ATI Teas 7 Respiratory System
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Upper Respiratory tract
nose and nasal passages, sinuses, tonsils, eustachian tube, pharynx, larynx, uvula, epiglottis.
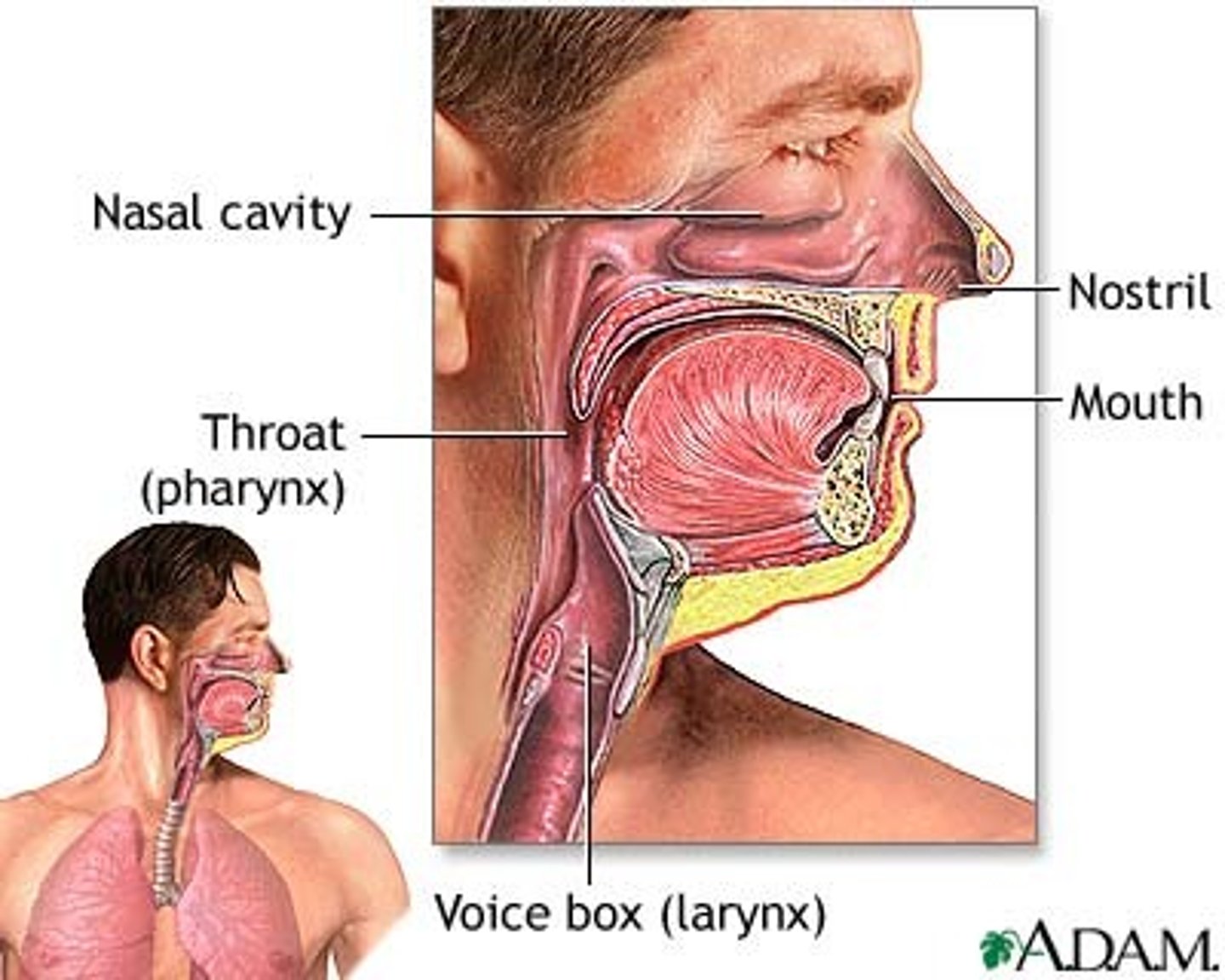
Nose and nasal passages
clean, warm, and humidify the air.
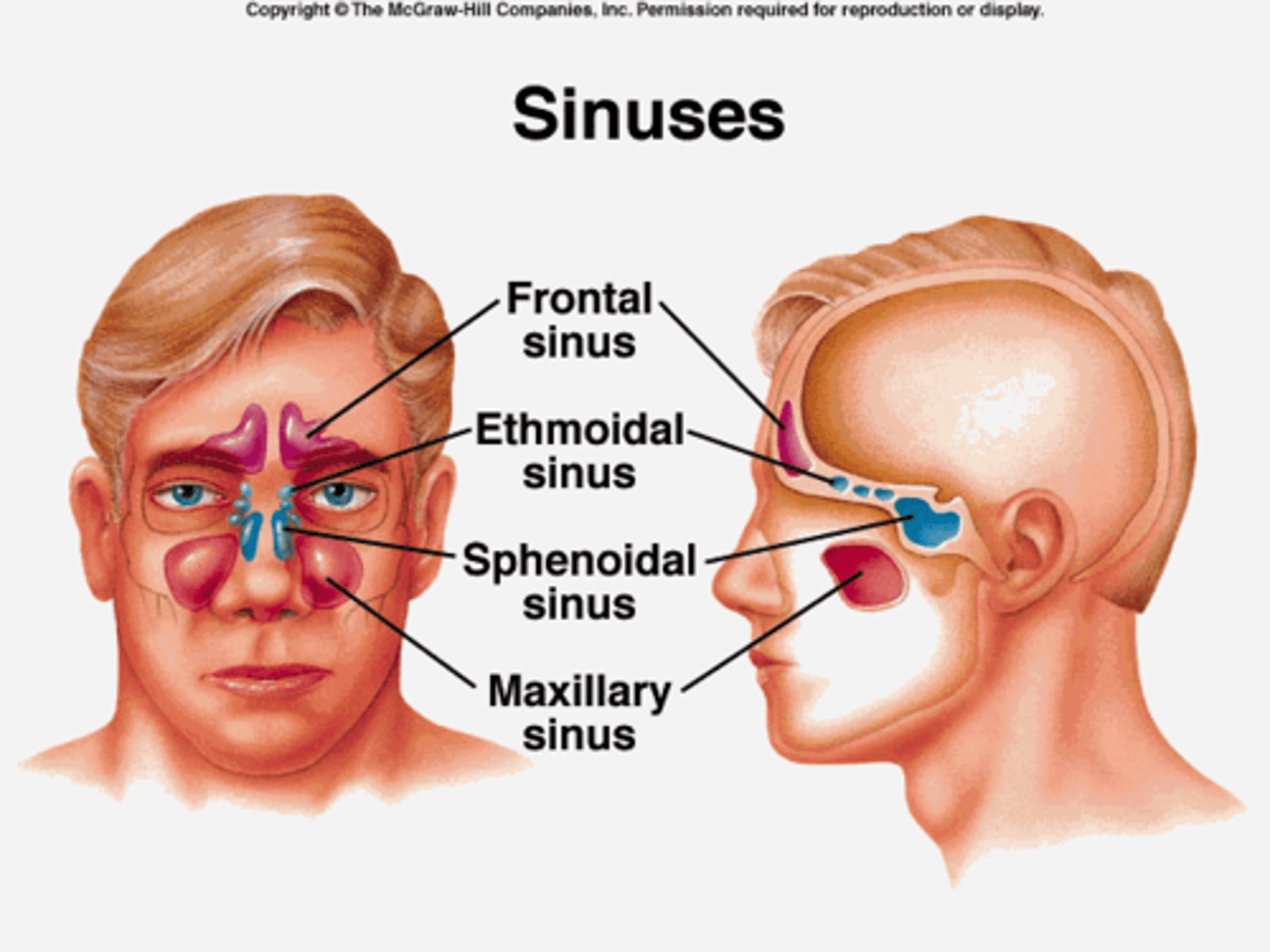
Sinuses
bone cavities lined with mucous membranes; drain to nasal passages; pathogens can enter.
Eustachian tube (auditory tube)
tube connecting the middle ear to the pharynx; equalizes pressure; pathogens can enter.
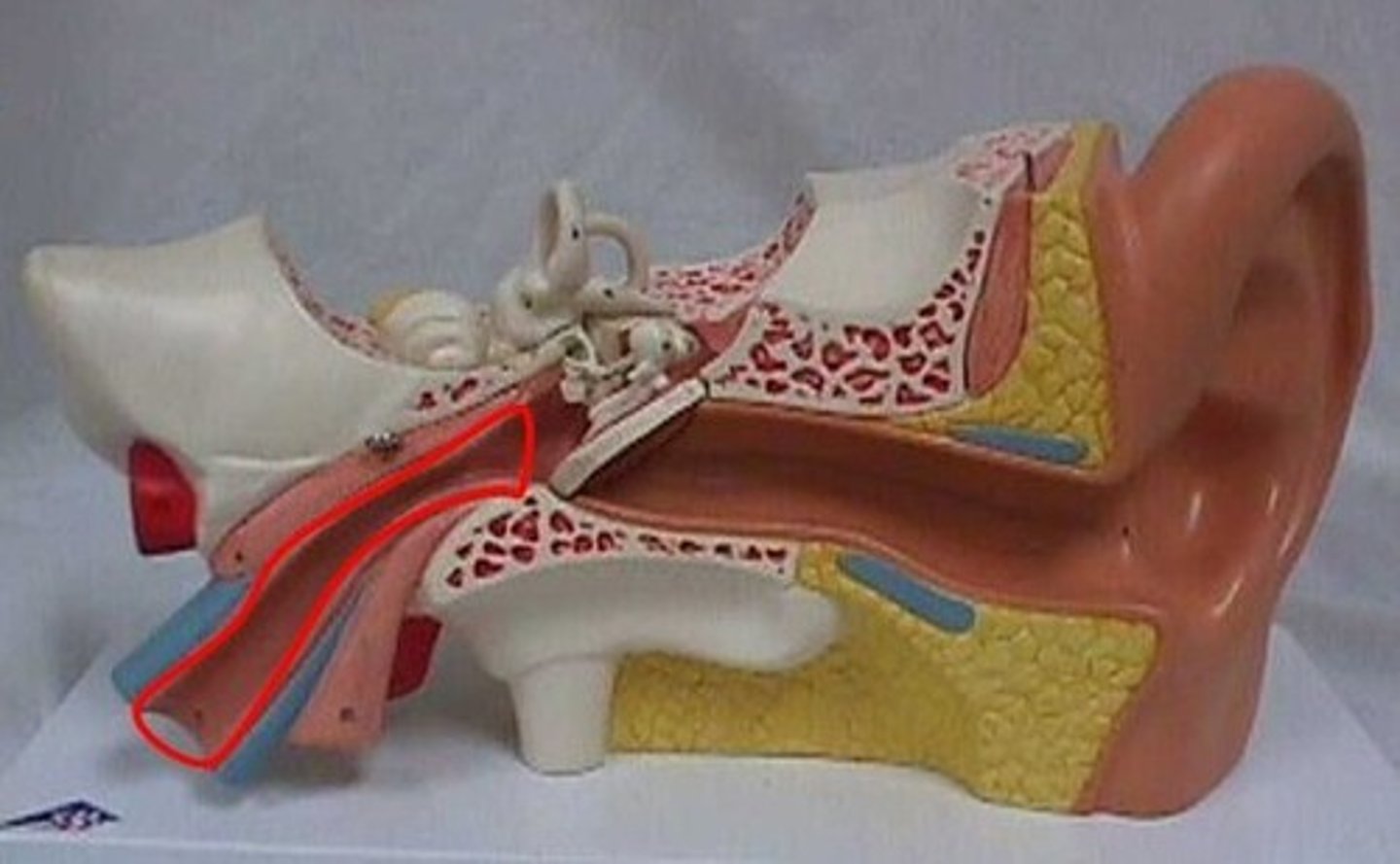
Tonsils
form a protective circle of lymphatic tissue around the entrance to the respiratory system. adenoids, palatine, and sublingual.
Adenoid
single mass of lymphoid tissue in the midline at the back of the throat.
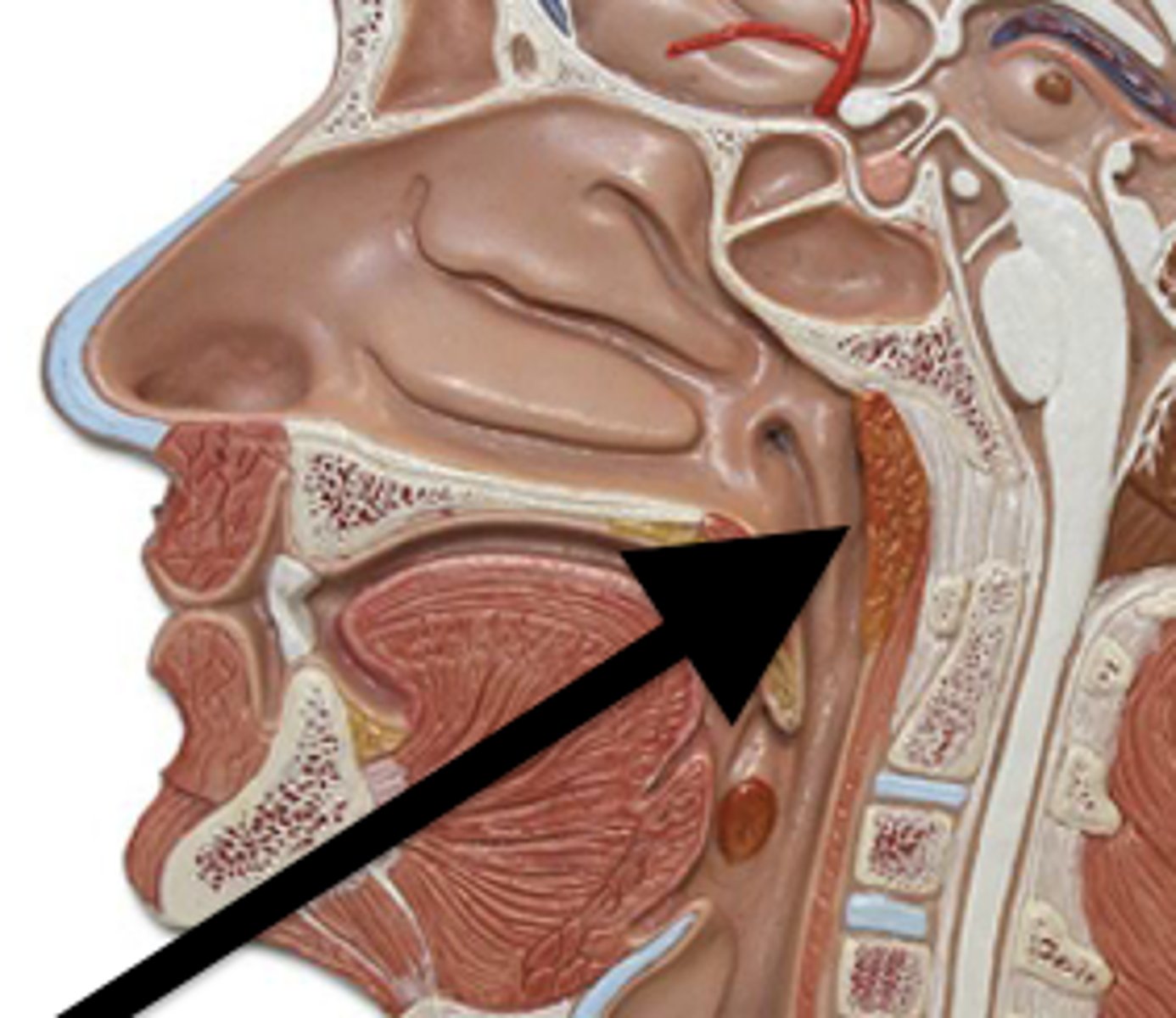
Palatine
located on the left and right sides of the throat in the area that is visible through the mouth.
