OTM II MIDTERM
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/139
Earn XP
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
140 Terms
1
New cards
Clinical uses for retinoscopy
objective measurement of refractive error, screening ocular disease, specialty retinoscopy
2
New cards
What are the 2 types of retinoscopy
static retinoscopy, dynamic retinoscopy
3
New cards
What type of test is retinoscopy?
objective method
4
New cards
How does retinoscopy work?
analyzes the optics of the patients eyes to determine the correction that the patient needs for their refractive error
5
New cards
How can the objective retinsocopy measurements of refractive error be used?
starting point for subjective refraction, used to prescribe where subjective refraction can’t be performed
6
New cards
How can retinoscopy be used to screen for ocular disease
keratoconus, media opacities
7
New cards
static retinoscopy: where does the eye focus and what does it determine
eye fixated at distance, **determines the refractive status**
8
New cards
dynamic retinoscopy: where does the eye focus and what does it determine
near with eye fixating, **determines accommodative function**
9
New cards
During retinoscopy what are we observing when we shine the streak of light back and forth?
red reflex within the pupil
10
New cards
What is the red reflex? What does it represent?
light reflected from the ELM, tells examiner where the patient’s far point is
11
New cards
What type of beams can the retinoscope produce? Which sleeve position is for each?
1. **d**ivergent ray - sleeve **d**own
2. convergent ray - sleep up
12
New cards
What does moving the sleeve of the retinoscope move?
the condensing lens up and down
13
New cards
What structures does the streak of light pass through during retinoscopy?
cornea, aqueous humor, crystalline lens, vitreous humor
14
New cards
What is the near triad?
1. accommodation
2. miosis
3. convergence
15
New cards
The ciliary muscle __ making the lens more __, and focal length is __
1. contracts
2. convex
3. shortened
16
New cards
What is the goal of retinoscopy when moving our streak of light?
neutrality
17
New cards
When you find neutrality in retinoscopy, what does that represent?
the patient’s far point is at infinity, the correct refractive error has been found!
18
New cards
What does with motion mean in retinoscopy? What lens would you use?
image is BEHIND retina
19
New cards
What does against motion mean in retinoscopy? What lens would you use?
image in FRONT retina, minus lens
20
New cards
What is the set up for retinoscopy?
* examiner wearing habitual RX
* pt NOT wearing habitual RX
* head must be positioned straight ahead
* pt NOT wearing habitual RX
* head must be positioned straight ahead
21
New cards
What is the target for retinoscopy?
Distance 20/400 letter with Red/Green screen (helps accommodation)
22
New cards
What is the lighting for retinoscopy?
dim room illumination
23
New cards
How do you explain retinoscopy to a patient? What do you instruct them to do?
* I am going to be getting an estimate of your glasses Rx by shining a light into your eyes
* Please look straight ahead at the big “E”, I am going to be shining a light across your eye a number of times. Please look at the “E” the entire time, dont look at me or my light, and please let me know if I ever get in your way
* Please look straight ahead at the big “E”, I am going to be shining a light across your eye a number of times. Please look at the “E” the entire time, dont look at me or my light, and please let me know if I ever get in your way
24
New cards
What 4 meridians do you need to AT LEAST test doing retinoscopy?
90 deg, 135 deg, 180 deg, 45 deg
25
New cards
What does a curved red reflex mean in retinoscopy?
very high astigmatism, corneal opacities, keratoconus
26
New cards
What does scissor reflex mean in retinoscopy?
corneal aberrations: very high cyl, corneal opacities, keratoconus
27
New cards
Is the degree of astigmatism related to a patient’s sphere power?
No
28
New cards
increased power of spherical & cylinder are increasingly associated with what?
ocular pathologies
29
New cards
about how many RXs are spherical?
