Chemistry - C2 (Elements, compounds, and mixtures) *GCSE OCR*
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
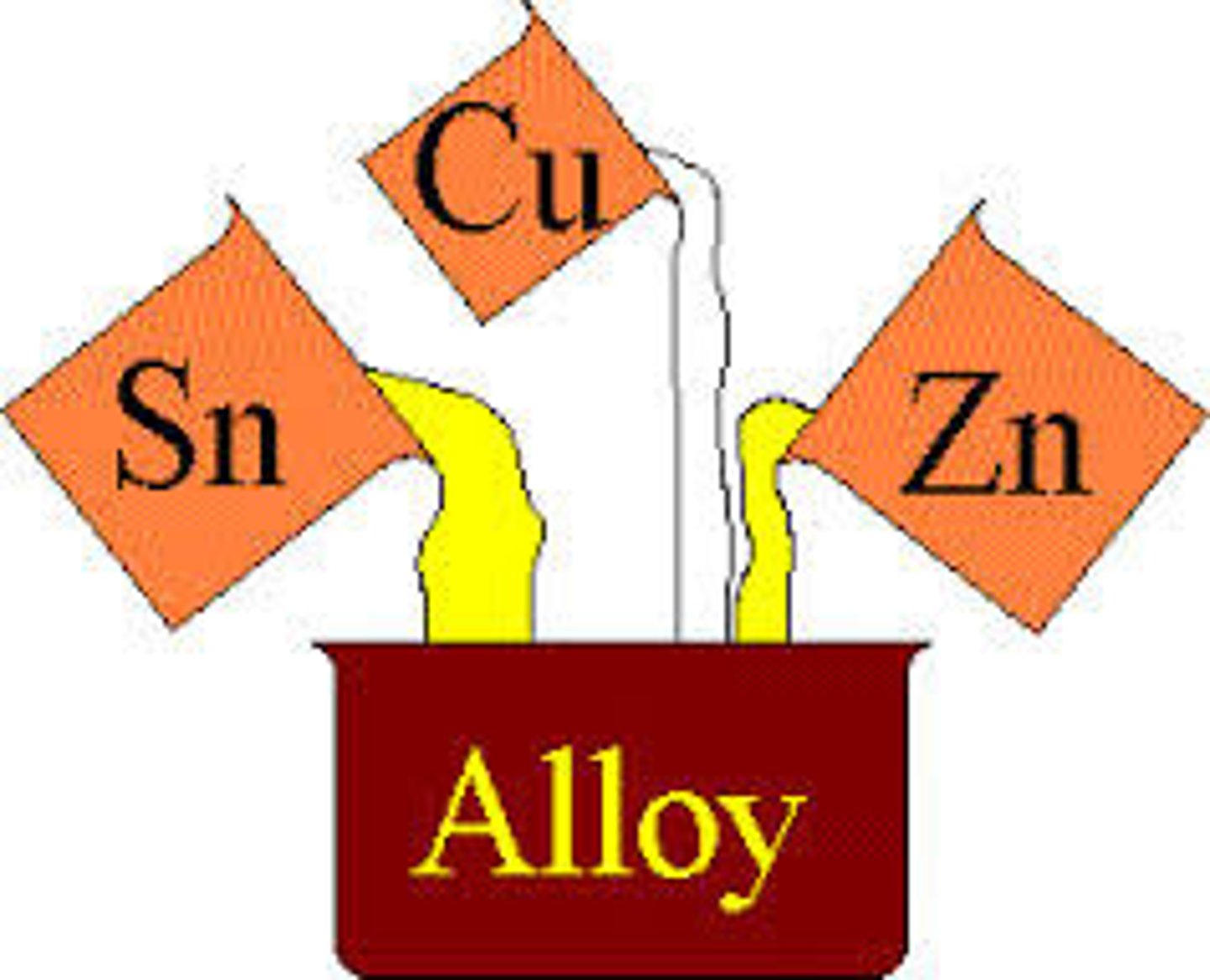
Alloys
- A metal compound made by combining two or more metals together
- This process is carried out to give greater strength or resistance to corrosion
Chromatography
- A process used to separate substances in a mixture
- Separation of the substance depends on distribution between a mobile phase and a stationary phase
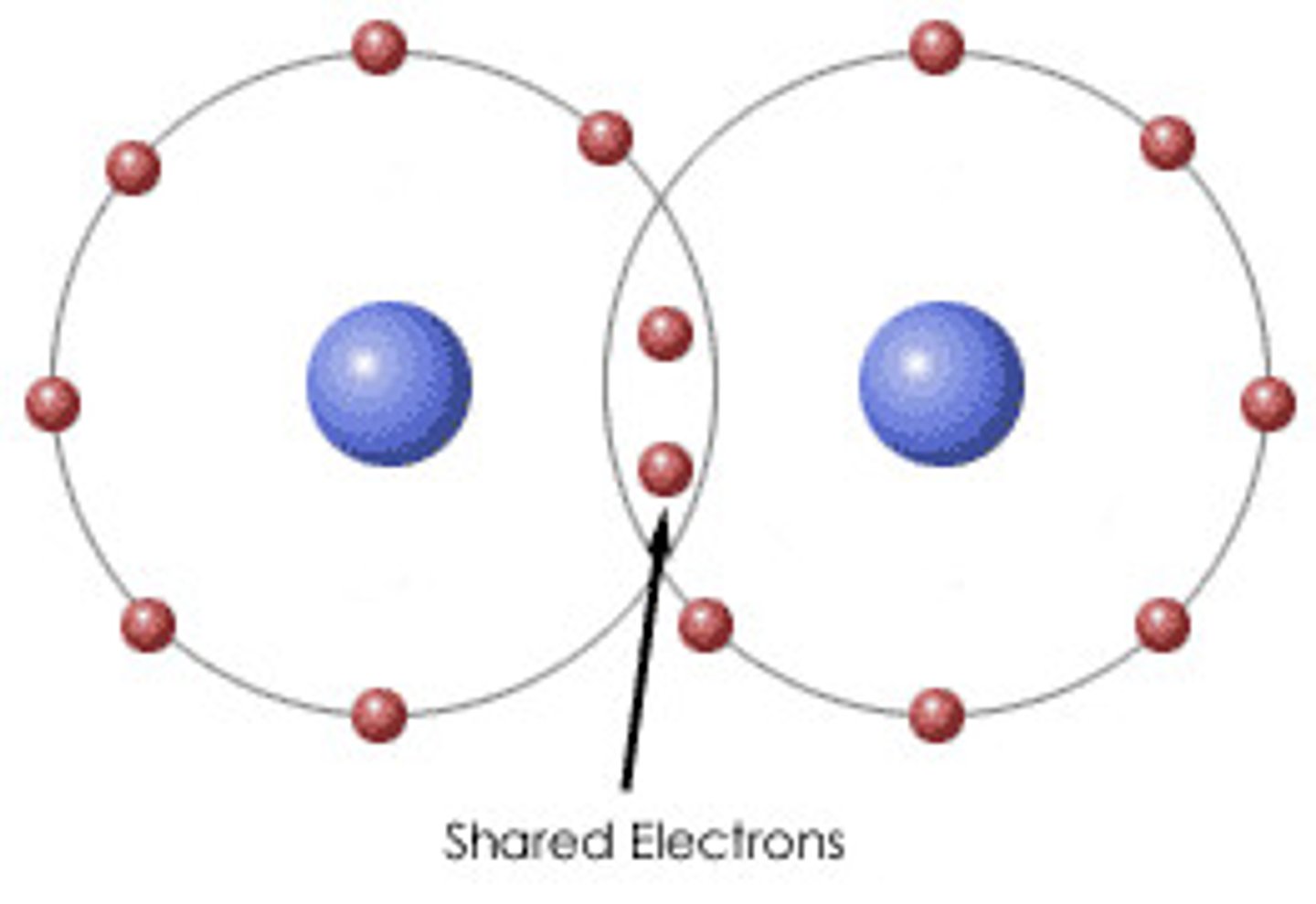
Covalent bond
A shared pair of electrons between two non-metals
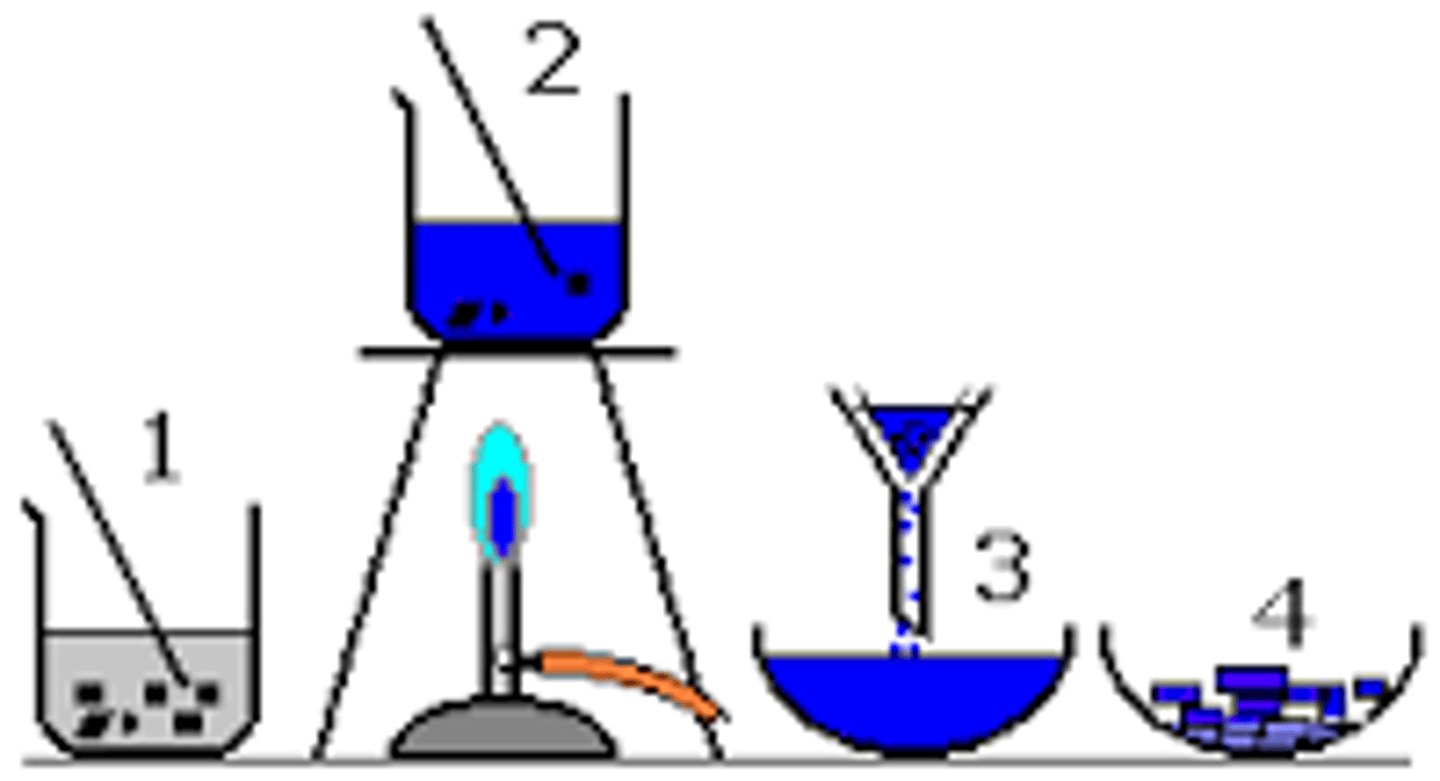
Crystallisation
- A separation technique to obtain soluble solids from solutions
- The process involves heating the solution until crystals start to form, leaving the solution to cool and then filtering the formed crystals from the solution
Allotropes - Diamond
- A giant covalent structure which is made up of carbon atoms, each of which form four covalent bonds with four other carbon atoms