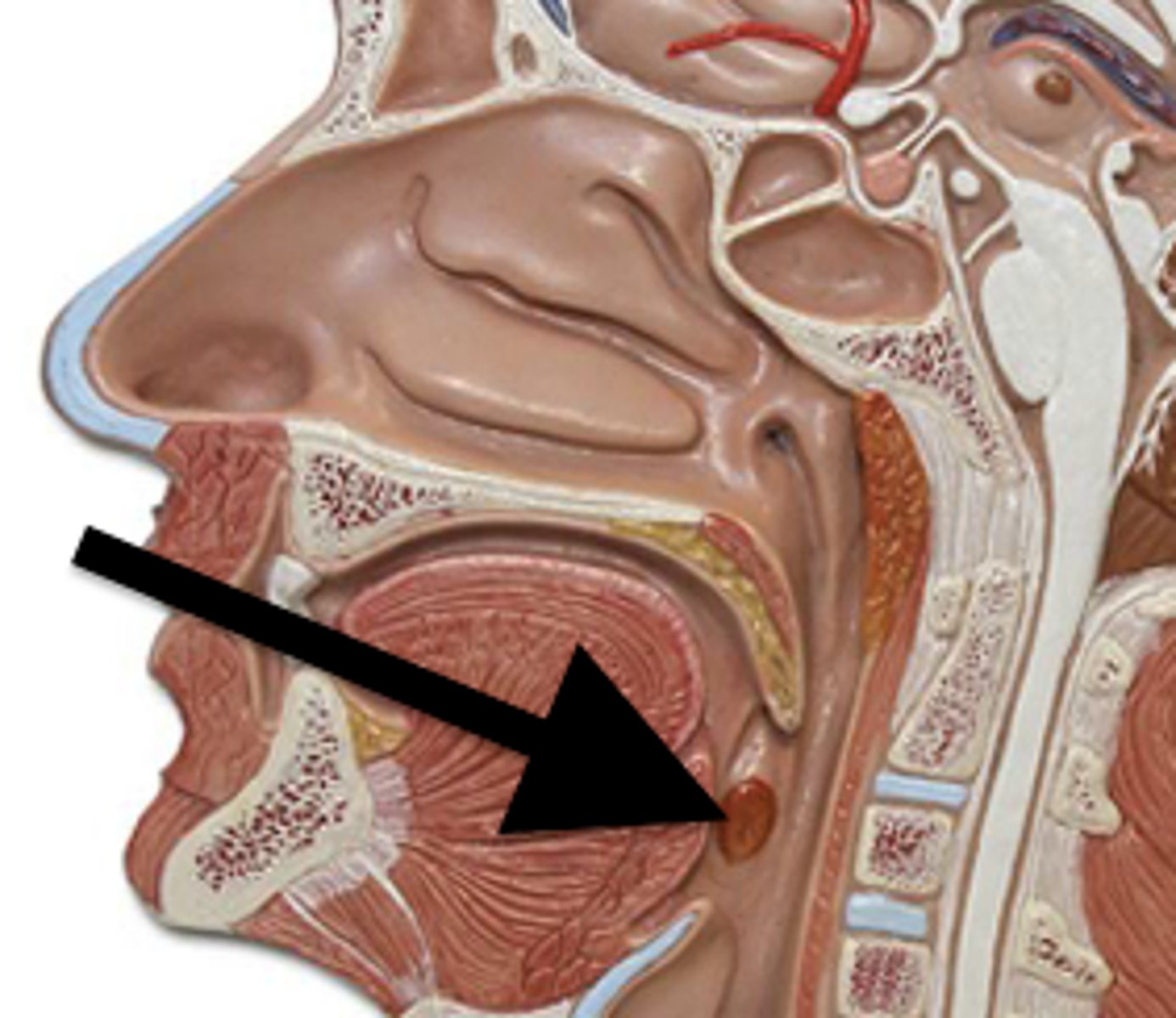
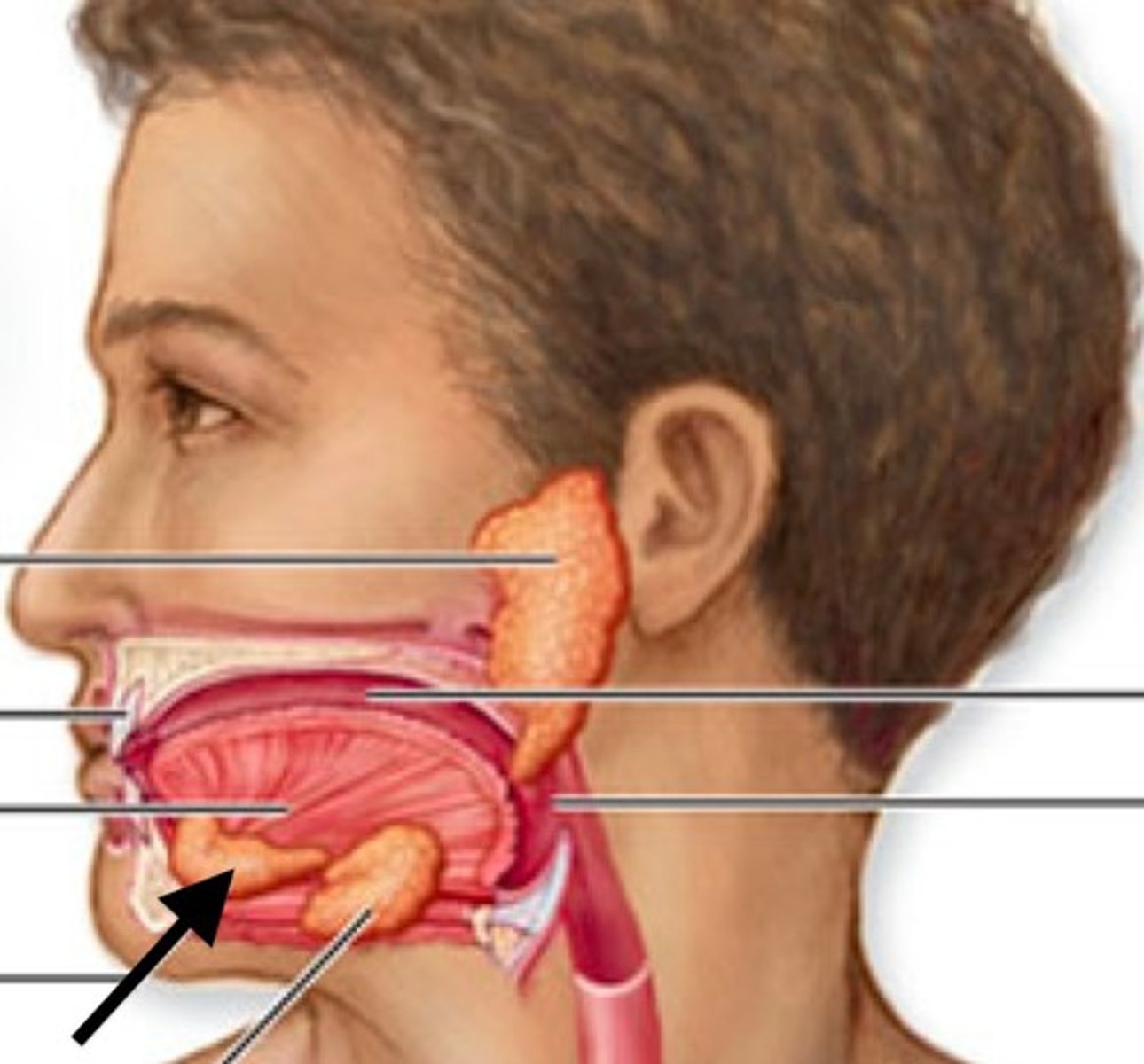
Sublingual
under the tongue.
Uvula
blocks nose from mouth.

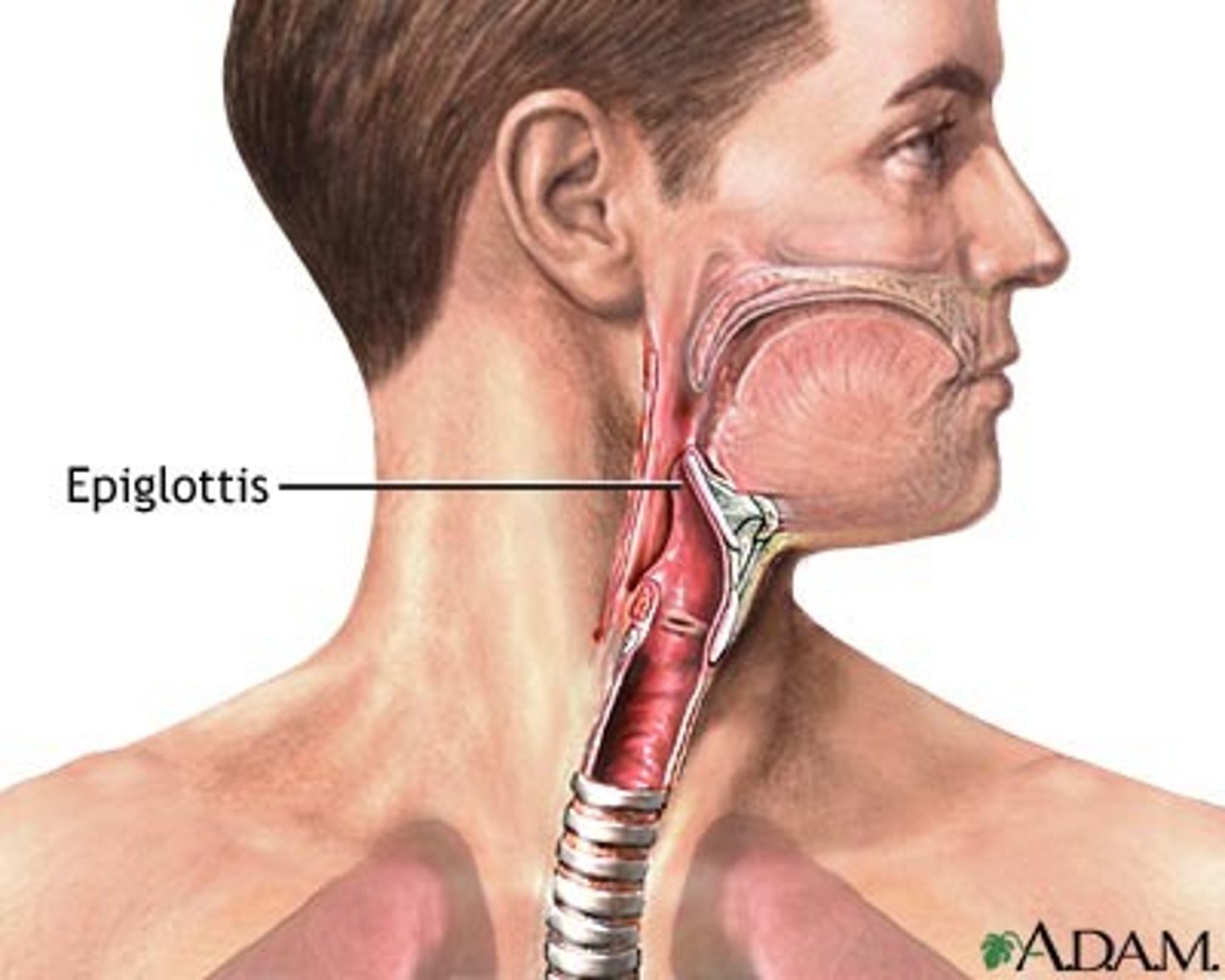
Epiglottis
blocks trachea from mouth.
