International Trade Chapter 6 Vocabulary
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
48 Terms
Differentiated goods
Products that are distinct from each other, not substitutes
Imperfect competiton
A form of competition in which firms can influence the price they charge
Monopolistic competition
Imperfect competition with two key features
Goods produced by different firms are differentiated
Because no perf competition, they do not have to accept the market price
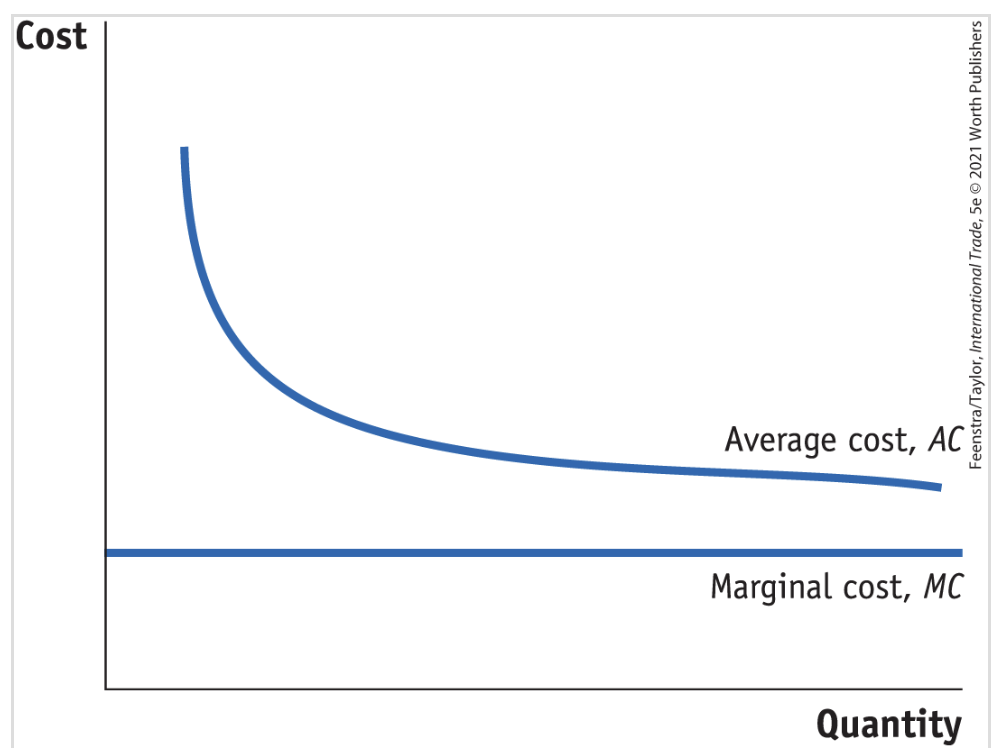
Increasing returns to scale
Increasing returns to scale
The average costs for a firm fall as more output is produced
Free-trade agreements
An agreement of free trade between a group of countries
CUSFTA 1989
Canada - US free trade agreement
NAFTA 1994
North American free trade agreement
USMCA 2018
US - Mexico - Canada agreement, a renegotiation of NAFTA
Intra-industry trade
Imports and exports in the same industry
What model explains intra-industry trade
Monopolistic competition
Gravity equation
Implication that large countries (as measured by their GDP) trade the most
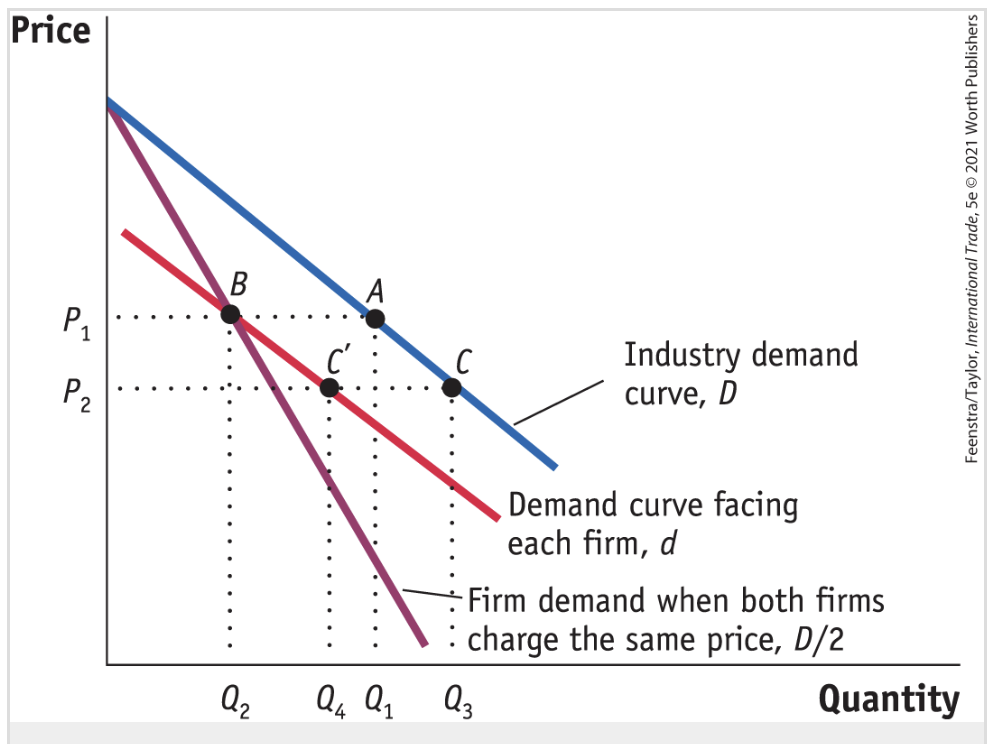
Duopoly
2 firms are selling a product
Marginal revenue
The extra revenue (sales) earned by a firm from selling one more unit of output
Marginal cost (MC)
The extra cost of production associated with one more unit of output
Monopoly equilibrium
MC = MR
Duopoly
Market structure in which 2 firms are selling a product
If both firms charged the price P1, then each firm’s demand is at a point on the curve
D/2
Duopoly graph
Trade under monopolistic competition assumptions
Each firm produces a good that is similar to but differentiated from the goods that other firms in the industry produce
There are many firms in the industry
Firms produce using a technology with increasing returns to scale
Because firms can enter and exit the industry freely, monopoly profits are 0 in the long run
Increasing returns to scale for technology
The average costs of production fall as the quantity produced increases
Relationship between AC and MC. If MC is lower than AC, then AC must be
Decreasing to meet MC
Monopoly profit occurs when
The price charged is above average cost
In short-run equilibrium, each firm maximizes profits by producing
Qo, the quantity at which marginal revenue equals marginal cost
In a monopolistically competitive market, new firms contintue to enter the industry as long as
They can earn monopoly profits
When new firms enter and there are more product varieties available to consumers, the do curves faced by each firm becomes more
elastic or flatter; because each product is similar to the others, the number of close substitutes increases, and consumers become more price sensitive
When is a monopolistic competition industry at long-run equilibrium
When monopoly profit is zero
Under the Ricardian model, countries with identical technology would or would not trade. Why?
Would not trade because their relative prices would be equal
Under monopolistic competition, countries with identical technology would or would not trade. Why?
They would because two identical countries will still engage in trade because increasing returns to scale
Ricardian model
What is the demand during free trade?
D / (N^A), with N^A representing the number of firms in the absence of trade
Free trade causes the number of firm and profuct varieties to
Double
CUSFTA
