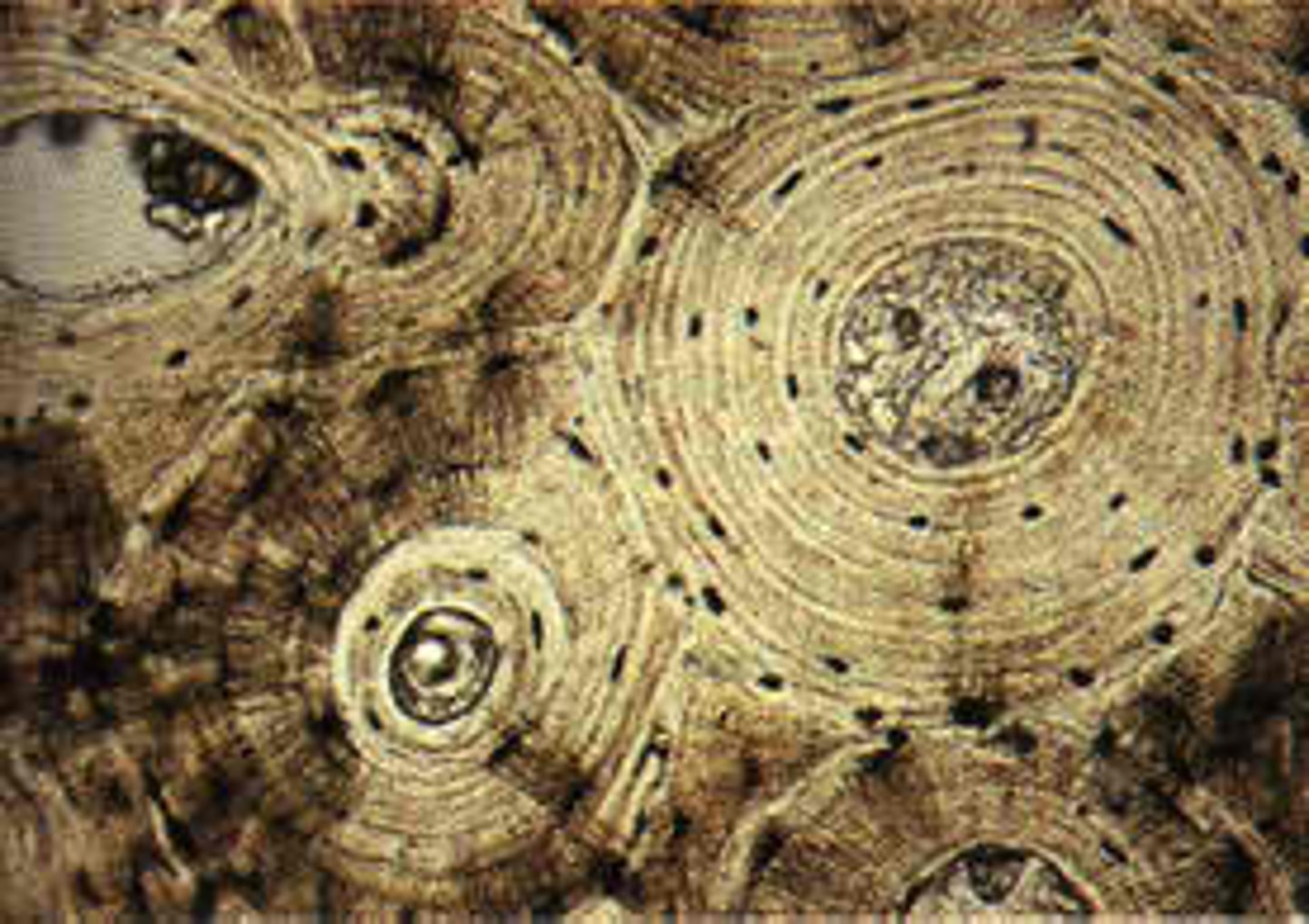
concentric rings of calcified matrix
lamellae
small spaces in bone or cartilage tissue that cells occupy
lacunae
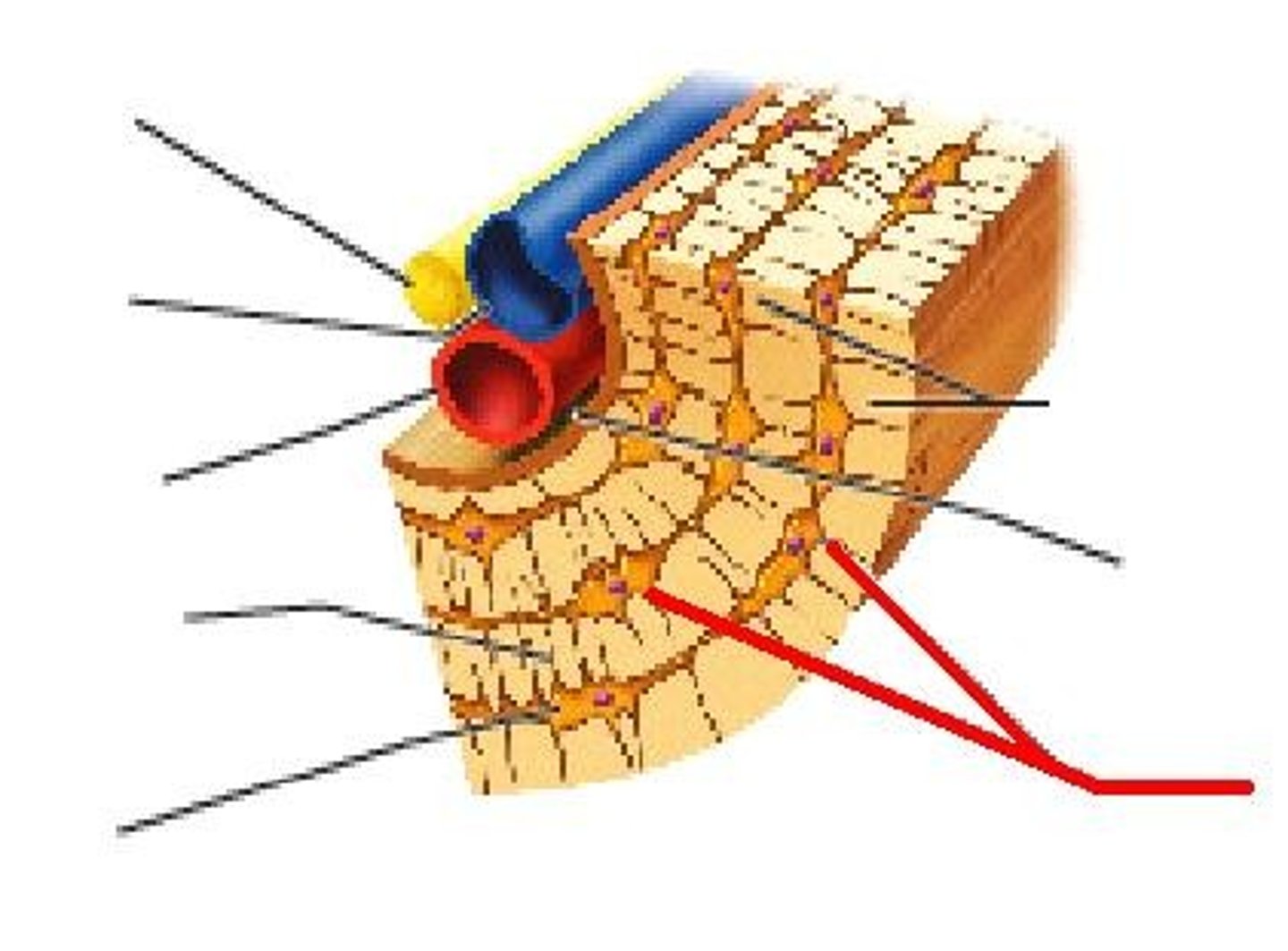
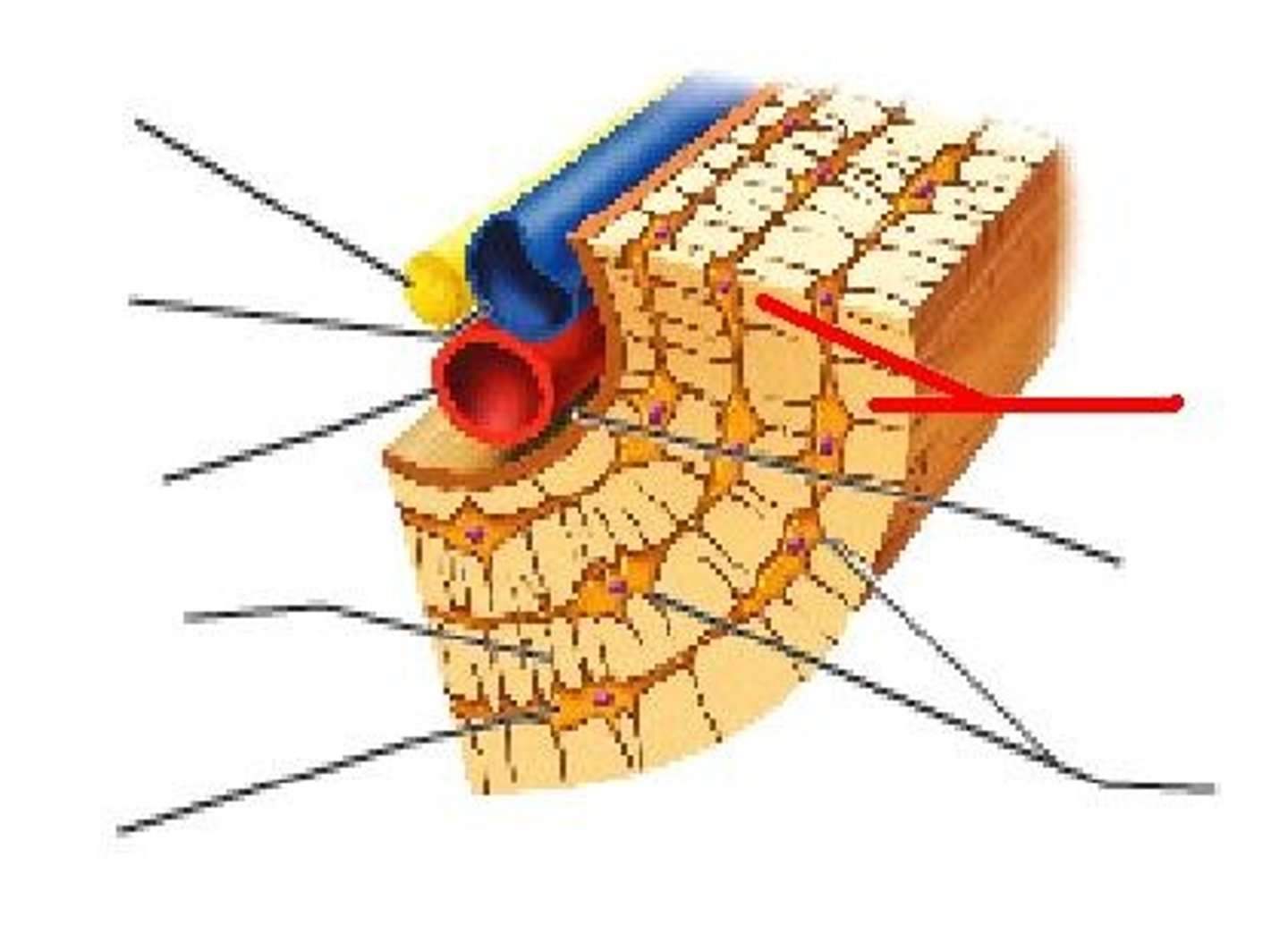
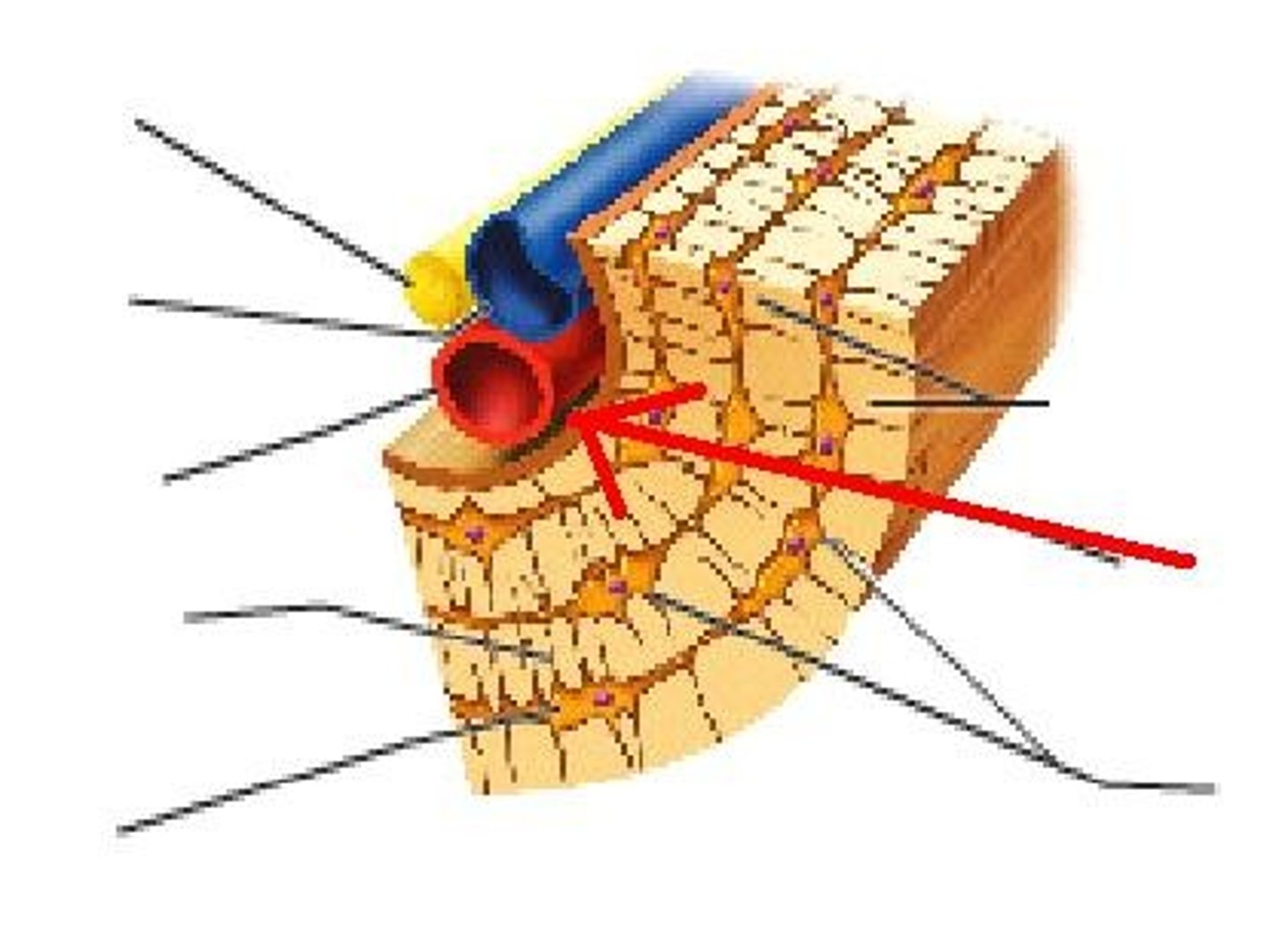