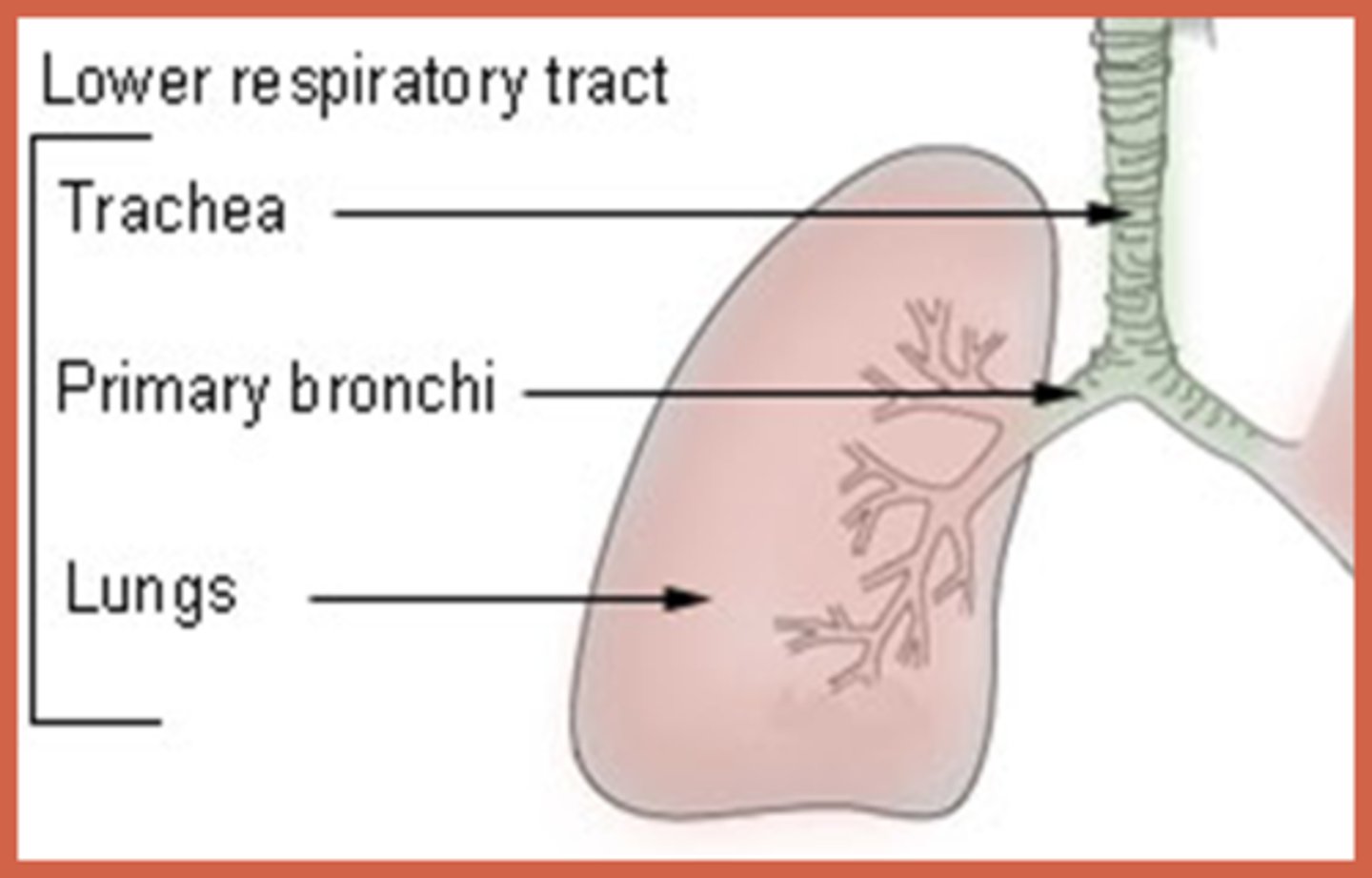
Lower Respiratory tract
larynx, trachea, bronchi, lungs.
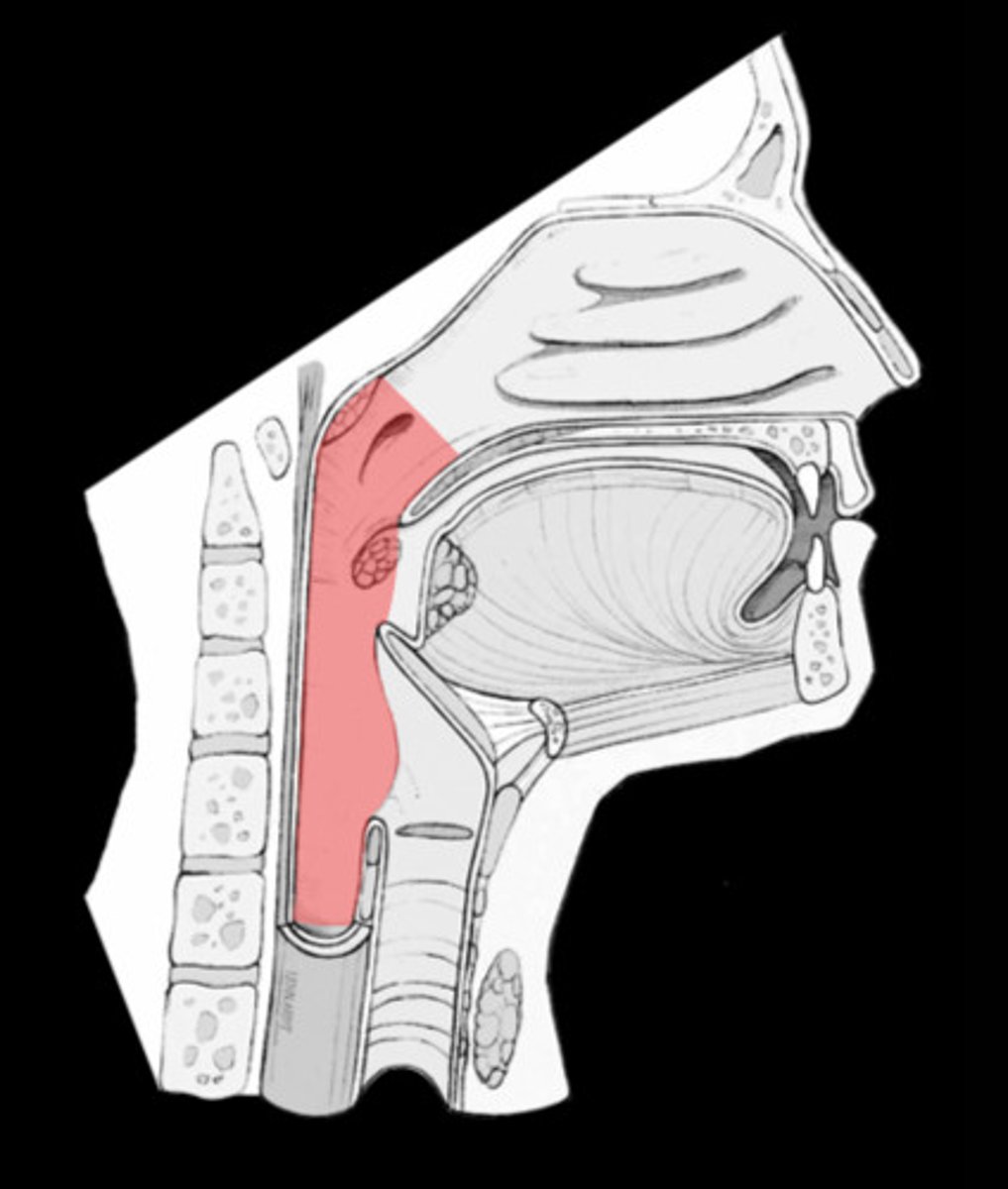
Pharynx (throat)
Passageway for air, leads to trachea.
Tracheal cartilages
keep the trachea from collapsing.
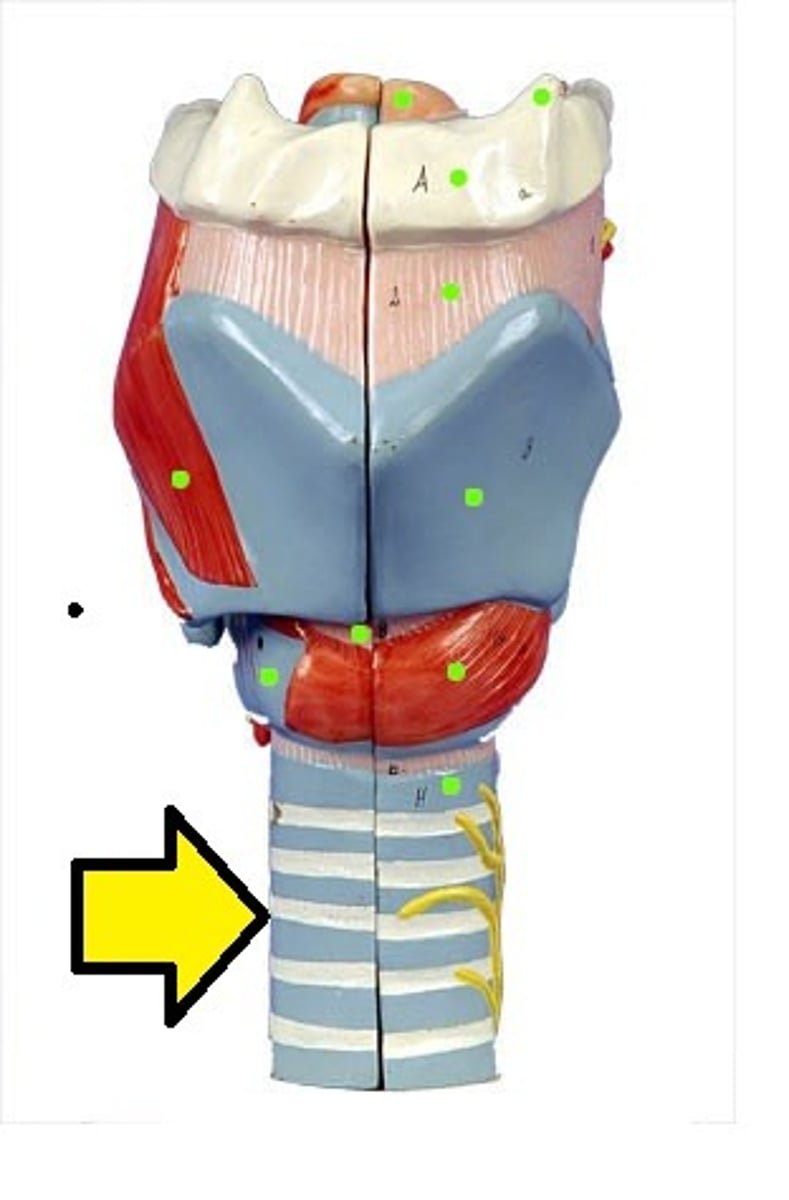
Trachea
windpipe. made of pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
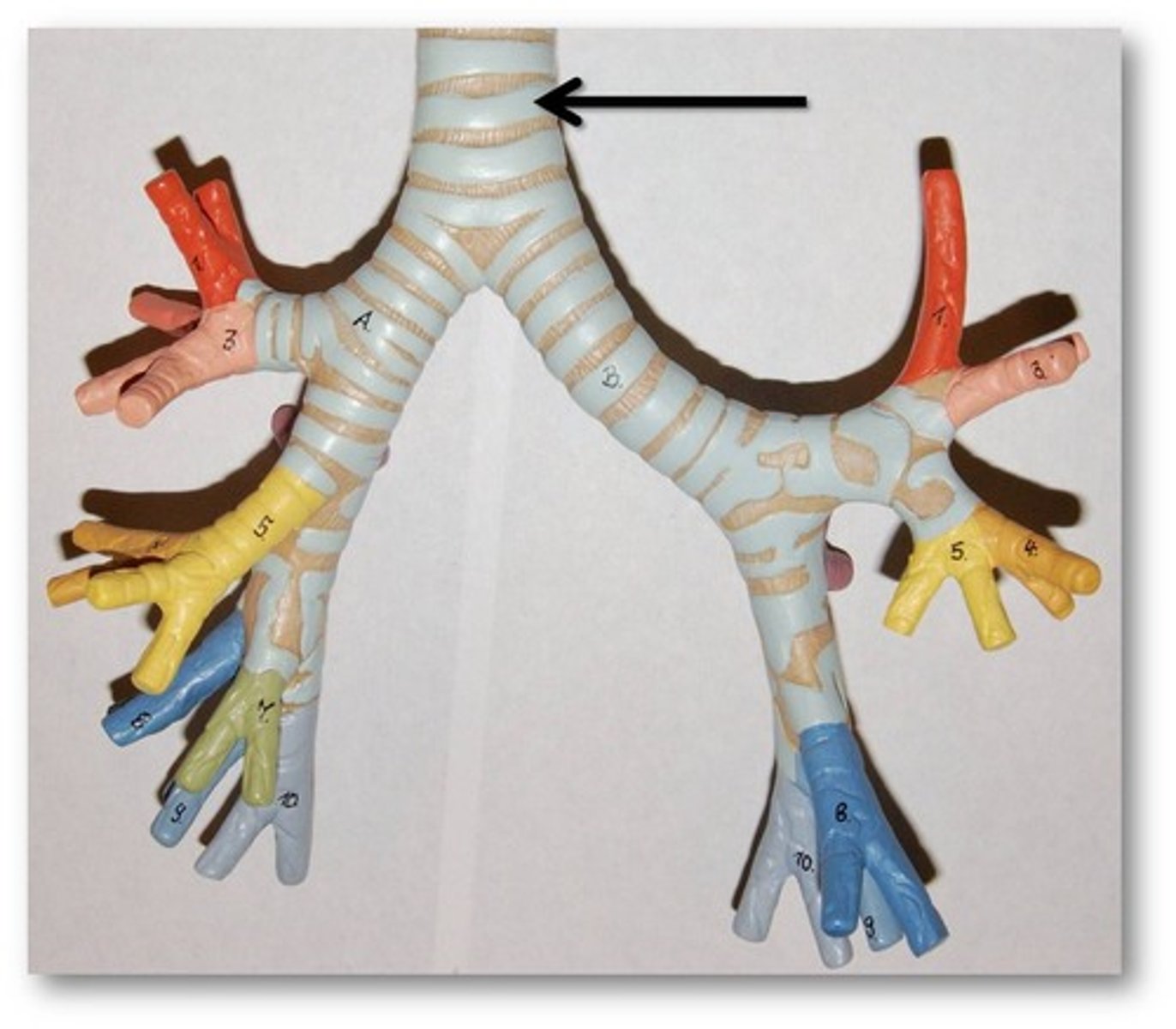
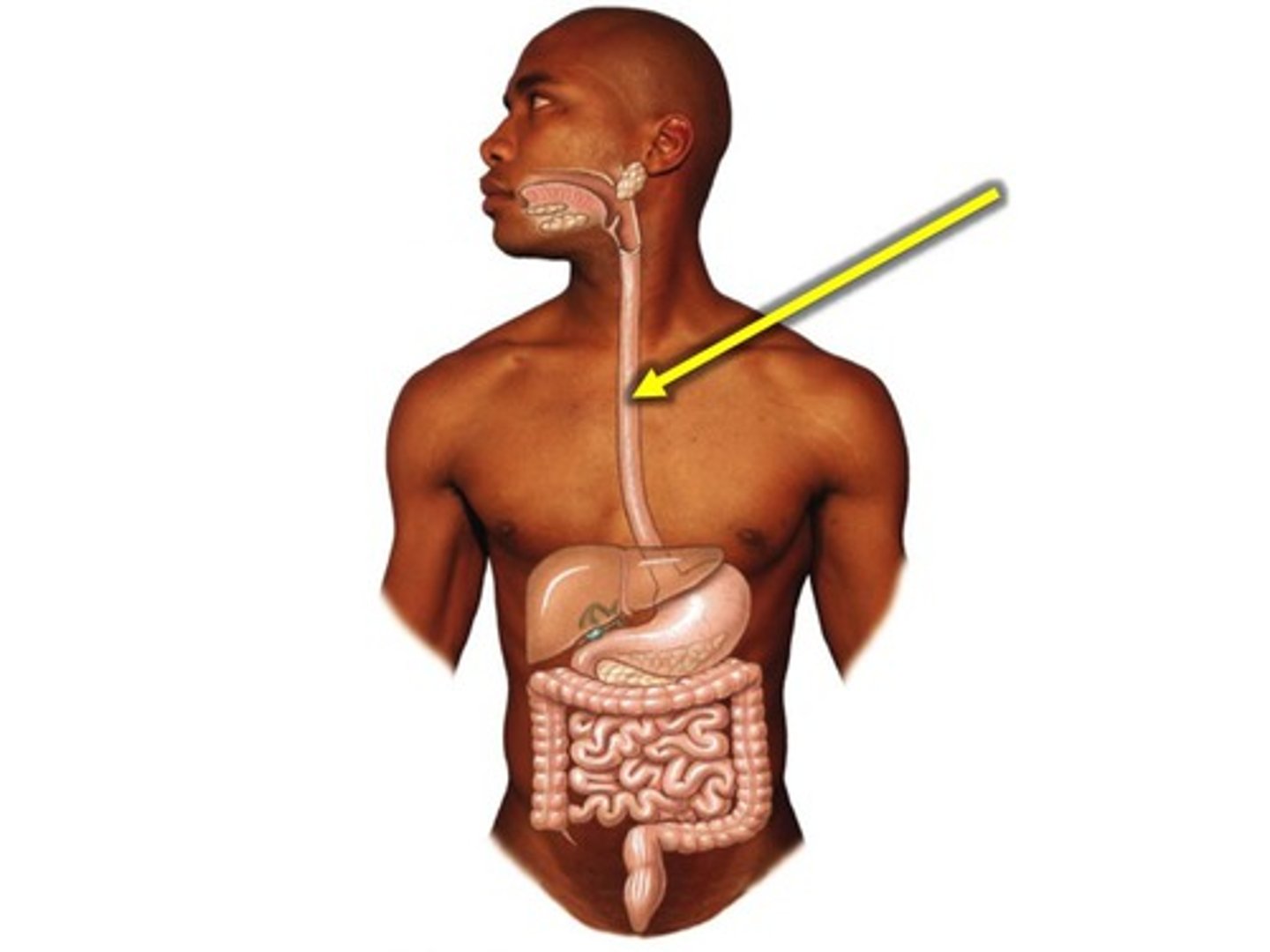
Esophagus
A muscular tube that connects the mouth to the stomach. Posterior to trachea.
