Things to note - when answering questions on topic 7 and 19:
1/7
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chemistry
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Give one advantage and one disadvantage of using a chemical test rather than infrared spectroscopy to determine whether any of the 2-methylpropan-2-ol remained.
Advantages:
cost associated with the chemical test is small and the result is very rapid
Disadvantage:
chemical test is not so sensitive / uses some of the sample which cannot easily be recovered
State why HOOCCH=CHOOH has E/Z isomers
restricted / limited rotation about the C=C double bond
each carbon atom on the double bond is attached to two different atoms/ different groups (of atoms)/ to a (H) atom and a COOH group
The relative molecular mass of 2-methylpropan-2-ol is 74. Give a possible reason why there is no molecular ion peak in the mass spectrum of 2-methylpropan-2-ol.
Molecular ion/ molecule fragments/ is unstable
TMS is an inert and non-toxic compound. State two other reasons why TMS is suitable for use as a standard when recording NMR spectra.
single peak / all H or all C in same environment
peak to the right / upfield
low boiling temperature / volatile
gives a strong signal so only small amount needed
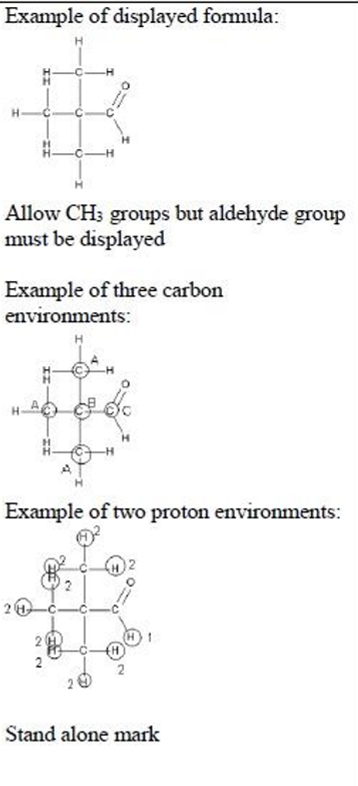
This question is about some carbonyl compounds with the molecular formula C5H10O. An aldehyde with molecular formula C5H10O has a 13C NMR spectrum with three peaks. The high resolution NMR spectrum of this aldehyde has two peaks and neither of them is split. Deduce the displayed formula of this aldehyde. Justify your answer by referring to both NMR spectra.
displayed formula of aldehyde (1)
three different carbon environments indicated (1)
two different proton environments indicated (1)
no splitting as there are no hydrogens on the adjacent carbon atom(s)
Explain why different compounds will have different retention times in the same column, under the same conditions.
retention time depends on the polarity or attraction/ affinity/ solubility/ of component for the stationary phase
the greater the attraction/ affinity/ solubility/ of the component for the stationary phase the greater the retention time
OR
retention time depends on boiling temperature of the compound
higher boiling temperature compounds spend less time in the gas phase/ mobile phase so have longer retention time
State why nitrogen and argon are suitable carrier gases for gas chromatography.
gases are inert and do not react with components of the mixture
The relative abundance of the abundance of the isotope 35Cl is 75.5%. The relative peak height of the isotope is 82.5 in the mass spectrum. Calculate the relative peak height of the missing peak caused by the isotope 37Cl.