- Covalent bonds are very strong and diamond has many of them meaning it has a high melting point and is very strong
- It has no delocalised electrons so it doesn't conduct electricity
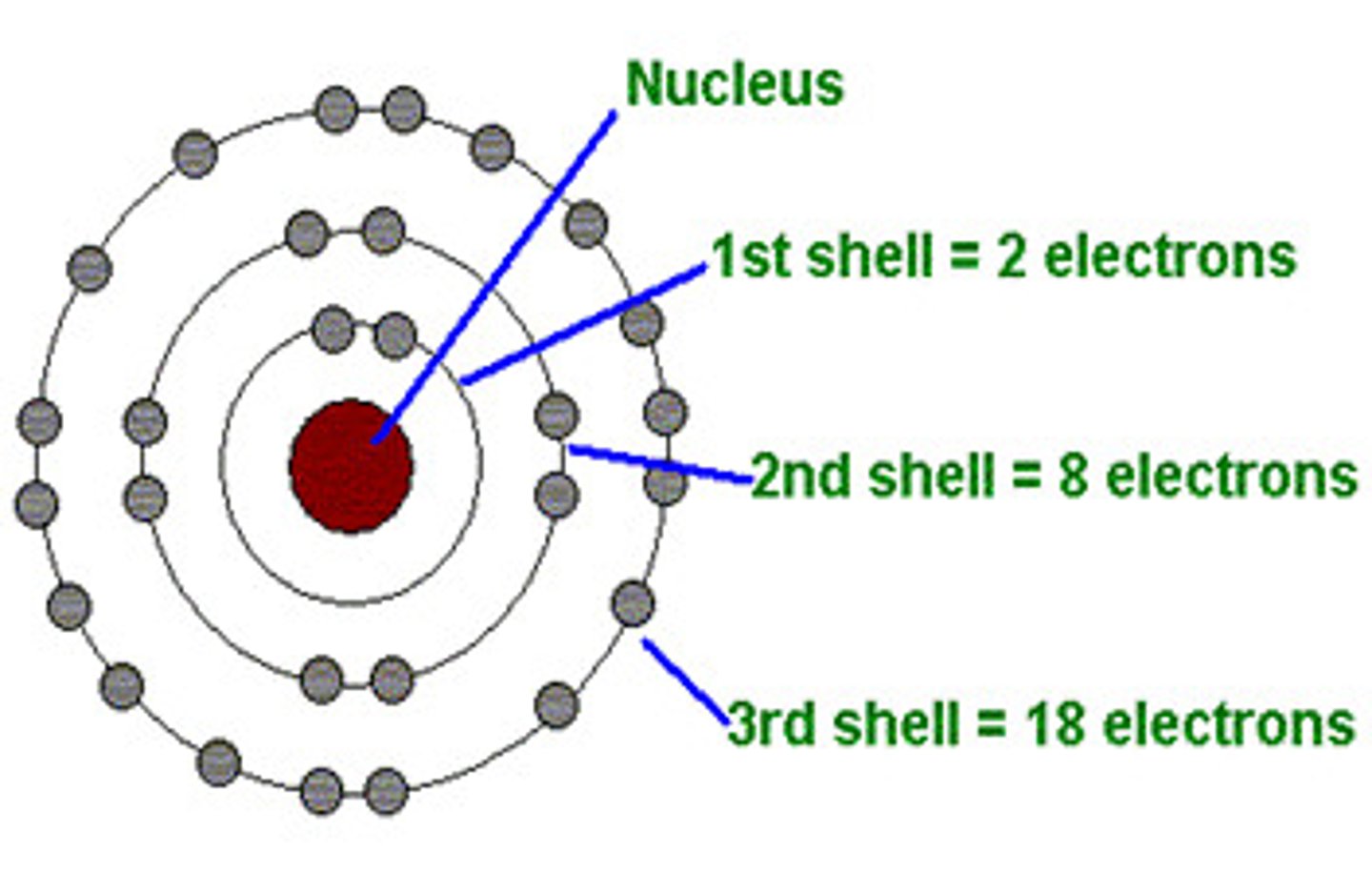
Electron shell
Different energy levels in atoms, occupied by electrons
Electrostatic forces
The strong forces of attraction between oppositely charged ions
Element
A substance made up of only one type of atom
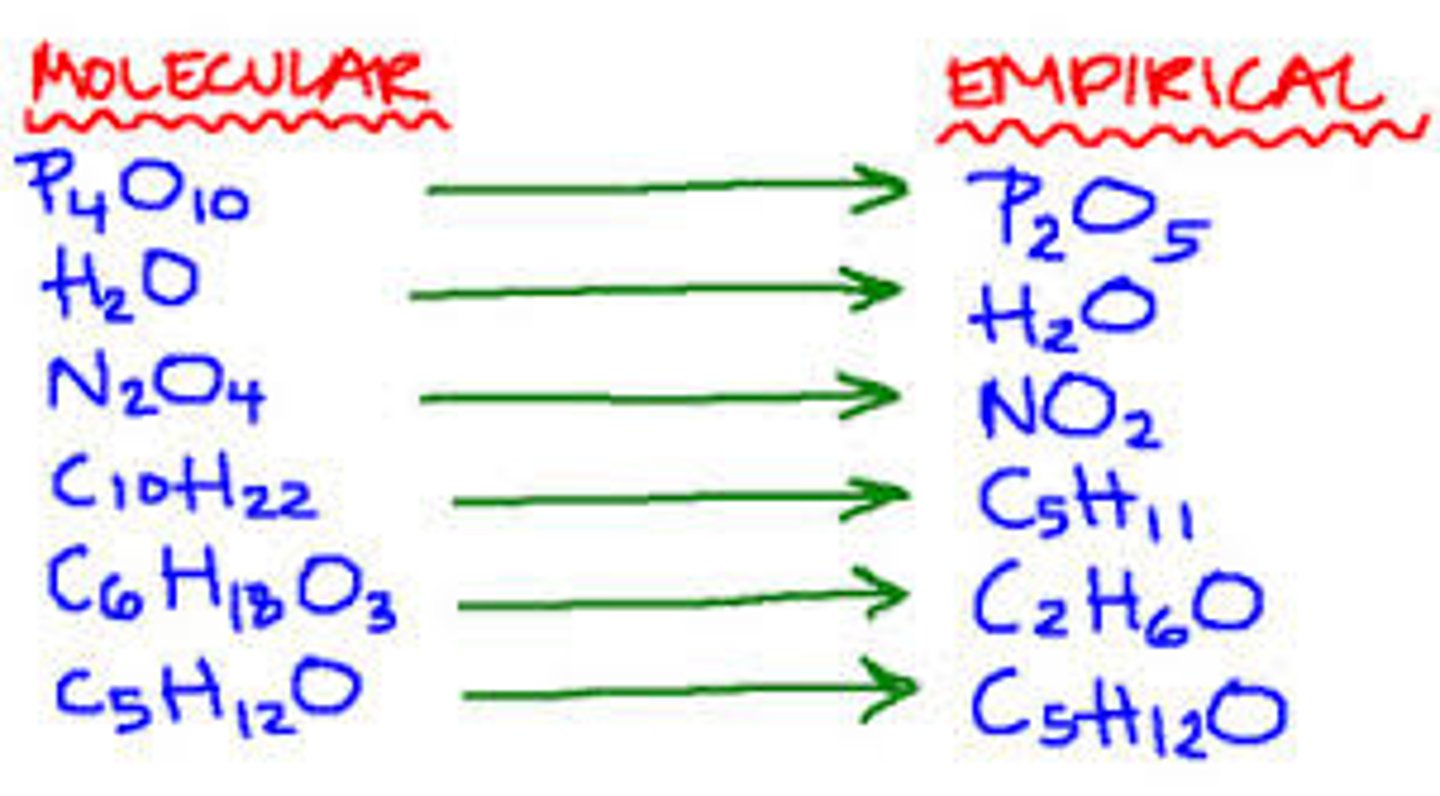
Empirical formula
The simplest whole number ratio of atoms of each element in a compound
Evaporation
- A separation technique to separate soluble solids from solutions
- The solution is slowly heated in an evaporating dish so that the solvent evaporates to leave the dry crystals
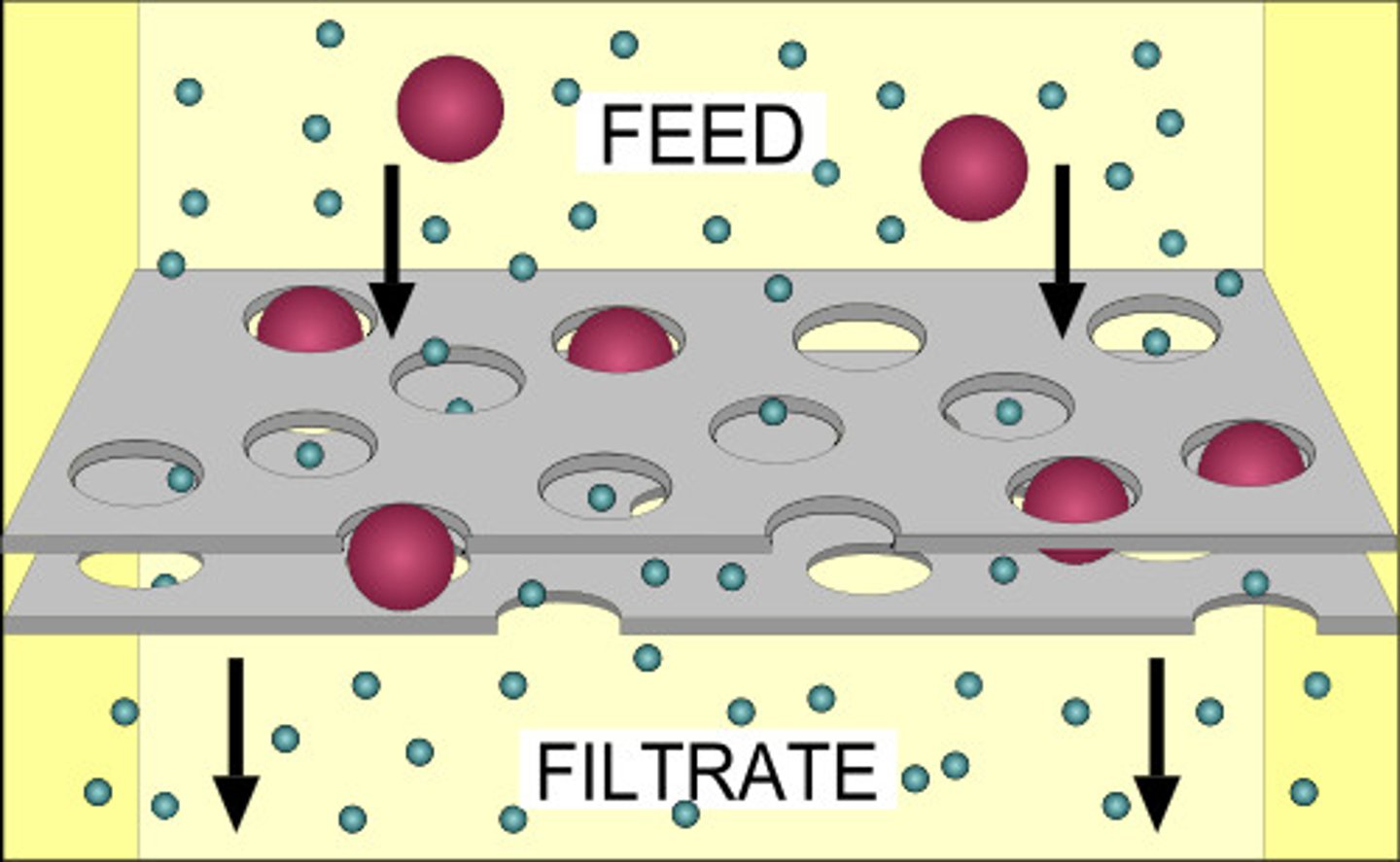
Filtration
- A separation technique used to separate an insoluble solid from a solution
- It works as filter paper has microscopic holes
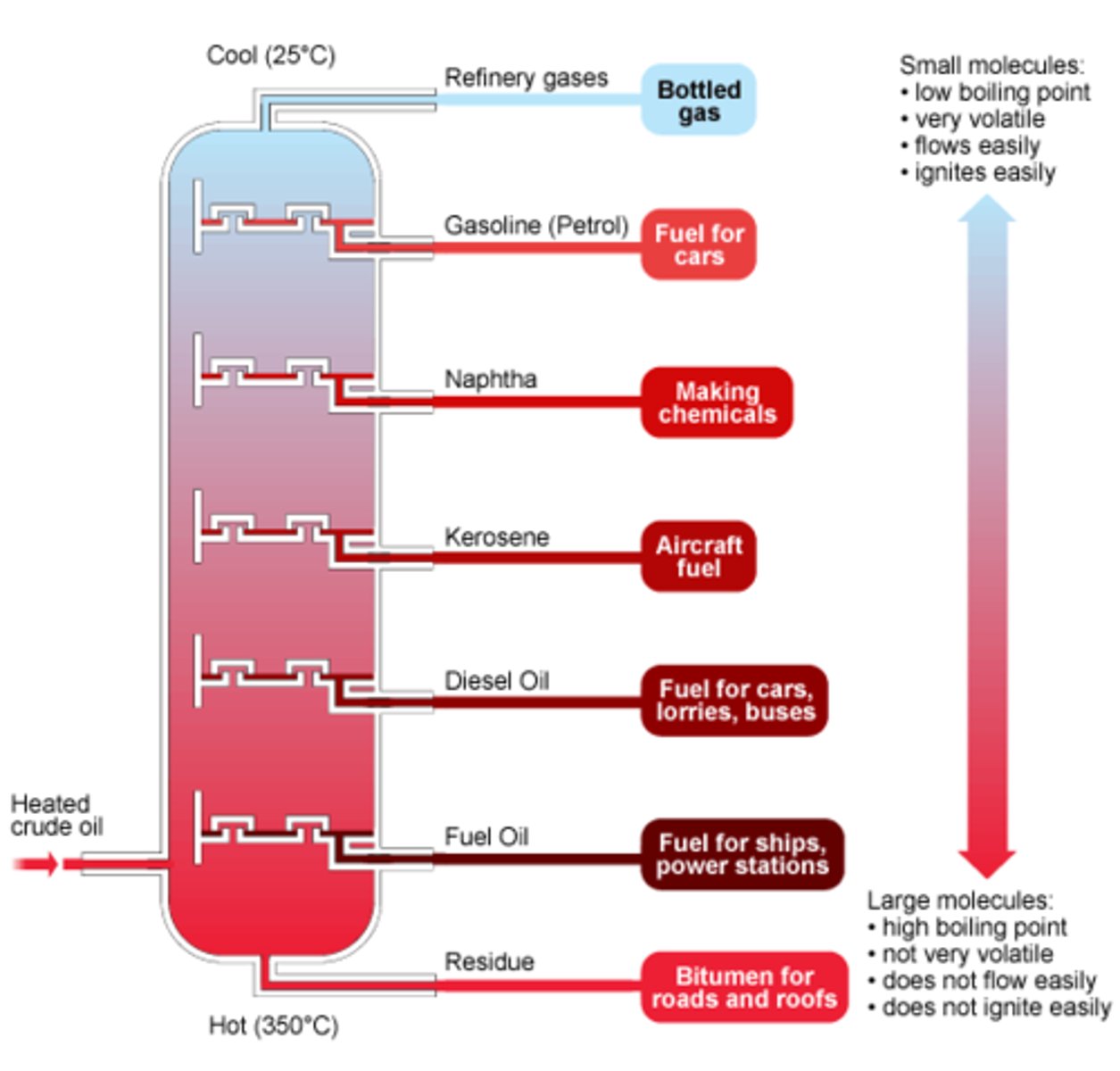
Fractional distillation
- A process used to separate a mixture of liquids