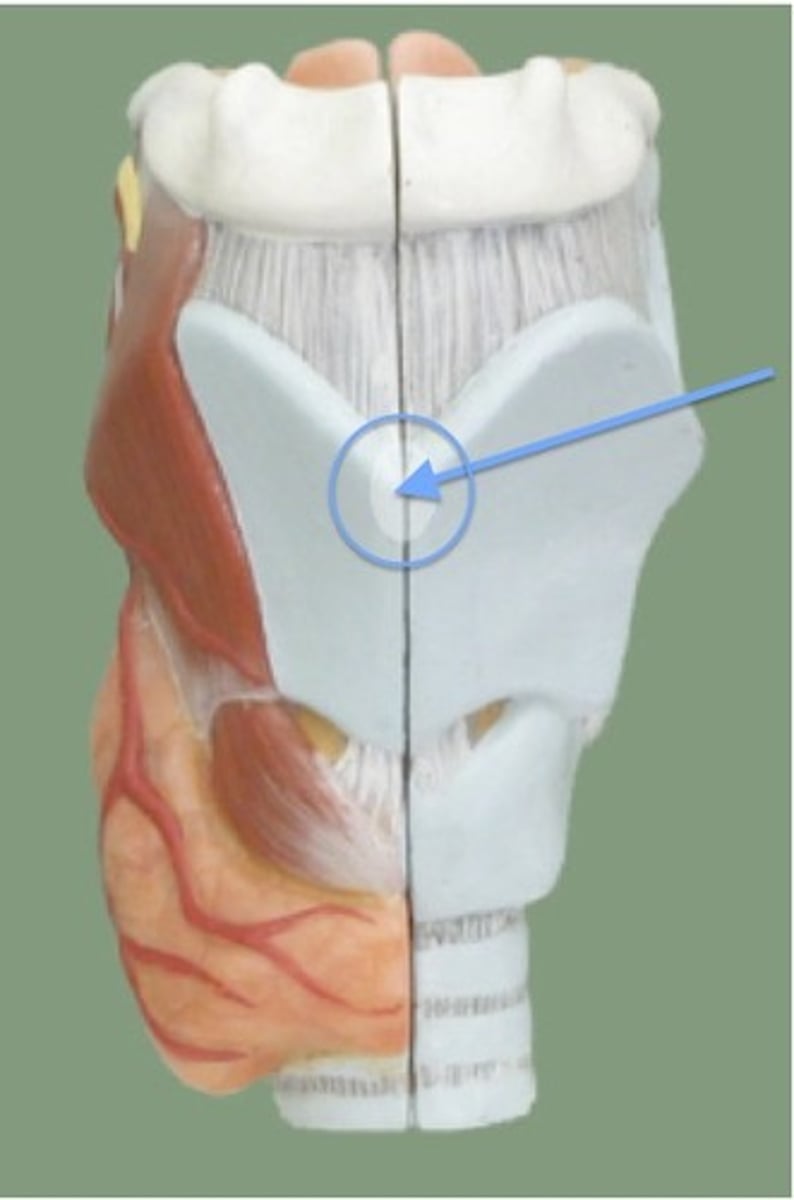
Larynx
voice box; passageway for air moving from pharynx to trachea; contains vocal cords.
Laryngeal cartilage
constructs the larynx; protects vocal cords.
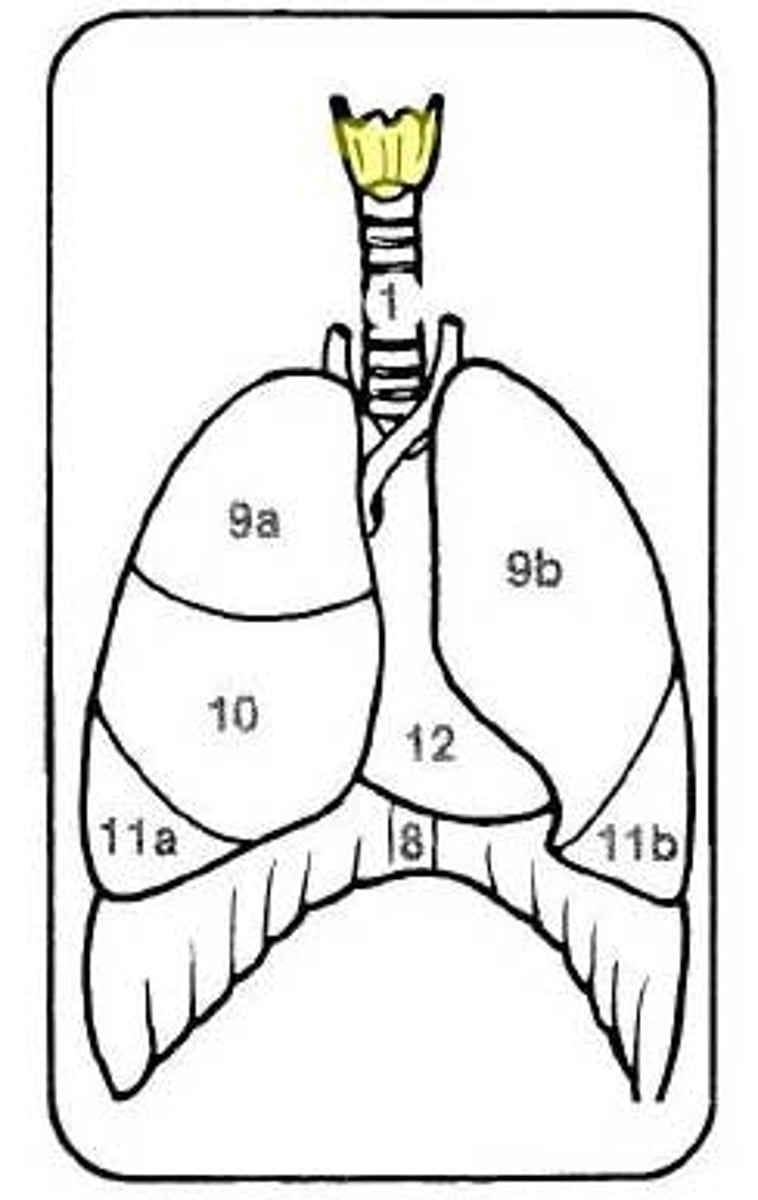
Bronchi
The passages that direct air into the lungs.
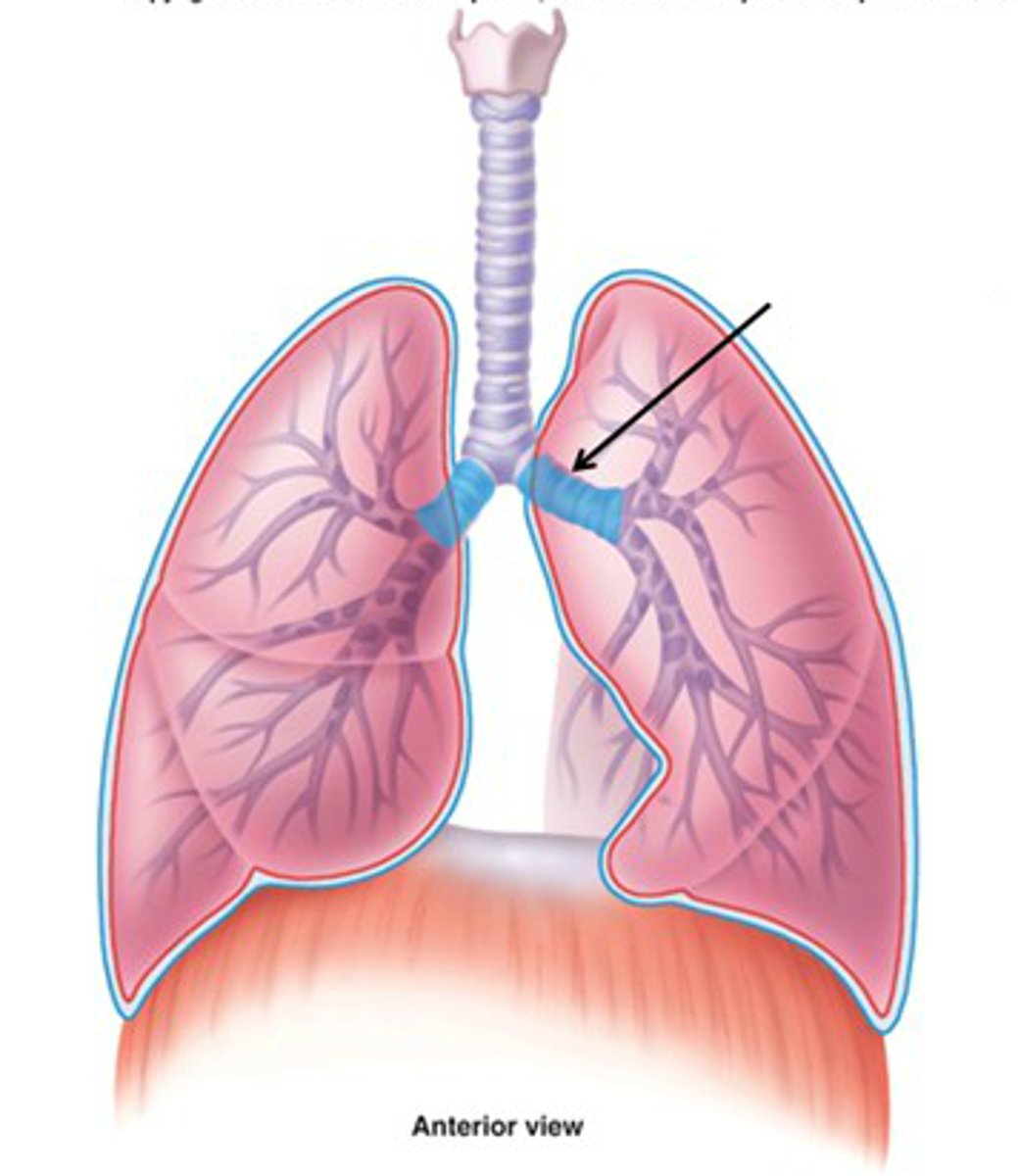
Bronchioles
smallest branches of airways in the lungs that lead from the bronchi to the alveoli.
