Glycogen and Glucose Storage
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What is glycogen? What is it held together by?
Main storage molecule for glucose
Glycosidic bonds
Chains found in glycogen
a(1-4) glucose: amylose chains
a(1-6) glucose: dextrans
Reducing end: reducing sugar (free hemiacteal on the 1-6 glucose
Non-reducing ends: amy sugar that is not the reducing sugar (non-reducing sugar)
Glycogen breakdown (steps)
Glycogen + Pi is catalyzed by glycogen phosphorylase to produce glucose-1-phosphate.
This is until the 3 glucose before the non-reducing end, then glucose is released through debranching enzyme. Glycogen phosphorylase continues after debranching.
G1P converted to G6P with enzyme phosphoglucomutase
Why is glycogen breakdown favorable?
entropically favorable because it is producing smaller motile products
Debranching enzyme includes
transferase; the glycogen debranchinng enzyme (of the 3 glucoses before the dextran to the lower row)
glucosidase; the hydrolase activity
produces a free glucose of the top a(1-6) bond.
What’s the different between the phosphoglyceratemutase used in glycolysis and the phosphoglucomutase?
Phosphoglycerate used His as the P group transfer. (pulls off desired P group and adds a new one)
Phosphoglucomutase uses Serine as the P group transfer and this reaction is fully reversible.
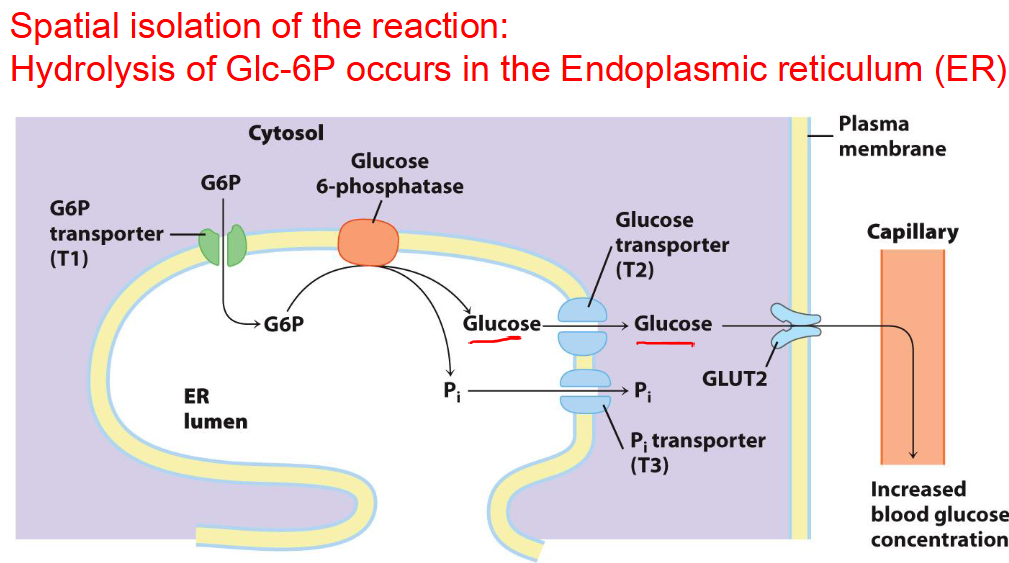
How is Glucose release into the blood stream by G6P phosphatase regulated?
Spatial isolation of the rxn:
Hydrolysis of G6P occurs in the ER
Glycogen synthesis (steps)
G6P converted back to G1P with phosphoglucomutase
G1P reacts with UTP to make UDP-glucose and Pi w/ enzyme UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase (enzyme named for the reverse rxn)
UDP-glucose is converted to glycogen by glycogen synthase, elongating the glycogen chain as more glycogen forms a(1-4) bonds
UDP-glucose is
a sugar nucleotide, also called Leloir glycosyl donor.
