Cytoskeleton and cell motility
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
What is the cytoskeleton? 2 points
network of proteins within the cell
gives shape and anchors organelles
What does the dynamic network of the cytoskeleton allow cells to do? (4 points)
move
contract
divide
pull/push
State the 3 proteins that the cytoskeleton is comprised of
microfilaments (actin filaments)
microtubules
intermediate filaments
What are actin filaments made up of?
2 strands of actin wrapped around eachother

Where are action filaments located?
below the cell membrane and throughout the cytoplasm.
List four functions of microfilaments
Muscle contraction
Cell motility (crawling)
Cytokinesis
Cell shape
Are actin filaments polar?
yes
What motor does actin filaments use?
myosin
How do actin filaments facilitate changes in cell shape?
slide close to eachother and further apart
How do actin filaments facilitate muscle contraction?
they interact with myosin to generate force and shorten the muscle fiber.
How do actin filaments facilitate cell movement?
psuedopodia
What are pseudopodia?
structures used by neutrophils to crawl in and out of blo9od vessels during diapedesis
What is diapedesis?
the process by which white blood cells move out of the circulatory system and into tissues to reach sites of infection or inflammation.
How are pseudopodia formed?
rapid polymerisation of actin in one direction, creating a hook
Diapedesis: step 1
hook wedges between endothelial cells of blood vessels
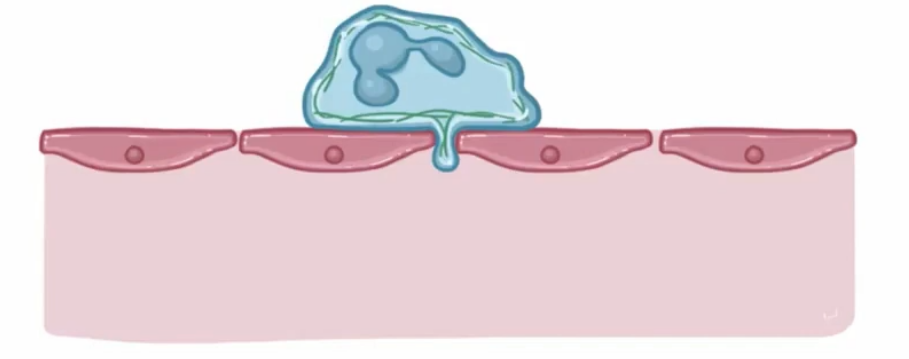
Diapedesis: step 2
neutrophil squeezes through to the other side of the endothelial layer.
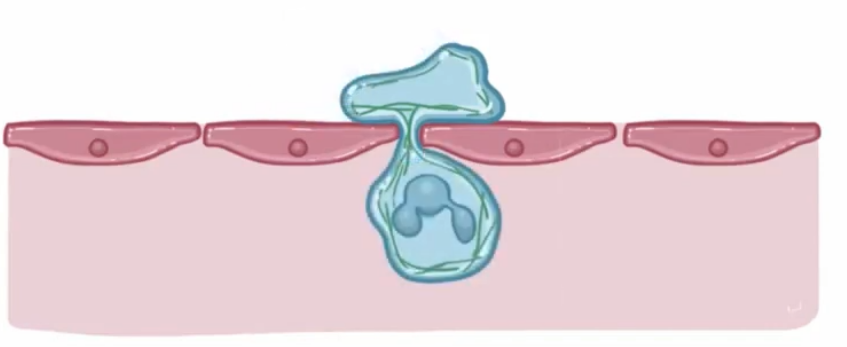
How do actin filaments facilitate cytokinesis movement?
ring of actin filaments form a contractile ring between the two nuclei that pinches the cell membrane, leading to cell division.
What is the largest protein structure in the cytoplasm?
microtubules
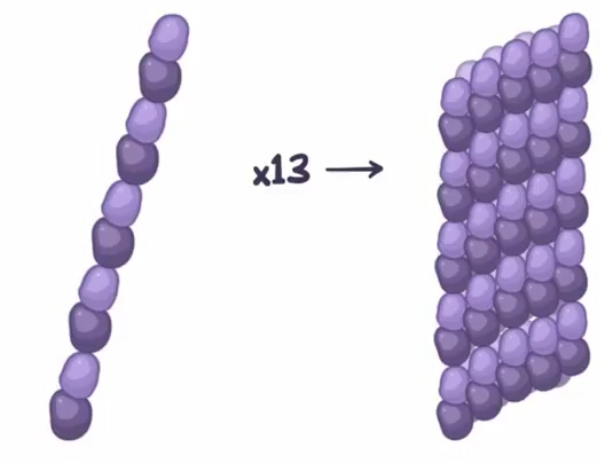
Describe the assembly of a microtubule (2 points)
two α and β tubulin line up to form a protofilament
13 protofilaments come together to form a microtubule
List 4 functions of microtubules
Mitotic spindle
Intracellular trafficking of organelles
Microtubule-based structures (cilia ,centrosomes, axonemes)
Resist compressive forces and so maintain the cells structure
Are microtubules polar?
yes
What motors do microtubules use?
kinesin and dynein
How do microtubules facilitate intracellular trafficking of organelles?
they span across the cell, allowing them to be used as railroads for intracellular transport
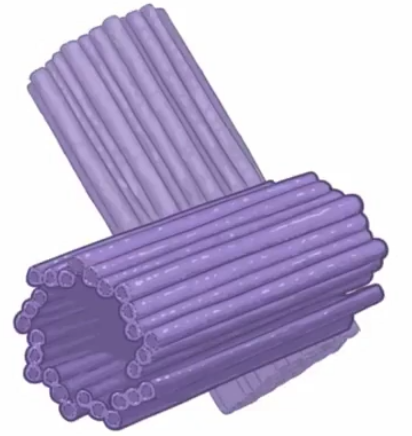
Describe the assembly of a centrosome (2 points)
9 microtubule triplets make up a centriole
2 centrioles at a right angle make up a centrosome

How do microtubules facilitate the formation of the mitotic spindle?
microtubules from the centrosome polymerise in the direction of kietochores (mitotic spindle) embedded in the centromeres of chromatids
How do microtubules facilitate cell movement?