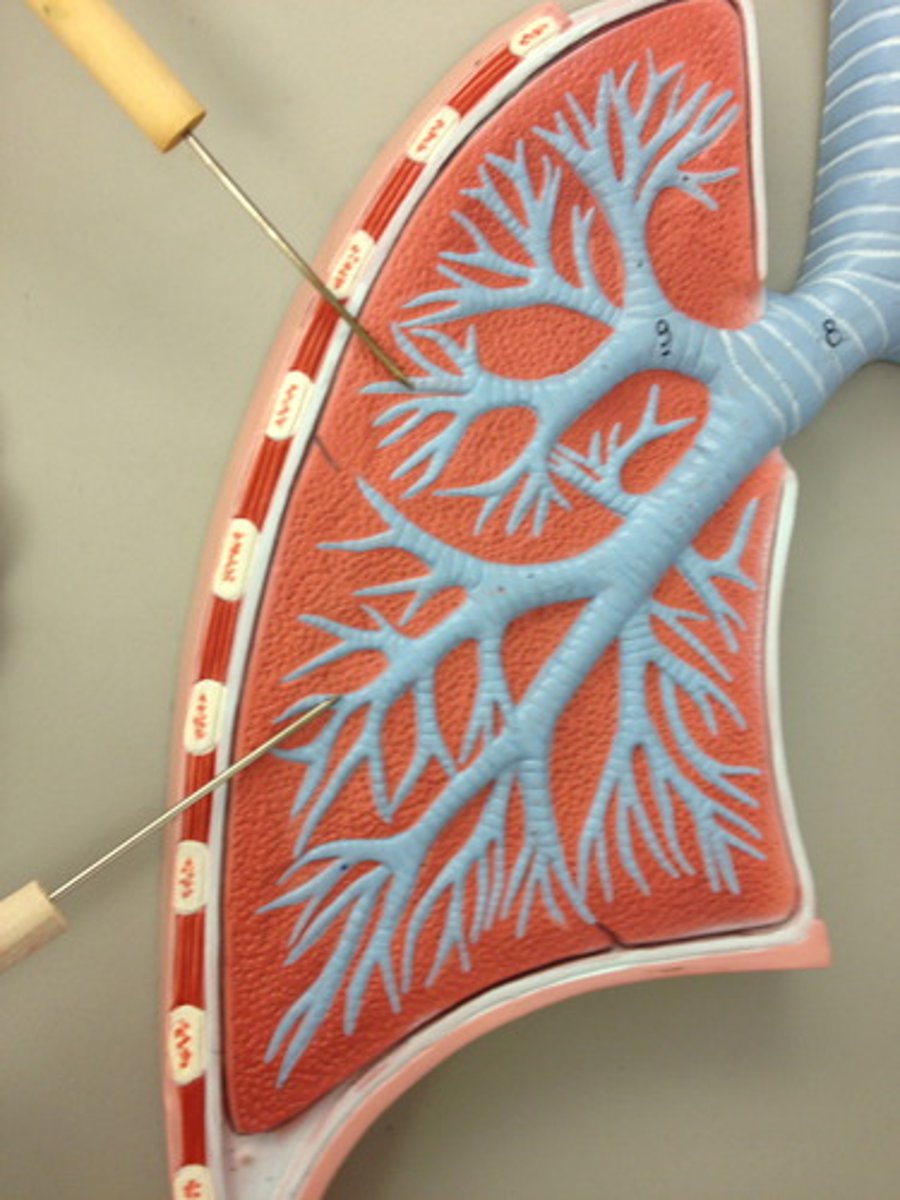
Right lung
3 lobes.
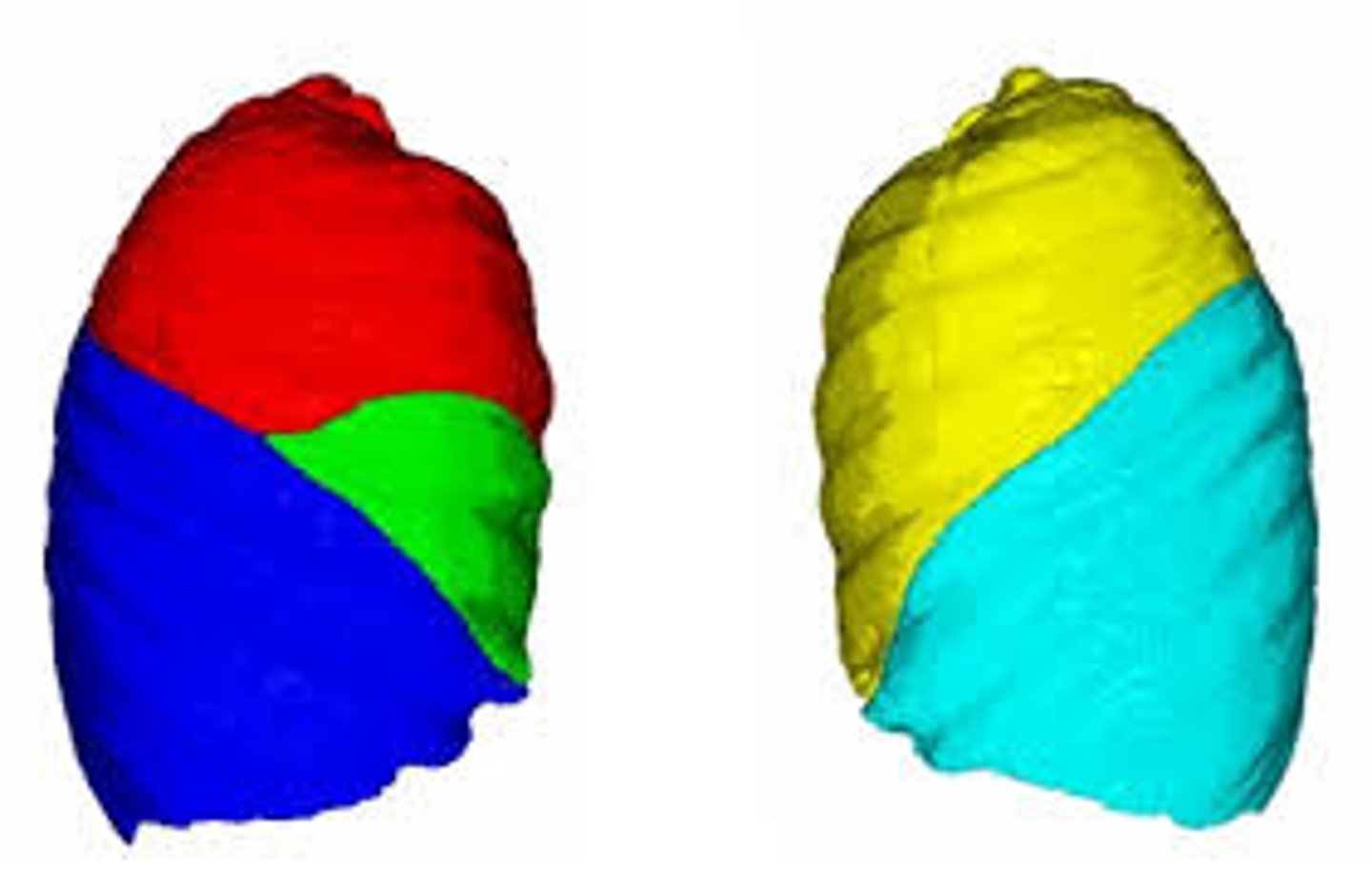
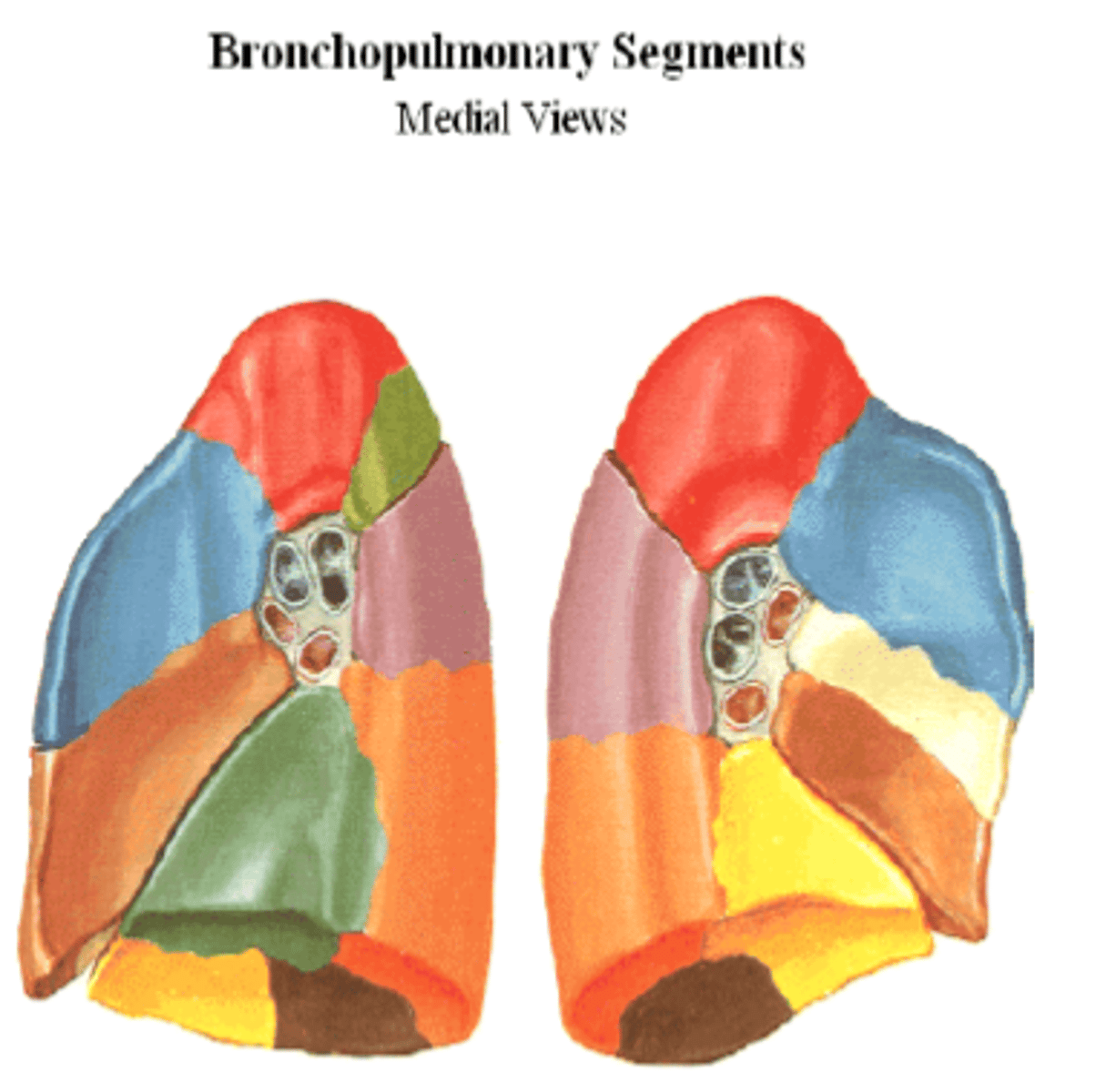
Broncho-pulmonary segments
subunits of lungs
Left lung
2 lobes.
The heart is more closer to
the left lung.
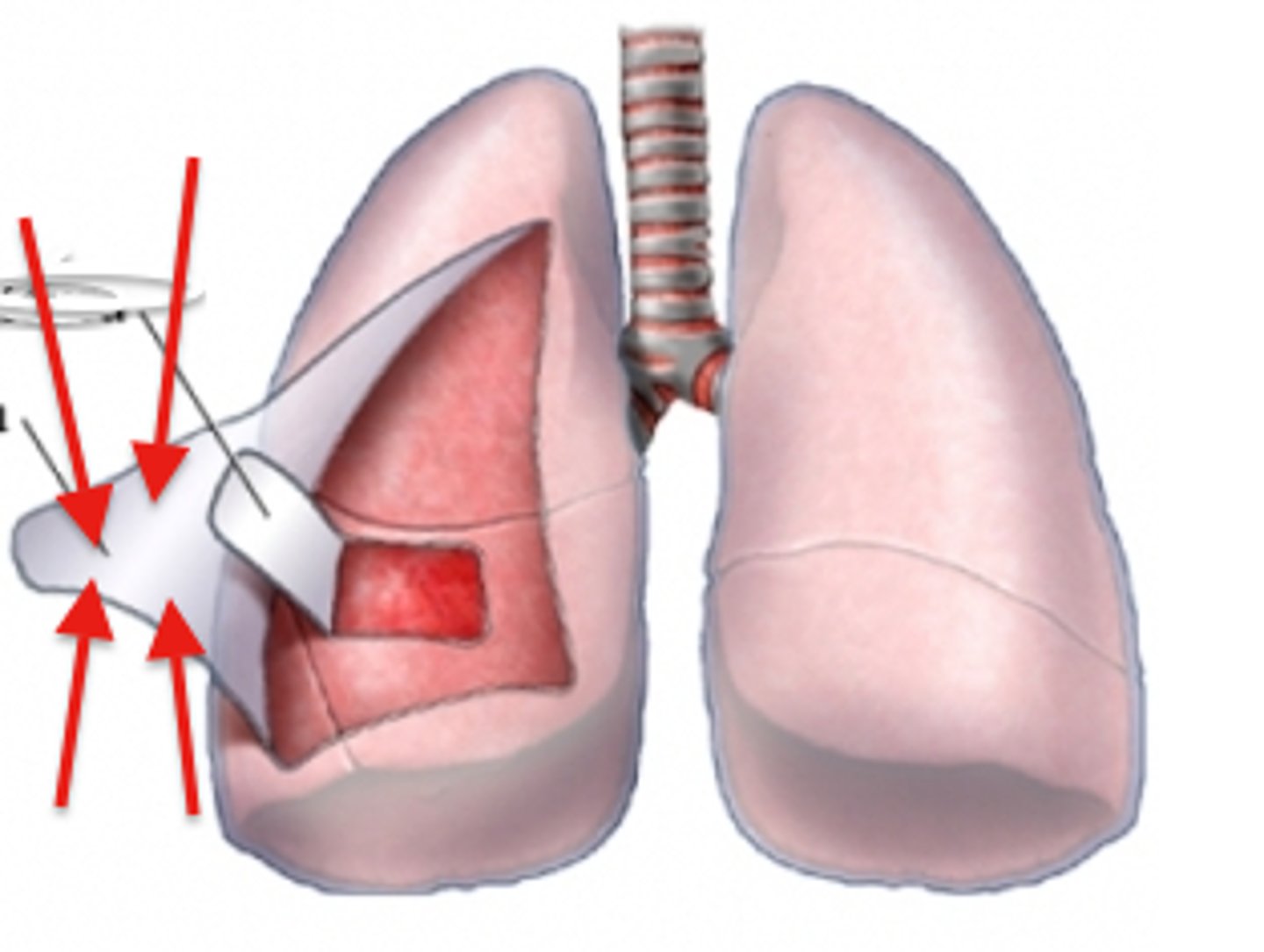
Parietal pleura
outer layer of pleura lying closer to the ribs and chest wall.