- The liquids have different boiling points so can be separated into different fractions within a fractionating column
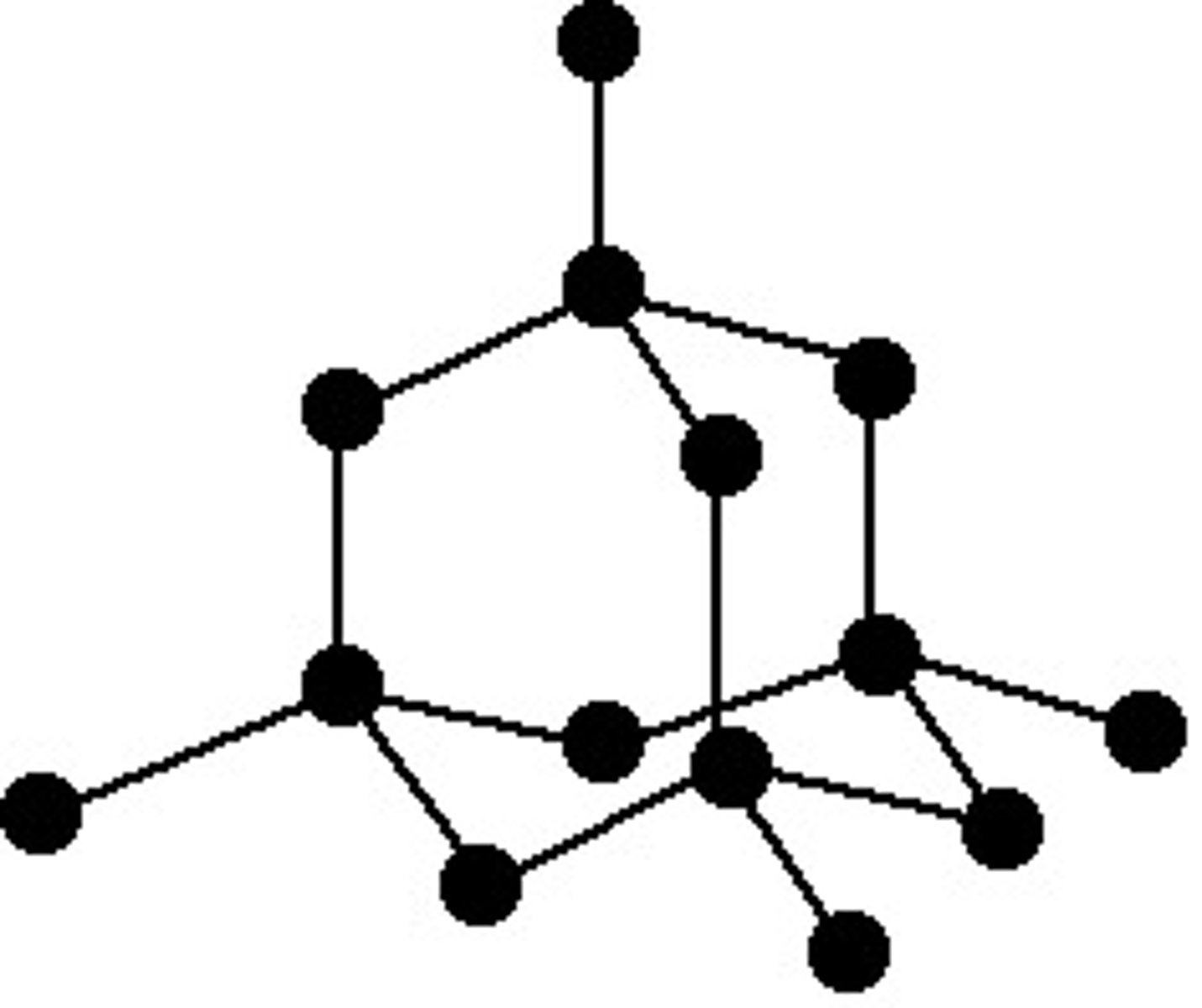
Allotropes - Fullerenes
- Molecules of carbon atoms with hollow shapes (tubes or balls)
- The structures are based on hexagonal rings of carbon atoms but they may also contain rings with five or seven carbon atoms
- A nanotube resembles a sheet of graphene rolled into a tube
- They are strong and used to reinforce sports equipment
- A BUCKYBALL resembles a sheet of graphene closed to make a hollow ball
- They are used as lubricants, their small size allowing them to pass through cell membranes
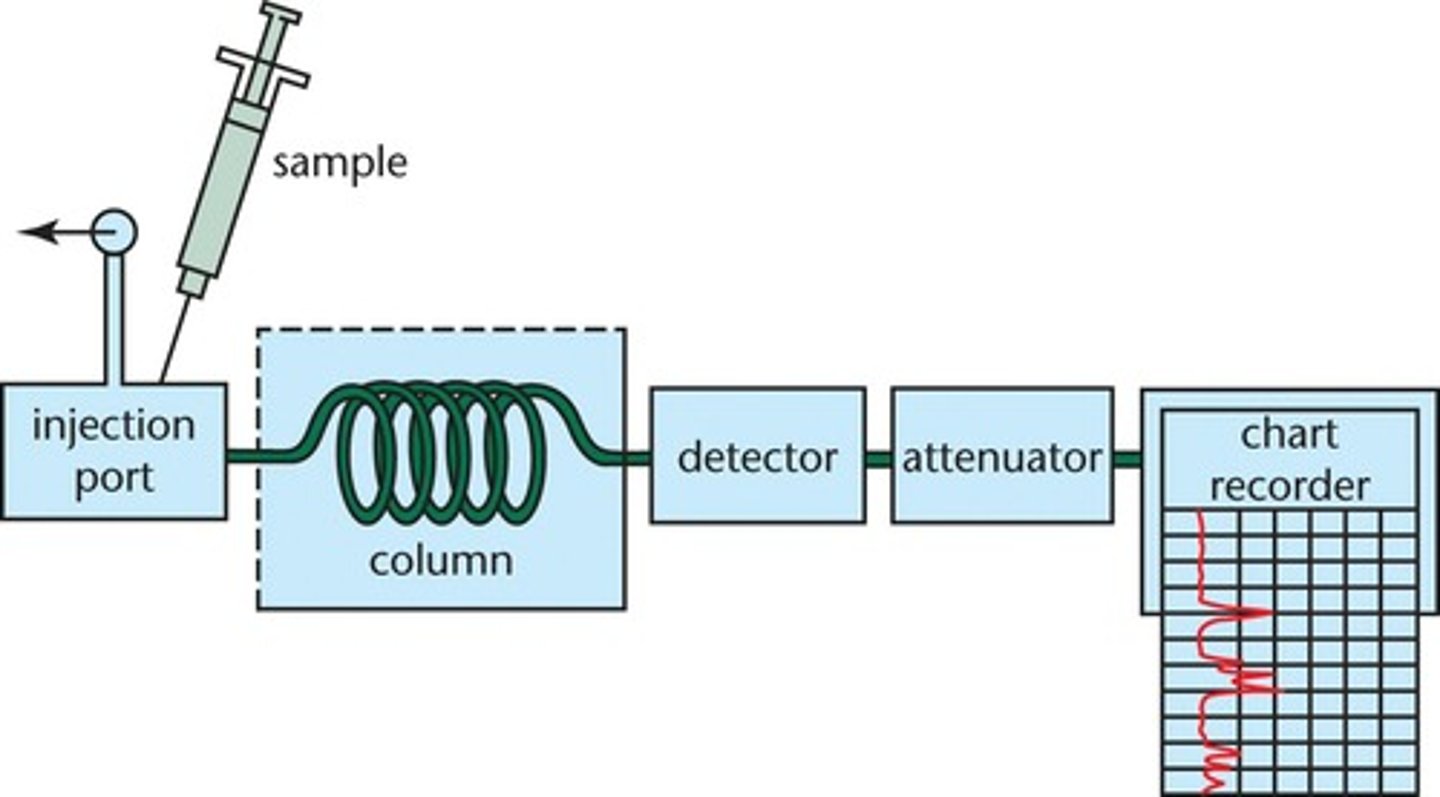
Gas Chromatography
- A technique used to separate a mixture of volatile liquids
- A tube is packed with a solid or a solid coated in a liquid (stationary phase) and a gas (mobile phase) is passed through the column under pressure at high temperature
- Each component takes a different time to pass through the tube
- This is called the retention time which can be used to identify the component.