\~ 1/3
30
New cards
What is WTR astigmatism
axis 180 (plus or minus 30)
31
New cards
What is ATR astigmatism
axis 90 (plus or minus 30)
32
New cards
simple astigmatism
one focal point on the retina, one off the retina
33
New cards
compound astimagtism
both focal points are **off** the retina
34
New cards
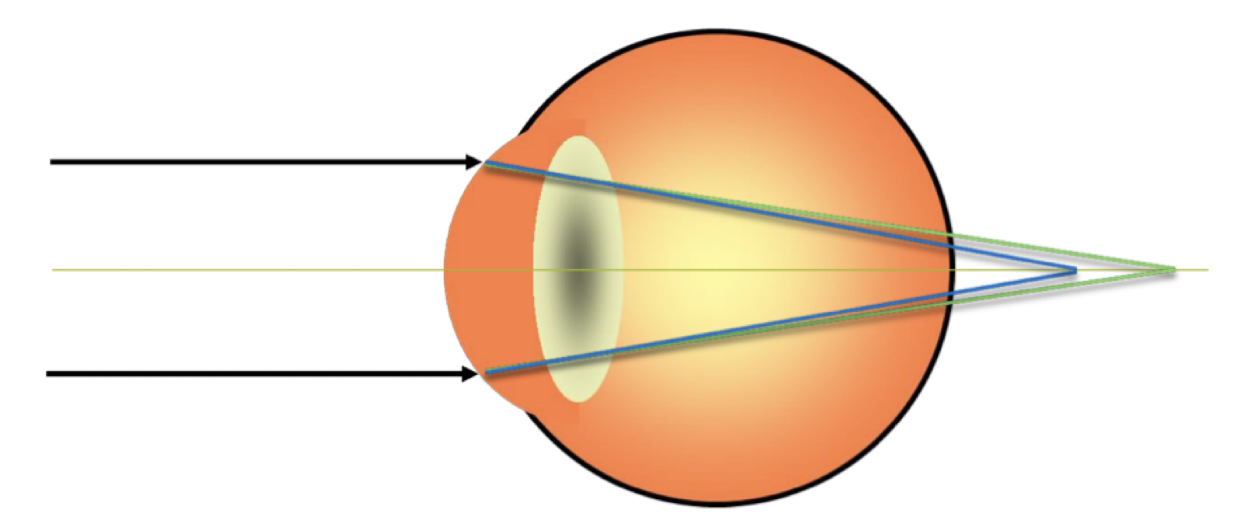
What type of astigmatism is this?
* compound hyperopic astigmatism
* both points are **behind retina**
* both points are **behind retina**
35
New cards
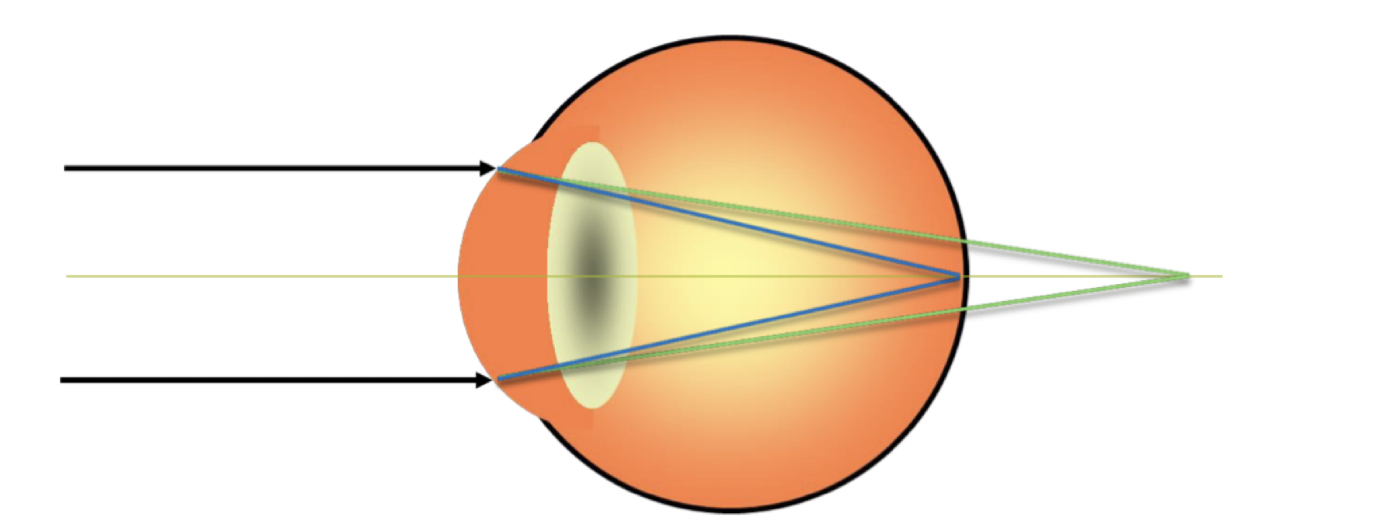
What type of astigmatism is this?
