Edexcel GCSE History - 5. Medicine in the British Sector of Western Front
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Context of The Western Front
oct 1914 - first battle of ypres where BEF stopped germans from advancing
april to may 1915 - second battle of ypres, germans first use of gas
july to nov 1916 - battle of the somme
april to may 1917 battle of arras
nov to dec 1917 - first tank battle at cambrai
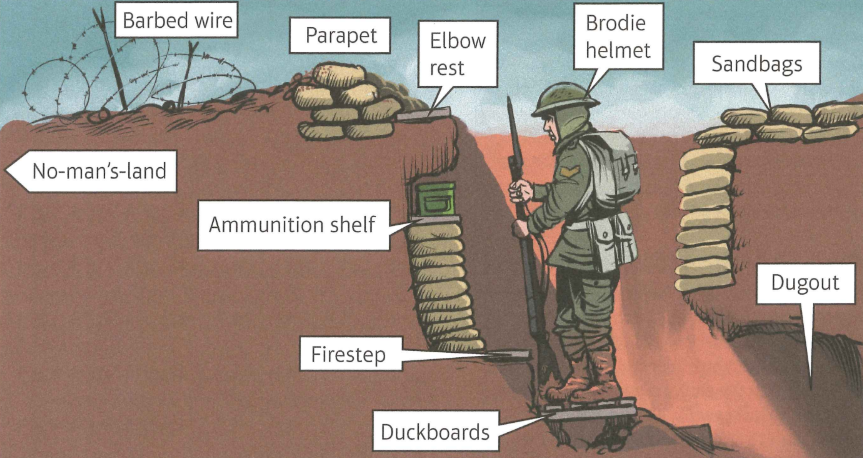
Cross section of a trench
The trench system
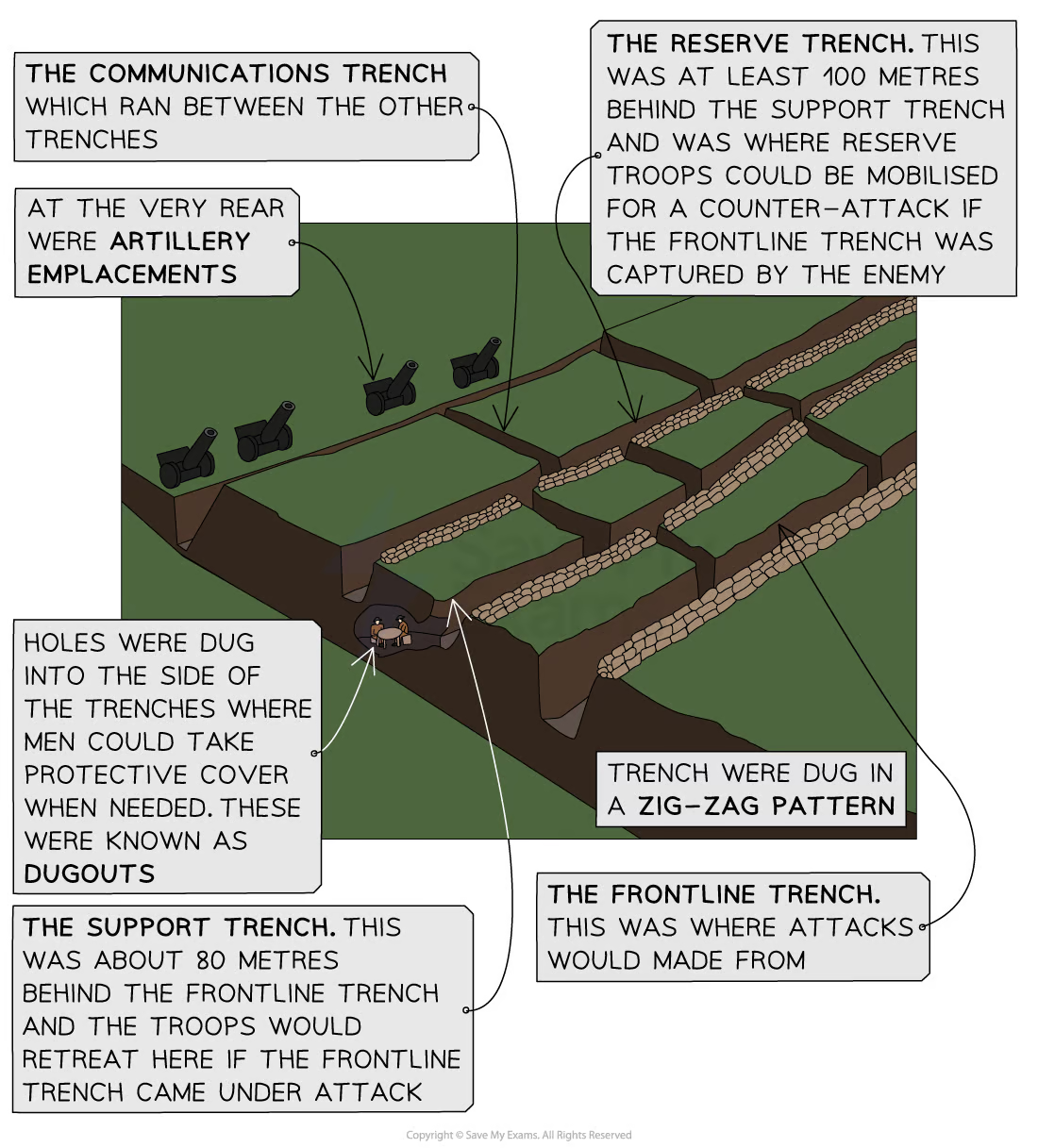
Impact of terrain
collecting the wounded from no mans land was dangerous and might have to be carried out under fire or at night
no mans land and the trenches could be deep in mud making movement difficult and dangerous
transporting the wounded: ambulances
horse drawn ambulances were unable to cope with the casualty numbers and often shook the patients making their injuries worse
motor ambulances made transport easier but were difficult to operate in the mud
transporting the wounded: Trains and Canal Barges
wounded men were sometimes carried by train to base hospitals, however thus was stopped when concerns were raised that they were clogging the rail network of northern france
canal barges were chosen as the alternative method. although they were slow they were comfortable and could transfer patients directly onto ships back to britain
Trench Foot
painful swelling of the feet, caused by standing in cold mud and water and then gangrene
rubbing whale oil into feet alongside keeping feet dry and regularly changing socks were common solutions
if gangrene developed the foot would need to be amputated to prevent it spreading to the leg
Trench Fever
flu-like symptoms - high temperature, headache and aching muscles
major problem because it affected 500k on the western front
by 1918 cause of trench fever discovered as contact with lice
delousing stations were set up[ and afterwards there was a decline in cases
Shellshock
symptoms included tiredness headaches nightmares loss of speech or even mental breakdowns
the condition was not well understood at the time
some sufferers were extradited to britain for treatment, while others were accused of cowardice and were punished or even shot
New Major Weapons: Rifles and Machine Guns
rifles had become more efficient
bolt action rifles allowed soldiers to carry more than one round in their gun and allowed them to shoot more rapidly
bullets were also designed with a more pointed shape