Giant Covalent Structure
- A molecular structure containing many non-metal atoms covalently bonded together and arranged in a repeating pattern (A GIANT LATTICE)
- The strong covalent bonds mean that giant covalent structures have high melting points
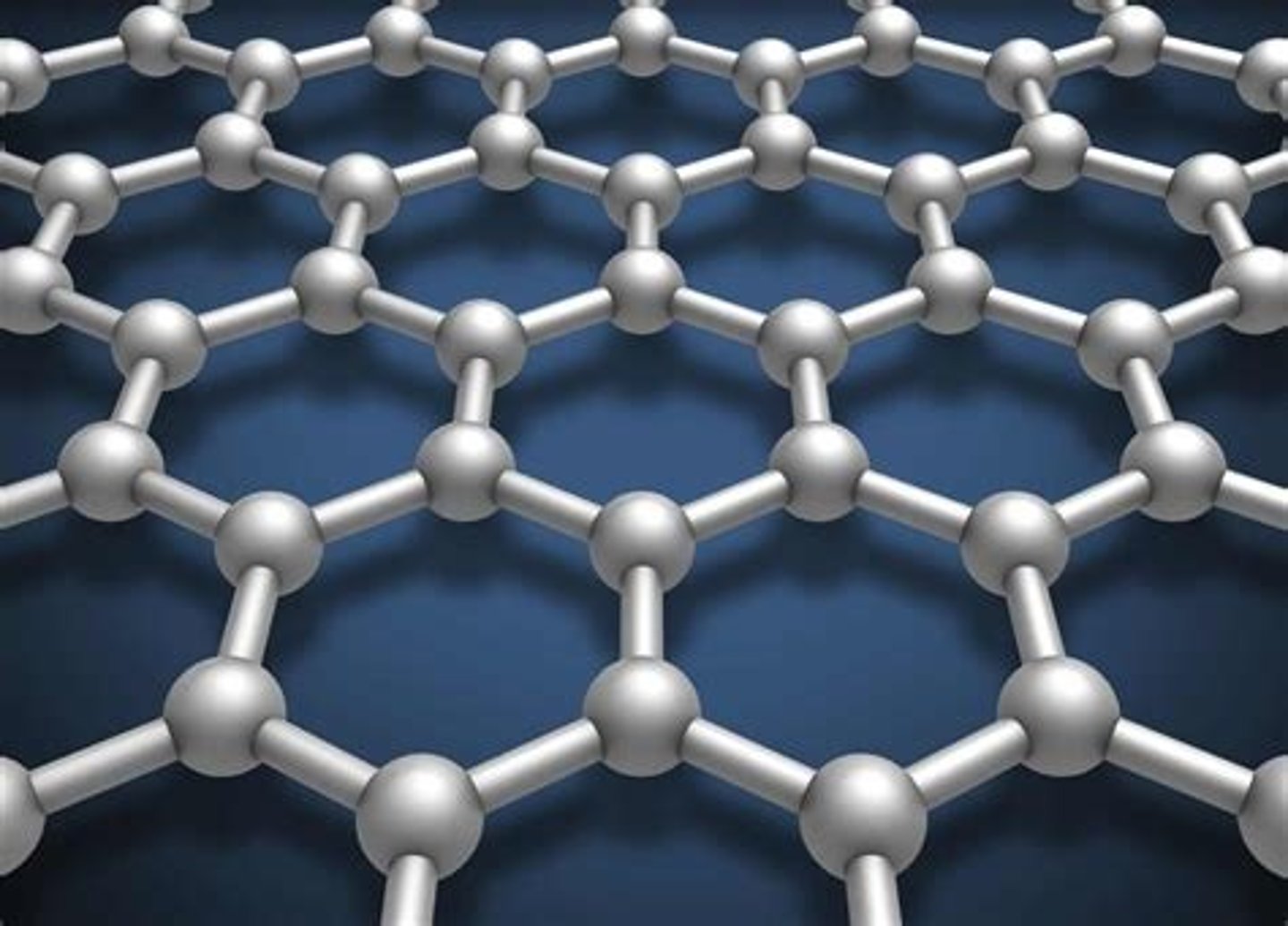
Allotropes - Graphene
- A single layer of graphite with properties that make it useful in electronics and composites
- It resembles a layer of graphite and is almost transparent
- It is extremely strong and can conduct electricity
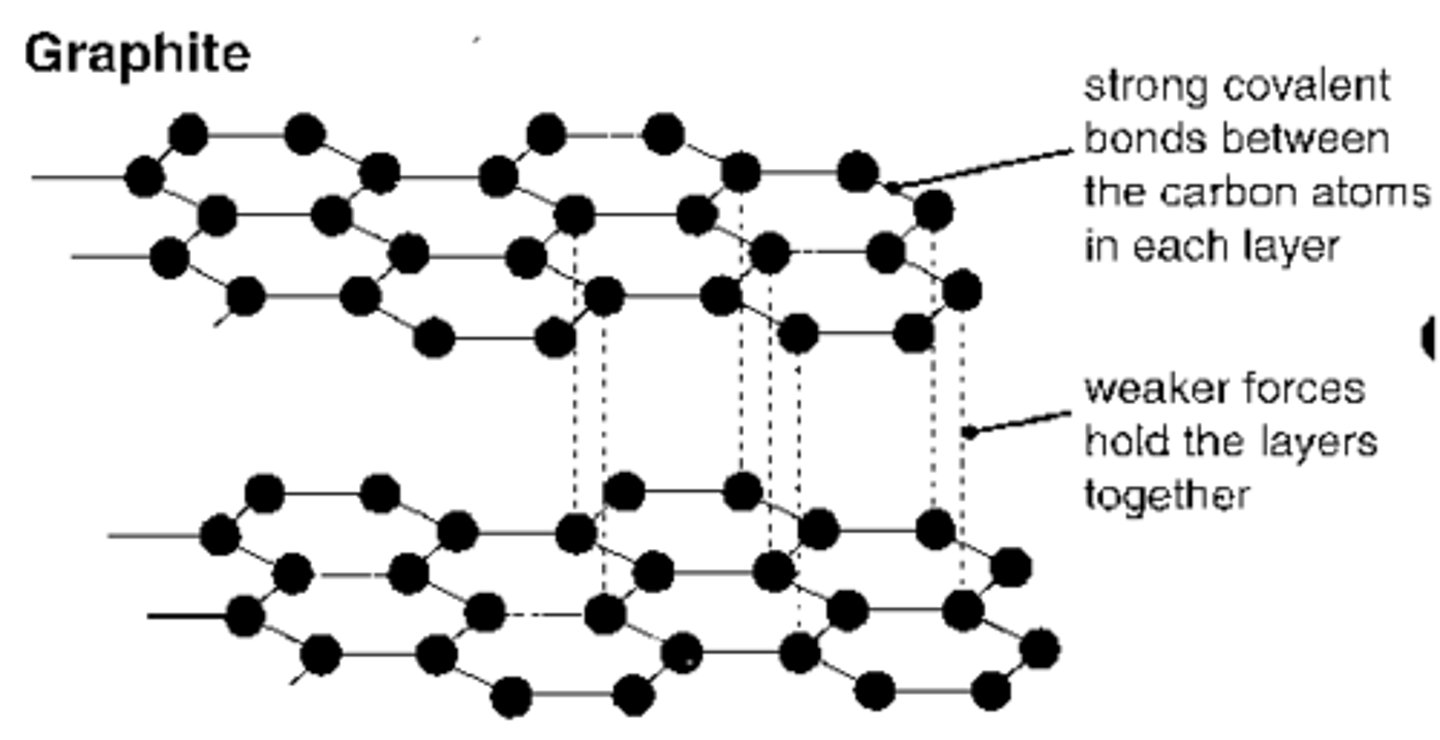
Allotropes - Graphite
- A giant covalent structure which is made up of carbon atoms each of which form three covalent bonds with three other carbon atoms, forming layers of hexagonal rings which have no covalent bonds between them
- There is one delocalised electron per carbon atom which is free to move to carry charge
- It has strong covalent bonds in the layers that give it a high melting point
- The forces between each layer is wea so layers easily slide over each other
Group number
- Determines how many electrons are in the element's outer electron shell
- E.g. elements in Group 2 have 2 electrons in their outer shell
Group (periodic table)
- A column of the periodic table
- Elements in the same group have similar chemical properties
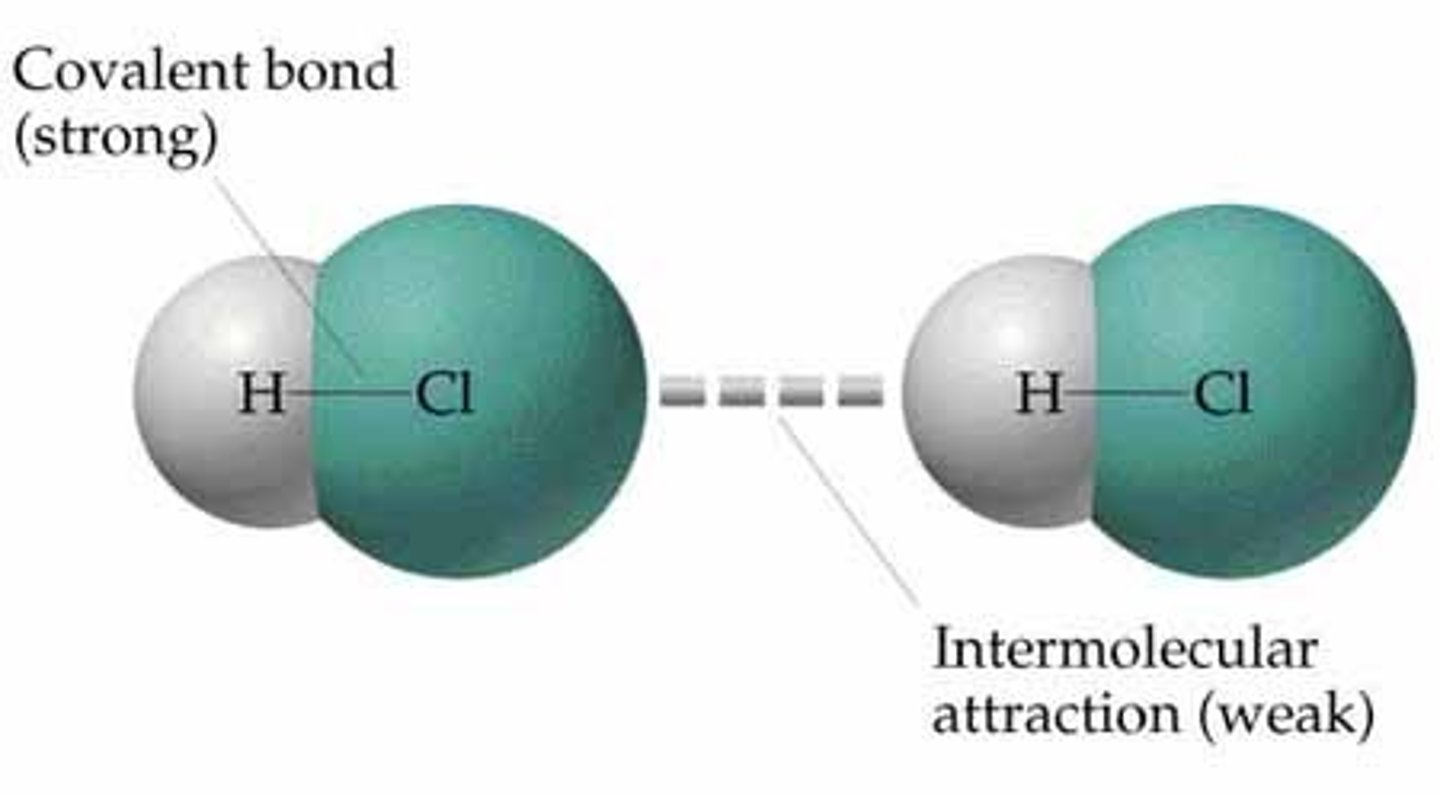
Intermolecular Forces
- The forces which exist between molecules
- The strength of the intermolecular forces impact physical properties like boiling/melting point
Ion
- An atom or molecule with an electric charge due to the loss or gain of electrons
- Metals lose electrons, non-metals gain electrons
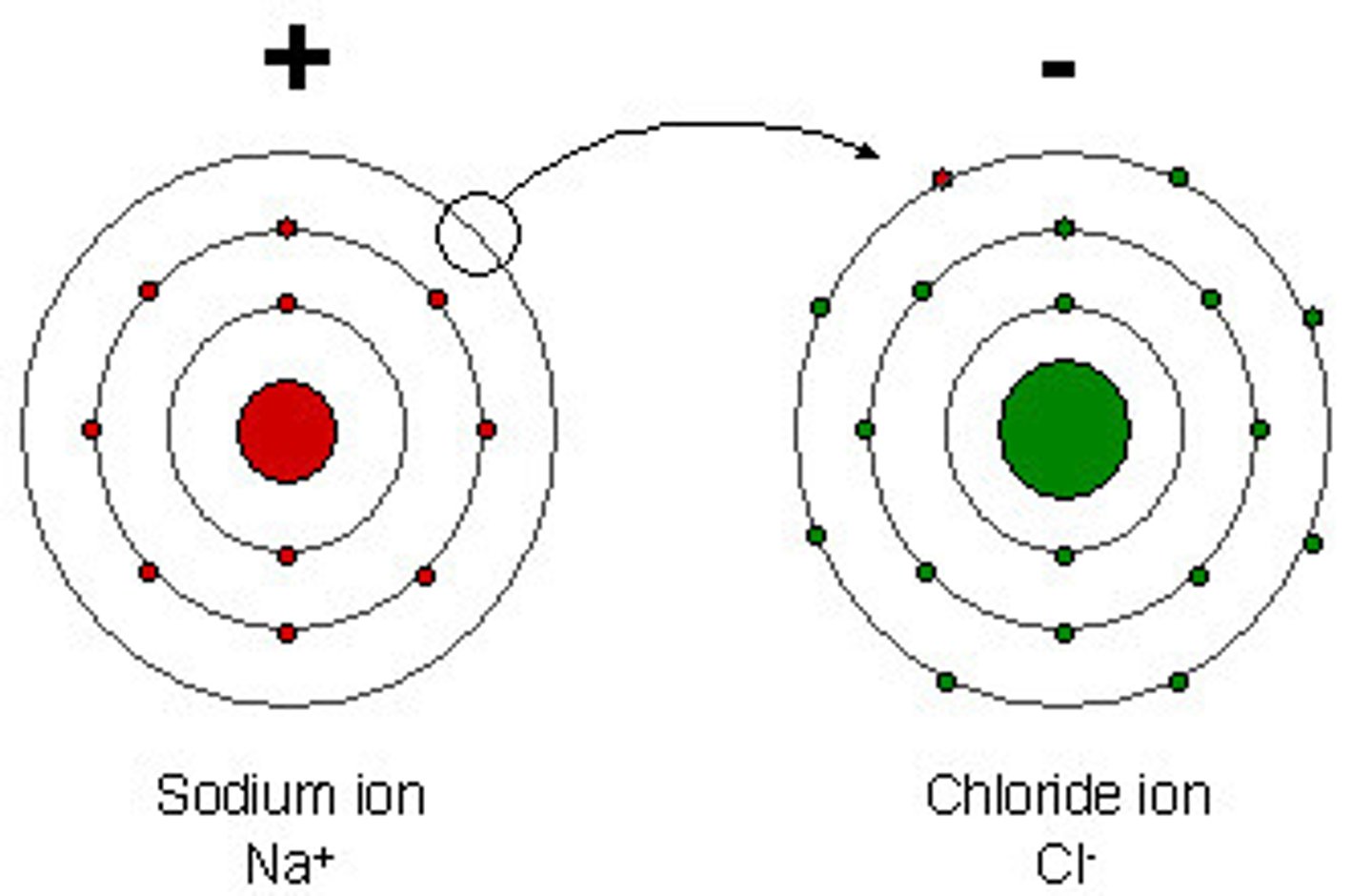
Ionic Bond
- The bond formed between the oppositely charged ions when a metal atom loses electron(s) to form a positively charged ion and a non-metal gains these electron(s) to form a negatively charged ion
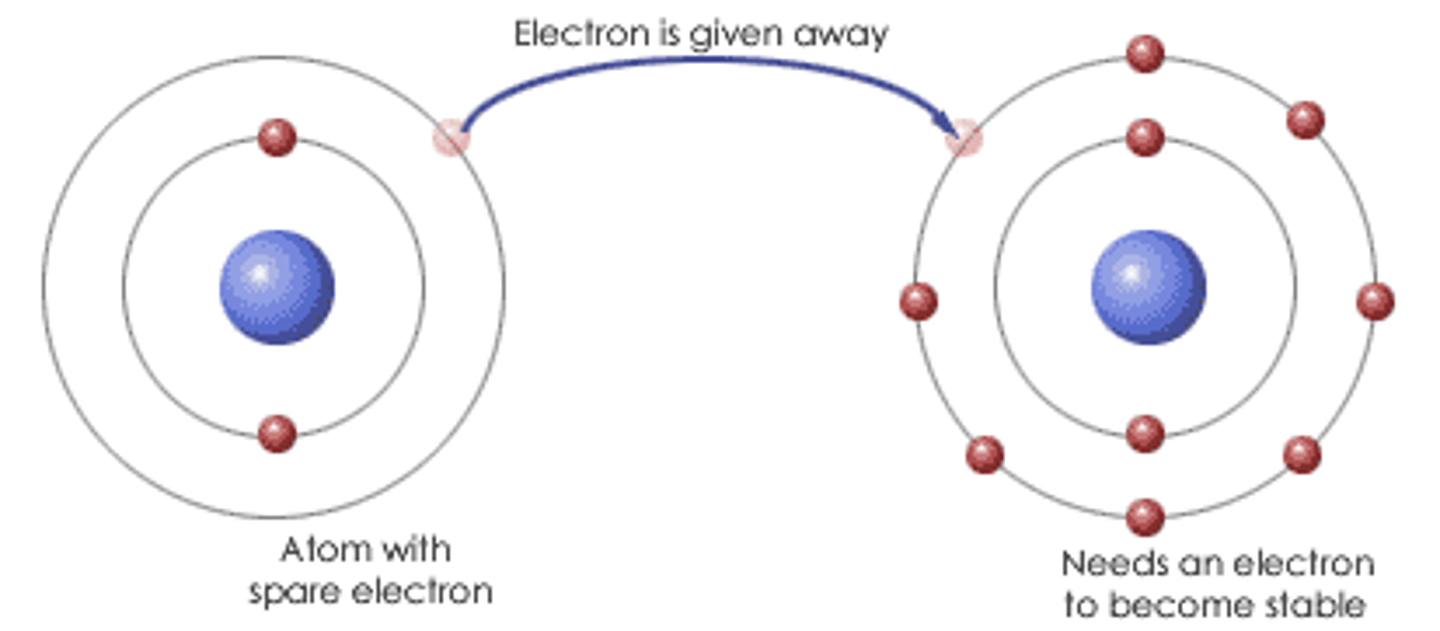
Ionic Compound
- When a metal reacts with a non-metal, electrons are transferred from the metal ion to the non-metal ion so they become more stable
- Ionic compounds in their solid state contain positive and negative ions arranged in a regular way (giant ionic lattice)
- Ions are held in place by ionic bonds that act in all directions and have strong electrostatic forces of attraction
