X-ray emission
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
rad elect
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
X-ray Exposure
Number of x-ray photons, aka radiation quantity or radiation
intensity
X-ray Exposure measured in…
roentgens (R ) (mR ) (Gyₐ) or C/kg
Factors contribute to x-ray quantity:
– mAs (primary)
– kVp
– distance
– filtration
mAs is the Primary control for…
radiographic density. Density is the overall degree of darkness of an x-ray film
Increase mAs…
increase quantity
Double mAs = double exposure
kVp controls the…
penetration power of the beam,
quality of the beam (primarily) but
affect quantity as well(secondary)
Increase kVp…
quality increases
15% rule
15% increased kV will double the density (equivalent to double mAs), kV decrease by 15 % will decrease density by ½
(equivalent to halving mAs)
X-RAY QUALITY
its ability to penetrate through tissue, Penetrability of the X-ray beam will also affect radiographic contrast
Factors of Quality
– kilovoltage potential (kVp)
– filtration
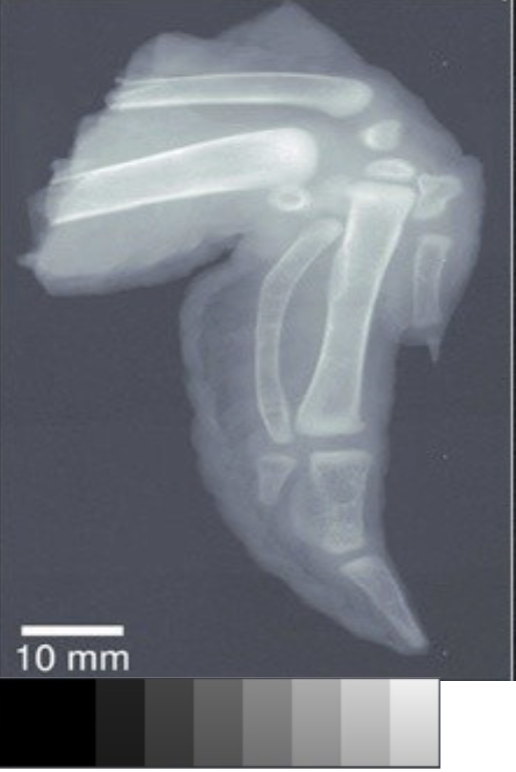
low contrast, wide latitude
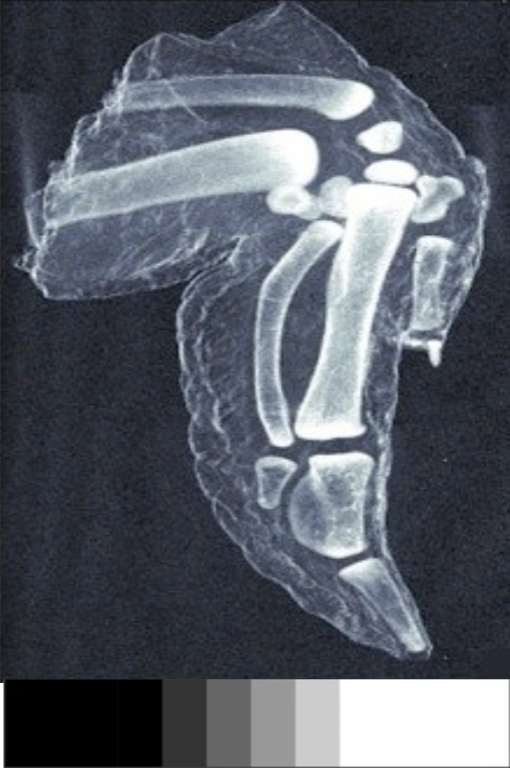
high contrast, narrow latitude
Increase kV…
INCREASE quality, exposure rate, penetration, scatter radiation, DECREASE contrast
Beam Filtration reduces…
patient exposure
Increase filtration…
increase quality
Half Value Layer (HVL)
thickness of absorbing material that will reduce intensity to ½ the original value
HVL increases, quality increases
4 types of filtration
inherent, added, total, compensating
Filtration - inherent
Tube construction
0.5 mm Al equivalent
Filtration - Added
• Al filters at port
• 2.0 mm Al equivalent
Filtration - Total
• Inherent + added
• 2.5 mm Al
Filtration - Compensating
• Compensates for differences in tissue thickness
• Examples: wedge, trough