Grade 10 Biotech Final
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
Amoeba
Unicellular organism that forms a false foot used for eating and moving; eats via phagocytosis, reproduces asexually by binary fission, and lives in freshwater.
Paramecium
Unicellular, freshwater organism that feeds on algae and microorganisms using cilia; has a thick outer membrane called the pellice; contains macronuclei for respiration, protein synthesis, and digestion, and micronuclei for reproduction; reproduces asexually by binary fission.
Euglena
Unicellular organism that can live in fresh or saltwater environments; has characteristics of plants and animals; can be heterotrophic and autotrophic; reproduces asexually by binary fission, and uses flagella for mobility.
Stentor
One of the largest unicellular organisms; reproduces asexually through binary fission; uses cilia around its horn to move and pull food into its mouth; have two nuclei and contractile vacuoles.
Spirostomum
Long tubular protists that have cilia and live in sediment deposits in aquatic environments; move by contracting; reproduce by asexual binary fission and sexual conjunction; used to test water quality.
Contractile Vacuole
A storage vessel for excess liquid in protists, which helps manage water intake due to osmosis.
Sexual Reproduction
Reproduction requiring two gametes, producing genetically variable offspring and influenced by environmental factors.
Asexual Reproduction
Reproduction that produces clones of a single gamete.
Cilia
A short hair from a cell that aids in movement and identification.
Flagella
A slender structure used for movement or directing food, also used for identification.
Binary Fission
The separation of a parent cell into two daughter cells; always asexual.
Volvox
Freshwater organisms that form spherical colonies, reproduce sexually and asexually, and have flagella for movement, chloroplasts, vacuoles, a nucleus, and an eyespot; they are autotrophs.
Cell Membrane
The phospholipid bilayer separating the inside of the cell from the outside.
Nucleus
Information storage organelle; some protists have a macro and micronucleus.
Cytoplasm
Liquid that fills up a cell, consisting of water, salts, and amino acids.
Pseudopod
Temporary arm of a eukaryotic cell.
Stigma
Also known as the eyespot; aids with photoreception.
Chloroplast
An organelle that conducts photosynthesis.
Pellice
Thick membrane that encloses a cell, different than a cell wall.
How are convex lenses used in microscopes?
Bends light to allow focus in one spot
Raw Data
Unprocessed information collected from experiments or observations before analysis.

What is this type of Microscope
Compound Microscope, used for basic microsopy
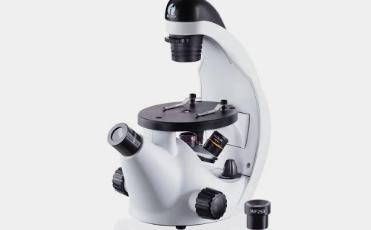
What is this type of Microscope
Inverted Microscope, typically used in tissue culture for observing the cells at the bottom of a flask

What is this type of Microscope
Scanning electron microscope, used to scan the surface of samples with electron to produce a highly detailed image of the surface.
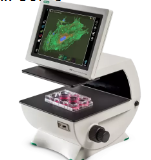
What is this type of microscope
Fluorescent Microscope, uses higher intensity light to typically image small organisms or enhance 3-D features.
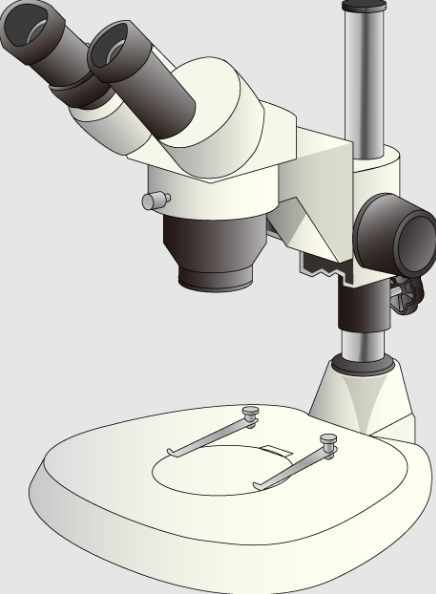
What type of microscope is this?
Stereo Microscope, used for observing solid specimens from above at low magnification.
What are controlled environments used in cell culture
Controlling conditions for precise growth and study during culture.
What is a Condition Feedback Loops
When data about a system is used to modify or reenforce activity in the system
What is aseptic Technique
Working to keep sterility to prevent contamination during laboratory procedures.
What is a Media Study?
An experiment where a culture is placed in different media or nutrient solutions to determine growth conditions
What is a protist?
Not a plant, animal, or fungi, Protists are their own category, they are all eukaryotes (membrane bound organelles.)
Where are protists typically found
aquatic environments, often found in symbiotic relationships
What is the problem of protists
Protists are a bunch of random assortment of organisms
How are protists classified
How they eat
What is an Animal Like Protist?
Heterotrophs that eat other organisms like bacteria or algae
What are plant like protists?
Autotrophs that make their own energy through photosynthesis
What is a fungi like protists
These protists absorb energy though other organisms
Describe an example of animal like protists
Unicellular organism called Amoeba that forms a false foot that is used to eat and move. Eats through phagocytosis (uses cell membrane to engulf another large cell) reproduces Asexually with binary fission and lives in freshwater.
What is Yeast and how does it work
Saccharomyces Cerevisiae (S. Cerevisiae) is a eukaryotic organisms that is classified as a fungi. It converts carbohydrates to CO2 and alcohols through fermentation
How can Yeast be used as a Technology?
Can be used as biofuel due to high cellulose content, Source of biocatalysts for chemical pharmaceuticals.
What company uses Yeast for research
Novo Nordisk uses yeast to manufacture chemicals and proteins
What is Yeast Media Called
Yeast Peptone Dextrose
How do you grow yeast culture
It can grow in broth or plates, incubation should be at 27-30C cells can be counted using a hemocytometer