Locating Agent
- A chemical which reacts with a colourless substance to produce a coloured product
- They are used in paper and thin layer chromatography to help identify the substances on the stationary phase
Melting Point Data
- Data which can be used to evaluate the purity of a substance - A pure substance should have a single melting point
Metals
- Elements that react to form positive ions
- Found to the left and towards the bottom of the periodic table
- They are shiny and have high melting and boiling points
- It is a solid at room temperature
- It is malleable and ductile
- It is a good thermal and electrical conductor
- It loses electrons to form positive ions
- They don't react with each other
- A metal oxide produces an alkaline solution
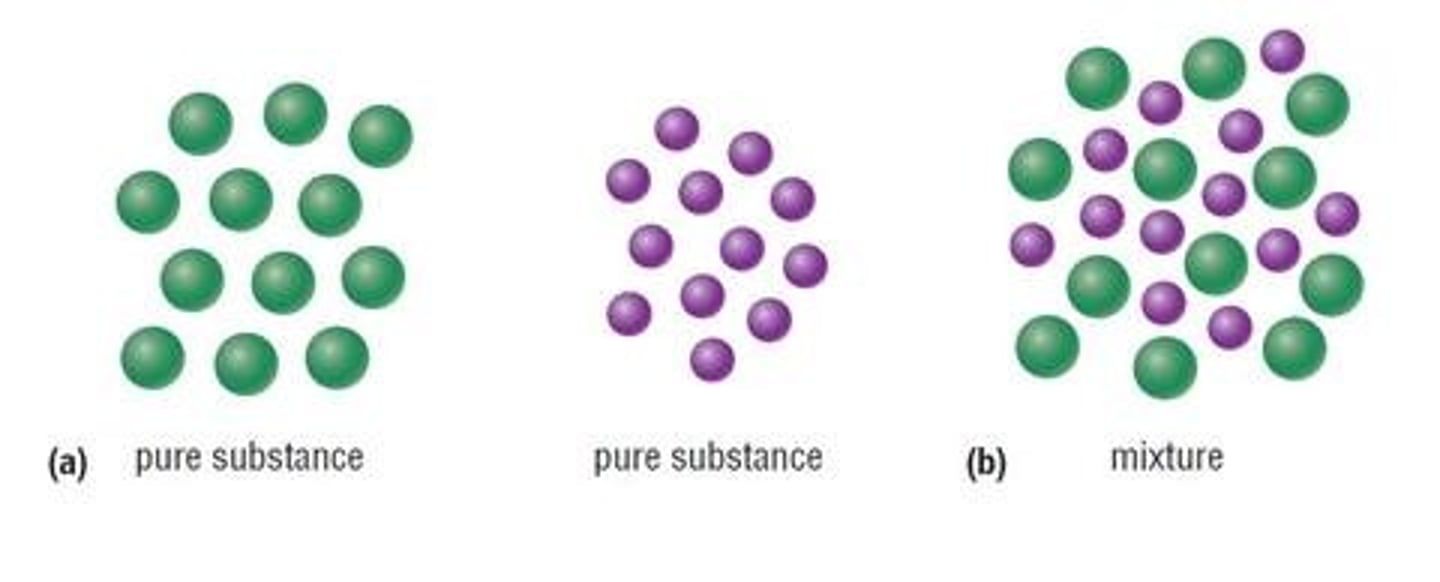
Mixture
- Contains at least two different elements or compounds which are not chemically bonded together
- Mixtures may melt or boil over a range of temperatures
Mobile Phase
The fluid (gas or liquid) which moves through the chromatography system, carrying the mixture which is to be separated
Molecule
A group of at least two atoms held together by covalent bonds
Nanoparticles
- Particles with diameters between 1 nm to 100 nm in size
- Nanoparticles can exhibit properties different to those for the same material in bulk
- They have a large volume to surface area ratio
- They are used in suns creams, paint, cosmetics and medicines
Non-metals
- Elements that react to form negative ions
- Found towards the right and top of the periodic table
- They are dull in appearance with low melting and boiling points
- They are brittle and non-ductile
- They are poor thermal and electrical conductors
- They gain electrons to make negative ions
- They react together to make compounds
- Non-metal oxides produce and acid solution
Paper Chromatography
- A type of chromatography which uses paper as the stationary phase and a solvent as the mobile phase
- The solvent carries the mixture up the paper where the substances in the mixture then separate, depending on how soluble they are in the mobile phase
Period (periodic table)
- A row of the periodic table
- Elements in the same period have the same number of electron shells
Period Number
- Determines how many electron shells the element has
