topic 7 - labour market and income inequality
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 7:38 AM on 8/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
1
New cards
equilibrium wage rate
established when the quantity demanded of labour is equal to the quantity supplied of labour
2
New cards
market demand curve
* downward sloping
* change in wage rate will bring about movement along demand curve
* example; hospitality industry - hotel chains in developing countries can hire more staff as wage rate is lower compared to the case of singapore
* change in wage rate will bring about movement along demand curve
* example; hospitality industry - hotel chains in developing countries can hire more staff as wage rate is lower compared to the case of singapore
3
New cards
factors affecting demand for labour
* demand for output
* other factor prices
* technology
* other factor prices
* technology
4
New cards
factors affecting market labour supply
* number of qualified people
* non wage benefits / costs of the job
* wage rate and non wage benefits in alternative jobs
* non wage benefits / costs of the job
* wage rate and non wage benefits in alternative jobs
5
New cards
demand for output
* when demand for firm’s products/services increases, firm needs to product more to meet the higher demand. meaning more workers needed to be hired to produce the additional goods or provide extra services
* for example, during festive seasons that there is a higher demand for output due to more orders and diners expected, labour is needed
* for example, during festive seasons that there is a higher demand for output due to more orders and diners expected, labour is needed
6
New cards
other factor prices
* when prices of other factors like capital/land/machines decrease, more machines can bought as a substitute for labour. labour demand decreases
* or when certain raw materials used to make products decreases in price, demand for labour increases
* or when certain raw materials used to make products decreases in price, demand for labour increases
7
New cards
technology
* advances in technology may bring about new jobs; technology improvement increases labour productivity
* firms more willing to pay the more productive and skillful workers who can handle high tech production
* leading to higher demand for the skillful workers
* firms more willing to pay the more productive and skillful workers who can handle high tech production
* leading to higher demand for the skillful workers
8
New cards
number of qualified people
* more people with the required qualifications, supply of labour for job/industry is higher
* this factor is influenced by factors like education systems, training programs, and skill development
* this factor is influenced by factors like education systems, training programs, and skill development
9
New cards
non wage benefits or costs of the job
* can impact the decision of individuals to work
* benefits - for example, health insurance, retirement plans, flexible working hours and job security
* costs - for example, physically demanding work, long commutes, or exposure to unpleasant conditions
* jobs with attractive benefits etc tend to have higher labour supply
* benefits - for example, health insurance, retirement plans, flexible working hours and job security
* costs - for example, physically demanding work, long commutes, or exposure to unpleasant conditions
* jobs with attractive benefits etc tend to have higher labour supply
10
New cards
wage rate and non wage benefits in alternative jobs
* wage rate is the amount of money paid to workers for their labour
* as wage rate increases, supply of labour increases
* however some individuals might be willing to work for lower wage rates if non wage benefits are considerable
* attractive benefits increase supply
* as wage rate increases, supply of labour increases
* however some individuals might be willing to work for lower wage rates if non wage benefits are considerable
* attractive benefits increase supply
11
New cards
income inequality
exists in all countries, with some workers earning much higher income than other workers
12
New cards
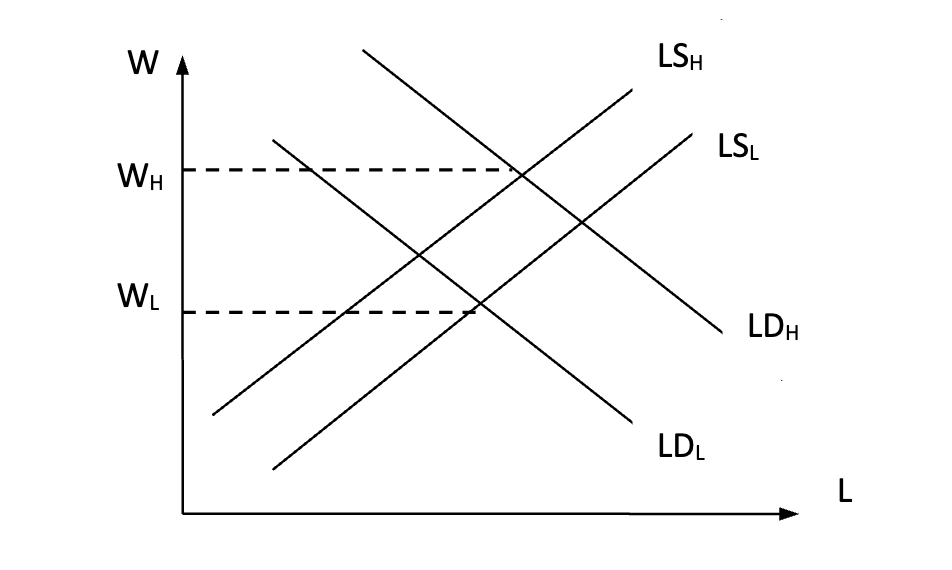
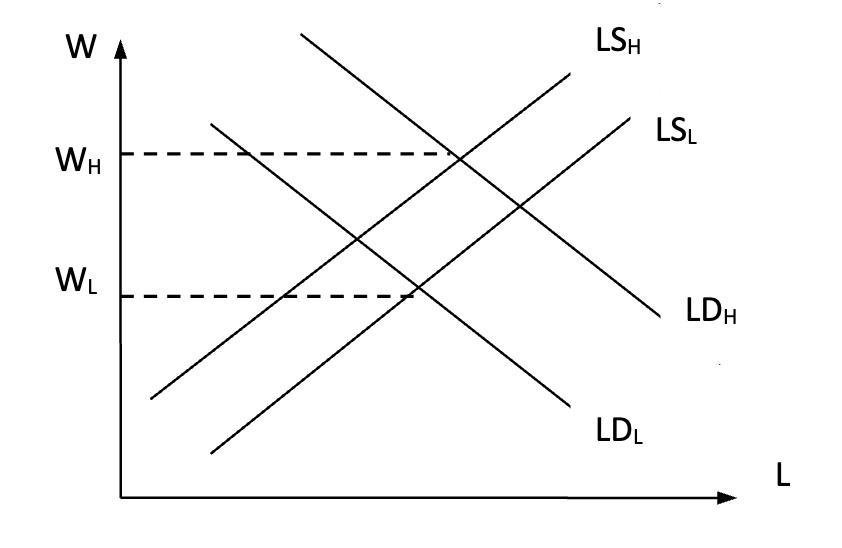
high skilled labour
high demand and low supply
13
New cards
low skilled labour
low demand and high supply