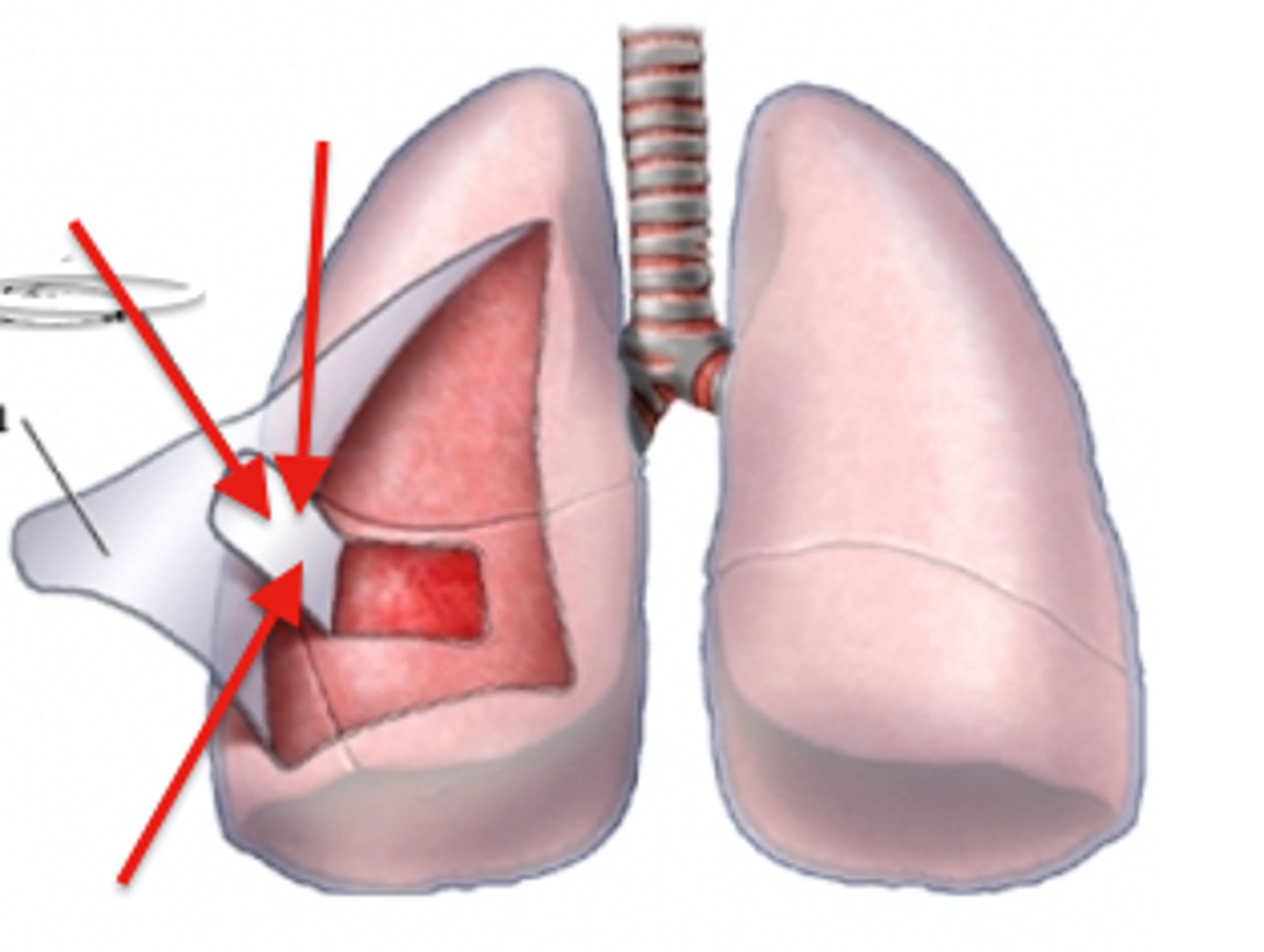
Visceral pleura
the inner layer of pleura that surrounds each lung.
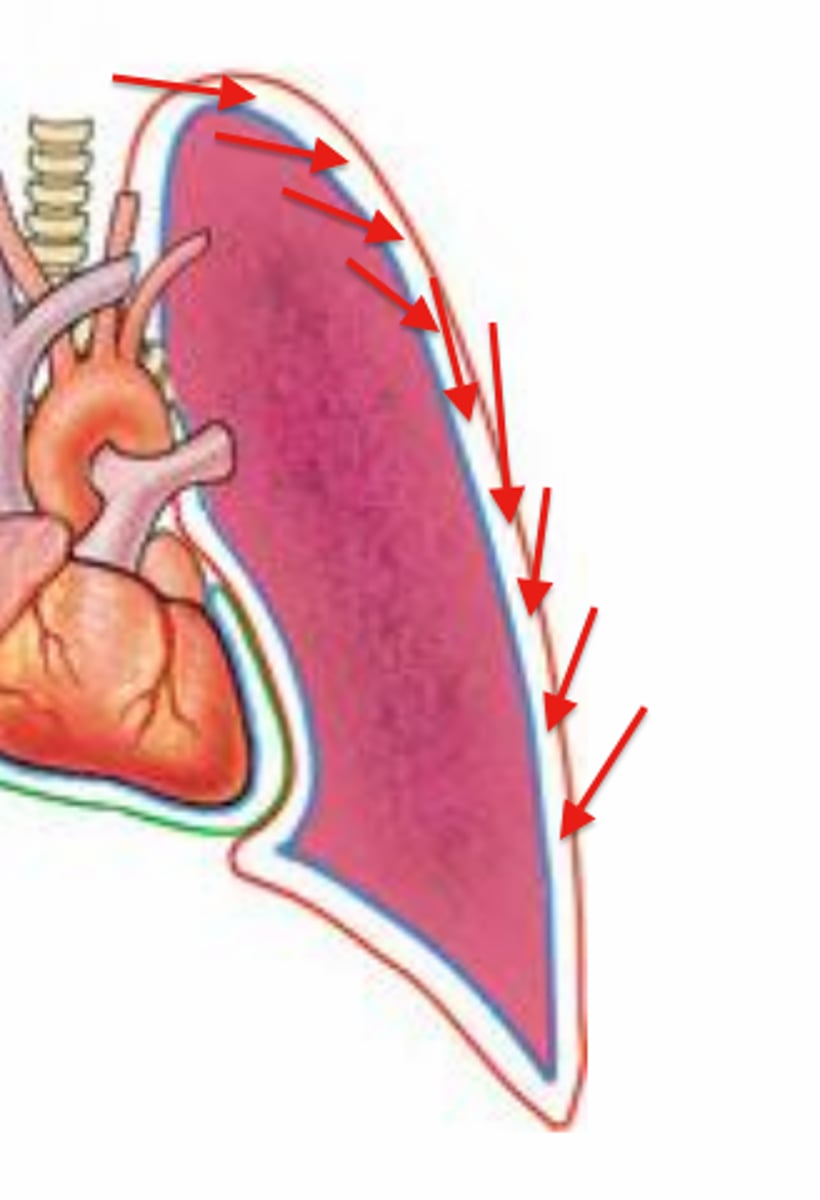
Pleural cavity
space between the folds of the pleura surrounding each lung.
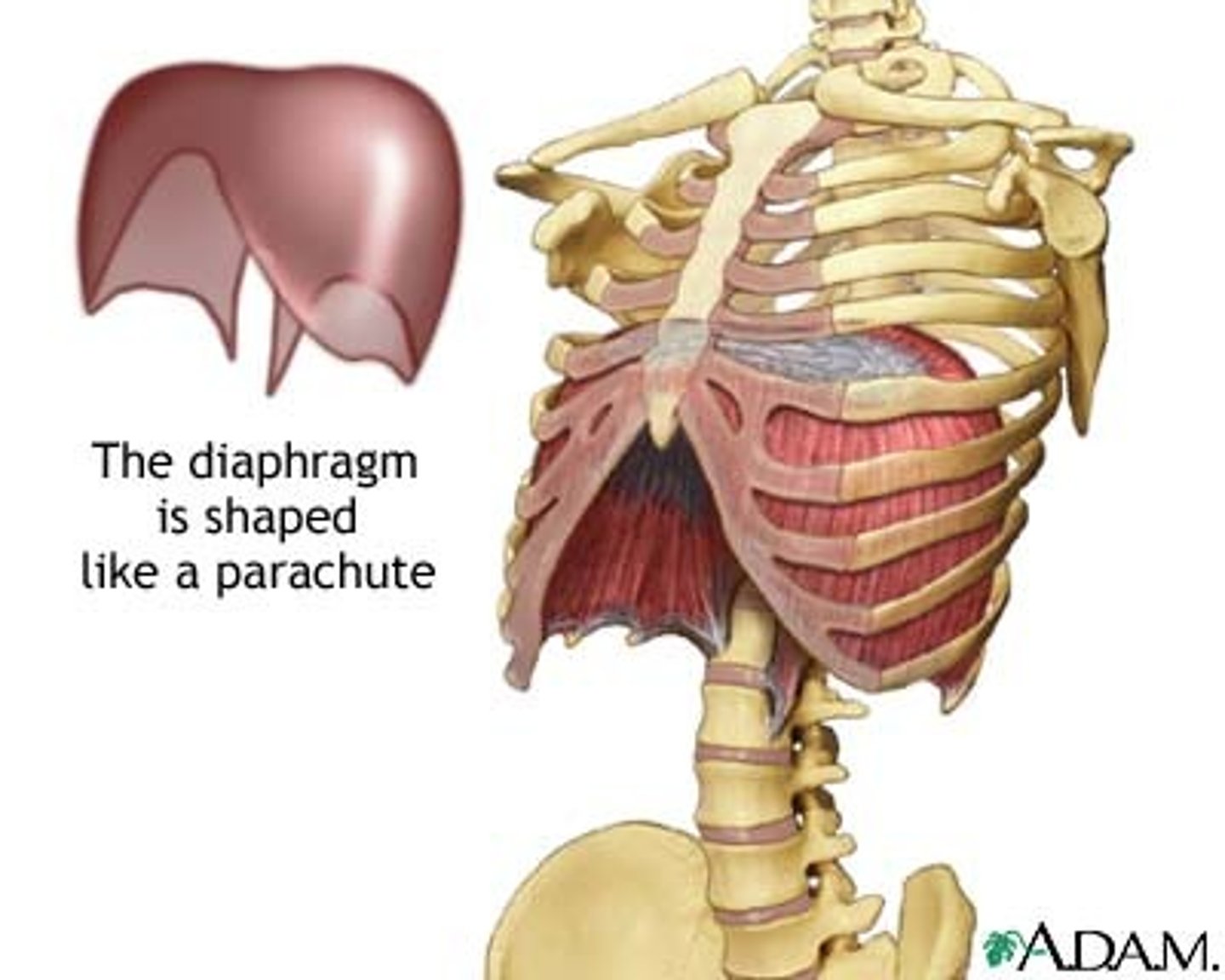
Diaphragm
Large, flat muscle at the bottom of the chest cavity that helps with breathing. Expands space, decreases pressure, and causes inhalation.
Terminal bronchioles
smallest bronchioles
Alveoli
Terminal air sacs that constitute the gas exchange surface of the lungs.
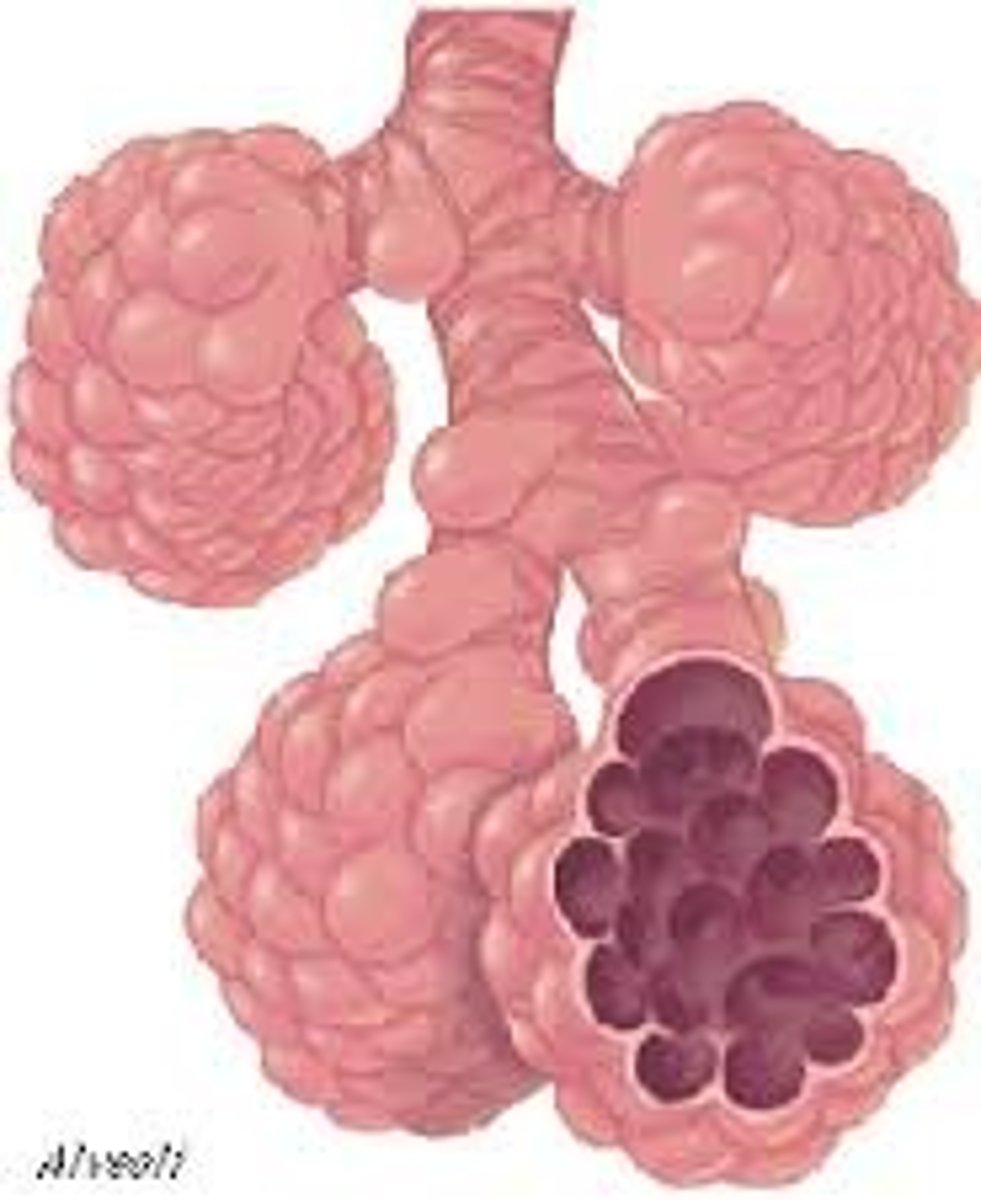
Alveolus
tiny air sac at the end of a bronchiole in the lungs that provides surface area for gas exchange to occur.