Formation of cilia and flagella
What are motile systems?
system of motor proteins and filaments that self-organise to produce movement and/or transport
List 2 types of microtubule based motility
Cytoplasmic microtubules
Axonemal microtubules
Cytoplasmic microtubules in cell motility
spindle fibre formation
Axonemal microtubules
cilia and flagella
What do centrioles form to nucleate cilia and flagella?
basal bodies
How long are cilia?
2 – 10μm
How do cilia move?
“oar-like” beating pattern
How long are flagellum?
10 – 200μm
How do eukaryotic flagella move?
propagated bending motion
How do prokaryotic flagella move?
rotating in a corkscrew-like motion
Describe the structure of cilia and flagella (2 points)
9-fold symmetry (9 + 2)
Microtubule sliding thanks to stepping of dynein between microtubules
State 4 proteins intermediate filaments can be
lamin
desmin
vimentin
keratin
List 3 functions of intermediate filaments
fastens organelles in place
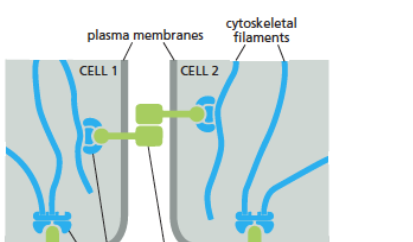
anchor cells to neighboring ones in cell to cell junctions
anchor cells to environment
Are intermediate filaments polar?
no
Describe the structure of intermediate filaments
eight protofilaments joined end-to-end with staggered overlap
What do molecular motors do?
use ATP to transport cargo, rearrange membranes and cytoskeletal networks by making steps along the filament
List the mechano-chemical cycle of kinesin stepping (3 points)
ADP: strongly bound state
ATP: power stroke
ADP∙Pi: release
What does cytoplasmic dynein handle?
movement of cargos along microtubules and cell division
What does axonemal dynein handle
beating of cilia and flagella
Dynein: direction
always minus-end directed
Dynein: can it backstep?
can back-step under load
Dynein: how many motors?
one motor, many adaptors (adaptors define cargo specificity)
Kinesin: direction
can be moving towards minus-end, plus- end, or non-motile
Kinesin: can it backstep?
typically does not back-step
Kinesin: how many motors?
multiple sub-families with multiple members
Myosin II (2 points)
muscles
contractile ring during cytokinesis
Myosin I & IV
“leading edge” of migrating cells
How do mictrotubules polymerise? (2 points)
polymerisation and depolymerisation coexist in steady state conditions
grow from both ends and switch stochastically
How do actin filaments polymerise?
two intertwined protofilaments
growth from barbed (+) end, shortening from pointed (-) end (treadmilling)
State 6 proteins that regulate actin polymerisation
profilin
thymosin
arp2/3
formins
capping proteins
ADF/cofilin
Profilin
binds ATP actin and promotes polymerization
Thymosin
binds ATP actin and blocks polymerization
Arp2/3
promotes nucleation and branching
Formins
bind actin filaments and promote elongation
Capping proteins
bind the ends of a filament; prevent further loss/addition of subunits
ADF/cofilin
binds G-actin and F-actin (also severs filaments)
What acts at microtubule ends to regulate microtubule dynamics? (2 points)
Catastrophe-promoting factors (EB, MCAK)
Rescue factors (CLASP, kinetochore proteins)
What acts at microtubule walls to regulate microtubule dynamics? (2 points
Severing enzymes (katanin): extract
a tubulin from microtubule lattice
Lattice stabilising proteins (tau)
Thick filaments in muscles
bundles of myosin II motors arranged via staggered coiled coils
Thin filaments in muscles (2 points)
actin that interdigitates with the thick filaments
tropomyosin and troponin stabilise the filament
Actin-based motility: endocytosis (2 points)
Clathin-coated pits
Actin polymerisation and myosin V motility helps to form and detach a vesicle
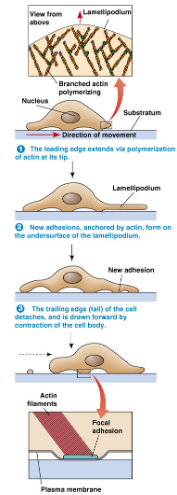
Cell migration: crawling (3 points)
crawling: extend protrusions
filopodia: thin, finger-like
lamellopodia: large, flattened
Cell migration: amoeboid (3 points)
amoebas and white blood cells
pseudopodia (false foot)
3D migration
Cell crawling and adhesion (4 points)
actin polymerisation drives protrusions of lamellopodia
new attachment sites form at the front of the cell
acto-myosin contraction pulls the rest of the cell forward
focal adhesions at the rear detach
Integrin receptors
link cells to the extracellular matrix (e.g. collagen)
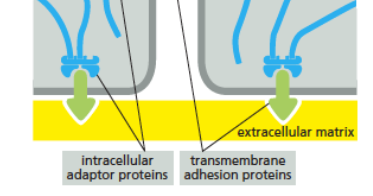
Cadherin receptors
link cells to other cells