Data Types
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
Identifier
an __________ is a name of a program component programmers use to uniquely identify namespaces, classes, methods, variables, constants, etc.
Identifiers
are user-defined words. For example, in the program shown in Code Listing 1, the __________ are
ConsoleApp, ComputeRectangleArea, length, width, area, WriteLine, and ReadKey.
The following are the syntax rules when naming an identifier in C#:
It must start with a letter of the English alphabet or an underscore character.
The identifier's name can only have any combination of letters, digits, and underscores. White spaces are not allowed.
Identifiers are case sensitive. For example, the identifier Area is not the same with identifiers area or AREA.
It cannot be a reserved keyword.
The classes and methods in C# must always begin with a capital letter.
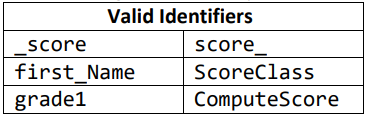
Valid Identifiers
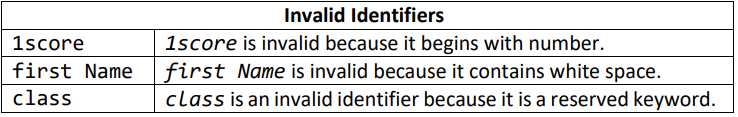
Invalid Identifiers
number
1score is invalid because it begins with ______.
white space
first Name is invalid because it contains __________.
reserved keyword
class is an invalid identifier because it is a _______________.
Keywords
are reserved words a programming language uses for its own use, and they have a special predefined meaning to the compiler.
Keywords
These cannot be used as identifiers. If you do use a _______in a program, the compiler will throw an error message.
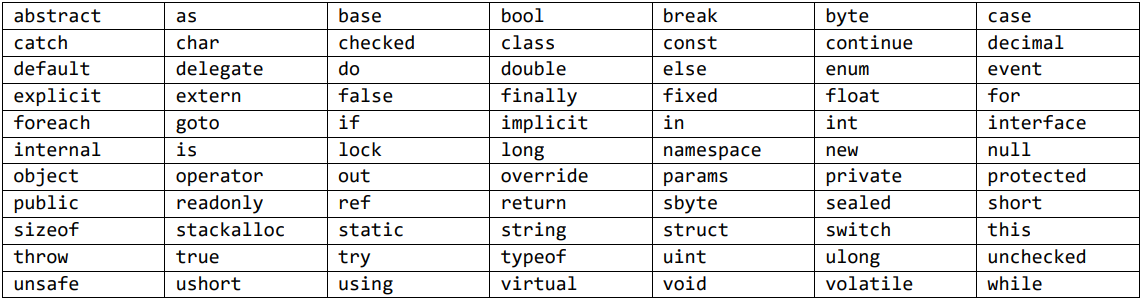
Table 3 shows the list of keywords in C#.
Variable
is an identifier and a memory location that stores a specific value.
Variable
holdd a value that can be changed during program execution.
For example, a variable named score assigned an initial value of 25. When the program starts, the value of variable score will change to 85.
data_type identifier;
The basic syntax of declaring a variable is _____________
identifier
is the name of the variable. For example, int score;
Variables
are initialized, or assigned a value, with an equal sign followed by the value. The following are some valid examples of declaring and initializing variables:
You can initialize a variable at the time of declaration. For example: int score = 25;
You can declare and initialize more than one (1) variable of the same time data type using a comma in a single statement: int score, age; score = 85; age = 24; int length = 8, width = 5;
When creating a program, you must define a variable with a meaningful name that is easy to understand what value must store on it. For example, the variables gameScore and age must store integer type values.
camelCase
Use _________notation that starts with
a lowercase letter for naming local variables. For example, numberOfStudents, age, totalPrice, etc.
Constant
is an identifier and a memory location whose value cannot be changed during program execution.
Constants
must initialize a value at the time of declaration.
const data_type IDENTIFIER = value;
The basic syntax of initializing a constant in C# is as follows: _____________________
const
Constants in C# are defined using the _____ keyword. For example: const double PI = 3.14159;.
In the example, the constant PI with the value of 3.14159 cannot be changed during program execution. The name of the constants must be in all capital to make it easy to identify that its value must not change.
Data types
are used to specify a set of values and their operations associated with variables or constants.