Free trade agreement between Canada and USA in 1994
CUSFTA effects in Canada
Short-term loss of jobs (100k jobs) but long-run gianed more jobs that offset the loss
Productivity rose 18% over 8 years
Manufacturing productivity rose 6%
Fall in proces for consumers
NAFTA
Free trade agreement between Canada, Mexico, and USA
NAFTA effects in Mexico
Mexican tariffs on US goods declined from 14% to 1% and US lowered tariffs on Mexican goods
Because Mexico went through a financial crisis right after NAFTA signing, can only see benefits after a few years
Took a while for some things to actually take effect. EX. Mexican trucks not allowed to deliver goods in US until 2011
Productivity effects of NAFTA in Mexico (maquiladora plants vs non)
For maquiladora plants, productivity rose 45% from 1994 to 2003
For non-maquiladora plants, productivity rose 25%
Mexico financial crisis
Large devaluation of the peso
1994 Mexico switched to a flexible exchange rate policy, leading to the devaluation
Workers had to pay higher prices for imported goods, a decline in real wages for workers
Higher-income workers fared better than low-skilled workers in the maquiladora sector and better than workers in the rest of mexico
What is the maquiladora sector?
Factories in Mexico owned my a foreign corporation that assemble products and export them back to the US and other countries
Trade adjustment assistance (TAA)
A program that offers assistance to workers in manufacturing who lose their jobs because of import competition. Gives an idea of unemployment caused by NAFTA
Displacement of workers in USA after NAFTA
1999-2001 4 million workers were displaced, about 1/3 in manufacturing
2015-2017 laid off workers lost 93k a year for $5.4 billion total lost wages
Rules of origin specifies
The amount of each product that must be made in North America in order for the product to be shipped tariff-free between NAFTA countries
Changes from USMCA to NAFTA
Total American content of an automobile must be 75%, increasing from 62.5%
30% of an automobiles content must be produced in N American plants where labor earns at least 16$ an hour
Mexico passed new labor laws making it easier to form unions. Law gave workers the rights to vote on unions and on labor contracts under secret ballots
US produced have access to ~3.6% of Canada’s dairy market
USMCA limits the liability the internet platforms such as Facebook and Twitter face in Mexico or Canada for 3rd part content that is hosted on their sites
The provisioins of the agreement will remain in effect for 16 years, unless the three countries agree after 6 years to extend that time
Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP)
Agreement among 12 countries in 2016, including the US, that was negotiated under Obama. Would have allowed US access to 3.25% of the Canadian dairy market. Trump pulled out shortly after being elected
The index of intra-industry trade tells us
What proportion of trade in each product involved both imports and exports, with 100% indicating an equal amount and 0% indicating the good is either imported or exported not both
Formula for index of intra-industry trade
Minimum of imports and exports (you choose the smallest of the two)
½ (imports + exports)
Gravity equation
Countries with larger GDPs, or that are closer to each other, have more trade between them
Gravity equation
B x [(GDP1 x GDP2)/ dist^n]