longitudinal channel in the center of each osteon; contains blood vessels, nerves, and lymphatic vessels; also known as the Haversian canal
central canal
basic structural unit of compact bone; made of concentric layers of calcified matrix
osteon
channel that branches off from the central canal and houses vessels and nerves that extend to the periosteum and endosteum
Volkmann's canal
mature bone cell
osteocyte
bone forms from fibrous cartilage
intramembranous ossification
bone forms with hyaline cartilage,
endochondral ossification
process by which osteoclasts resorb old or damaged bone at the same time as and on the same surface where osteoblasts form new bone to replace that which is resorbed
remodeling
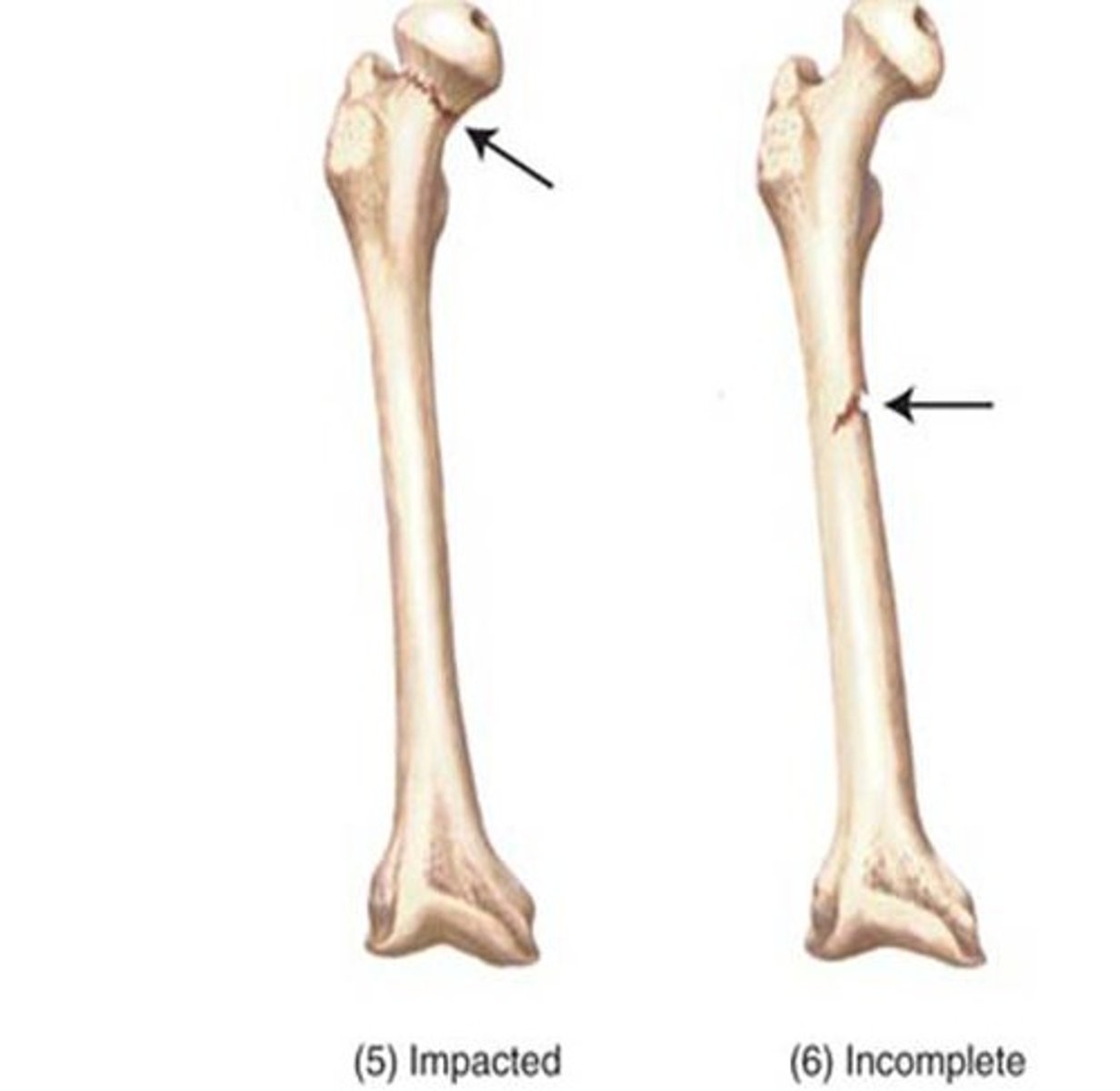
break in a bone
fracture
break that does not penetrate the skin
closed simple
broken bone that penetrates through the skin
open compound
bone breaks all the way through
