P.V, breasts, lymphatic system
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Peripheral vascular system
small and large vessels that circulate oxygenated and deoxygenated blood throughout the body
Lymphatic system
complementary component of the circulatory system; carries lymph fluid (proteins, water, impurities, and waste products) throughout our circulation
Primary function of lymphatic system
drain excess fluid and plasma proteins from body tissues and return them to venous system
Secondary function of lymphatic system
defends body against microorganisms
Third function of lymphatic system
absorb fats (lipids) from SI to blood stream
Lymph nodes
round/oval, around 1 to 2 cm normally; soft, nontender, and nonpalpable
Lymphadenopathy
lymph nodes are greater than 2 cm with/without tenderness
Hard and fixed lymph nodes may indicate
malignancy
The thinnest and most fragile parts of the arterial system are the
Capillaries
Diagnostics
CT scan, duplex ultrasound, MRA, angiogram, angioplasty, lymph node biopsy
angiogram
imaging x-ray that uses a special dye to visualize blood flow through arteries or veins, ordered if obstruction/blockage in coronary or pvs
angioplasty
a balloon is placed in the blocked area and inflated to break up the plaque, widen the diameter of the artery, and increase blood flow
CT, duplex ultrasound, MRA
noninvasive tests that can help the medical specialist map the blood flow in the affected areas
Health History
pain, cramping, edema, lumps, skin changes, PH, FH - atherosclerosis, varicose veins, diabetes, DVT, hypertension, coronary disease, PMH - heart disease, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, overweight, DVT, blood vessel surgery, psychosocial history - work, travel, mobility, prolonged sitting, smoking, meds - blood thinners, cholesterol, oral contraceptives, neuropathy, aching, heaviness, burning in feet, ED, lymph node enlargement, skin color change, blood clots, loss of hair, temp change, ulcers, varicose veins
most severe clinical manifestation of PAD
limb ischemia
CAD vs PAD
same causes, different s/s and treatments
CAD - plaque buildup in coronary arteries
PAD - affects arteries of limbs or peripheral areas, mostly in legs
Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) aka PAD
a slow and progressive circulation disorder. Narrowing, blockage, or spasms in a blood vessel can cause, legs and feet most commonly caused
Peripheral artery disease (PAD)
plaque buildup in the leg arteries
plaque that narrows arteries
atherosclerosis
What occurs if blood can’t get through to nourish organs and other tissues?
damage and death (gangrene), happens most in toes and feet
Coronary artery disease (CAD)
limits blood flow in the coronary arteries, which deliver blood to the heart muscle
Plaque can arise from
high cholesterol or other substances
Most common CAD symptom
chest pain
CAD can lead to
heart attack, arrhythmia, heart failure
Arterial insufficiency and chronic venous insufficiency both affect the
lower extremities
s/s of arterial insufficiency
decreased/absent pulse, cool, pale, shiny skin, loss of hair, pain in legs/feet, toe ulcerations, deep red color of foot, thick, rigid nails
s/s of chronic venous insufficiency
ankle ulcerations, difficulty palpating pulse, edema, cyanotic foot, hyperpigmentation, warmth
Sequence of assessment
IP
Preliminary steps
comfortable room, temp, help change positions if needed, remove clothing, footwear, socks, jewelry
Purpose of assessing lymph nodes
assess for signs of inflammation or disease
Organs containing lymphatic tissue
spleen (largest), thymus, tonsils and adenoids, appendix, lymph nodes, peyer patches, bone marrow
Functions of lymphatic system
WBC production, fluid and protein balance, immune functions of body; first line of defense against disease
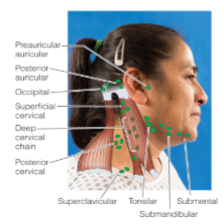
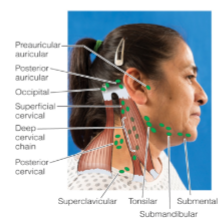
Lymph node sites in head and neck
Preauricular
Postauricular
Suboccipital
Tonsillar
Submandibular
Submental
Superficial cervical
Posterior cervical
Deep cervical chain
Supraclavicular
Normal Lymph node findings
not palpated, less than 2 cm, discrete/soft, moveable, nontender
Abnormal lymph node findings
enlarged (2 cm <), matted/fixed, rubbery/hard, tender
What lymph nodes located in back of the neck and head?
