Comprehensive Guide to Pharmaceutical Suspensions: Types, Preparation, and Stability
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
What is a suspension?
A 2-phase system consisting of a finely divided solid dispersed in a liquid.
Why are suspensions used for certain drugs?
They ensure chemical stability while permitting liquid therapy, provide flexibility in dosing, and alleviate disagreeable taste.
What are the desired features of a suspension?
Uniform dispersion, slow settling, readily redispersed, constant particle size, and easy to pour and administer.
What factors affect the stability of a suspension?
Particle size, viscosity of the vehicle, and the ability to prevent caking.
What is Stokes' Equation used for?
To analyze the rate of sedimentation in suspensions.
What does Stokes' Equation include?
Rate of settling, particle diameter, viscosity of dispersion medium, acceleration due to gravity, and densities of dispersed phase and dispersion medium.
What are the assumptions of sedimentation rate in Stokes' Equation?
Particles are uniform, spherical, in a very dilute suspension, settling without turbulence or collisions.
What is the unit of viscosity?
Centipoise (cps).
How does particle size affect sedimentation rate?
Decreasing particle size exponentially decreases the rate of settling.
What is the effect of viscosity on sedimentation rate?
Increased viscosity inversely affects the rate of settling; doubling viscosity reduces settling rate by half.
What is the ideal particle size for pharmaceutical suspensions?
Between 1-50 μm.
What is flocculation in suspensions?
The intentional formation of a less rigid aggregation of particles to prevent caking.
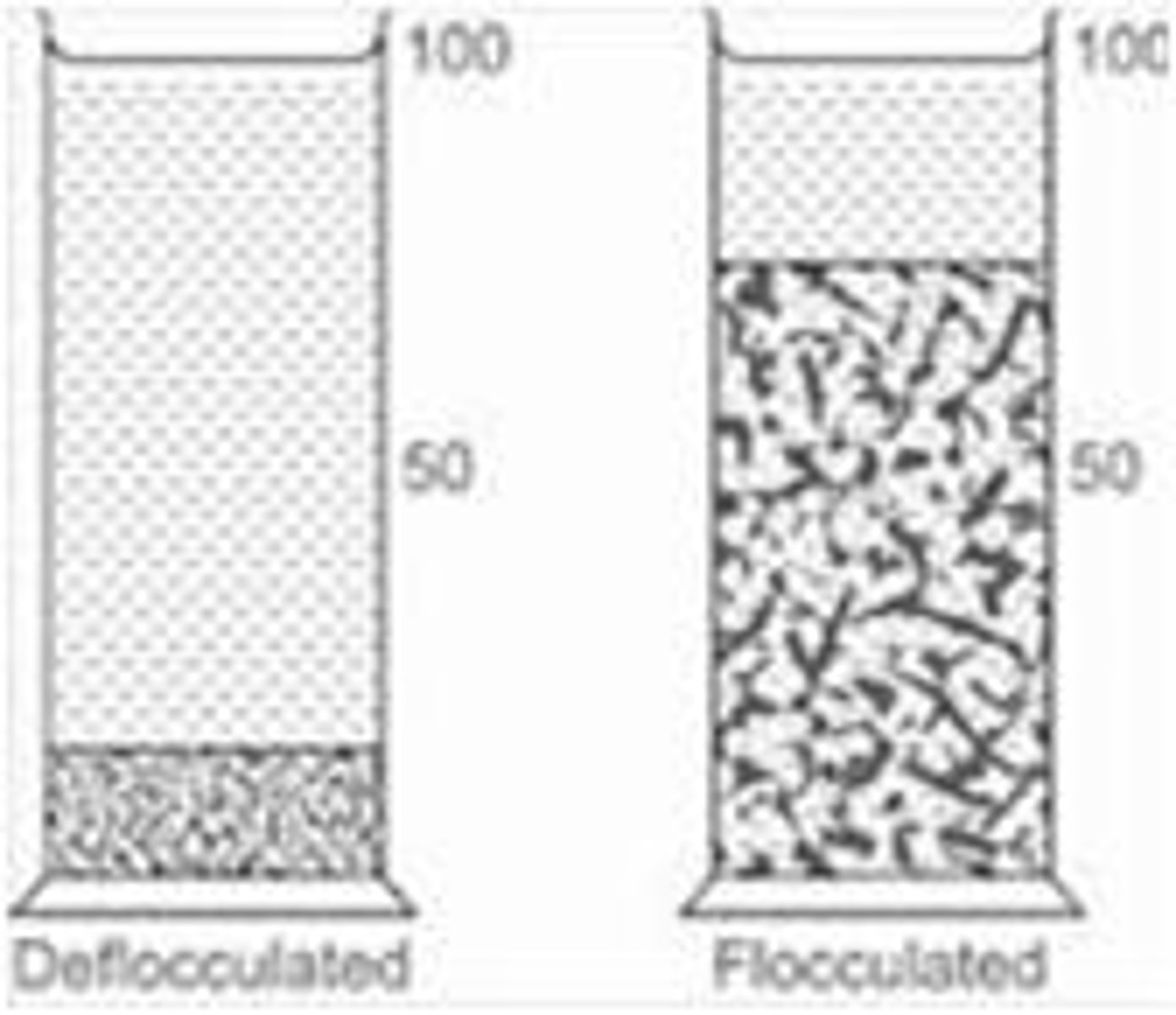
What is the difference between flocculation and coagulation?