- E.g. elements in period 3 have 3 electron shells.
Periodic Table
Table of elements arranged in order of increasing atomic number and such that elements with similar properties are in the same column (group)
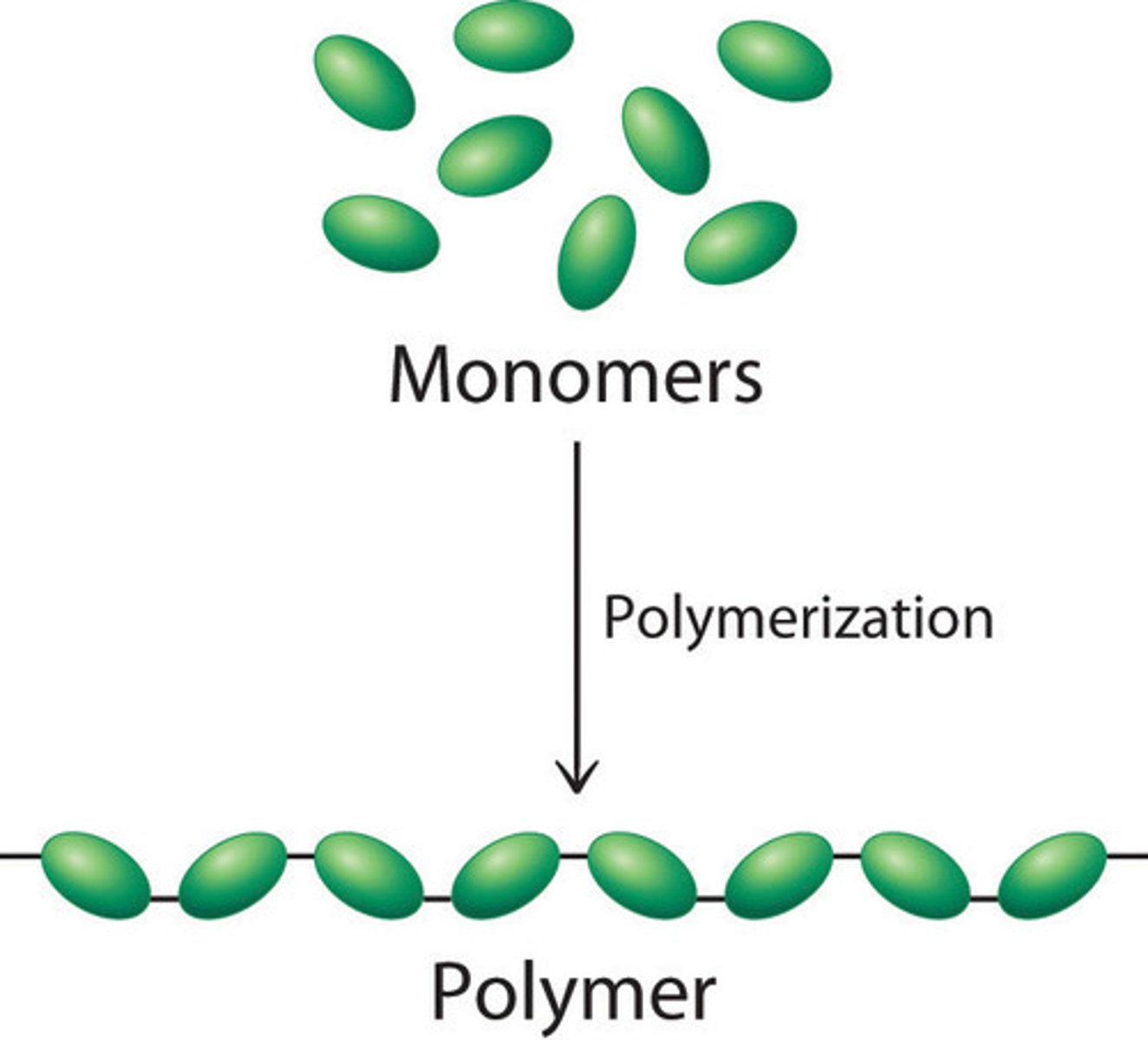
Polymer
- A large, long-chain molecules made up of lots of small monomers joined together by covalent bonds
- They can be artificially made or natural
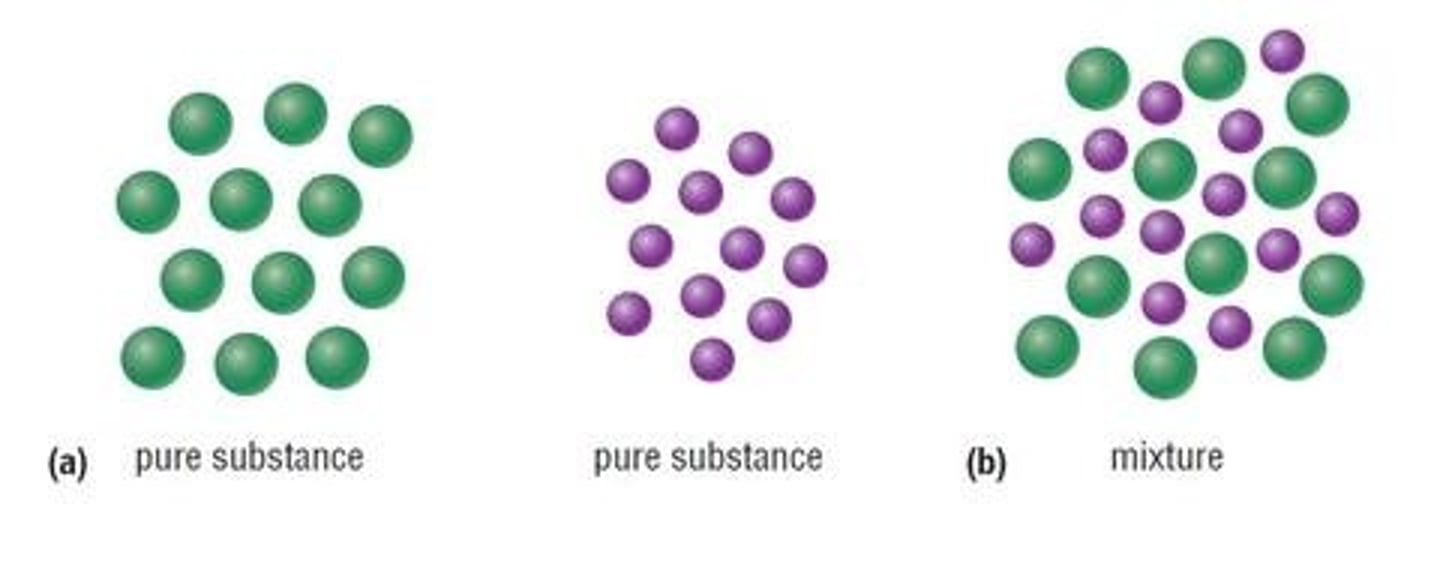
Pure Substance
- It is a substance which contains only one compound or element
- Pure substances can be identified using melting point
Relative atomic mass
- The average mass of an atom of an element compared to 1/12th the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
- Relative Atomic Mass (Ar) is the mass of a subatomic particle - a proton
Relative Formula Mass (Ar)
- The sum of the relative atomic masses of the atoms in the numbers shown in the formula
- It is numerically equal to the mass of one mole of a substance in grams
Relative Molecular Mass
The average mass of one molecule of an element or compound compared to 1/12th the mass of an atom of carbon-12
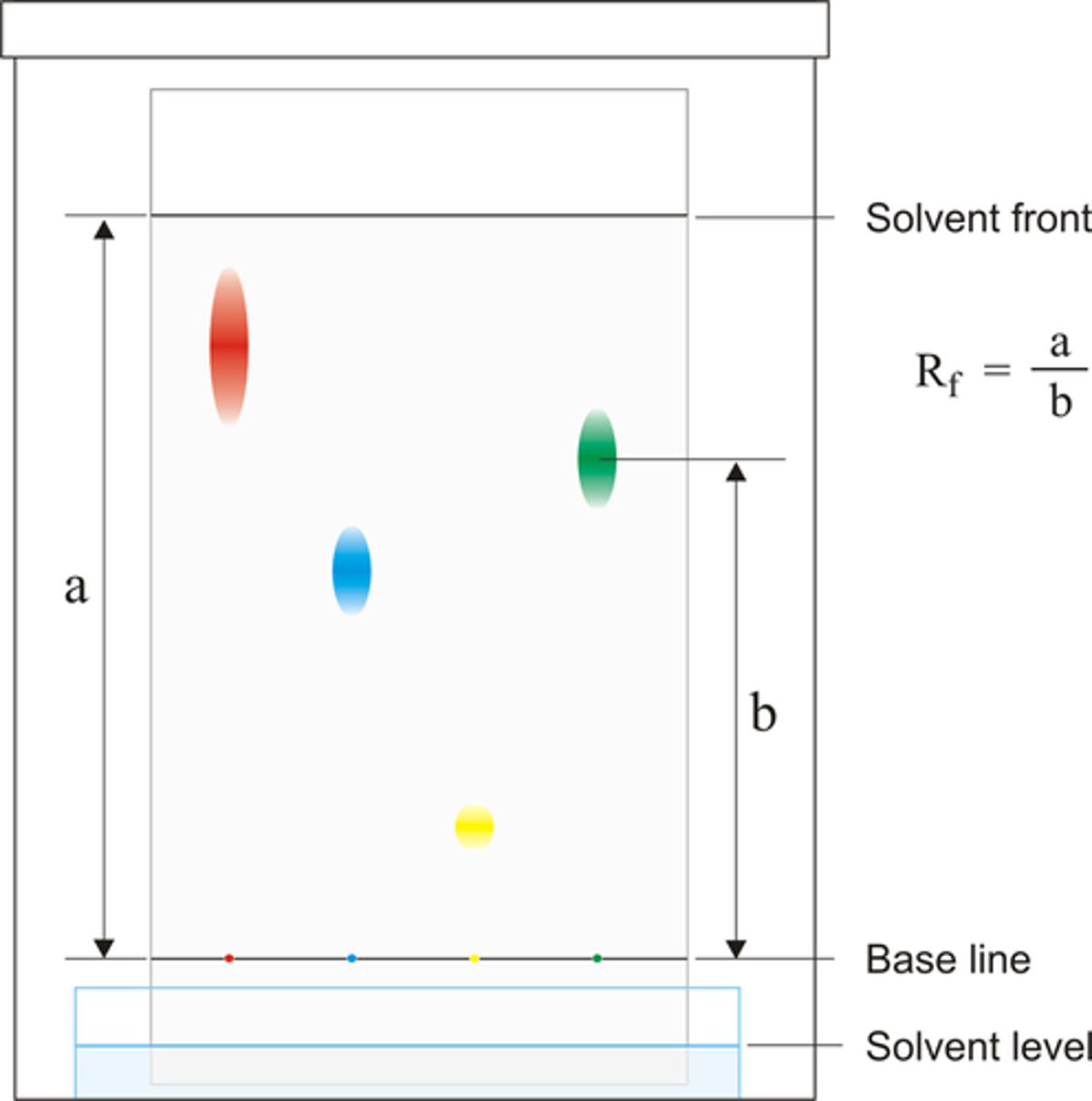
Rf Value
- A value used in chromatography which is calculated as the distance travelled by the dissolved substance divided by the distance travelled by the solvent
- It can be used to identify substances within a mixture

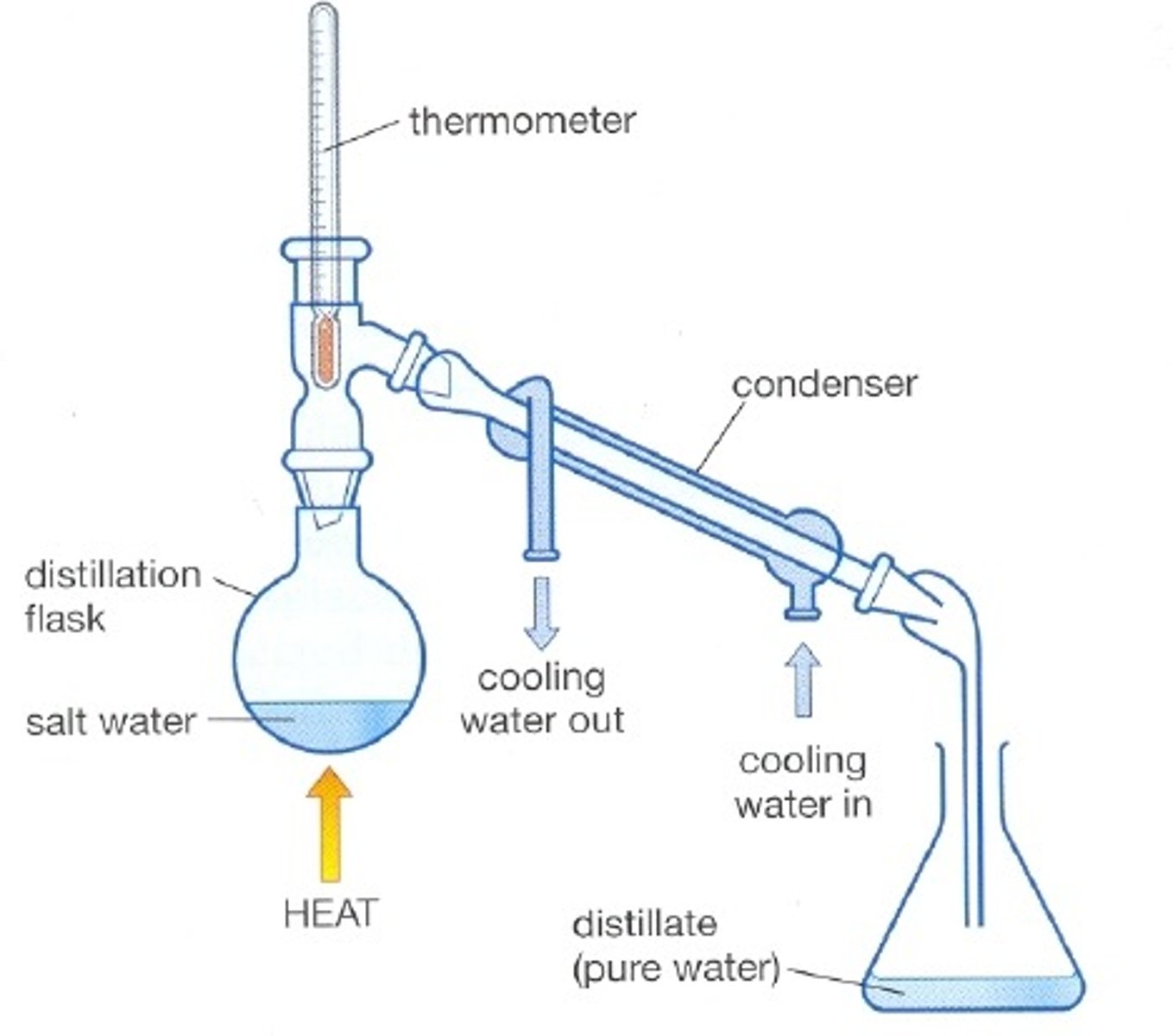
Simple Distillation
- A separation technique used to separate a liquid from a solution
- The solution is heated so that only the liquid with the lowest boiling point evaporates
- This gas is then condensed in a condenser before being collected as a liquid
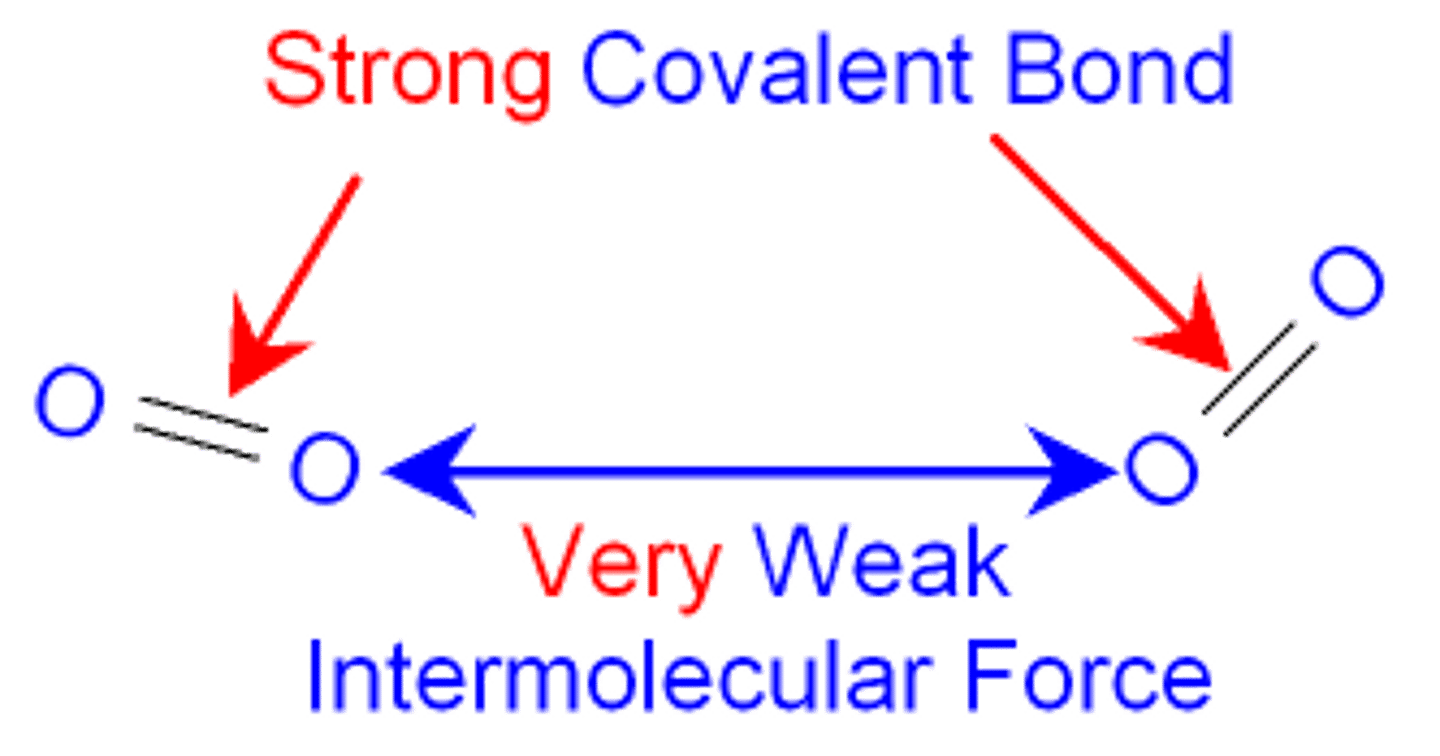
Simple Molecules
- Molecules containing a fixed number of atoms covalently bonded together
- They have low boiling points since they have weak intermolecular forces which are easy to overcome
- They have strong covalent bonds
Stationary Phase
The non moving phase which the mobile phase passes over during chromatography
Thin Layer Chromatography
- A technique used to separate mixtures
- The stationary phase is a thin layer of alumina or silica fixed to a metal or glass plate
- The plate is dotted with the mixture and placed in a beaker of solvent which is allowed to travel up the plate