* simple hyperopic astigmatism
* one point is **on** the retina, one point is **behind retina**
* one point is **on** the retina, one point is **behind retina**
36
New cards
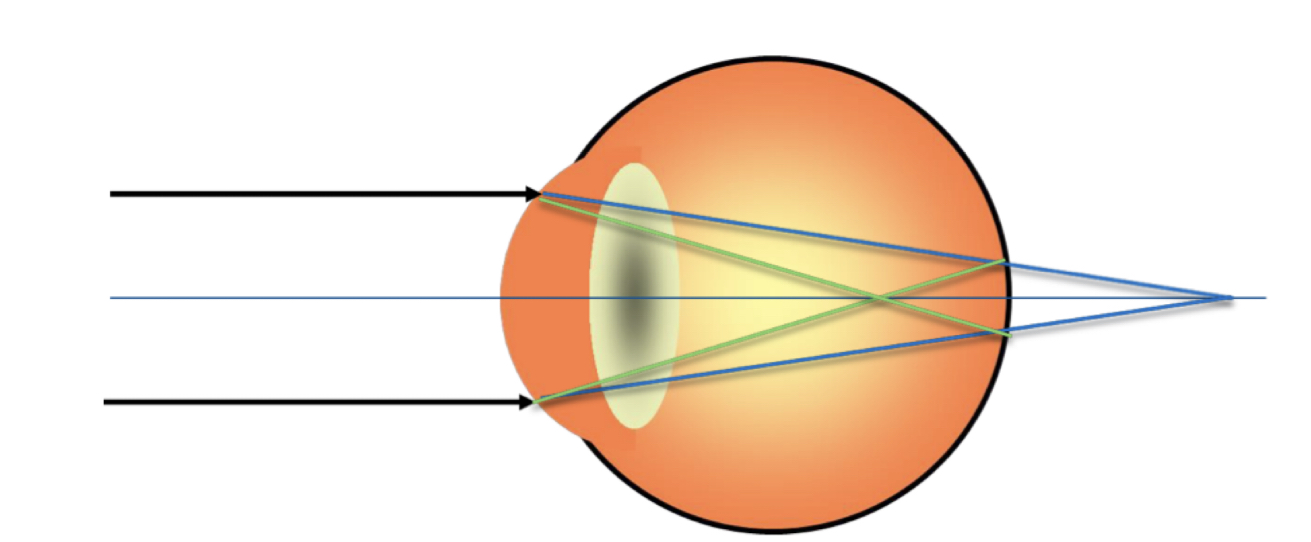
What type of astigmatism is this?