Suboccipital
I/P upper extremities purpose
assess for peripheral circulation
Inspect each arm for
size/symmetry, color, edema, texture
Inspect nail beds for
color, thickness, clubbing, temperature, radial/ulnar/brachial pulses, capillary refill
Why is palpating lymph nodes in axillary region done in breast exam?
breast cancer can metastasize to lymphatic regions, causing swelling/enlargement
Breast function
reproductive organ, production + storage of milk, sexual stimulation
HH of breast
lumps, nodules, swelling, redness, warmth, dimpling, rashes, change in size/firmness, nipple retraction/discharge, pain/tenderness, disease, trauma, surgery, biopsy, implants, breast cancer, hormone therapy/oral contraceptives, alcohol, tobacco use, high-fat diet, caffeine use, self exam
Breast health promotion/prevention
self exam monthly, physician exam yearly, mammogram (age/risk dependent), education of risk factors
Normal findings of I/P upper extremities
symmetrical arms, uniform color, no edema/ulcerations, normal venous pattern, warm temp, 2+, pink fingernail beds, even thickness, 160-degree, capillary refill <2 s
I/P upper extremities abnormal findings
altered peripheral circulation, discoloration, change in skin texture, cool extremities, bilateral/unilateral edema, enlarged epitrochlear nodes, cellulitis, edema, ulcerations, capillary refill > 2 s
What do you use when you cannot find pulse
Doppler
Edema
localized or generalized condition in which body tissues contain an excessive amount of tissue fluid in the interstitial spaces, d/t cardiac, p.v., renal/liver disease, lymphedema/thrombosis
Lymphedema
accumulation of lymph fluid in the tissues, most common cause is obstruction of lymphatic vessels
Unilateral edema
if in upper/lower extremity, can indicate DVT
Thrombosis
blood clot
2 types of edema
pitting, nonpitting
Peripheral edema
accumulation of fluid in feet / legs
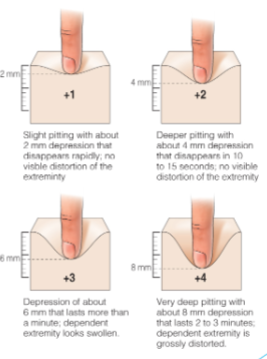
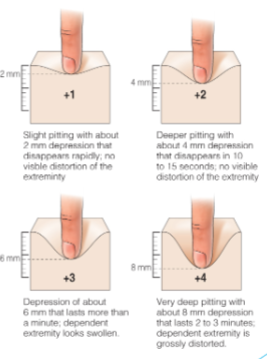
Pitting edema
1-4 scale,
Assessing capillary refill purpose
assess tissue perfusion
What do you note in capillary refill
amount of time it takes nail to return to pink color
Normal cap refill
less than 2 s
Abnormal cap refill
more than 2 s
I/P lower extremities purpose
assess arterial or venous circulation
Inspect each leg for
size/symmetry, color, texture, edema, venous pattern, hair distribution, ulcerations
Inspect toe nails for
color, thickness, capillary refill,
Pulses assessed in lower extremities
femoral, popliteal, dorsal pedis, posterior tibial
Pulse strength
0-4
Normal lower extremity findings
symmetrical, uniform color, no edema/ulcerations, pink, evenly thick toenails, warm temp, even hair distribution, regular femoral venous pattern, nondistended veins, capillary refill <2 s
How to remember pitting edema
x2 - +1 = 2 × 1 = 2 mm, +2 = 2 × 2 = 4 mm …
Abnormal findings of lower extremities
discoloration, decreased texture, loss of hair, cool temp, thick toenails, raynaud disease, cellulitis, arterial/venous insufficiency wounds, bilateral/unilateral edema, varicose veins, lymphedema, PVD, varicosities, thrombophlebitis
You are performing the Blanch Test on an 85-year-old patient. Your assessment finding is 4 seconds. What is a normal finding?
less than 3 secs

What is this
Raynaud’s Syndrome
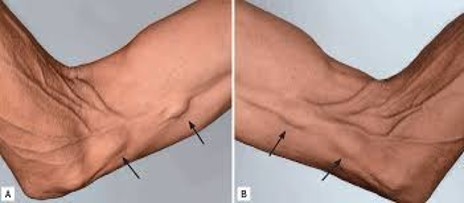
What is this
Enlarged epitrochlear nodes
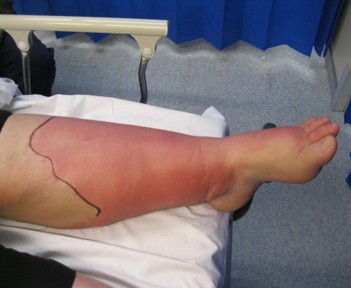
What is this
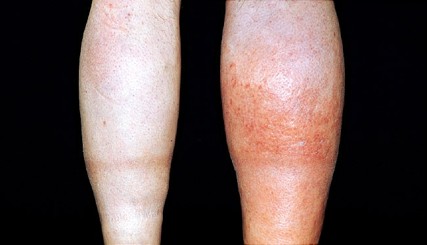
What is this
DVT