complete fracture
bone does not break all the way through
incomplete fracture
bone breaks incompletely
greenstick
disease that causes gradual loss of bone density and strength, gradual collapse of the vertebrae
osteoperosis
osteocyte
a mature bone cell

compact bone
hard, dense bone tissue that is found in the diaphysis of a long bone

yellow marrow
fatty tissue found in the medullary cavity of most adult long bones
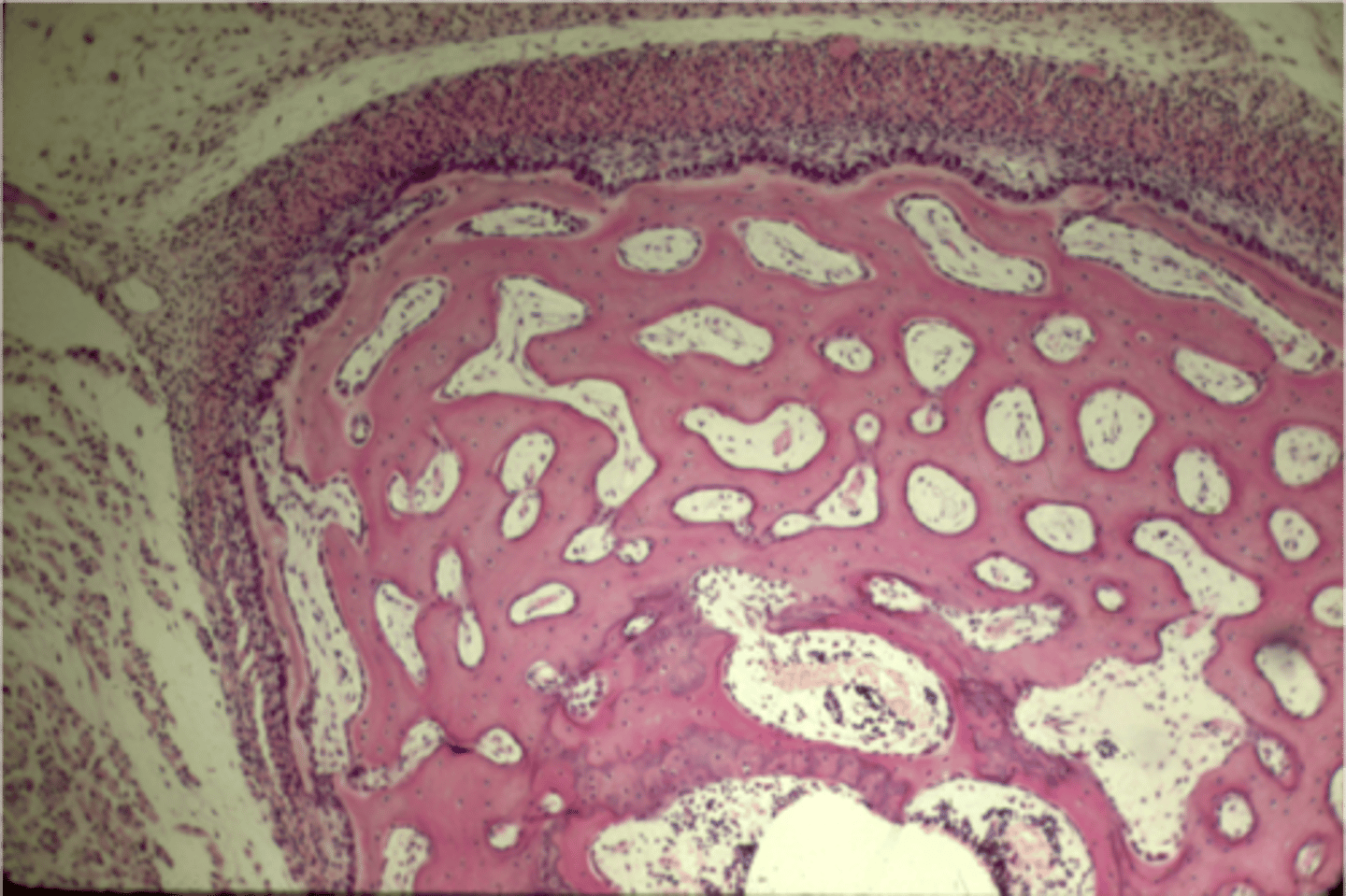
cancellous bone
spongy bone
red marrow
produces blood cells
ossification
Bone formation
epiphysis
end of the long bone