- The mixture separates due to the components having different solubilities in the mobile phase
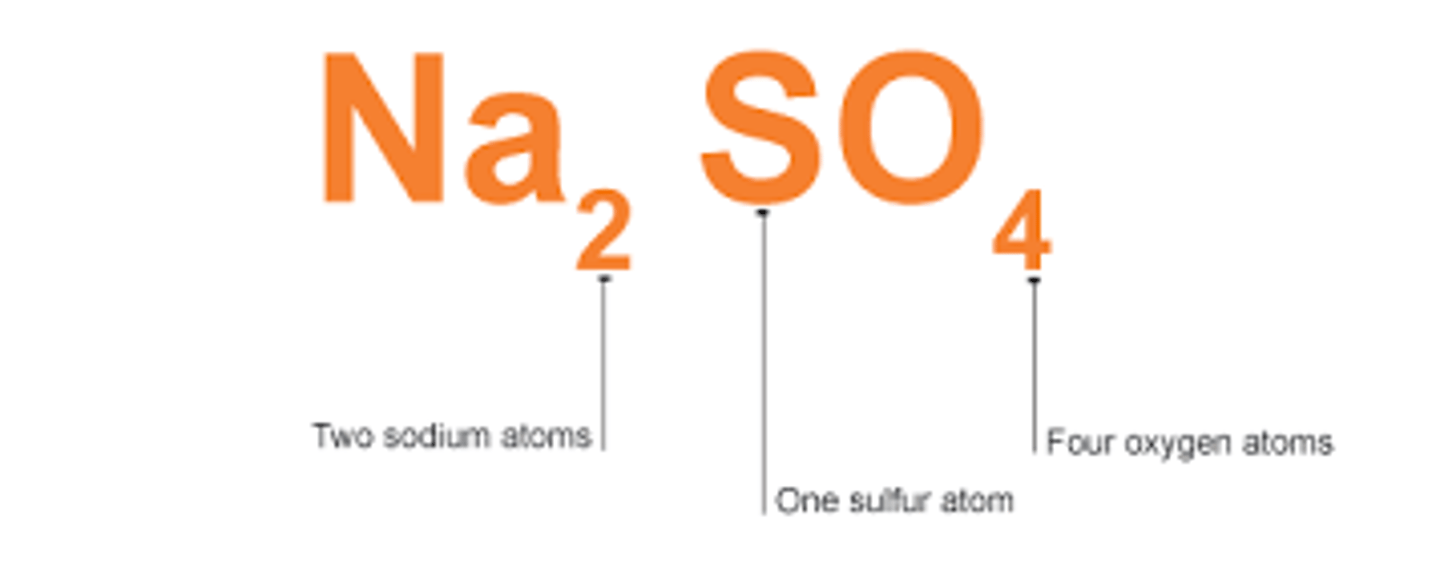
Chemical Formula
It tells you how many of each element there are in a unit of substance
Impure Substances
They are mixtures and contain more than one element or substance
Balance Chemical Equations
It shows the simplest whole number ratio of the atoms of each element in a compound
C + 02 = CO2
1x12 + 2x16 = 44
Solute
A substance that dissolves in a solvent
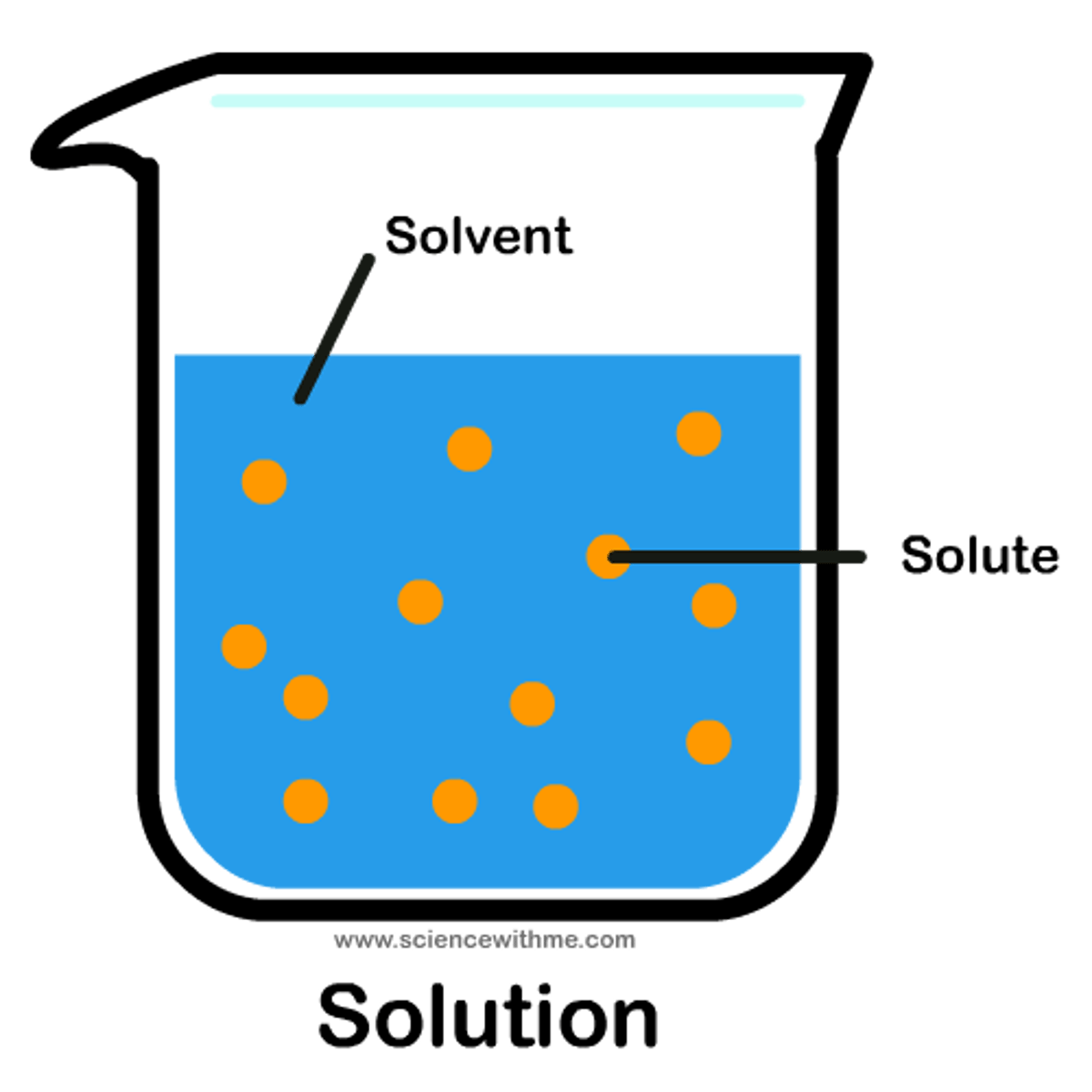
Solvent
A liquid substance capable of dissolving other substances
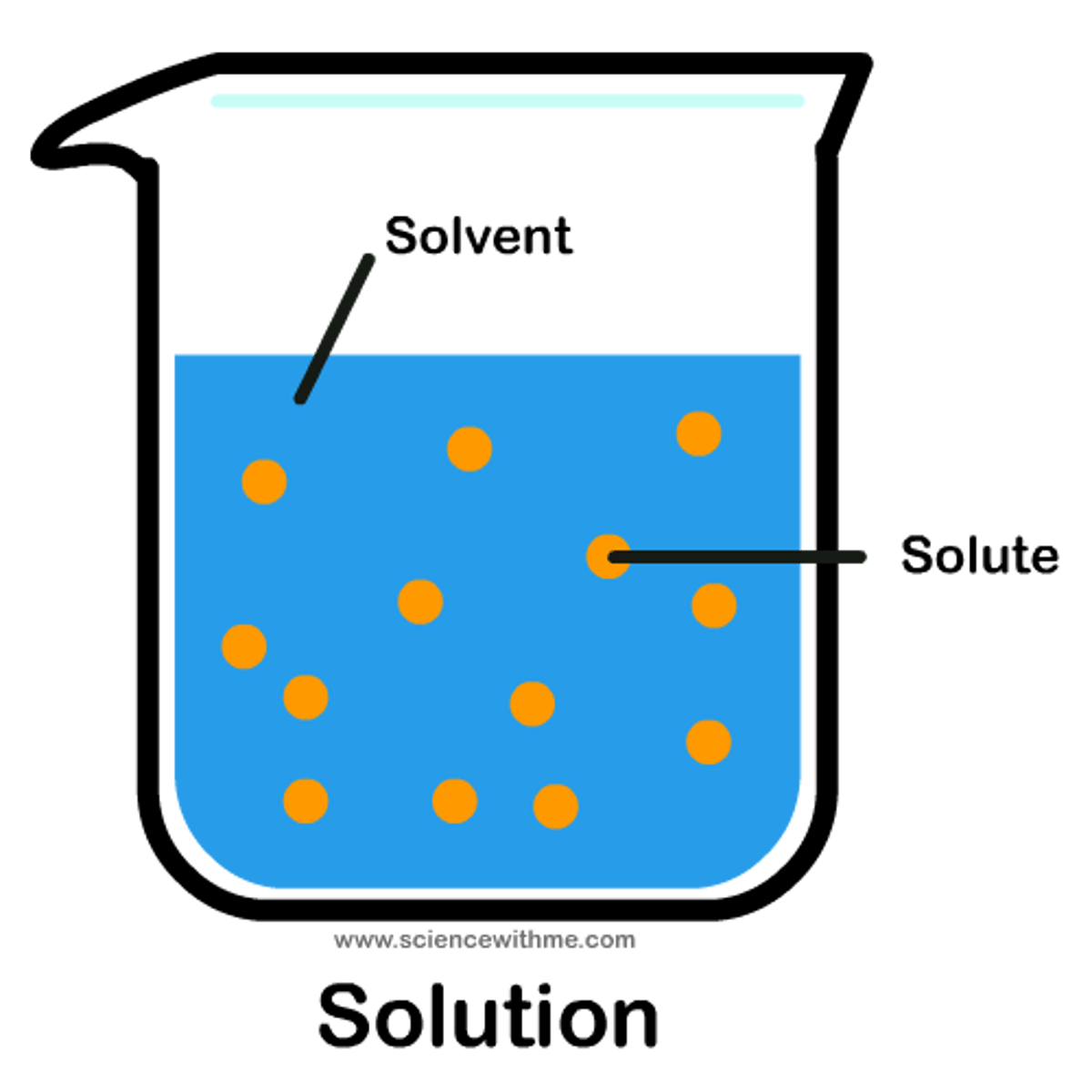
Solution
A mixture that forms when one substance dissolves another
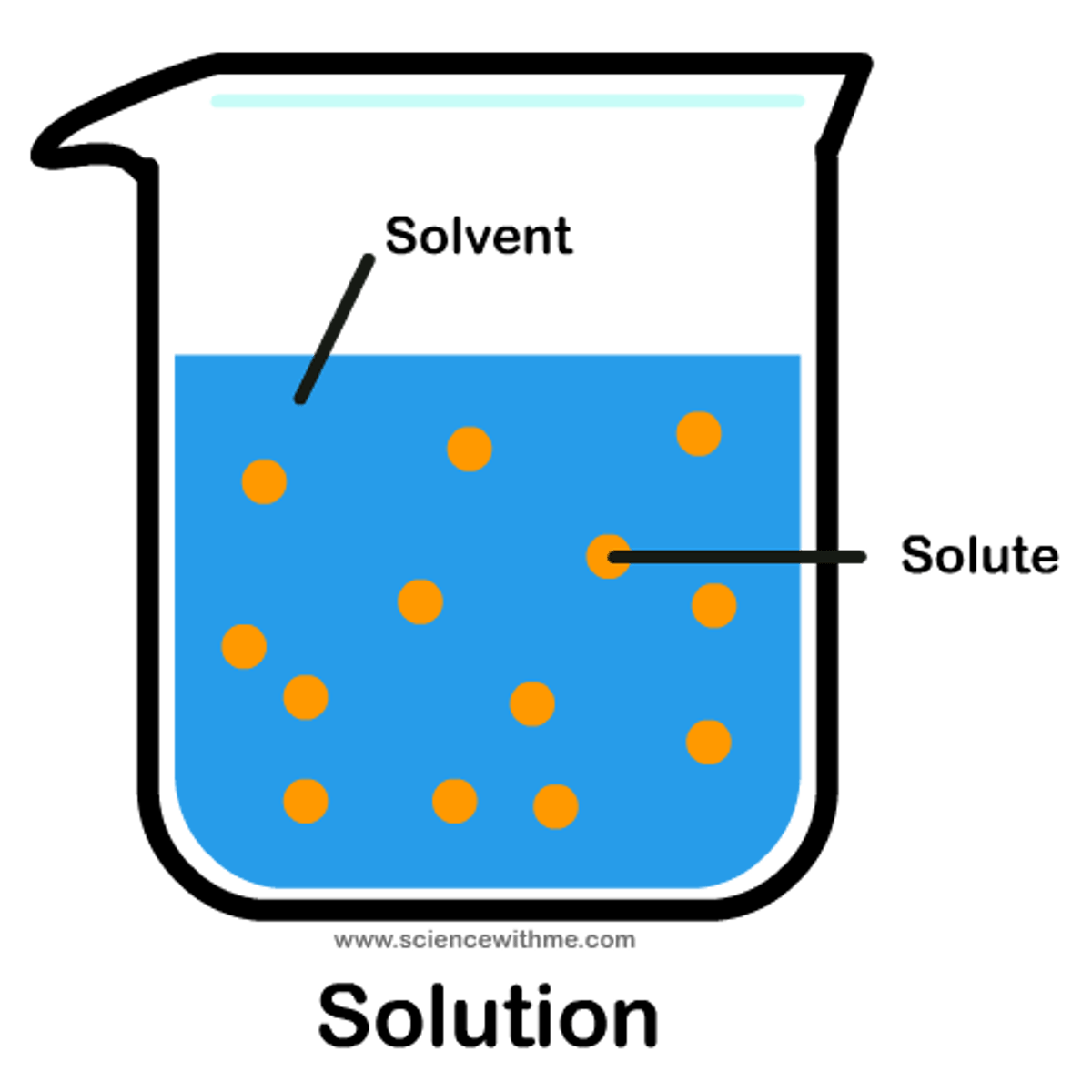
Soluble
A substance capable of being dissolved in a particular substance (can be insoluble in other solvents)
Insoluble
A substance incapable of being dissolved in a particular substance (can be soluble in other solvents)
Thermosoftening Polymers
- Contain individual polymer chains entwined together with weak forces between the chains
- You can melt these plastics and remould them
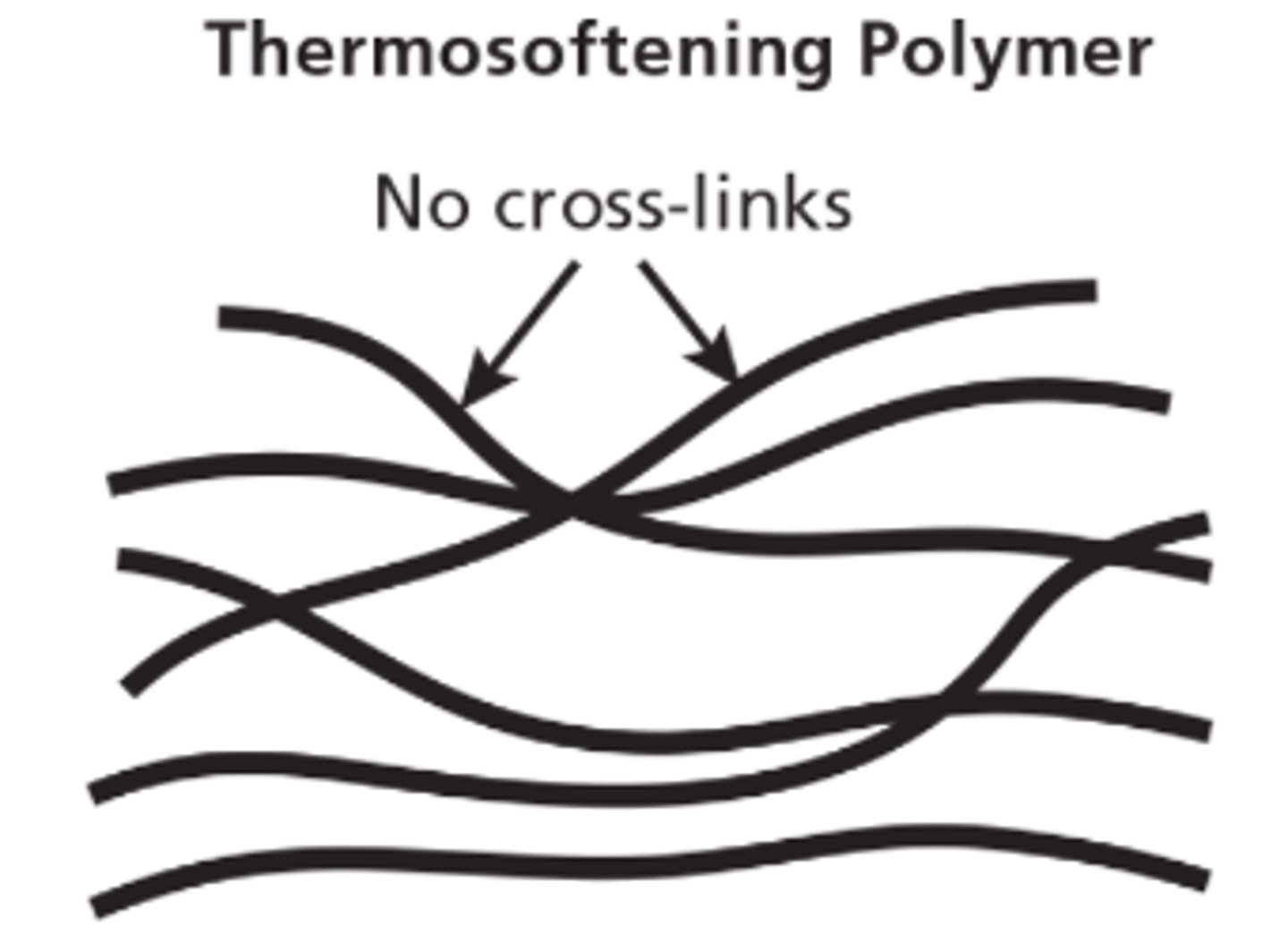
Thermosetting Polymers
- Have CROSS LINKS holding the polymer chains together creating strong covalent bonds
- They do not break when heated

Nanoparticles - Dangers
- They are small enough to be breathed in and absorbed into the skin so can enter cells
- They take a long time to break down once released into the environment
- Toxic substances stick to their surface
Conducting Electricity
- It it has charged particles that are free to move then they can conduct electricity
- Metals conduct electricity in solid and liquid states as their delocalised electrons are free to move
- Simple molecules do not conduct electricity as they have no delocalised electrons
- Ionic compounds conduct electricity when molten on in solution but not when they are in a solid state
Choosing a Separation Method - Insoluble and Soluble Substances
Dissolving followed by filtration
Choosing a Separation Method - Solute dissolved in Solvent
Crystallisation and simple distillation
Choosing a Separation Method - Two or More Substances
Fractional distillation
Choosing a Separation Method - Coloured Soluble Substances
Paper / Thin-layered chromatography
Electron Diagrams