Data types
The values have particular __________ because they are stored in memory in the same format and have the same operations defined for them.
Variable
A ________ or constant stores data of a specific type.
When declaring a variable or constant to store a data, the appropriate data type for that data must be identified.
The data type will instruct the compiler what kind of value a variable or constant can hold and its operations.
There are two (2) types of primitive data types in C#:
Value types
These data types store the value directly. The data type int is a value type that stores its value in a memory location directly.
Reference types
These data types do not store the actual value in a variable or constant. Instead, they store the reference (or address) where the value is stored.
The class objects, strings, and arrays are reference types because they hold references to blocks of memory and are managed on the heap.
Value type
A data type is a ___________ if it holds the data within its own memory allocation.
Value types
directly store the values within the variable.
For example, consider the following figure:
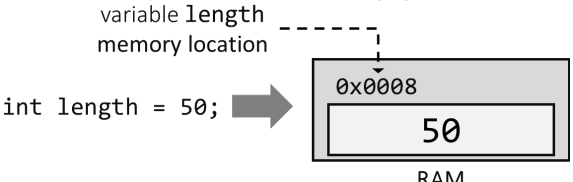
Figure 1. Memory allocation for value type
In Figure 1, the variable length of int type is assigned a value of 50. When this statement is executed, the compiler will instruct the computer system to directly store 50 in the memory space allocated for the variable length.
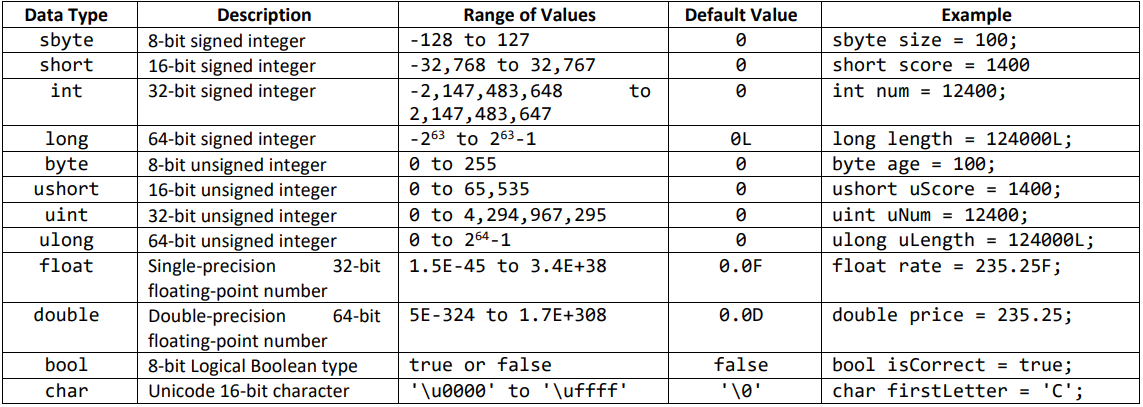
Table 4. Value types in C#
Reference type
does not store an actual value, but it stores the address where the value is stored.
Reference types
contain the memory locations of where the value is stored.
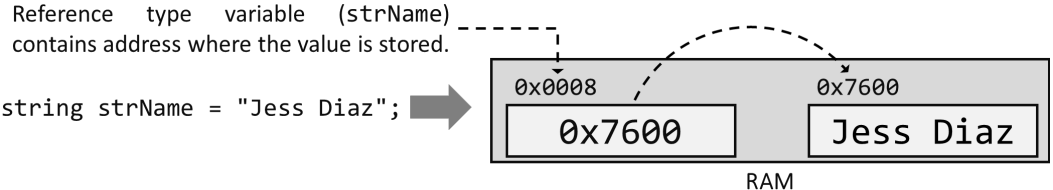
Figure 2. Memory allocation for reference type
In Figure 2, the compiler will instruct the computer system to select a different memory location for the variable strName. The content of the variable strName is "0x7600", which is the address or memory location of the actual string value "Jess Diaz".
Strings, Objects, Arrays, and Delegates
What are the reference types in C#?
Type conversion / type casting
is the process of converting a value of one (1) type of data to another data type.
Type conversion / type casting
This is used to ensure that a function correctly processes the variables.
Type conversion
Converting a string to an integer is an example of _______________.