Glucose donor
What kind of enzyme is glycogen synthase? What does it do in the last step of glycogen synthesis?
It’s a glycosyltransferase enzyme
Adds the majority of the a (1-4) glucose
UDP is formed as a side product of the rxn
Glycogenin protein (dimer)
is a primer and enzyme that catalyzes the assembly of new chains; adds the first ~8 glucose.
How glycogenin serves as the scaffold for glycogen biosynthesis
Uses hydroxyl group of Tyr on glycogenin to transfer a glucose w/ glucosyltransferase activity
UDP released
Another UDP-glucose comes in and attaches to hydroxyl on 4C of glucose attached to Tyr on glycogenin
Chain extending activity of glycogen synthase takes over (still making UDP as a side product) and repeats this reaction 6 times.
Glycogen branching enzyme
creates new nonreducing ends by introducing a(1-6) branch points (similar to the glycogen debranching enzyme)
Functions as a transglycosidase, transferring segments of glucose chains to form branch point a(1-6)
Coordinated regulating of glycogen synthesis and breakdown involves
Breakdown by glycogen phosphorylase and synthesis by glycogen synthase. Both are reciprocally regulated. (Triggers a cascade)
Glycogen breakdown is activated by
low blood glucose (glucagon) or
a result of fight-or-flight response (epinephrine) by posttranslational modification of glycogen phosphorylase
(think rapid muscle movements = rapid ATP use)
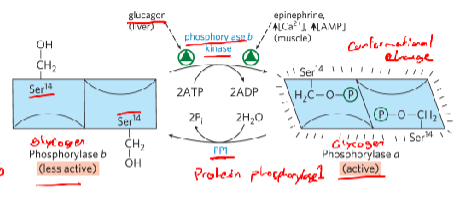
When blood glucose levels are __ (insulin signaling) glycogen phosphorylase a is
high
both allosterically inhibited by glucose and dephosphorylated by PP1 (protein phosphorylase 1)
Phosphorylase b (T state)
The less active form (default), transferring phosphoryl group Ser on each subunit triggers conformation change
Phosphorylated glycogen phosphorylase a (R state)
the enzyme glycogen phosphorylase’s active form (Serine chain with P group inside)
Phosphoprotein phosphatase 1 (PP1) removes P groups from Phosphorylase a, converting to less active state
Glycogen synthase is reciprocally regulated by both __ and __ signaling
insulin and glucagon;
Insulin can inhibit, glucagon can enhance, glycogen synthase b is inactive and phosphorylated, PP1 is enhanced by insulin and G6P but inhibited by glucagon and epi.
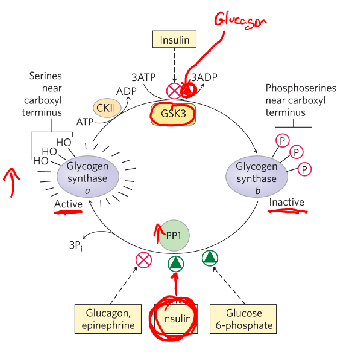
Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3)
adds phosphoryl group to three ser residues on glycogen synthase a, converting to synthase b, inactivates unless G6P or insulin is present; Insulin stimulates glycogen synthesis by activating PP1 and by inactivating GSK3.
High blood glucose leads to (cascade effect down)
Inc insulin, inc insulin-sensitiive protein kinase or synthesis of HKII, PFK-1m pryuvate kinase, inc PP1 decreased glycogen phosphorylase for glycogen breakdown. From synthesis of HKII, Inc glycolysis.
Low blood glucose leads to (cascade)
inc glucagon, inc [cAMP], inc PKA, inc FBPase-2, dec F2,6BP, dec PFK-1, dec glycolysis
dec pyrutvate kinase, dec glycolysis
Inc PKA, inc glycogen synthase
Inc PKA, inc phosphorylase kinase, inc glycogen phosphorylase, inc glycogen breakdown