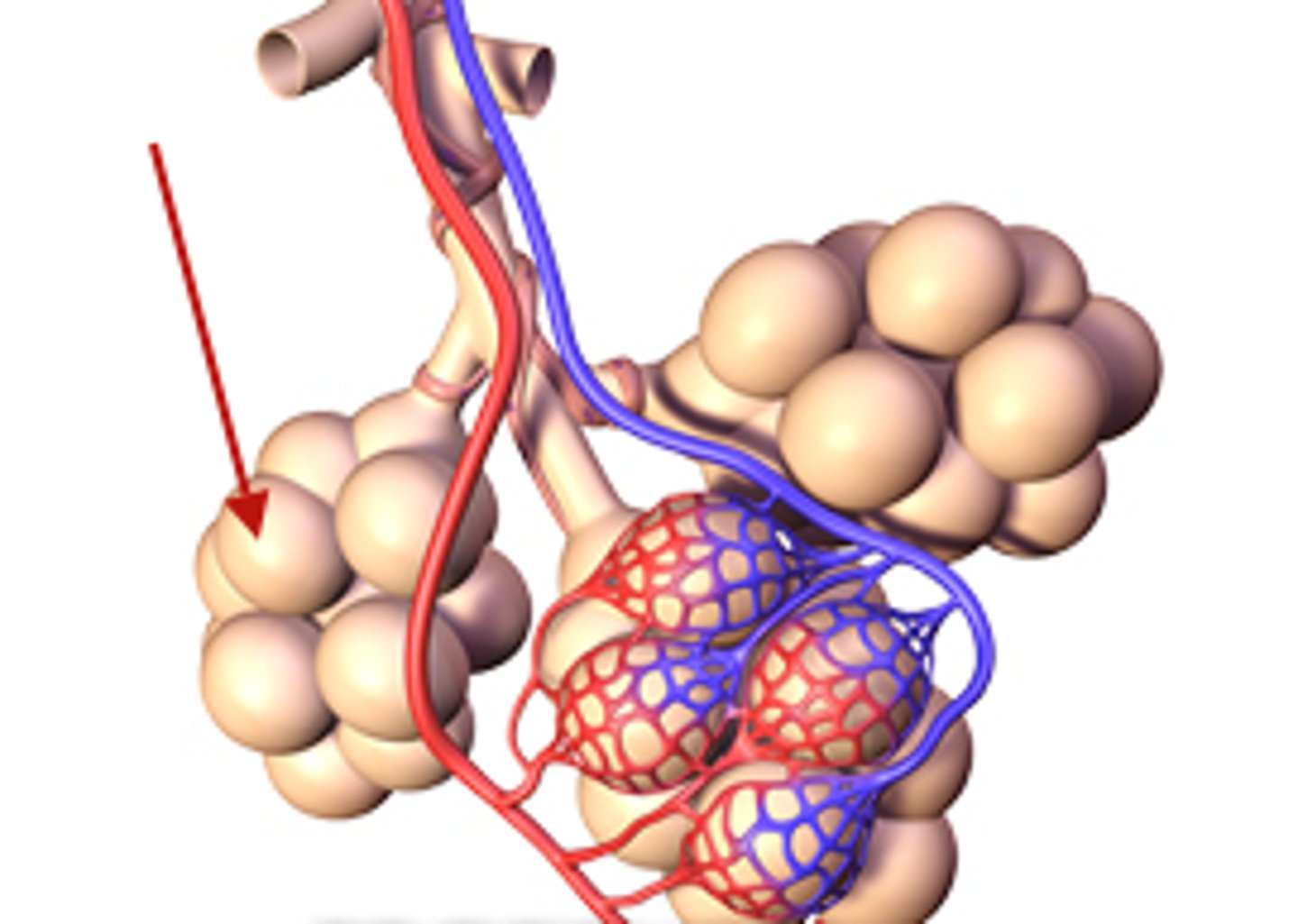
Gas exchange
the process by which oxygen is transported to pulmonary capillaries and carbon dioxide is transported to alveolus.
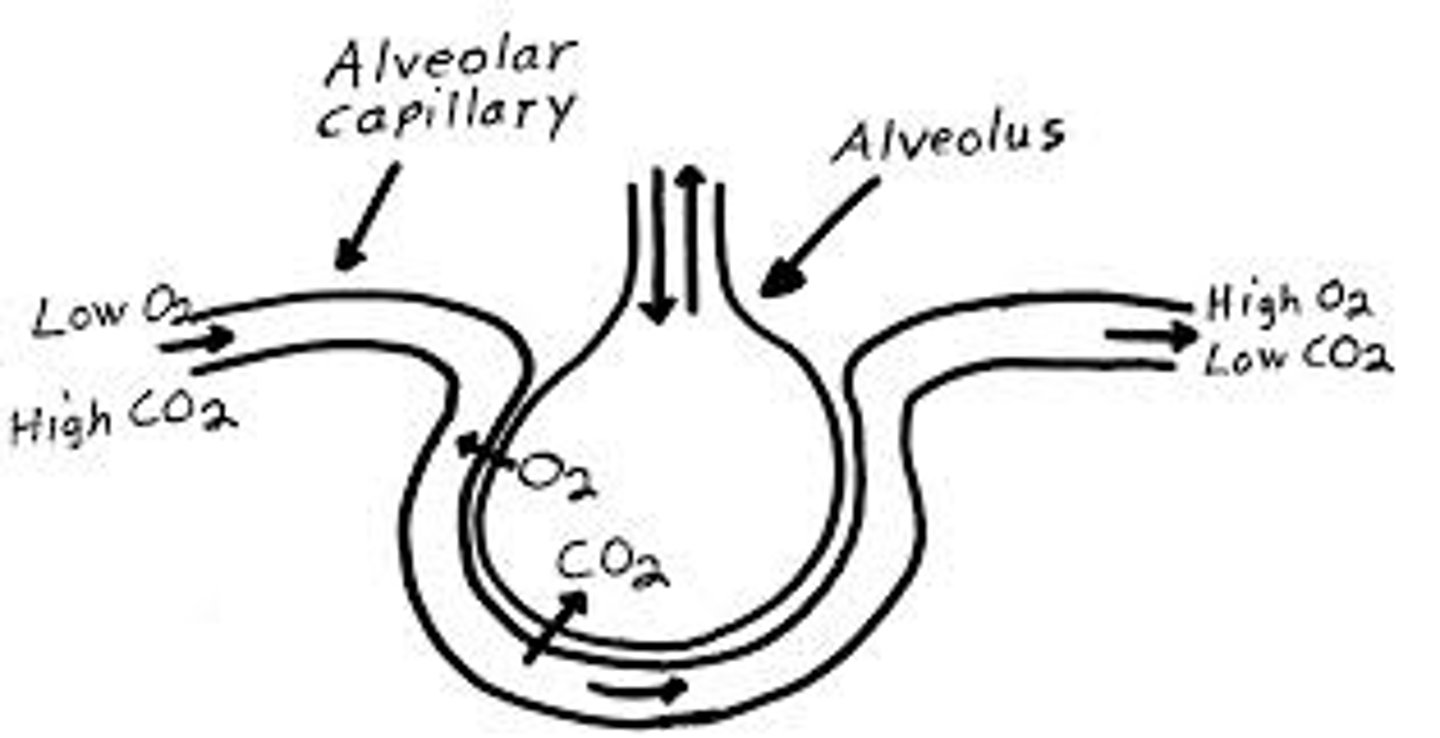
Pulmonary blood capillary
has a thin respiratory membrane made of simple squamous epithelia. RBCs deliver carbon dioxide and carry oxygen.
Surfactant cells
control/manage surface area and reduce surface tension in gas exchange. inside alveolus.
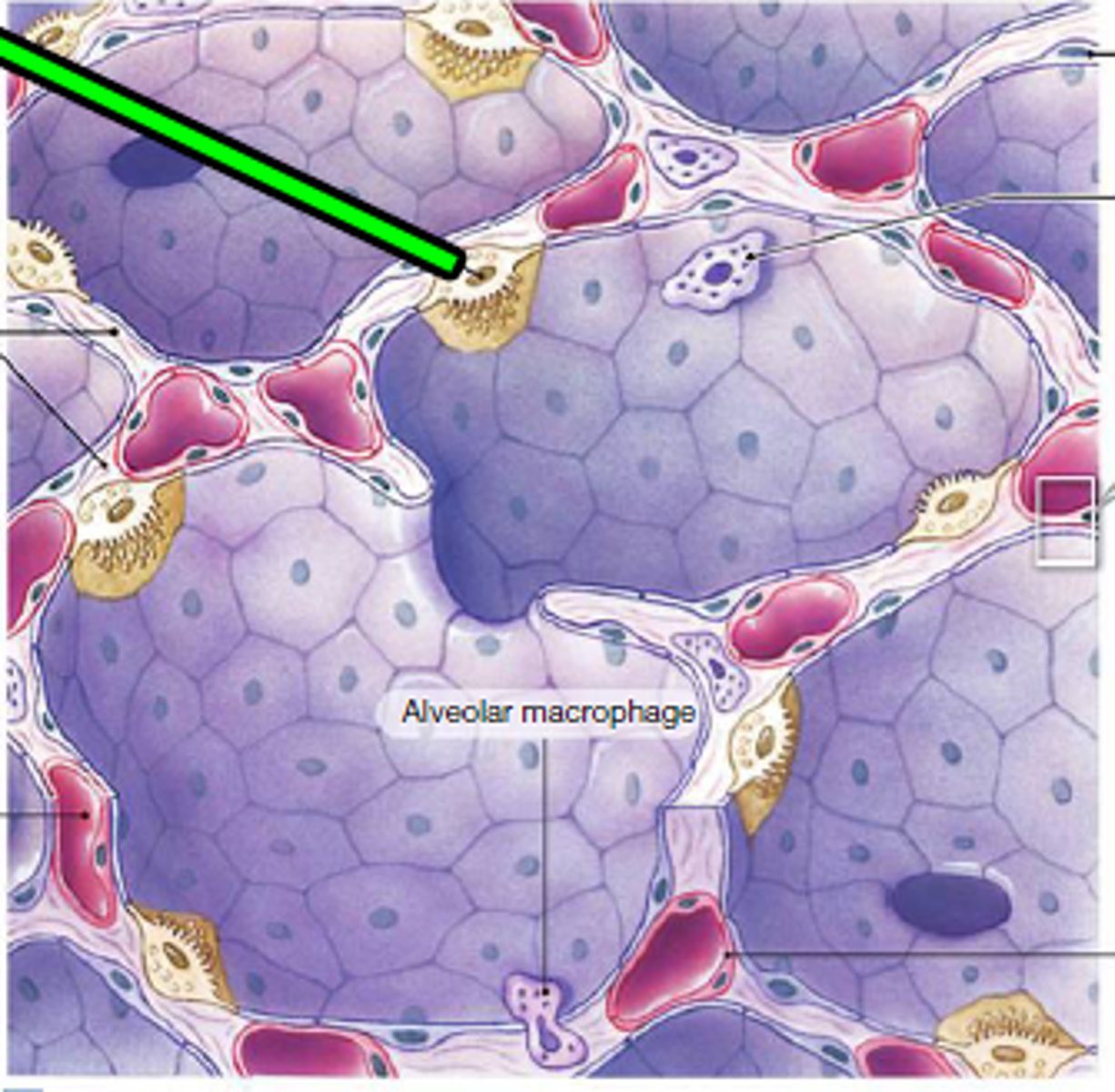
Alveolar macrophage
immune system cell of the alveolus that removes debris and pathogens.