- Used to represent the electron structure in the atom
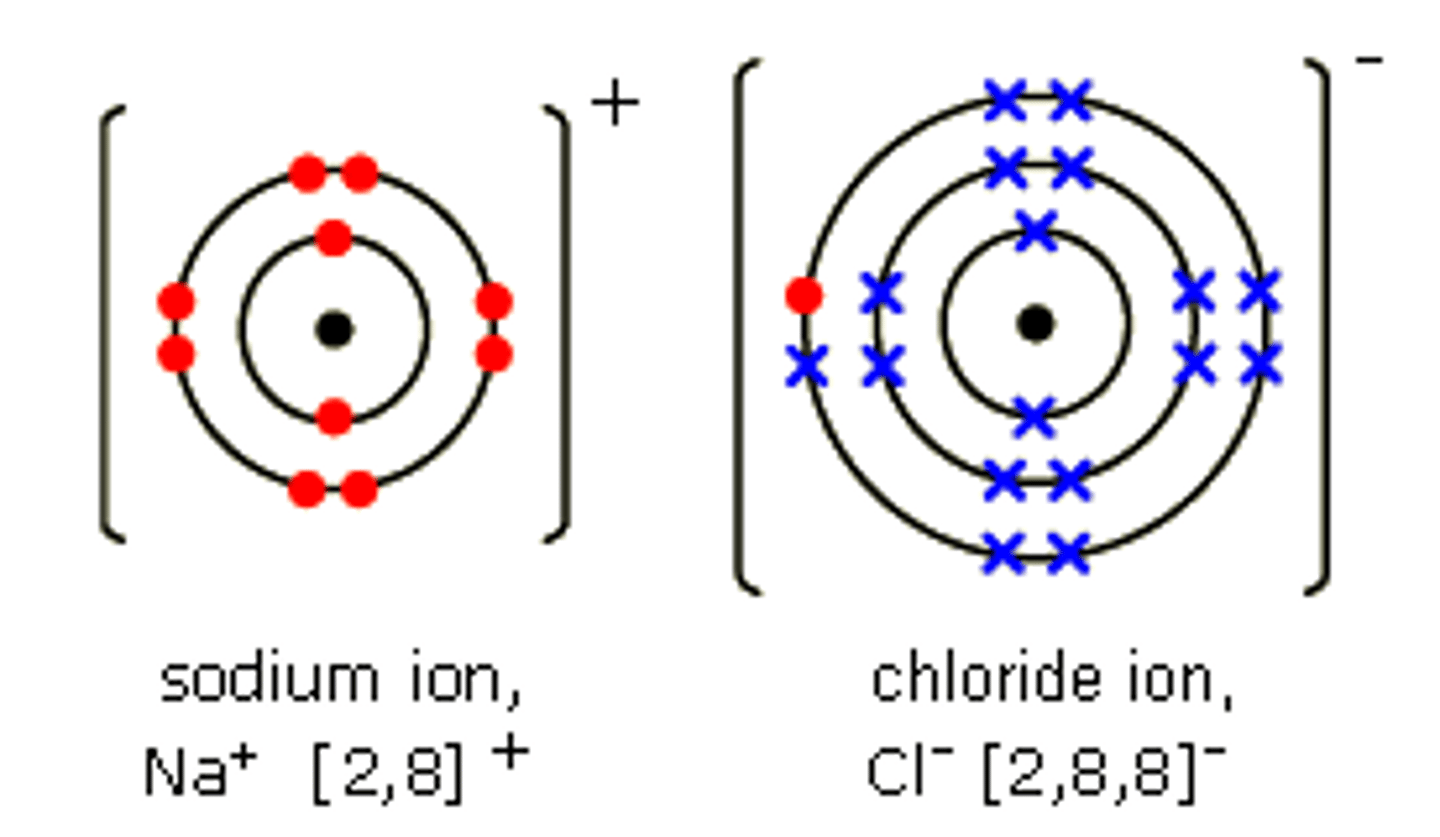
Metallic Bonds
- Metals lose electrons from their outer shell to form positively charge ions and a form a 'sea' of electrons around the positively charged metal ions
- These electrons are free to move and are called DELOCALISED ELECTRONS
- Metallic bonds have strong electrostatic forces of attraction
Mendeleev
- He was the most successful at organising elements into a table
- He arranged elements in order of increasing atomic weight and similar chemical properties
- He swapped Tellurium and Iodine around as their chemical properties matched better
- He left spaces for elements he thought would exist but weren't discovered yet
Carbon Compounds
They have 4 electrons in their outer shell that can form 4 covalent bonds
Allotropes
They are different forms of an element in the same state but with different arrangements
Changing State
- When substances melt or boil, forces of attraction between its particles are overcome
- Some bonds break going from solid to liquid states and the remaining bonds break going from liquid to gas
- The stronger the bonds the more energy must be transferred to break them
- When a substance condenses or freezes, some bonds form going from gas to liquid and many bonds form when going from liquid to solid
Breaking Bonds - Metal
- Bonds Involved = Metallic Bonds
- Strength of Bonds = Strong
- State at Room Temperature = Solid
- Examples = Iron, Mercury
Breaking Bonds - Ionic Compounds
- Bonds Involved = Ionic Bonds
- Strength of Bonds = Strong
- State at Room Temperature = Solid
- Examples = Sodium Chloride
Breaking Bonds - Giant Covalent Structures
- Bonds Involved = Covalent Bonds
- Strength of Bonds = Strong
- State at Room Temperature = Solid
- Examples = Diamond, Silica
Breaking Bonds - Simple Molecules
- Bonds Involved = Intermolecular Forces
- Strength of Bonds = Weak
- State at Room Temperature = Liquid / Gas / Easily melted Solid
- Examples = Oxygen, Wax, Water
Brittle Substances
They crack and break easily when force is applied (shattered when hammered)
Malleable Substances
They change shape without cracking or breaking (bent without shattering)
Ductile Substances
Can be pulled onto wires (stretched easily)
Non-ductile Substances
Cannot be pulled into a wire (snap when pulled)