* mixed astigmatism
* focal points straddling the retina
* focal points straddling the retina
37
New cards
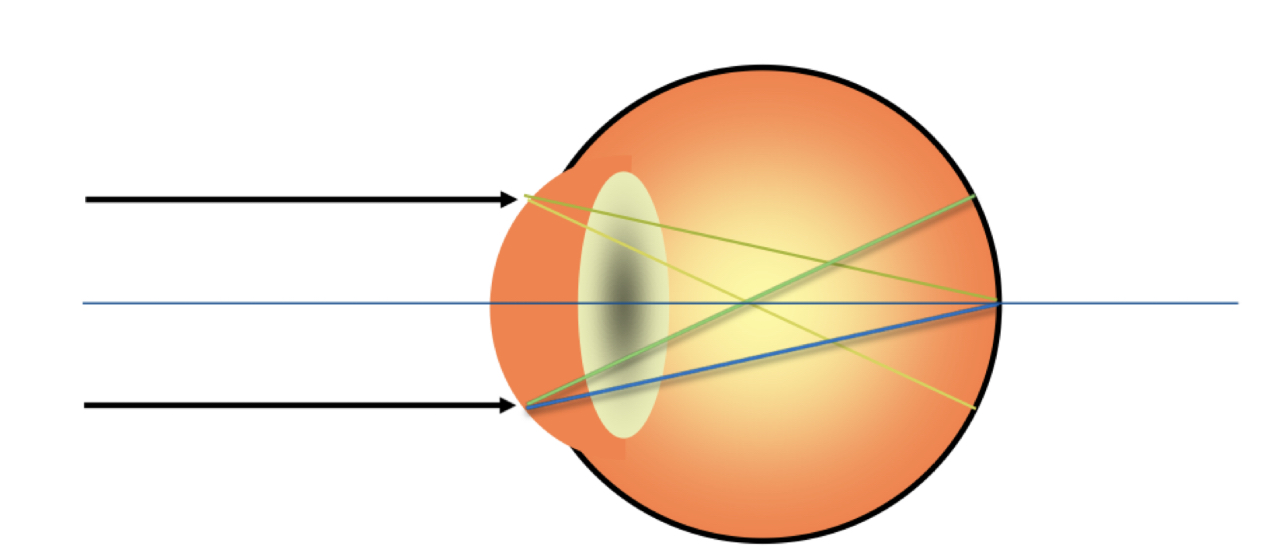
What type of astigmatism is this?
* simple myopic astigmatism
* one **in** **front** of retina, one **on** **retina**
* one **in** **front** of retina, one **on** **retina**
38
New cards
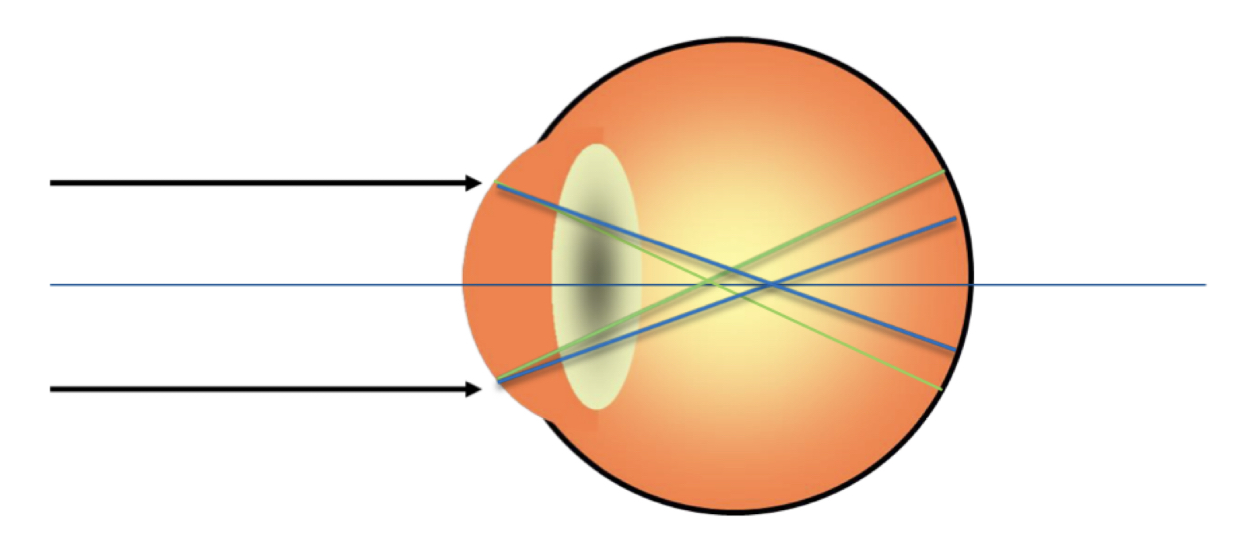
What type of astigmatism is this?