Flocculation involves weak attractions that can be overcome by shaking, while coagulation involves strong attractions that make separation nearly impossible.
What are common methods to produce flocculated suspensions?
Using clays, electrolytes, surfactants, and adjusting pH.
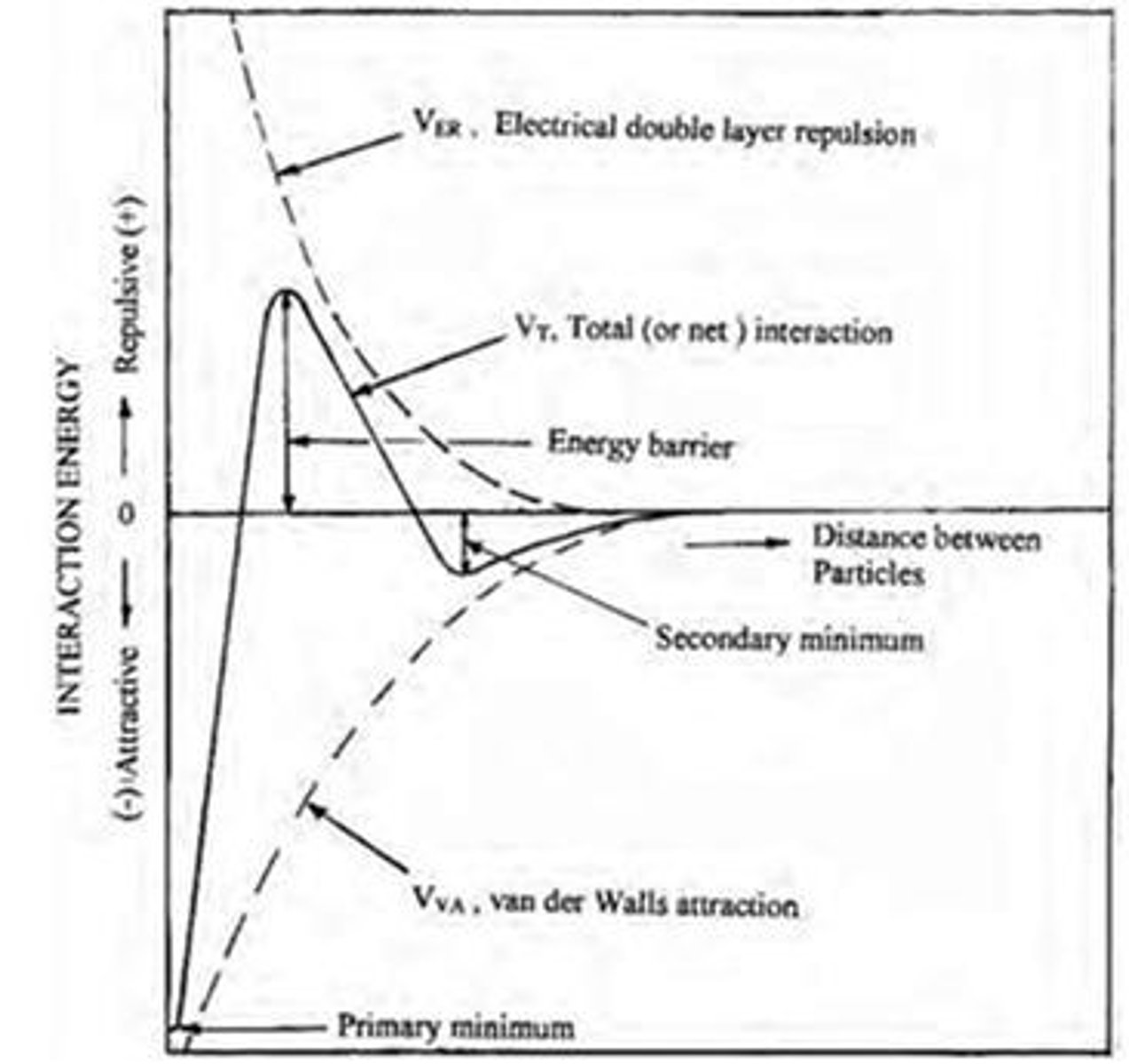
What is the DLVO theory?