new guns which could fire 500 rpm and were a major part of trench defenses
were mass produced by both sides
New Major Weapons: Artillery and Shrapnel
bigger and more powerful renditions of cannons
could shoot a 900kg shell 12 miles
would be used to bombard to enemy for weeks
caused 50% of casualties
shrapnel was a new type of shell filled with steel or lead balls, which would explode above an enemy to cause maximum casualties
Chlorine Gas
First used by the Germans in 2915 at the second battle of Ypres
led to death by suffocation
Gas masks were given to all soldiers in July 1915, however before soldiers hat to improvise and used cotton pads soaked with urine
Phosgene and Mustard
Phosgene first used at the end of 1915 near Ypres, it was similar to chlorine but killed faster
Mustard was used by the Germans in 1917
an odourless gas which worked within 12 hours and could cause internal and external blisters
Royal Army Medical Corps
RAMC was the medical group assigned to the army
were in charge of transporting injured troops from battlefield to base hospital depending on severity
in 1914 most of the nurses were from the Queen Alexandra Nurses who were well trained
but due to the rising casualties more women were employed as volunteer nurses however they were mostly left to do menial jobs as they were inexperienced
Arras Underground Hospital
Hospital built in tunnels underneath the town of arras
had a capacity of 700, an operating theatre, waiting rooms and a mortuary
had running water and electricity, but was abandoned in 1917 when a shell destroyed the water supply
New medical developments: Aseptic surgery
a septic surgery had become normal by 1900:
surgeons were dressed in gowna and wore gloves
the air ws sterilised by being pumped over the heating system
all medical staff were required to wash their arms faces and hands
New medical developments: X-Rays
X-Rays were developed by William Roentgen in 1895
X-Rays allowed Doctors to make diagnoses easier which greatly helped medical treatment
New medical developments: Blood tranfusions
Blood coagulation was resolved by using a soluble sodium citrate solution to slow clotting
Blood rejection was solved when an Austrian doctor discovered the existence of blood groups
Path to Treatment (1)
Stretcher bearers - recovered the dead and wounded, administered basic treatment, 16 stretcher bearers per battalion
Regimental aid Post - within 200m of the frontline, could not deal with serious injuries, purpose was to give immediate first aid