* compound myopic astigmatism
* both focal points are **in front** of retina
* both focal points are **in front** of retina
39
New cards
What type of test is retinoscopy? What type of test is refraction?
* objective
* subjective
* subjective
40
New cards
What is the goal of subjective refraction?
improve patient’s vision to ***best*** ***corrected***
41
New cards
What are some reasons that patient’s will not be able to see 20/20?
* retinal disease
* media opacity
* amblyopia (refractive/strabismic)
* neurological issues
* media opacity
* amblyopia (refractive/strabismic)
* neurological issues
42
New cards
What objective and subjective findings should we take into account when creating the final prescription?
* patient visual complaints
* patient daily visual demands
* habitual rx
* visual acuity measurements
* patient daily visual demands
* habitual rx
* visual acuity measurements
43
New cards
What are some examples of patients who we should not perform manifest refraction?
* very young kids
* non-verbal patients
* intellectual disabilities
* malingering patients
* non-verbal patients
* intellectual disabilities
* malingering patients
44
New cards
What are some myopic symptoms that you will hear before doing a refraction?
* blurred distance
* holding objects closer to see
* needing to squint
* pushes glasses back to the face
* holding objects closer to see
* needing to squint
* pushes glasses back to the face
45
New cards
What are some hyperopic symptoms that you will hear before doing a refraction?
* adults = trouble reading
* younger = intermittent blur, esp when fatigued
* children/teens - may avoid up close work
* pull glasses down nose
* younger = intermittent blur, esp when fatigued
* children/teens - may avoid up close work
* pull glasses down nose
46
New cards
What are some astigmatic symptoms that you will hear before doing a refraction?
* complaints present at both distance and near
* head tilting if oblique axis
* squinting
* ghosting/doubling of images
* higher astigmatism = poorer acuity
* head tilting if oblique axis
* squinting
* ghosting/doubling of images
* higher astigmatism = poorer acuity
47
New cards
Reduced vision at **EITHER** distance or near
refractive error is **LIKELY** the culprit
48
New cards
Reduced vision at **BOTH** distance and near
refractive error **POSSIBLY** the culprit
49
New cards
For simple myopia, how much does each line of decreased VA equal?
around -0.25 DS
50
New cards
For compound myopia, how much does each line of decreased VA equal?
around -0.25 spherical equivalent
51
New cards
Uncorrected ATR astigmatism has __ impact on acuity that WTR astigmatism of the same amount
greater
52
New cards
What type of astigmatism has the highest impact on acuity?
oblique
53
New cards
Low amounts of astigmatism have __ impact on acuity
little
54
New cards
What two things does the estimation of refractive error for astigmats depend on?
1. amount of cyl
2. orientation of cyl
55
New cards
When you push a lens closer to the eye, what happens to the power?
more **minus** power (less plus)
56
New cards
What happens to the power when you move a lens away from the eye?
more **plus** power (less minus)
57
New cards
What is the JND for a patient?
Just noticeable difference, how much difference a patient needs to appreciate which lens it better
58
New cards
How can you estimate the JND for a patient?
divide the snellen denominator by 100
\
ie: 20/200
200/100 = 2.00D, JCC needed +/- 1.00D
\
ie: 20/200
200/100 = 2.00D, JCC needed +/- 1.00D
59
New cards
What is the set up when performing a monocular subjective refraction?