A theory describing the forces between charged surfaces in a liquid medium, combining van der Waals attraction and electrostatic repulsion.
What is the role of suspending agents in suspensions?
To slow down the settling process and maintain consistency without interfering with drug availability.
What is the significance of particle shape in suspensions?
Symmetrical shapes are more stable, while asymmetrical shapes can lead to caking.
What is the goal of suspension formulation?
To ensure that the suspension can be re-homogenized by gentle shaking and to prevent caking.
What is the sedimentation volume (F)?
The ratio of the final volume of sediment (Vu) to the original volume of sediment (Vo).
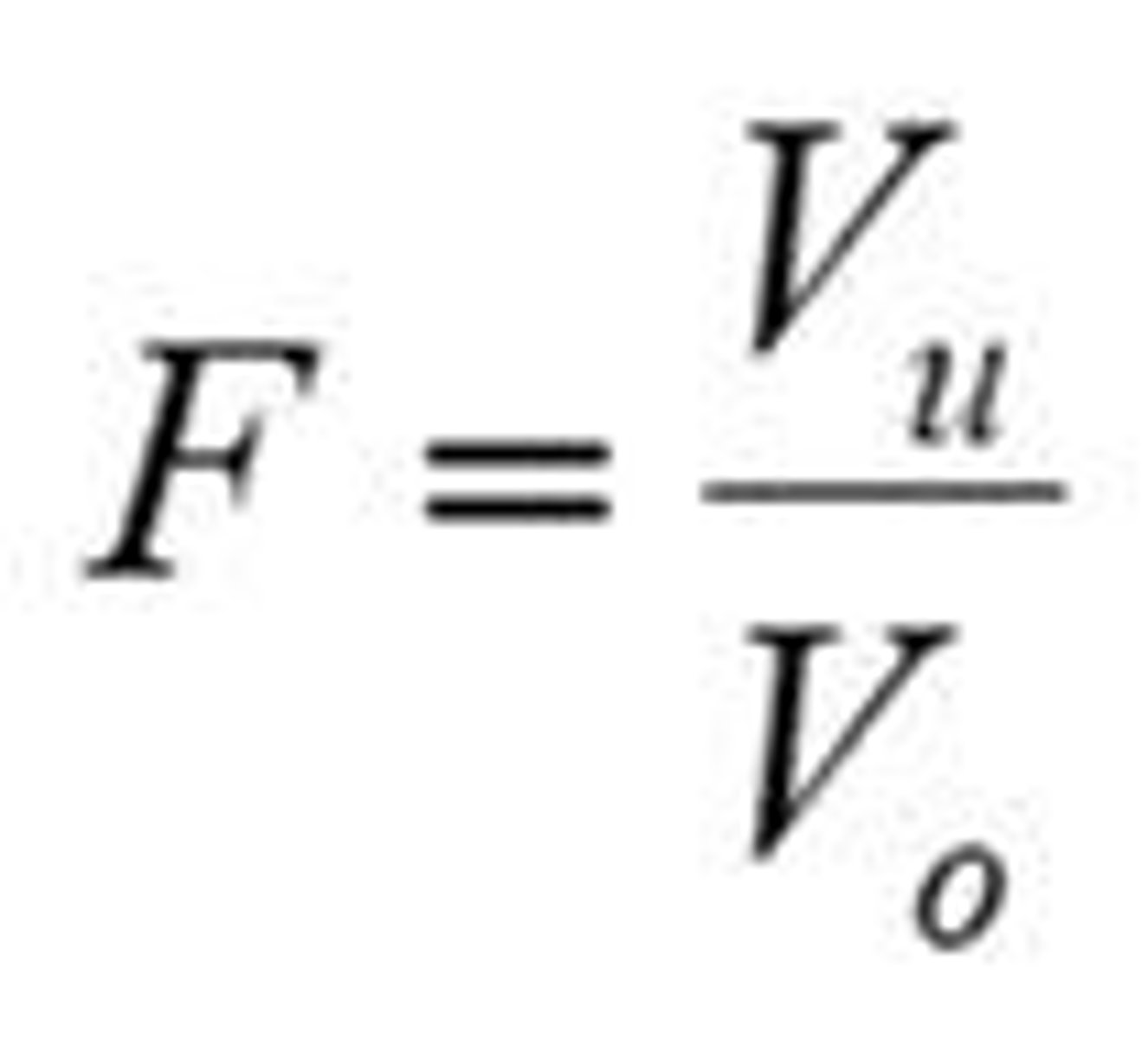
What is the consequence of reducing particle size too much?
