exercise 24 KTTK: Mannitol salt agar (micro. lab)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Mannitol salt agar (MSA) is
selective and differential medium
selective
due to high concentration of NaCl, or salt, (7.5%) which dehydrates and kills most bacteria
differential
• Organisms able to ferment mannitol produce acidic end products
• Phenol red is pH indicator indicating presence or absence of acidic end products
• Yellow below pH of 6.8
• Red from pH of 7.4 to 8.4
• Pink at or above pH of 8.4
phenol red
is pH indicator indicating presence or absence of acidic end products
yellow
below pH of 6.8
red
from pH of 7.4 to 8.4
pink
at or above pH of 8.4
why phenol red is added to the agar
to indicate a change in pH, usually to detect the production of acid from carbohydrate fermentation by bacteria
Know what kind of organisms thrive on the agar and why
Staphylococci thrive on mannitol salt agar due to high salt tolerance (live on
salty skin)
which organism is able to ferment the mannitol and what happens if it does
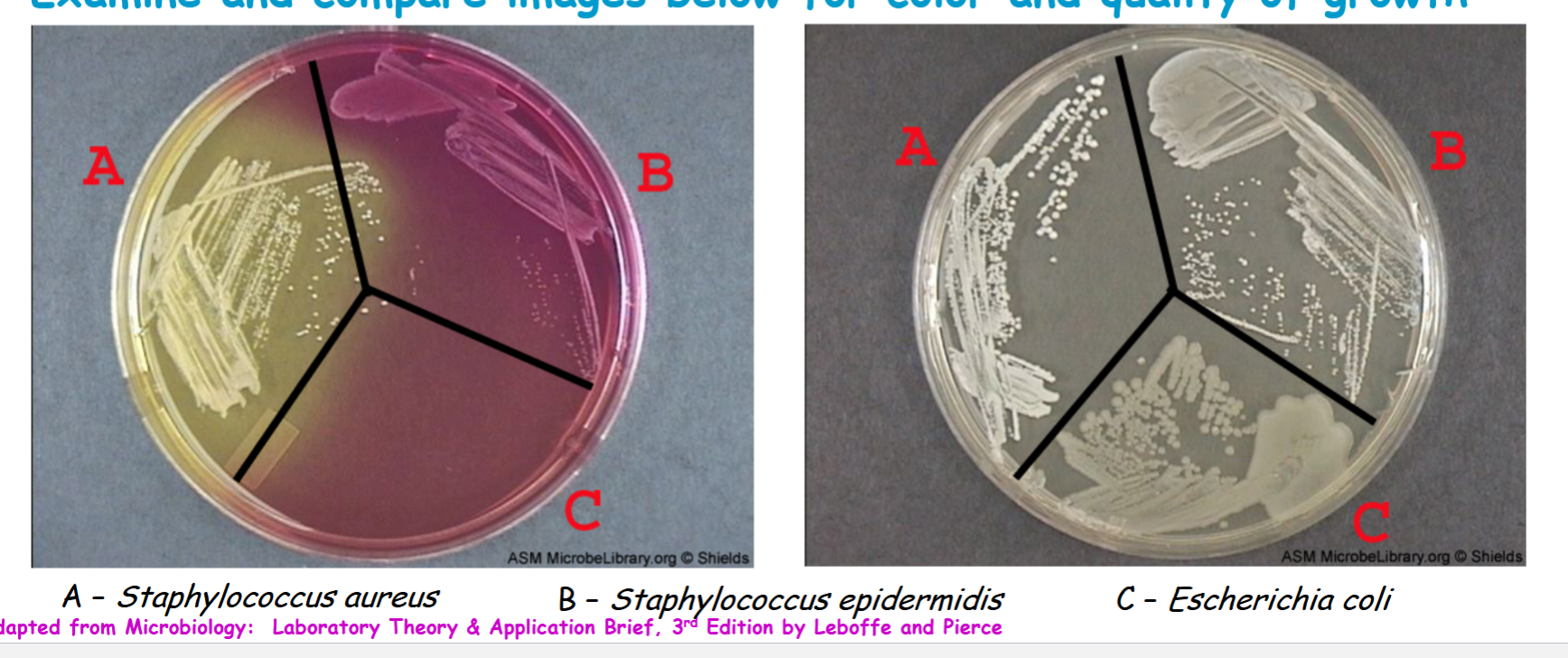
Staphylococcus aureus is able to ferment mannitol to acid end products, so pH is lowered below 6.8 leading to appearance of yellow colonies
Know why (application) mannitol salt agar is used