Dressing Station - A mobile support unit for Doctors, nurses and support staff. Often set up in tents or derelict buildings between a quarter and a whole mile from the frontline
Path to Treatment (2)
Casualty Clearing Stations - first large well equipped facilities, could hold 1000 casualties, contained mobile operating theatres
Base Hospital - Contained specialist centers like gas treatment, located near the coast for easy transport back to Britain, could take 2500 casualties
Treating Wounds and Infection
new techiques included
removing tissue around a wound to stop infected tissue from spreading
using a sterilised salt silution in the wound through a tube - however the solution didnt last long so was only made when needed
However if all else failes amputation was done to stop infection taking over the whole body and killing the patient
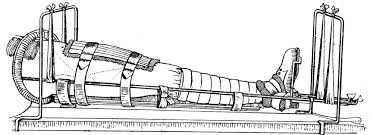
The Thomas Splint
The Thomas splint pulled the leg in an effort to make it more tense. This stopped the break in the bone from moving and stopped internal bleeding
Survivual rate from leg injuries increased to 82% after the thomas aplint
Mobile X-Rays
X-Rays ere very useful for surgeons because it allowed them to pinpoint where shrapnel was and remove minimal flesh
Between 1914 and 1916 three mobile X-Rays were equipped to allow rotation while others were on cooldown
However X-Rays overheated quickly and the patient had to stay still for an uncomfortable amount of time
Blood Transfusion
Blood transfusions were necessary because without them soldiers would often go into shock and die
Lawrence Robertson used an indirect method of transfer where the blood was mioved using a syringe
Geoffrey Keynes designed a portable blood transfusion kit able to be used on the frontline
Blood Storage
1915 - Richard lewison discovers adding sodium citrate can allow indirect transfusions
1915 - Richard Weil discovers blood can be stored wirh sodium citrate for 2 days
1916 - Rous and Turner discover sodium citrate glucose and blood can be stored for up to 4 weeks
Brain Surgery
Doctors realised men with head injuries who were operated on faster had a better survivual chance
Casualties were given blood beforehand to decrease the chance of death by shock
Local anaesthetic was used because General anaesthetic made the brain swell
Plastic Surgery
Mainly used to currect facial injuries
Skin was grafted from the chest onto the face