Fine particles can settle together and form a cake, which is undesirable.
What is the relationship between particle size and sedimentation rate?
Smaller particles lead to a reduced sedimentation rate and a more uniform rate of settling.
What happens when the density of suspended particles equals that of the suspending medium?
Settling should not occur.
What is the effect of increasing the density of the vehicle in a suspension?
It can slow down the settling of particles.
What is the purpose of controlled flocculation?
To produce suspensions that maintain stability while allowing for easy redispersement.
What is the significance of viscosity in suspension preparation?
It must be balanced to prevent the suspension from being too viscous to agitate or pour.
What are suspending agents?
Substances that thicken the dispersion medium and help suspend the suspensoid, such as Carboxymethylcellulose (CMC), Methylcellulose, Polyvinyl pyrrolidone, Bentonite, and Xanthan gum.
What factors affect the support of the suspensoid by the dispersion medium?
The density of the suspensoid, whether it is flocculated, and the amount of material requiring support.
What is levigation in the context of suspensions?
The process of wetting, separating, and reducing particle size of particles prior to suspension by forming a thin paste in a suitable wetting agent.
What are common wetting agents for aqueous suspensions?
Water, the suspending medium itself, alcohol, glycerin, and propylene glycol.
What are wetting agents for oleaginous suspensions?
Animal, vegetable, or mineral oil, the suspending medium itself, alcohol, glycerin, and propylene glycol.
How do wetting agents function in suspensions?
They displace air in crevices of the particles, disperse the particles, and allow the dispersion medium to penetrate into the powder.
What is the step-by-step protocol for extemporaneous compounding of suspensions?
Empty capsule contents into a mortar or crush tablets, levigate with a wetting agent, add suspending medium slowly, mix to create a paste, dilute to the desired volume, and shake well before use.
What should be avoided in neonatal liquid suspensions?
Preservatives, flavorings, and alcohol due to potential adverse effects.
What is the importance of packaging and storing suspensions?
They should be packaged in wide-mouth containers with adequate airspace and stored in tight containers protected from freezing, excessive heat, and light.
What is an oral suspension?
A sweetened, flavored, liquid preparation containing the active drug and excipients as insoluble materials.
What are examples of oral suspensions?
Antacids (Alumina, magnesia), Anthelmintics (Thibendazole), Antibacterial (Ciprofloxacin), Antidiarrheal (Subsalicylate), Antifungals (Nystatin), and Psychotropic (Paroxetine HCl).
What are dry powders for oral suspension?
Official and commercial preparations of dry powder mixtures or granules intended to be suspended in water or another vehicle prior to oral administration.
What is the process for reconstituting dry powders for oral suspension?
Loosen the powder, add the designated amount of purified water, shake well to mix and create the suspension.
What are topical suspensions?
Liquid preparations that contain solid particles dispersed in a suitable liquid vehicle intended for application to the skin, often referred to as lotions.
What is barium sulfate used for?
As a radiopaque contrast medium for visualizing the GI tract, introduced into medicine around 1910.
What precautions should be taken with barium sulfate?
It is water insoluble and safe in large doses, but should not be confused with soluble forms of barium, which are poisonous.
What is the role of preservatives in suspensions?
To prevent bacterial and mold contamination.
What is the significance of shaking suspensions before use?
To ensure uniform distribution of solid in the vehicle and proper dosage.
What is the effect of pH on the stability of compounded drugs?
pH can affect the stability of drugs in liquid vehicles, with some drugs being more stable in specific pH conditions.
What is the purpose of flavoring agents in suspensions?
To improve the palatability of the suspension, especially for pediatric patients.
What is the typical container for suspensions?
Wide-mouth containers with adequate airspace for easy mixing, shaking, and pouring.
What is the significance of using light-resistant containers for suspensions?
To protect the suspension from light, which can degrade some components.
What is the role of stabilizing agents in dry powders for oral suspension?
To maintain the integrity and effectiveness of the suspension once reconstituted.
What should be monitored in compounded suspensions?
Color changes or consistency changes that may indicate instability.