Mannitol salt agar (MSA) is used for isolation and differentiation of Staphylococcus aureus from other Staphylococcus species
MSA is not used
o determine whether organism can ferment mannitol or not
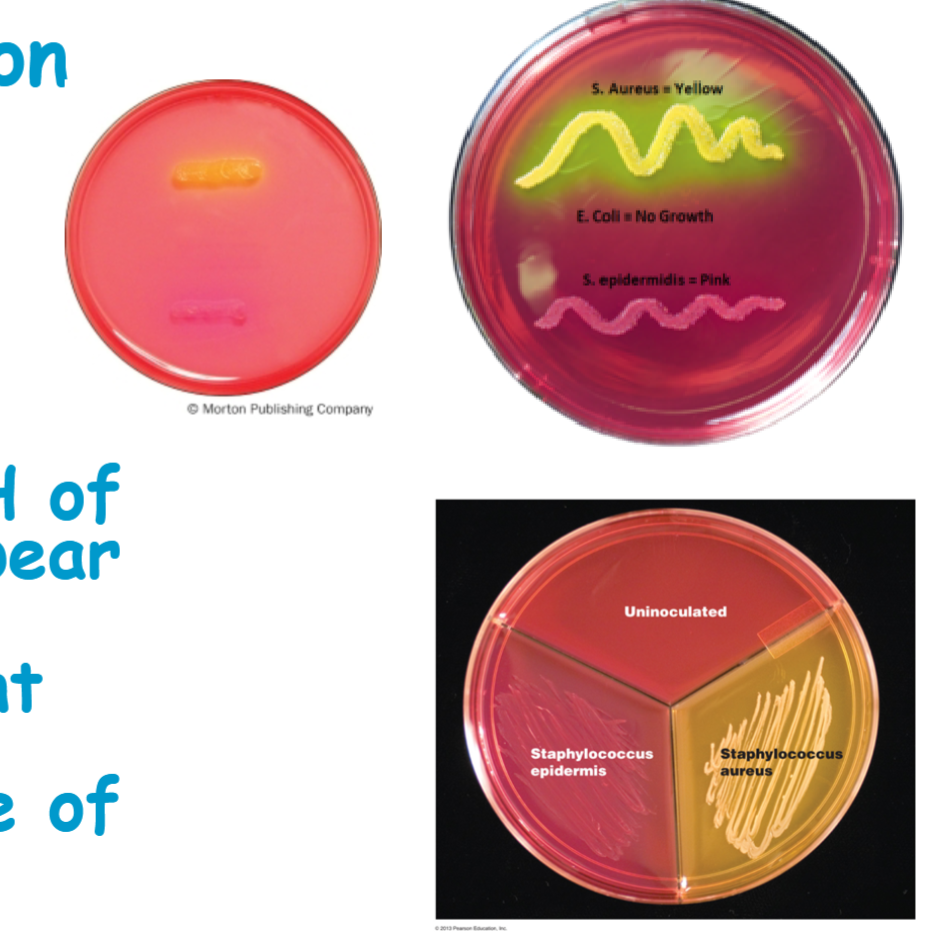
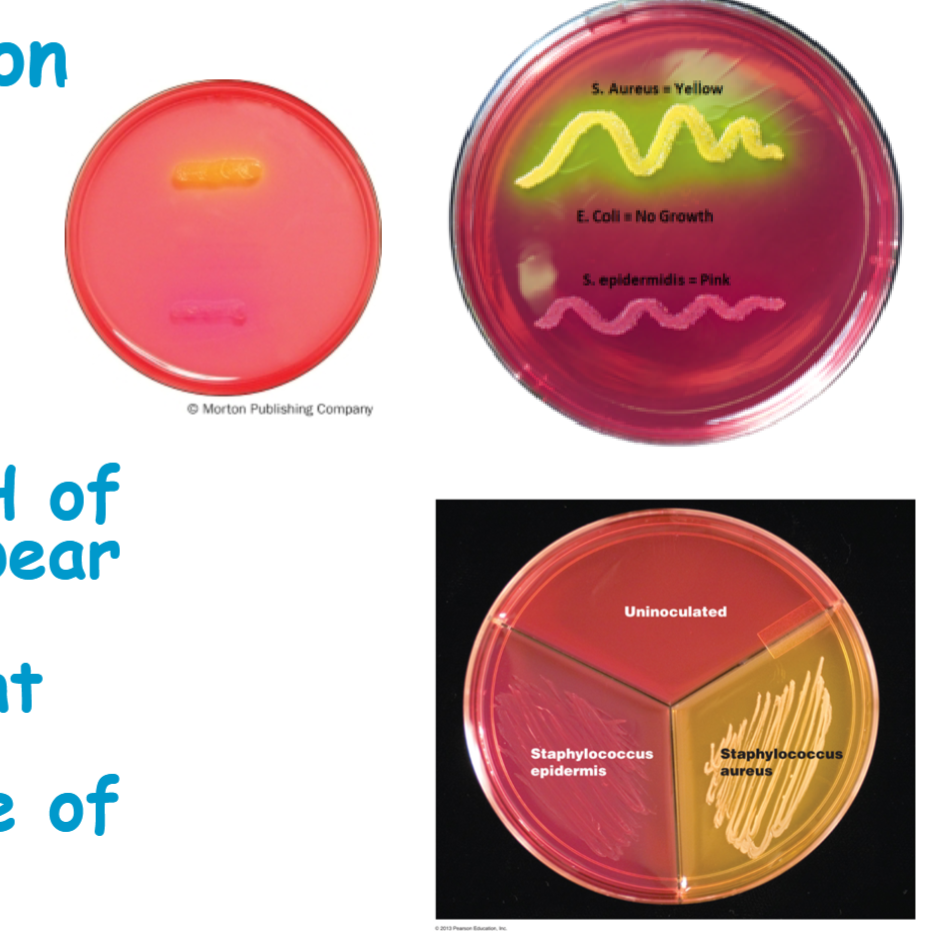
know staphylococcus aureus results
Staphylococcus aureus is able to ferment mannitol to acid end products, so pH is lowered below 6.8 leading to appearance of yellow colonies