trabeculae
bony portions of the spongy bone that surround the open spaces

diaphysis
elongated shaft of a long bone
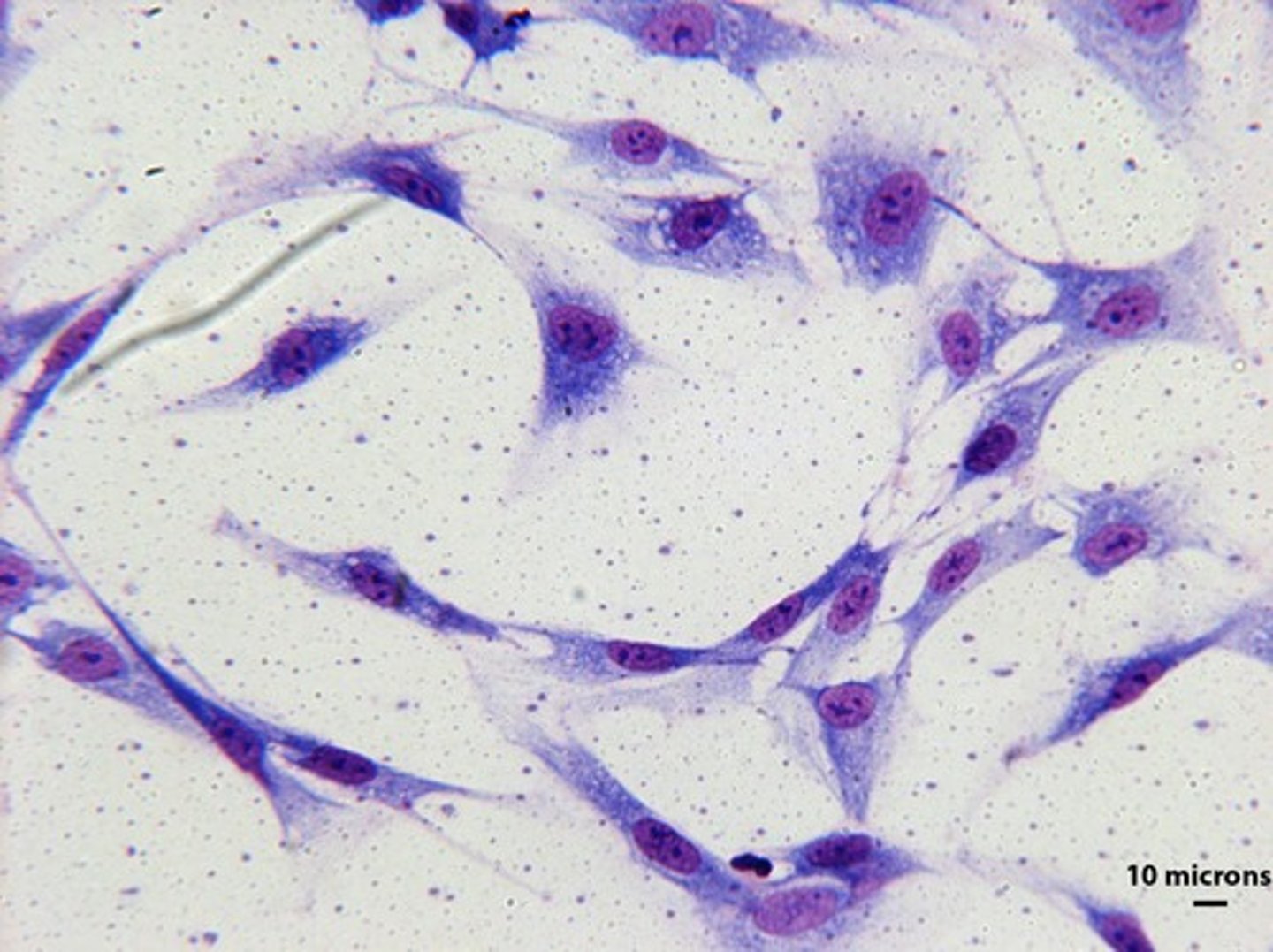
osteoblast
bone-building cells
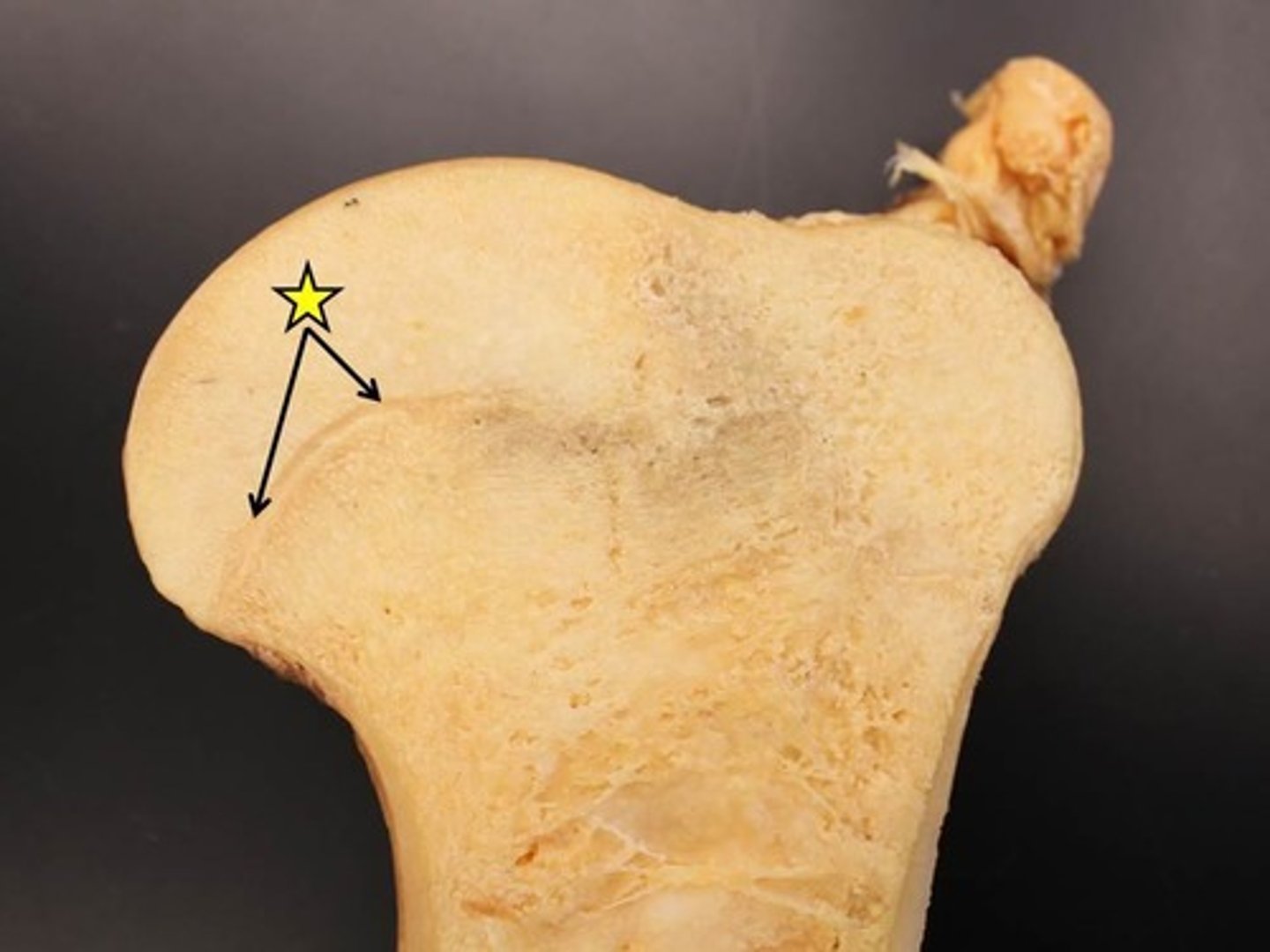
epiphysial line
where bone growth takes place
hydroxyapetite