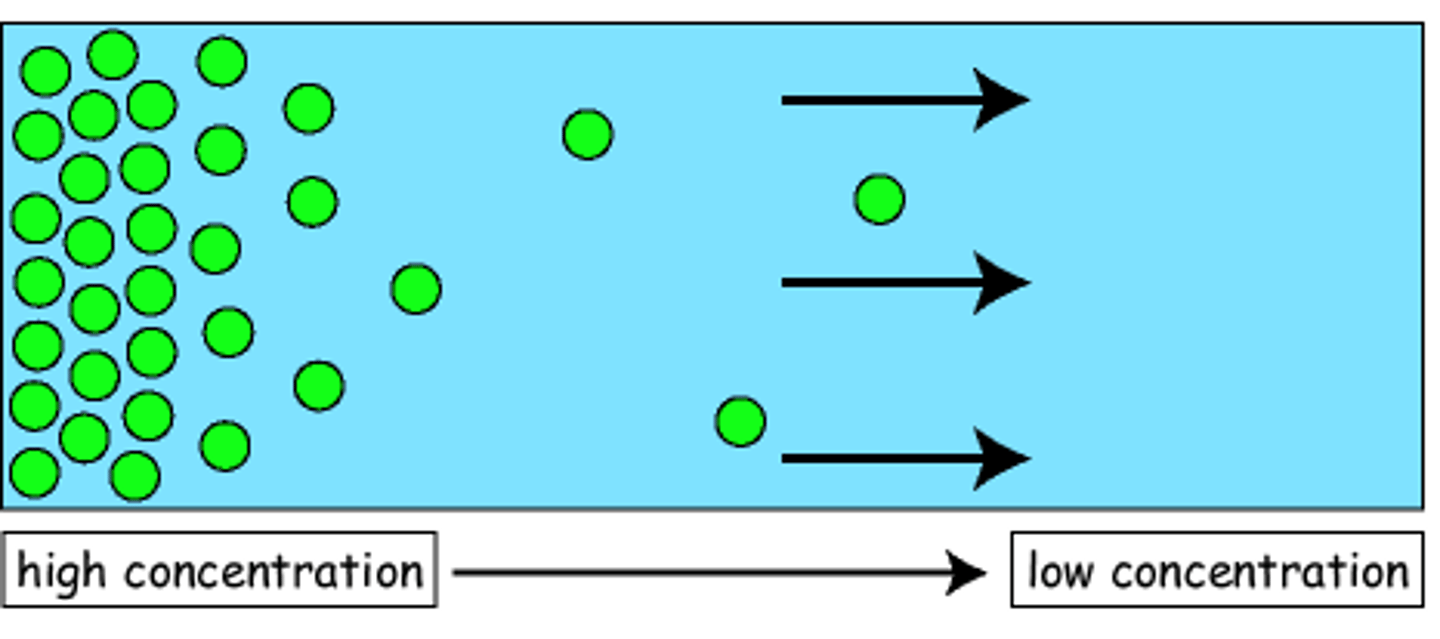
Diffusion
higher surface area and concentration gradient, higher rate. further distance, lowers rate.
The alveolus and pulmonary capillary membranes are thin because
it allows for faster diffusion.
Ventilation
movement of air in and out of the lungs. occurs via muscle action and pressure change.
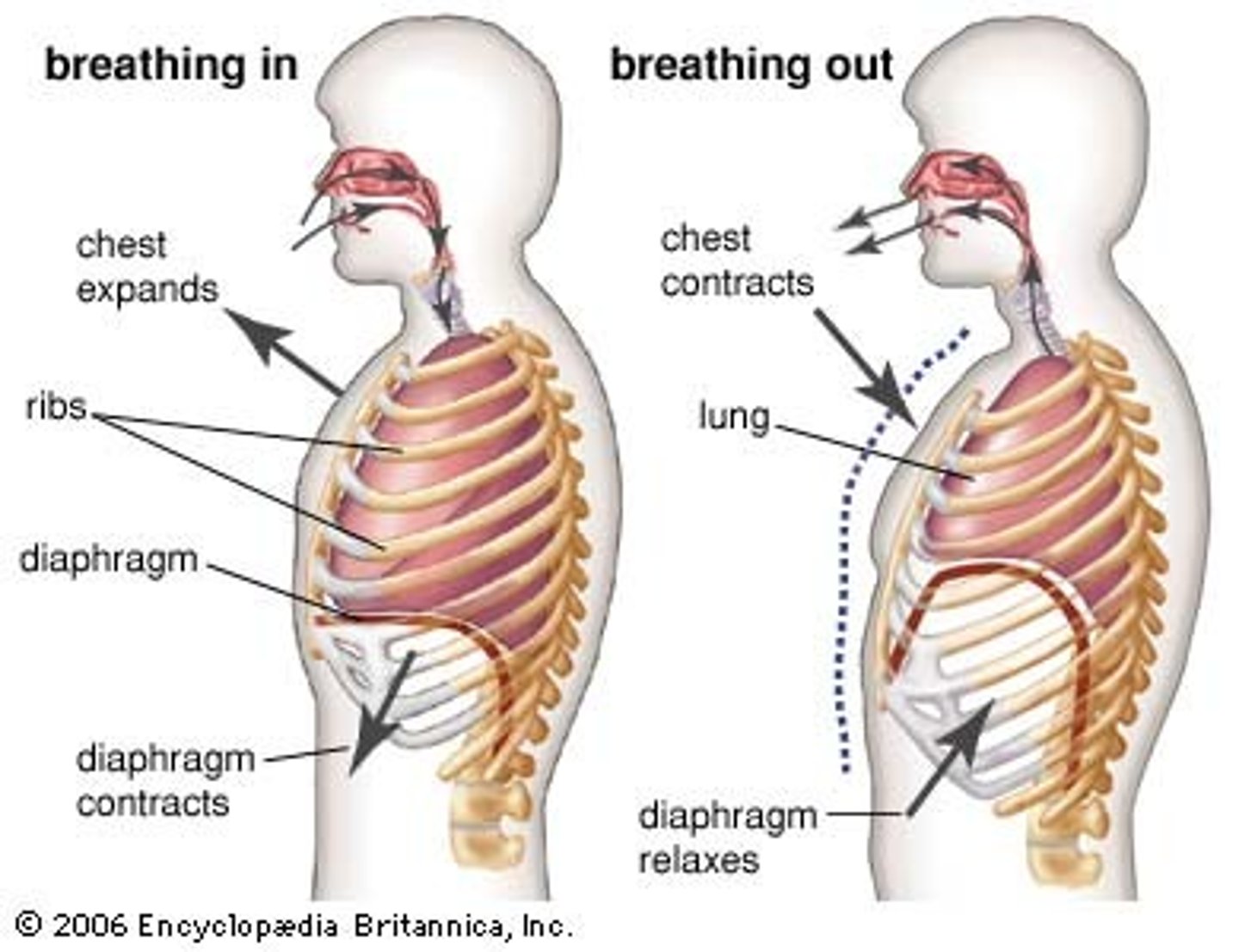
Inhalation
active process. diaphragm and intercostal muscle contracts, volume of thoracic cavity increases while pressure decreases, allowing for air to draw in.
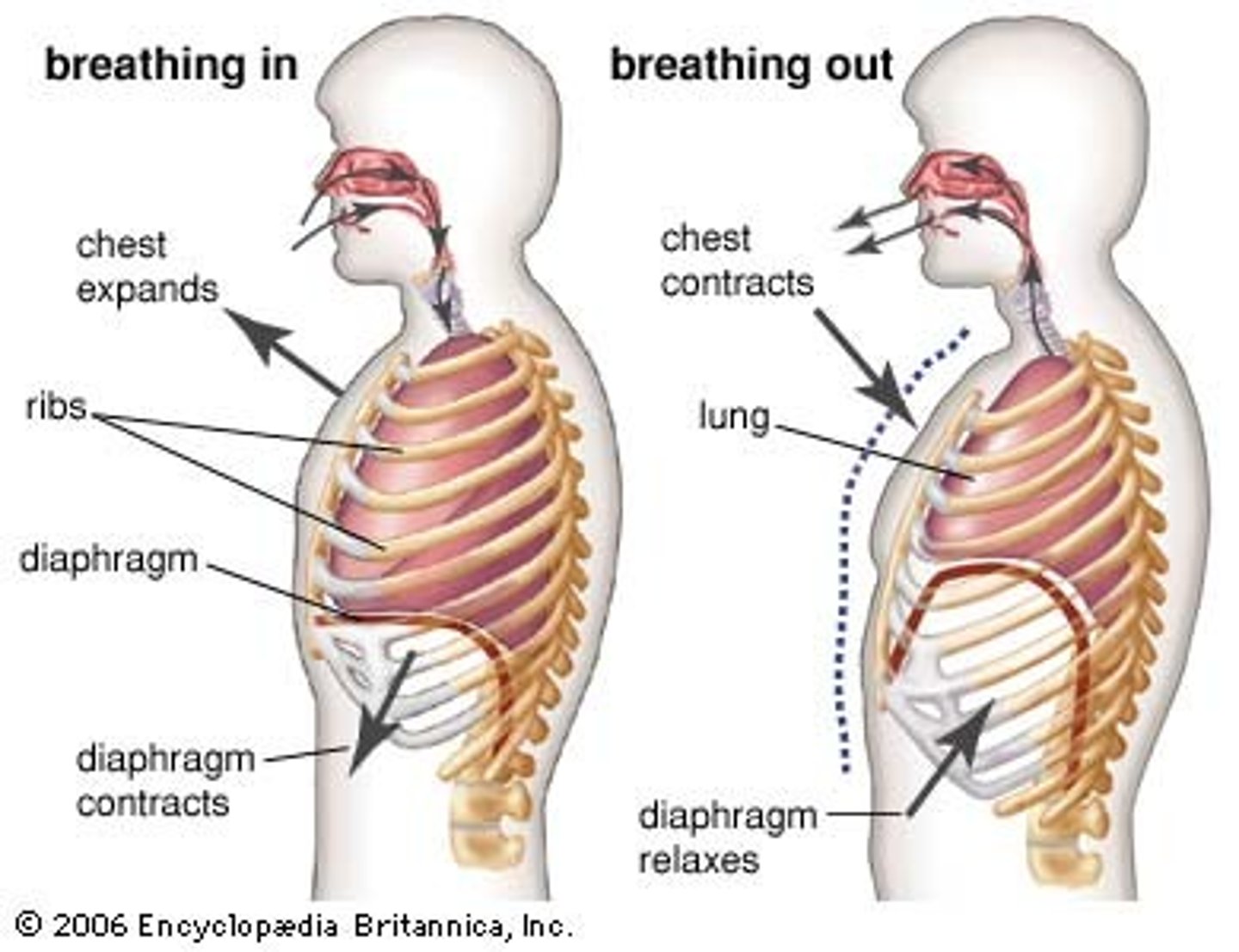
Exhalation
passive process. diaphragm and intercostal muscles relax, decreasing volume of thoracic cavity and increasing pressure, allowing for air to be let out.
CO2 accumulation leads to more
hydrogen, making blood acidic.
Breathing is controlled by
medulla oblongata.
Medulla oblongata monitors
carbon dioxide concentration and blood pH.
Tidal volume
amount of air inhaled and exhaled with each breath under resting conditions.
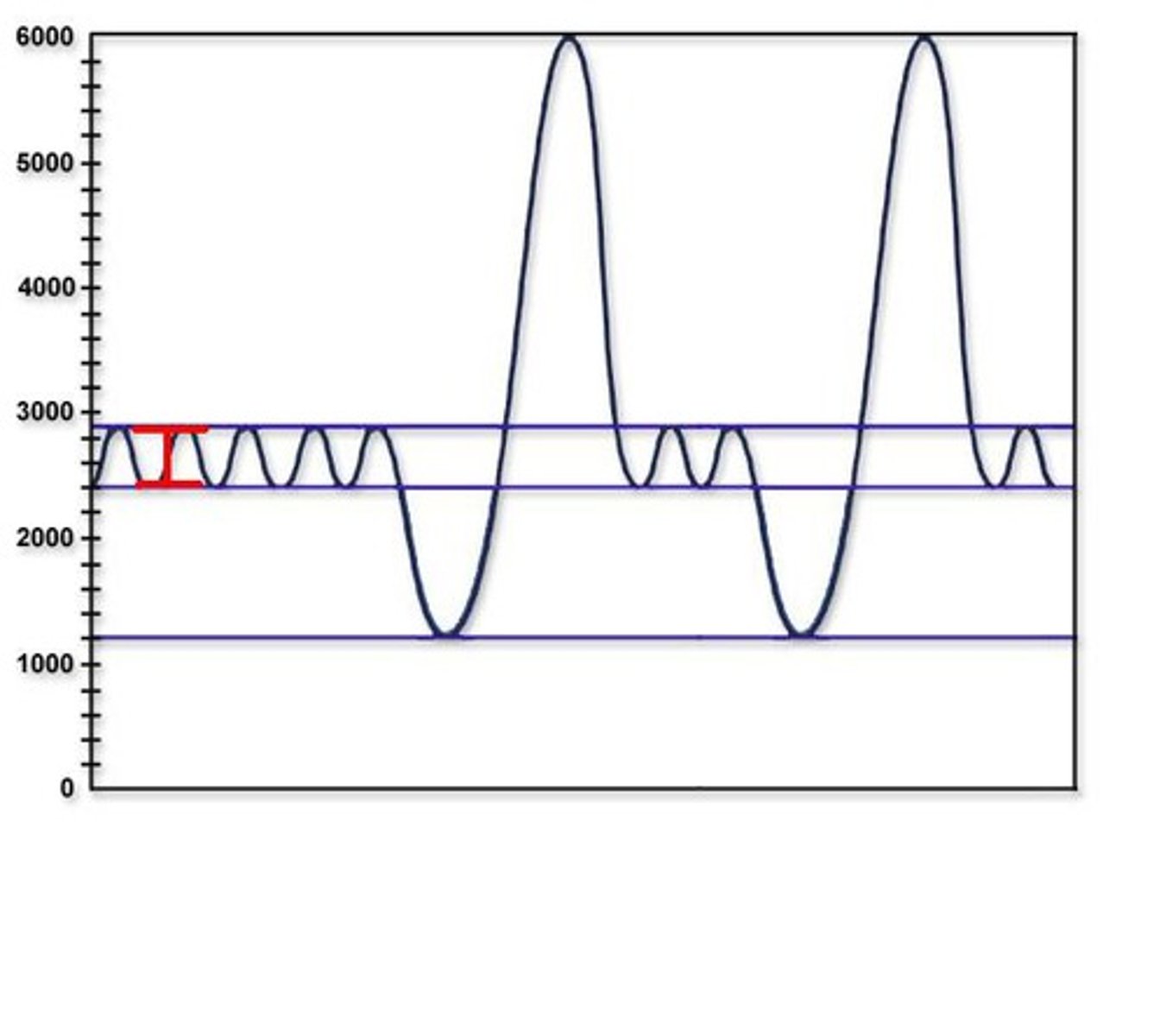
Residual volume
Amount of air remaining in the lungs after a forced exhalation.