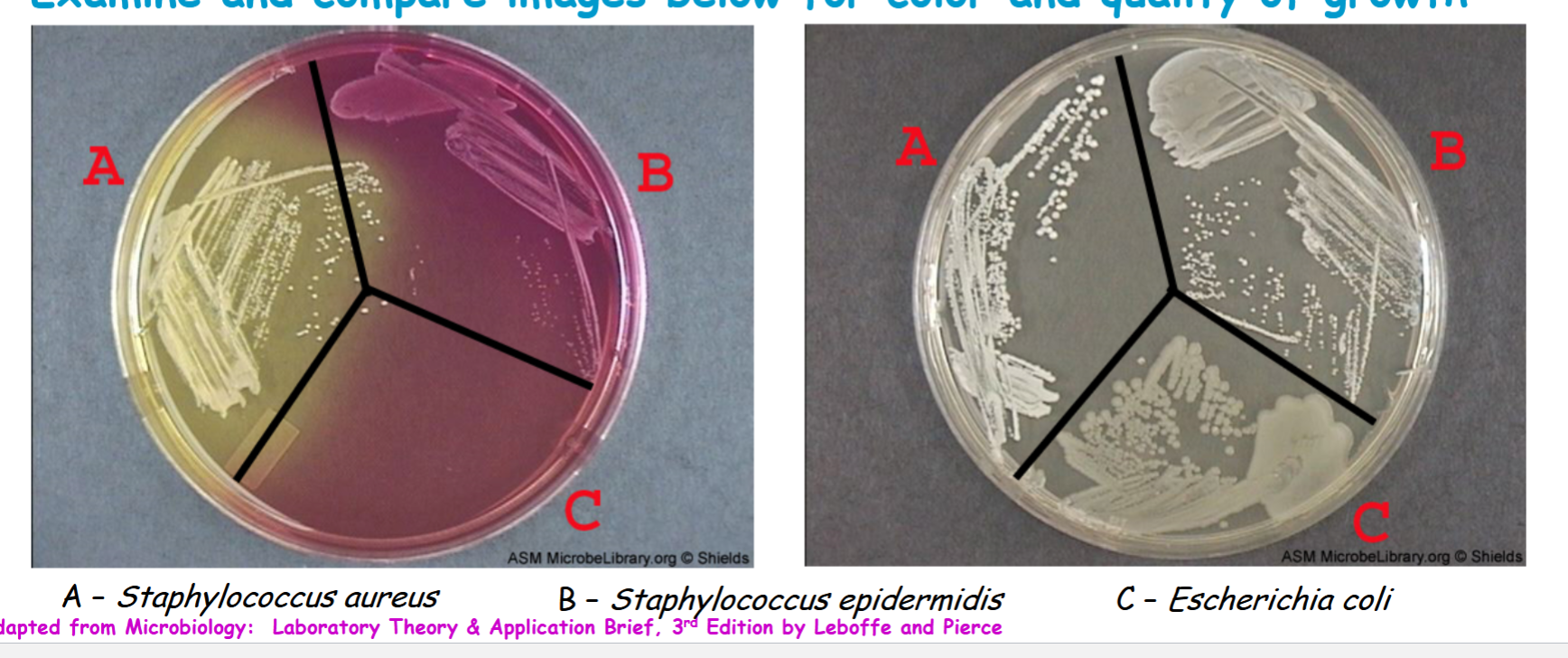
know staphylococcus epidermidis results
don’t ferment mannitol, pH remains above appear red or pink
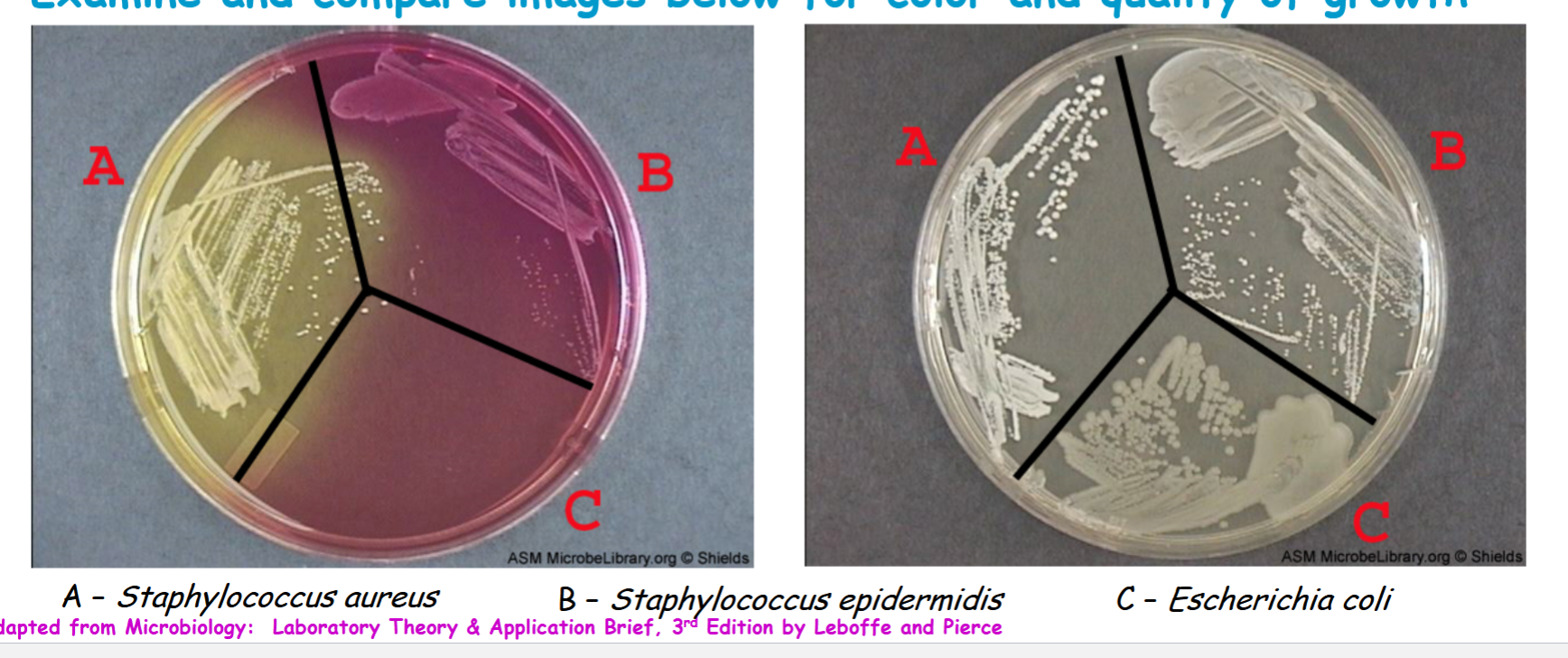
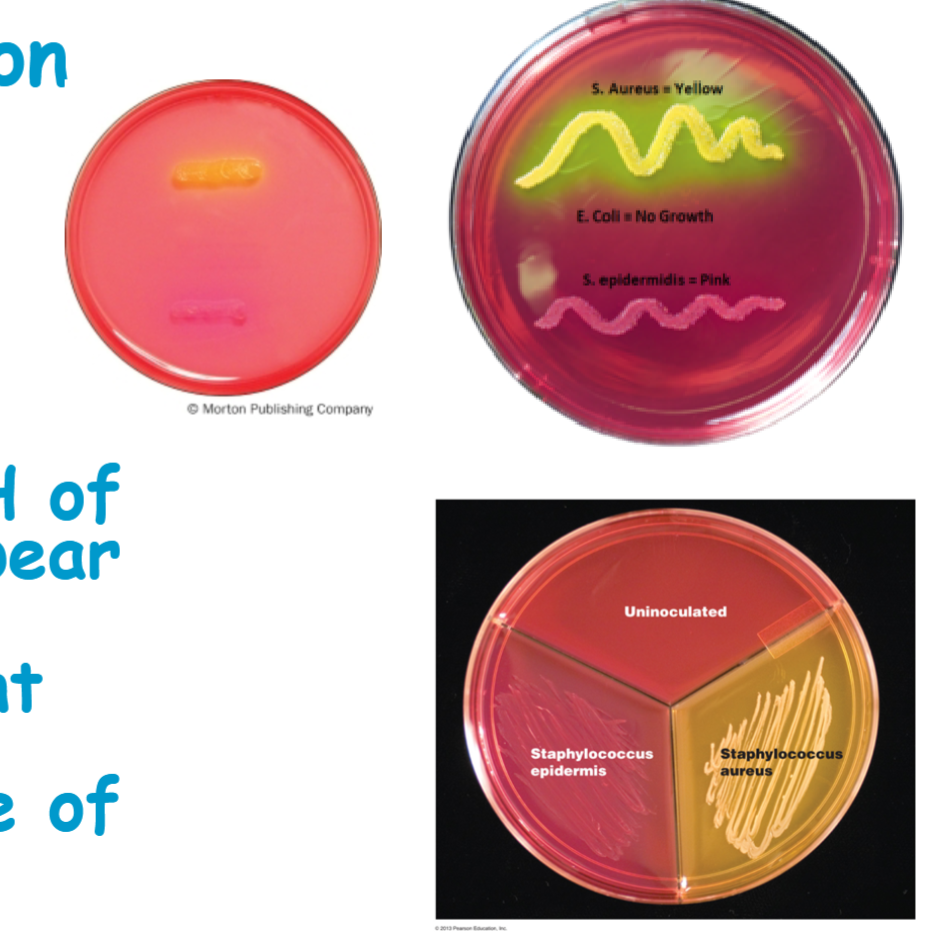
know Escherichia coli results
no growth not fermented the mannitol
mannitol salt agar (MSA) medium recipe
beef extract, peptone, sodium chloride, D-mannitol, phenol red, agar, distilled/deionized water