* patient is not wearing habitual RX
* head must be positioned straight ahead
* forehead touching the forehead rest
* both eyes are **OPEN**
* correct PD
* head must be positioned straight ahead
* forehead touching the forehead rest
* both eyes are **OPEN**
* correct PD
60
New cards
What is the target when performing a monocular subjective refraction?
Distance VA chart
61
New cards
What is the lighting for a monocular subjective refraction?
dim room lighting, stand lamp behind patient so they are not blinded
62
New cards
What are the steps of a monocular subjective refraction?
1. gross sphere power determination
2. cylinder axis refinement
3. cylinder power refinement
1. cylinder power search
4. sphere power refinement
63
New cards
What does fogging a patient mean and do?
it means to add plus, which relaxes the patients accommodation
64
New cards
When doing cyl axis refinement, how much do we move the axis when we are chasing the red dot? How much do we move backwards by when we hit reversal of the red dot?
low cyls (
65
New cards
What is the region between the horizontal and vertical focal lines in an astigmatic system?
interval of sturm
66
New cards
When images are in planes other than the horizontal and vertical focal lines, what do they form?
blur ellipses
67
New cards
Circle of least confusion
the closes thing to a point image on the retina for a point object in space
68
New cards
What is the dioptric midpoint between the horizontal and vertical focal lines?
Circle of least confusion
69
New cards
If a WTR eye is fogged sufficiently, where is the interval of sturm located?
forward, both focal lines will be located in front of the retina
70
New cards
Where does the unfog process place the CLC? What happens if we add -0.25D?
1. OLM of retina
2. moves the CLC closer to the macula
71
New cards
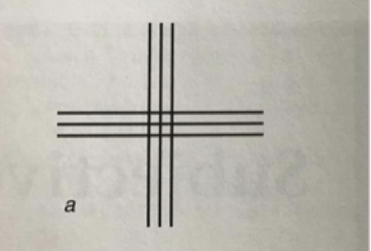
If shown this image, what lines would appear sharper for a WTR patient?
vertical
72
New cards
If shown this image, what lines would appear sharper for an ATR patient?
horizontal
73
New cards
For cylinder power, what happens when the white dot is chosen?
\-0.25D is SUBTRACTED from the cyl in the phoropter
74
New cards
For cylinder power, what happens when the red dot is chosen?
\-0.25D is ADDED to the cyl in the phoropter
75
New cards
Why do we do binocular balance?
* sometimes able to relax accommodation in one eye more than other
* pt may accept more PLUS in the binocular settings compared to monocular
* esp hyperopic patients
* need for this test decreases as patients age and become presbyopic
* pt may accept more PLUS in the binocular settings compared to monocular
* esp hyperopic patients
* need for this test decreases as patients age and become presbyopic
76
New cards
When do we perform binocular balance?
only perform when there is one line or less of BVA difference between the eyes
77
New cards
What techniques are there for performing binocular balance?
* prism dissociation
* alternate occlusion
* humphriss immediate contrast
* alternate occlusion
* humphriss immediate contrast
78
New cards
What is the procedure for prism dissociation?
* have patient close eyes or sit back
* isolate a line at least 2 lines better than BVA
* partially fog patients vision by +0.50DS OU
* put 3BU and 3BD
* explain to pt that they will see 2 lines on top of each other
* make sure patient can read both sets of lines
* isolate a line at least 2 lines better than BVA
* partially fog patients vision by +0.50DS OU
* put 3BU and 3BD
* explain to pt that they will see 2 lines on top of each other
* make sure patient can read both sets of lines
79
New cards
How does the duochrome test work?