The following are the two (2) forms of type casting in C#:
Implicit conversion
This is the conversion of a lower precision data type to a value of higher precision data type.
A compiler automatically performs implicit conversion if the precision of data type to convert is lower than precision of preferred data type.
For example, a variable of short data type is capable of storing values up to 32,767, and the maximum value allowed into a byte is 255; so, there will be no problem when you convert the value of byte type into a value of short data type.
An example of implicit conversion includes converting the value of int data type to a value of double data type, because int data type has a lower precision than double data type.

Table 5. Implicit numeric conversions
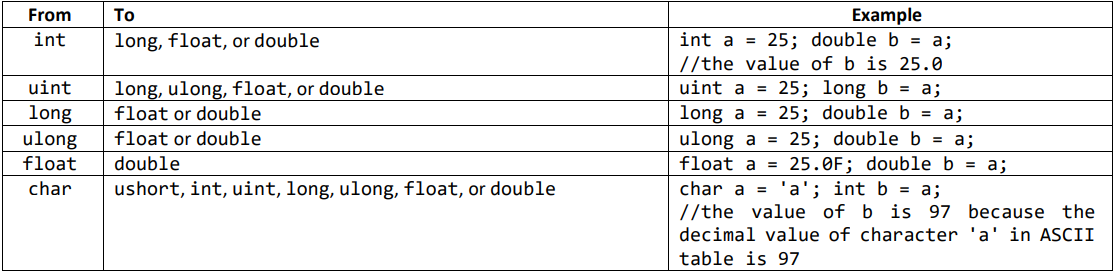
Table 5. Implicit numeric conversions in C#.
Note: There is no implicit conversion of any data type to char type, so the values of the other integral types do not automatically convert to the char type.
The bool and double data types have no possible implicit conversions to the other data types.
Explicit conversion
Converting a higher precision data type to a lower precision data type is invalid, and the compiler will return an error.
For example, the statements
double num1 = 25.0;
int num2 = a;
will return an error because the precision of variable num1 of double data type is higher than the variable num2 of int type.
Cast operator
However, explicit conversions allow the users to convert a value of higher precision data type into a value of lower precision data type by using a ______________.
(data_type) data_to_convert;
The following is the general syntax of performing explicit conversion in C#:
(data_type)
is the cast operator that will create a converted copy of the value in data_to_convert. For example, the following statements uses a cast operator to explicitly convert data types: //first example int num = 25; byte b = (byte) num; /
//first example
int num = 25;
byte b = (byte) num;
//second example double price = 75.5; int varA = (int) price; //the value of variable a will be 75
In the first example, the value 25 is assigned to the variable num of int type, then the converted copy of value from variable num is assigned to the variable b. The value stored in variable num is still an integer type because the cast operator created a converted copy of its value as byte data type.
Explicit conversion involves the risk of losing information, i.e., from double to int data type.
For example, in the second example, the value of the variable price of double data type is copied and converted into int data type then stored in the variable varA of int data type. The cast operator dropped the decimal part of the floating-point number 75.5 to convert it to 75 as int data type.
The following statements shows some of the ways on how to use the cast operator:
int a = (int) 7.9;
//the return value of a is 7
double b = (double) (5 + 3);
//the value of b is 8.0
Console.WriteLine((int) 2.5);
//the output is 2
int c = 64; char d = (char) c;
//the return value of d is the character '@'
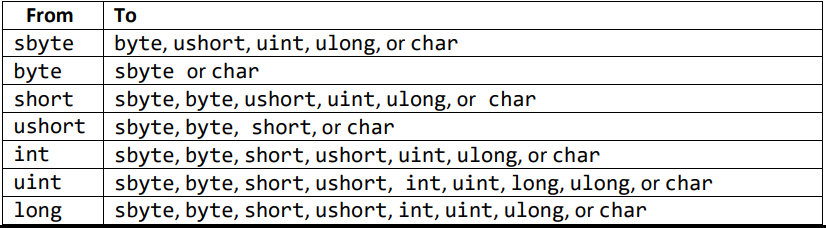
Table 6. Explicit conversions

Table 6. Explicit conversions
The explicit conversion of a data type to char data type will return the corresponding character of the value from the ASCII table.
int a = 64;
char b = (char) a;
//the value of b is the character '@' because it is the corresponding character of decimal value 64 in ASCII table