seds and soil final
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
What is a depositional environment?
an environment where sediments are deposited by distinct processes
What is a facies?
a set of physical features formed my similar sedimentoligical, biogenic, and chemical processes
What is the walthers law?
every modern depositional environment that occurs laterally has a corresponding facies occurring vertically
What is an iconoclastic facies?
fossils that form a assemblage characteristics of a particular environment
what are the important differences between meandering and braided river environments?
meandering has a single channel with high bank stability while braided has multiple channels with low bank stability
What is lateral accretion?
process which builds up point bars
Sedimentoligical characteristics of lateral accretion?
trough to ripple cross strata
What is vertical accretion?
Process which builds up levees and flood plain deposits
What are common sedimentoligical features of vertical accretion?
lamination and silt and sand layers
For what type of river would you expect to find well developed lateral and vertical accretion deposits forming?
meandering
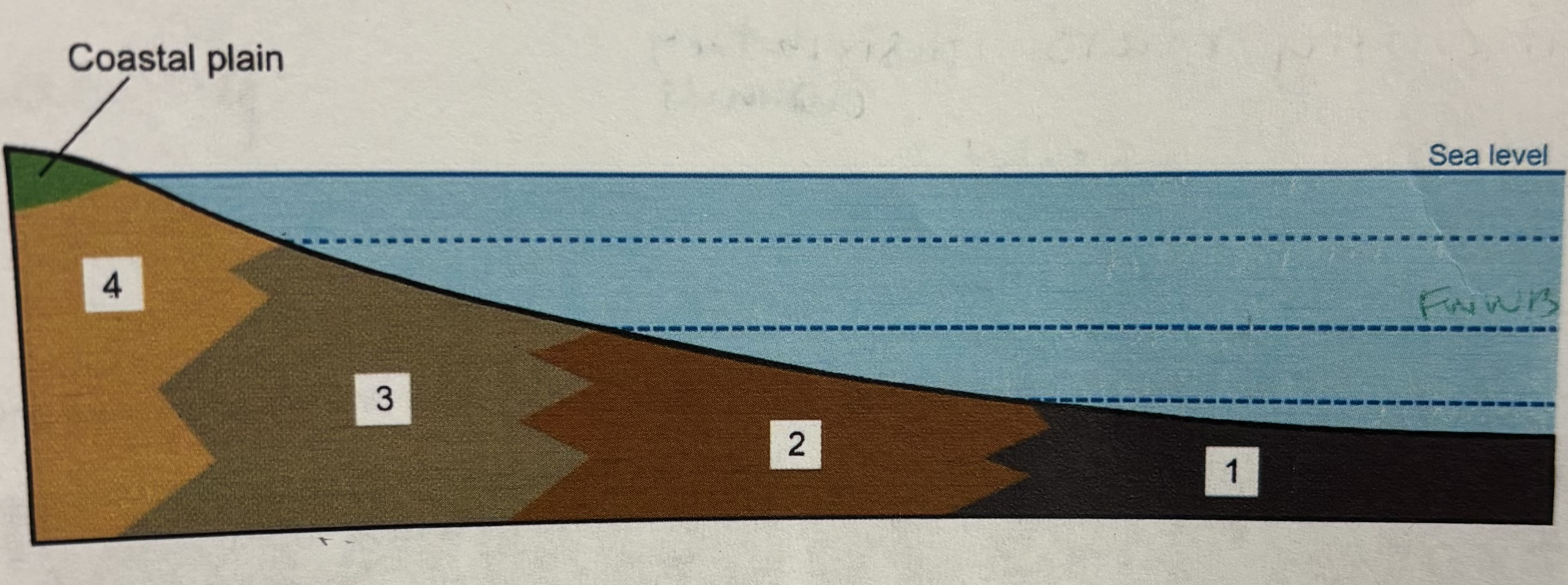
1- offshore 2- offshore transition 3-shore face 4- foreshore
What role does long shore drift play in the distribution of sediment along a coast line?
It distributes sediment parallel to the coast forming splits and barriers
List four main components of sedimentary rocks
framework grains, matrix, cement, pores
What components are present at the time of deposition?
framework grains, matrix, pores
What is a detail grain?
the product of weathering that forms outside the basin.
What are the properties you look for to determine the maturity?
roundness and sphericity, sorting, % of matrix, % of quartz
List four types of carbonate grains?
pisoids, ooids, peloids, ichnofacies
What are the components of shear stress?
height from surface, viscosity, velocity
How does decreasing flow depth affect shear stress?
it increases it
How does increasing flow velocity affect shear stress?
it increases it
List three transportation processes in current flow?
rolling, saltation, suspension
What is wave base?
The depth at which surface energy of a wave dies out
Orbital and oscillatory influences on movement of sediment?
orbital occurs in deep water causing dunes and ripples while oscillating occurs in shallow waters causing vortex ripples
What type of sedimentary structures is load structures?
deformational
What are two major types of erosional sedimentary structures?
scour and tool marks
What is the diffrence between clastic and non clastic grains?
Clastic form outside the basin from weathering and erosion
No clastic form inside the basin from biogenic sources
What is cement and how does it form?
Cement is formed by diagenesis which is when a rock is buried and pressure and heat is added to crystallize the matrix