It utilizes difference in refraction or different wavelengths of light
\
the rays from the green filter are refracted to a greater extent, the rays from the red filter are refracted less
\
the rays from the green filter are refracted to a greater extent, the rays from the red filter are refracted less
80
New cards
What is the goal of the monocular bichrome test?
To balance the red/green light so they are of equal distance from the retina
81
New cards
What is the procedure of the monocular duochrome test?
* choose isolated line of letters 20/30+
* Fog by +0.50D
* Occlude OS, ask the pt which is clearer (should report RED)
* decrease power by -0.25DS until pt reports equal or GREEN
* Fog by +0.50D
* Occlude OS, ask the pt which is clearer (should report RED)
* decrease power by -0.25DS until pt reports equal or GREEN
82
New cards
How is binocular duochrome different than monocular duochrome?
prism is added to the test
83
New cards
Presbyopia
the slow, normal, naturally occurring age-related, irreversible reduction in maximal accommodation
84
New cards
When is presbyopia first generally reported?
between 40 and 45 years old
85
New cards
When is the peak onset of presbyopia
42-44 years
86
New cards
When MAY the peak onset of presbyopia occur
38-48 years
87
New cards
what are the 2 theories of presbyopia?
1. Donders-duane-fincham
2. Helmholtz-hess-gullstrand
88
New cards
Donders-duane-fincham
* muscle based theory
* ciliary muscle and none to the lens/lens capsule
* ciliary muscle and none to the lens/lens capsule
89
New cards
Helmholtz-Hess-Gullstrand
* lens based theory
* lens capsule/lens and none to the ciliary muscle
* lens capsule/lens and none to the ciliary muscle
90
New cards
3 biological factors causing presbyopia
1. elasticity of the lens capsule decreases
2. elasticity of the lens substance increases
1. lens sizes/volume increases progressively with age
91
New cards
other factors that cause presbyopia
* anterior shift of the equatorial fibers occurs because of increased lens growth
* equatorial zonular fibers decrease in number becoming less dense
* reduction of inward and forward movement of the entire ciliary muscle and ciliary muscle ring
* equatorial zonular fibers decrease in number becoming less dense
* reduction of inward and forward movement of the entire ciliary muscle and ciliary muscle ring
92
New cards
Accommodation
* the process by means of which the optical system of the eye caries its focal length in response to visual stimuli
93
New cards
What are the steps of accommodation physiologically?
1. ciliary muscle contracts
2. pulls the ciliary muscle forward and inward
3. stretches the choroid and posterior zonules
4. the anterior zonular tension decreases and relax
5. lens capsule and lens become more spherical and overall power of the lens increases
94
New cards
Development of accommodation
* amplitude and accuracy of accommodation increases rapidly during the first 3 months of life
* accommodative responses are almost adult-like at 6 months
* amplitude of accommodation starts to decrease during school years
* accommodative responses are almost adult-like at 6 months
* amplitude of accommodation starts to decrease during school years
95
New cards
Amplitude of accommodation
the maximal accommodative level, or closest near focusing response, that can be produced with maximal voluntary effort in the fully corrected eye
96
New cards
Patient be able to accommodate _ times the accommodative demand to function without symptoms
2 times
ie: needs +2.50D to see, so needs +5.00D
ie: needs +2.50D to see, so needs +5.00D
97
New cards
Ways to *determine* __**tentative**__ ADD:
1. age-expected normals
2. plus build up
3. amplitude of accommodation equation
4. fused cross cylinder
98
New cards
Ways to *refine* tentative ADD
1. NRA/NPA
2. Range of clarity
3. individual patient demands
99
New cards
Ways to *finalize* tentative ADD
1. tentative near VA’s with the ADD
2. trial frame
100
New cards
Amplitude of accommodation equation
Tentative ADD = working distance (D) - 1/2 Amplitude (D)
\
ie: tentative ADD = 2.50D - 1/2(3.00D) = +1.00D
\
ie: tentative ADD = 2.50D - 1/2(3.00D) = +1.00D