large crystal-like molecule in bones
osteoclast
break down bone
periosteum
double-layered connective tissue that covers and nourishes the bone
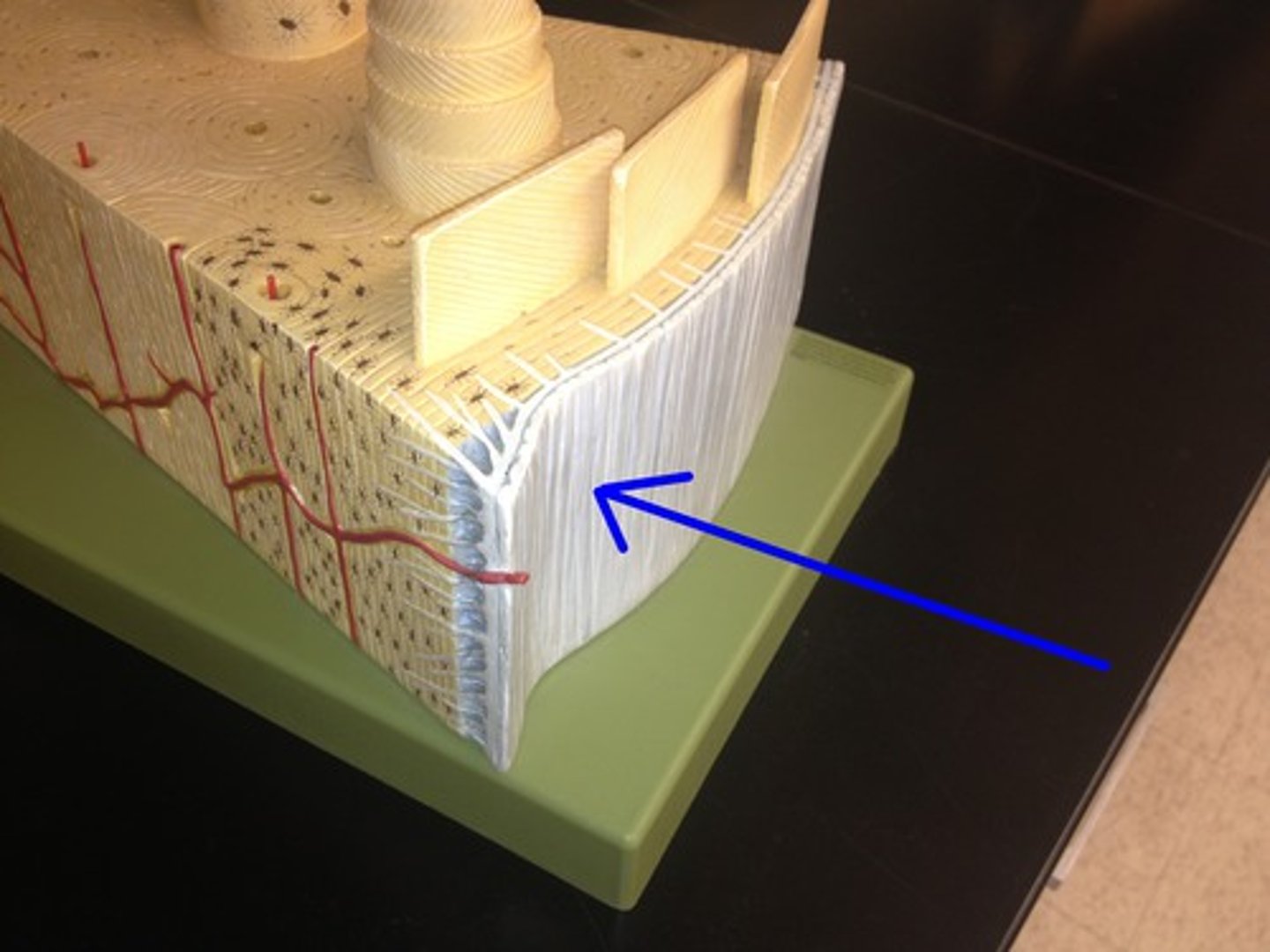
haversian canal
any of the many tiny canals that contain blood vessels and connective tissue and that form a network in bone